Carbohydrates - Intro and Monosaccharides
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
How are carbohydrates defined based on the organic functional groups present?
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxyl aldehydes or ketones, or molecules that yield polyhydroxyl aldehydes or ketones upon hydrolysis.
General formula of a carbohydrate
Cₙ(H₂O)ₙ, where n ≥ 3.
What is a monosaccharide based on size?
A monosaccharide is a carbohydrate with a single monomeric unit
What is a disaccharide based on size?
A disaccharide contains two covalently linked monosaccharide units.
What is an oligosaccharide based on size?
An oligosaccharide is a carbohydrate with 3 to 20 monosaccharide units.
What is a polysaccharide based on size?
A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate with more than 20 monosaccharide units.
Glycoconjugates definition
Polymers that contain something and sugars so we can have a glycoprotein, proteoglycans, and glycolipids.
Glycoproteins vs proteoglycans
The first part of the word is the substance that is found in largest. glycoproteins have more carbohydrates than proteins.
How are monosaccharides classified based on the number of carbon atoms?
They are classified as trioses (3C), tetroses (4C), pentoses (5C), hexoses (6C), heptoses (7C), etc.
Aldose definition
Aldehyde functional group on carbon 1
Ketose definition
Ketone functional group on carbon 2
Ketotriose definition
3 carbon monosaccharide with ketone on carbon 2
Aldopentose definition
5 carbon monosaccharide with aldehyde on carbon 1
Ketohexose definition
6 carbon monosaccharide with ketone on carbon 2
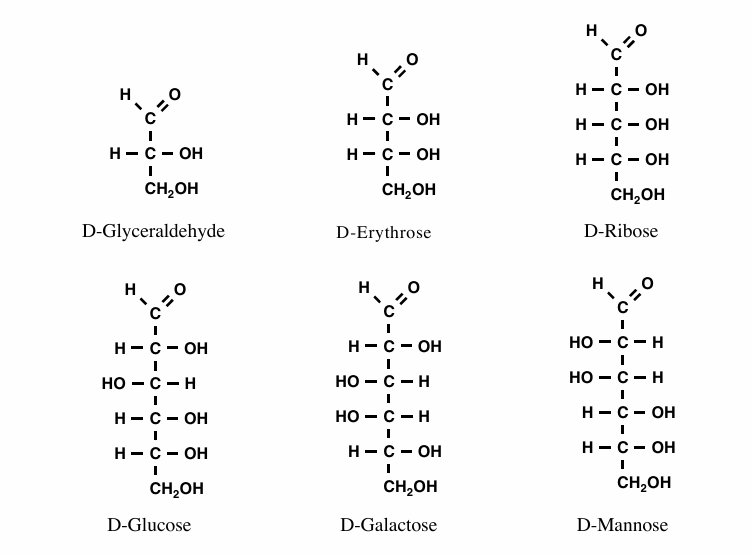
Aldose names (6)
D-glyceraldehyde
D-erythrose
D-ribose
D-glucose
D-galactose
D-mannose
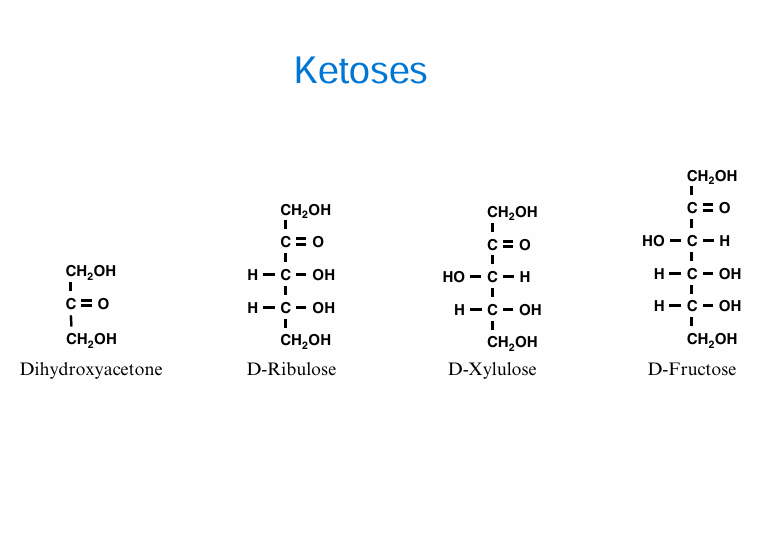
Ketose names (4)
Dihydroxyacetone
D-ribulose
D-xylulose
D-Fructose
What is the significance of stereoisomerism in carbohydrate structure and function?
Stereoisomerism allows for enantiomers and diastereomers, which affect recognition by enzymes and biological activity. Only D-sugars are commonly metabolized in cells.
How do you identify a D or L sugar from a Fischer projection?
Look at the hydroxyl group on the last chiral carbon: if it points right, it’s a D-sugar; if it points left, it’s an L-sugar (compared to D- or L-glyceraldehyde).
Enantiomers
mirror images (D vs. L forms)
diastereomers
differ at one or more but not all chiral centers (e.g., glucose vs. galactose or mannose)
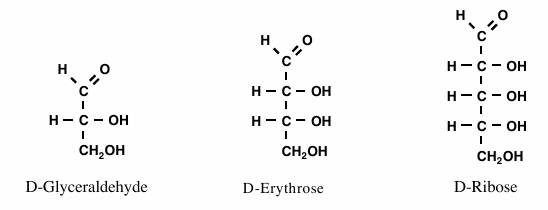
Number of chiral centers on image
Glyceraldehyde has 1; Erythrose has 2; Ribose has 3
What are epimers in carbohydrate chemistry?
Epimers are stereoisomers that differ in configuration at only one specific chiral carbon atom.
Which monosaccharides are C-2 epimers of each other?
D-Glucose and D-Mannose are C-2 epimers.
Which monosaccharides are C-4 epimers of each other?
D-Glucose and D-Galactose are C-4 epimers.
What organic functional group forms when an aldose cyclizes?
When an aldose cyclizes, it forms a hemiacetal functional group.
What organic functional group forms when a ketose cyclizes?
When a ketose cyclizes, it forms a hemiketal functional group.
What are anomers?
Anomers are isomers of a cyclic sugar that differ only in the configuration around the anomeric carbon.
What is the anomeric carbon?
The anomeric carbon is the carbon derived from the carbonyl carbon (C=O) during cyclization; it becomes the new stereocenter in the ring form.
Which monosaccharides are anomers of each other?
α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose are anomers of each other, differing at the anomeric carbon.
What is mutarotation?
Mutarotation is the spontaneous interconversion between α and β anomers of a sugar in aqueous solution, reaching an equilibrium mixture.
How can you recognize a monosaccharide from its Haworth projection in α- and/or β-cyclic forms?
By identifying the orientation of the hydroxyl group at the anomeric carbon: down for α-anomer, up for β-anomer in D-sugars.
How do you convert a Fischer projection into a Haworth projection, or vice versa?
Groups on the right of the Fischer projection point down in the Haworth ring; left groups point up. The anomeric OH determines α (down) or β (up) configuration in D-sugars.