MS1 Epithelium
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the 4 Basic Tissues?
Epithelium
Nerve
Connective
Muscle
Basic dye
cation
Carries a positive charge
Reacts with anions of the tissue (phosphate groups of the nucleic acids, sulphate groups of GAGs, carboxyl groups of proteins)
Basophilic
Basic specific dyes
Hematoxylin (with mordants)
Toluidine blue
Methylene blue
Basic fuchsin
Carmine
Structures that are basophilic
Fewer structures are basophilic than acidophilic
Heterochromatin and nucleoli
Cytoplasm
extracellular matrix
Acidic dye
Anion
carries a negative charge and reacts with cations of the tissue
Acidophilic
Acidic specific dyes
•Eosin (Eosinophillic)
•Orange G
•Phloxine
•Anilin blue
•Light green
•Mallory
Aniline blue – for collagen
Acid fuchsin – for cytoplasm
Orange G – red blood cells
Structures that are acidophilic
More structures are acidophilic than basophilic
Cytoplasmic filaments
Intracellular membranous components
Extracellular fibers (Collagen)
Epithelium is composed of _______ and a ________ ________
cells
basement membrane
Epithelium is ______ and support depends on __________.
avascular
diffusion
Epithelium is renewed continuously though _________.
mitosis
Epithelium selective barriers
external surface – skin (protective layer)
“tubes” and cavities – mucosa/endothelium and mesothelium
Epithelium is absent from:
articular cartilage
anterior surface of iris
enamel of teeth
Functions of Epithelium
Protection & support (skin, meninges)
Absorption (intestines)
Filter stuff (kidneys, lymphatics)
Transport & delivery
nutrients (gut, blood vessels)
waste (kidney, blood vessels)
gases (airway)
Make stuff (secretions from glands)
exocrine
endocrine
Movements of organs
mesothelia: pleura, pericardium, peritoneum
Sensory receptors for special senses:
olfactory epithelium, hair cells, taste buds, rods/cones
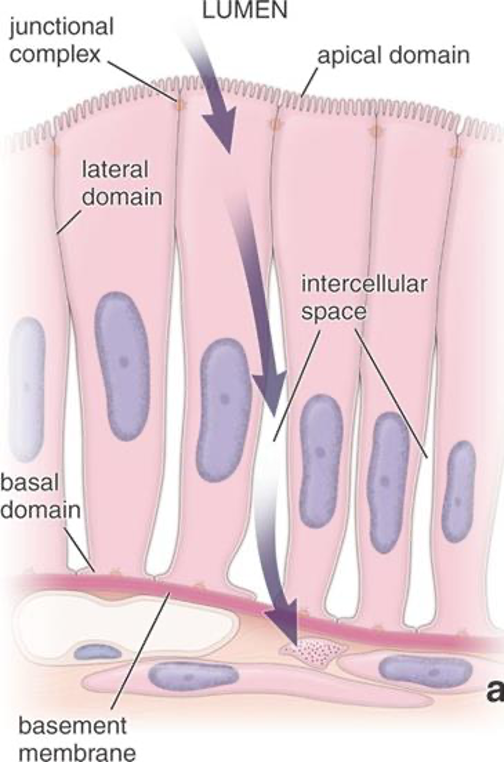
Three main common features of epithelial cells
Closely apposed and linked (junctions)
Polarized
free, apical domain
lateral domain
basal domain
Anchored to the basement membrane
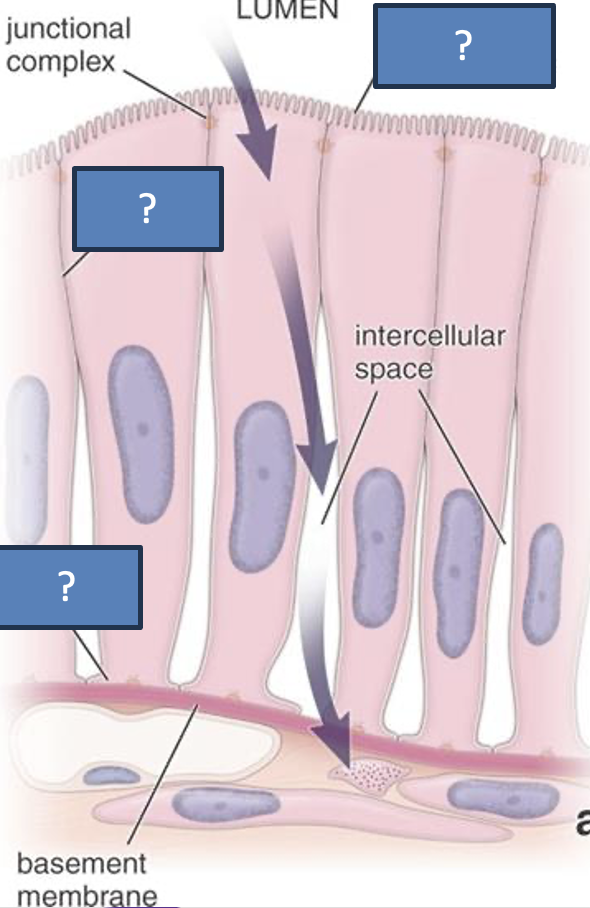
Label!
basal domain
lateral domain
apical domain
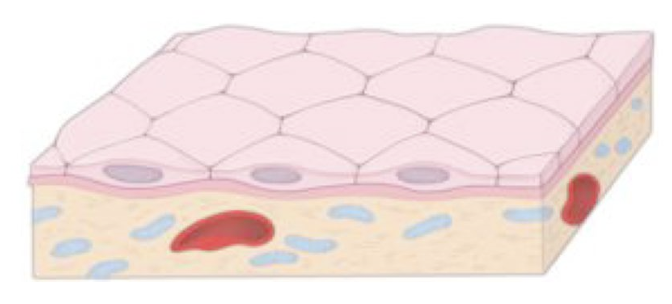
Identify!
simple squamous
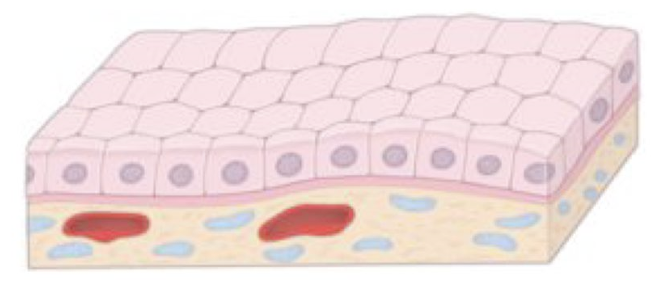
Identify!
simple cuboidal
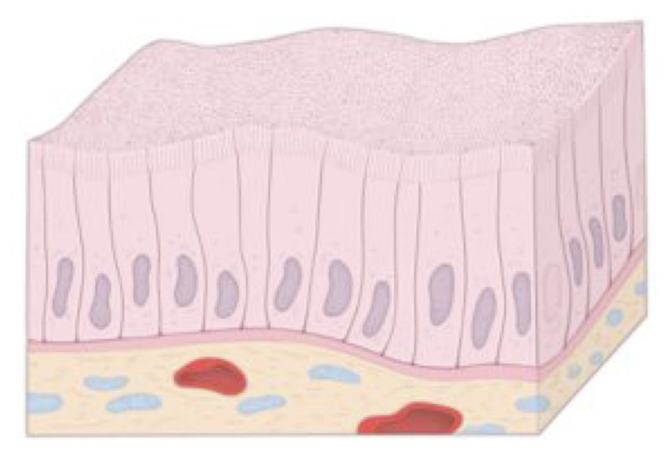
Identify!
simple columnar
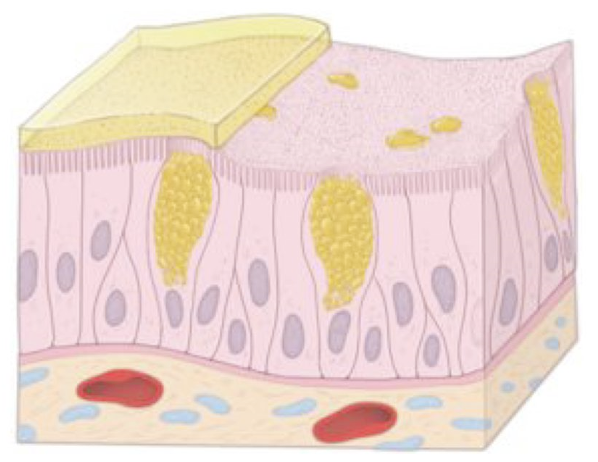
Identify!
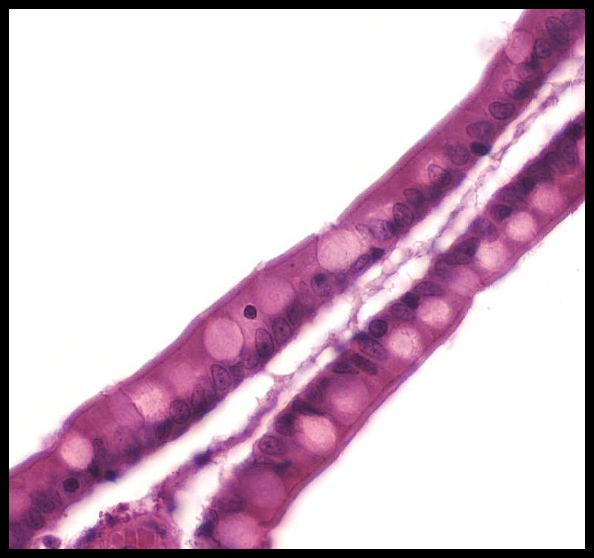
Pseudostratified
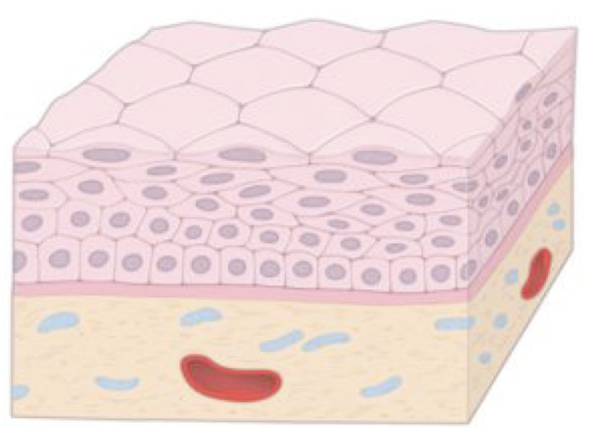
Identify!
Stratified squamous
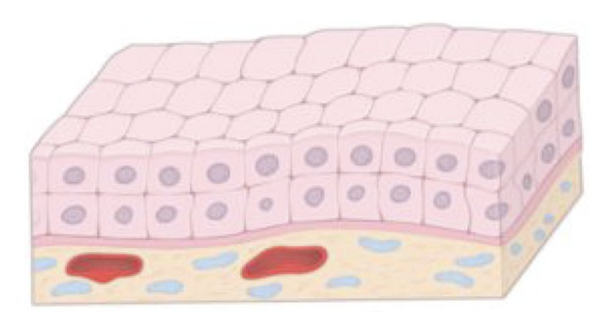
Identify!
Stratified cuboidal
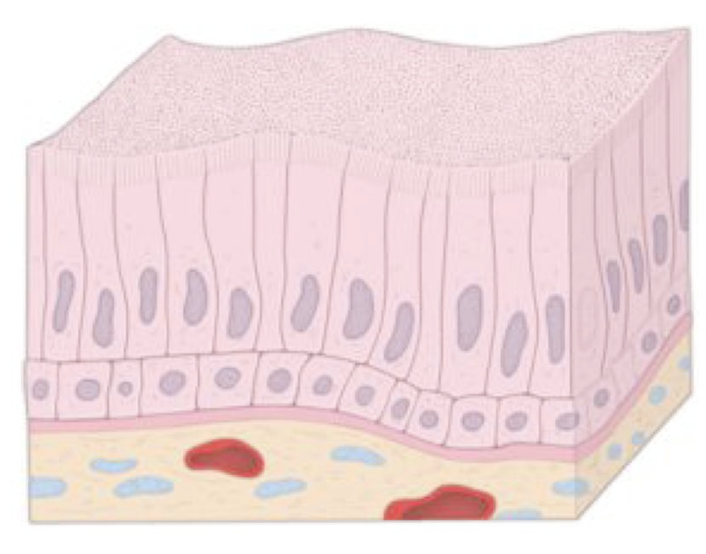
Identify!
Stratified columnar
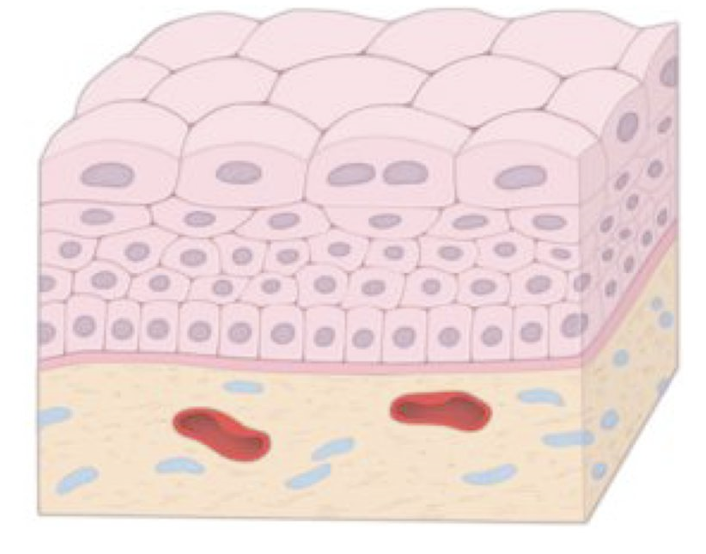
Identify!
Transitional
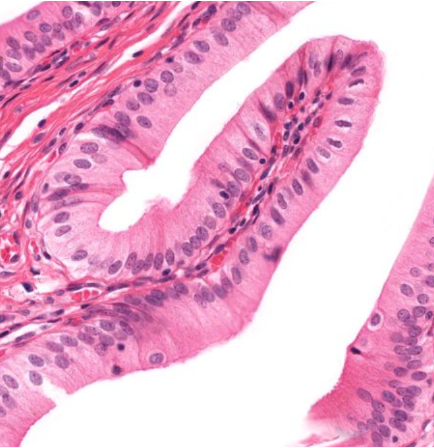
Identify!
Simple columnar
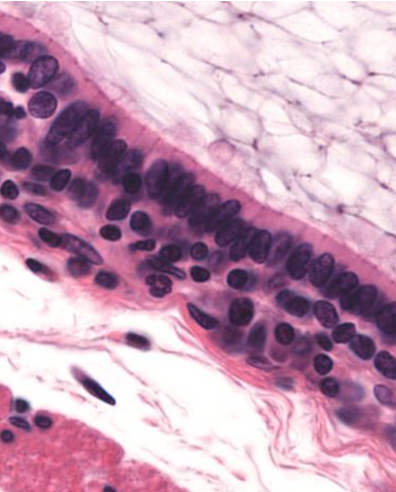
Identify!
Stratified columnae
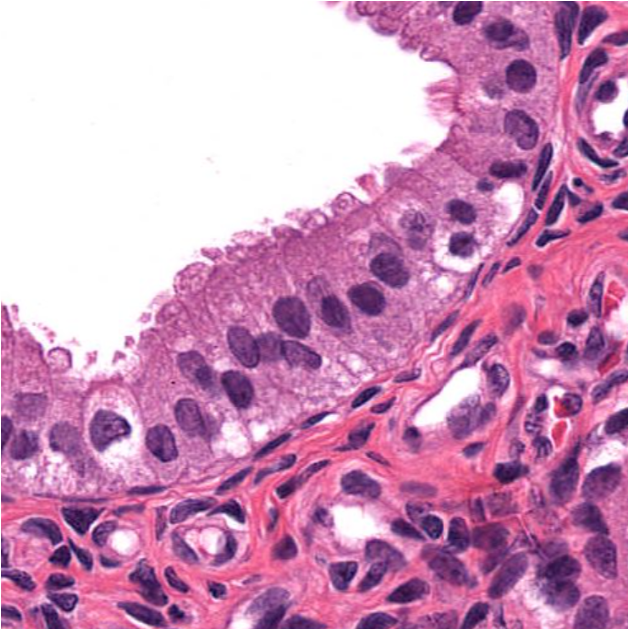
Identify!
simple columnar
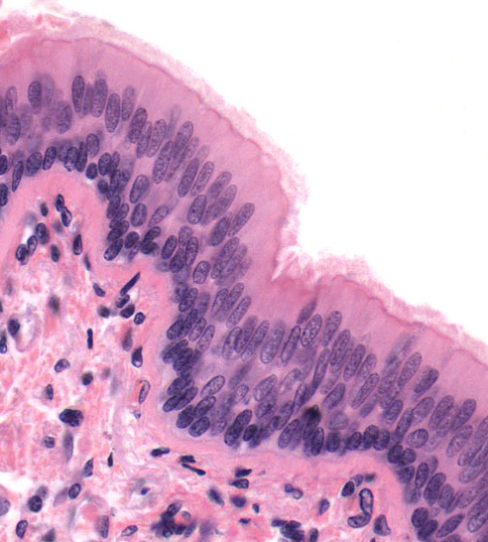
Identify!
Pseudostratified
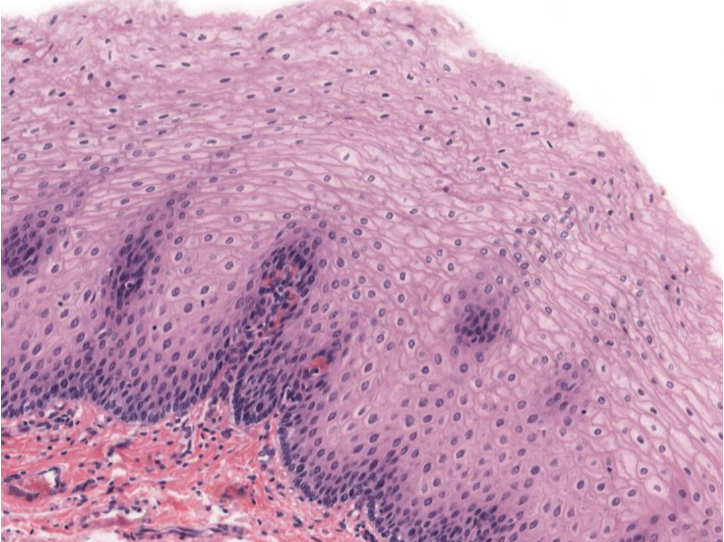
Identify!
Stratified squamous
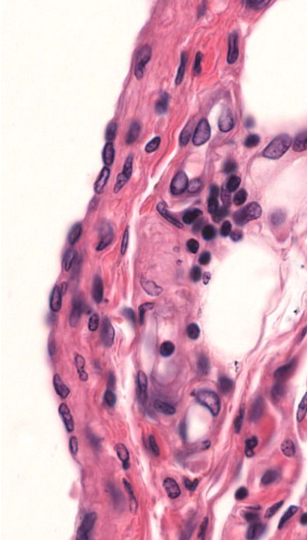
Identify!
Simple squamous
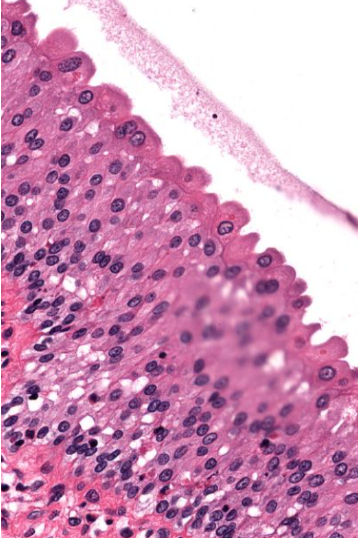
Identify!
Transitional
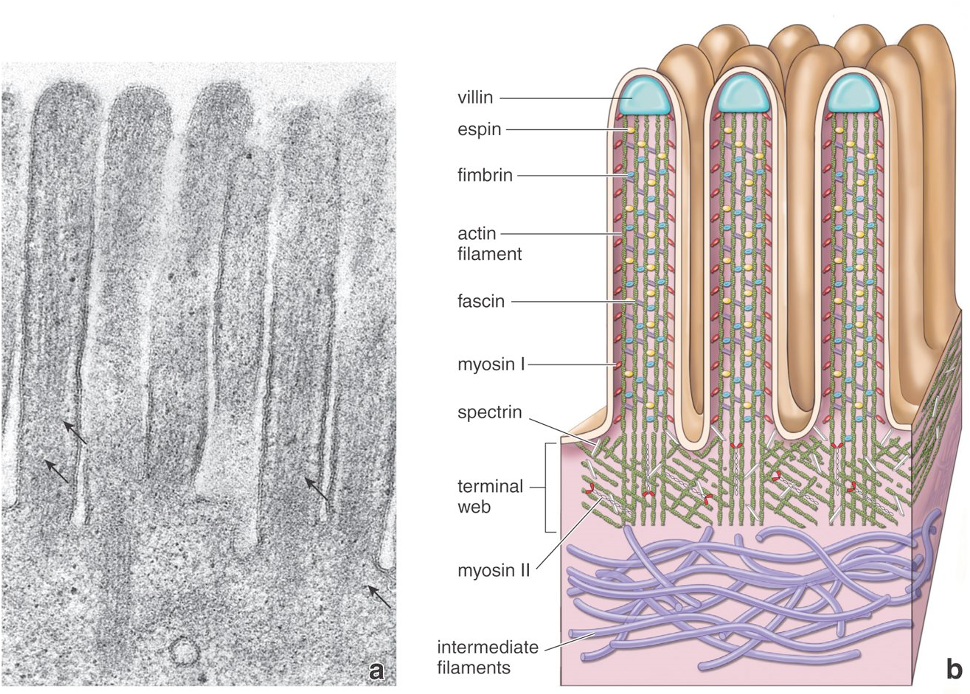
Identify!
Microvilli
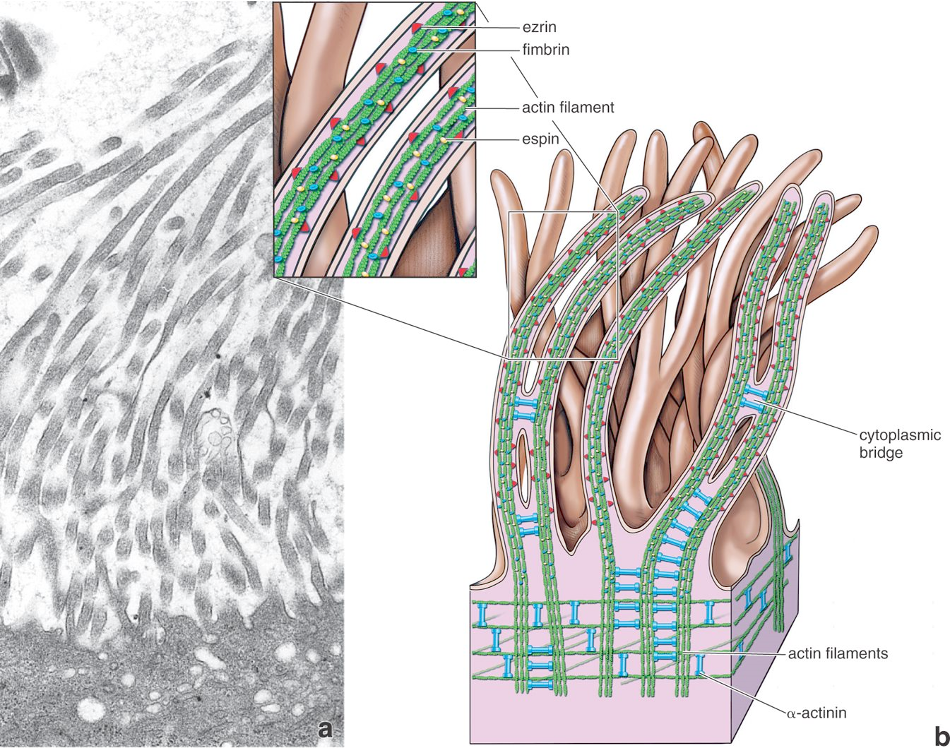
Identify!
Stereocilia/Stereovilli
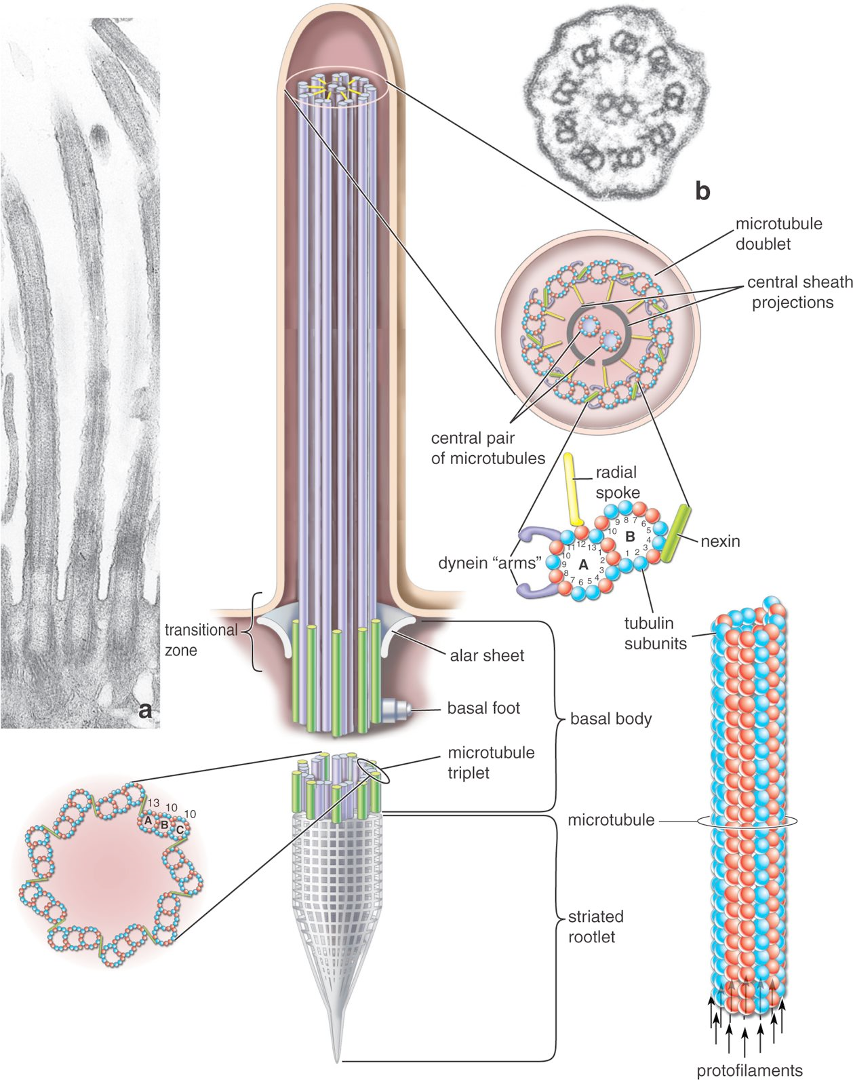
Identify!
Motile Cilia
move in synchronous, undulating patterns
move particles, oocytes through the tubes
cilia are anchored to cytoskeleton via basal body
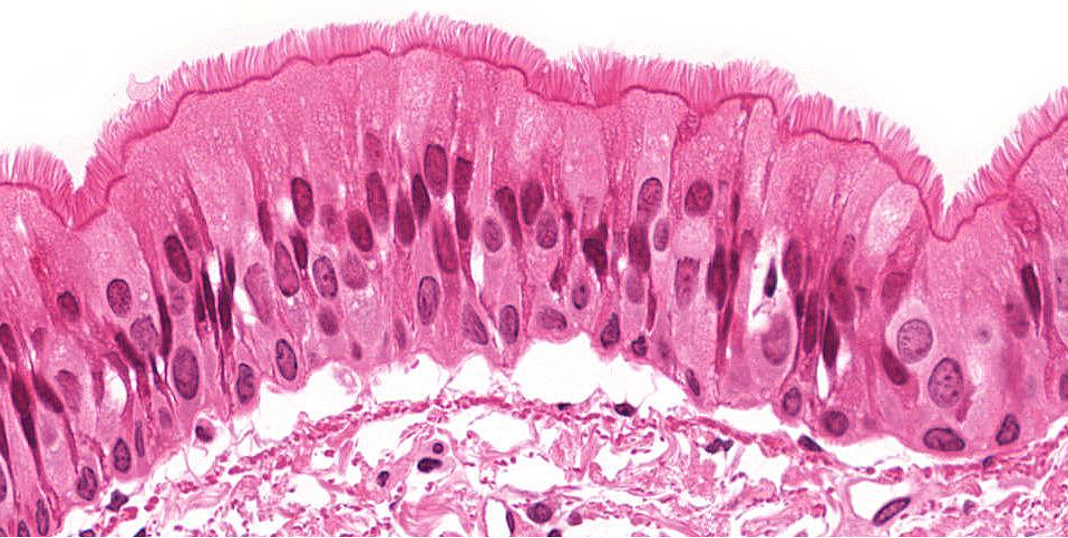
Identify!
Pseudostratified Epithelium
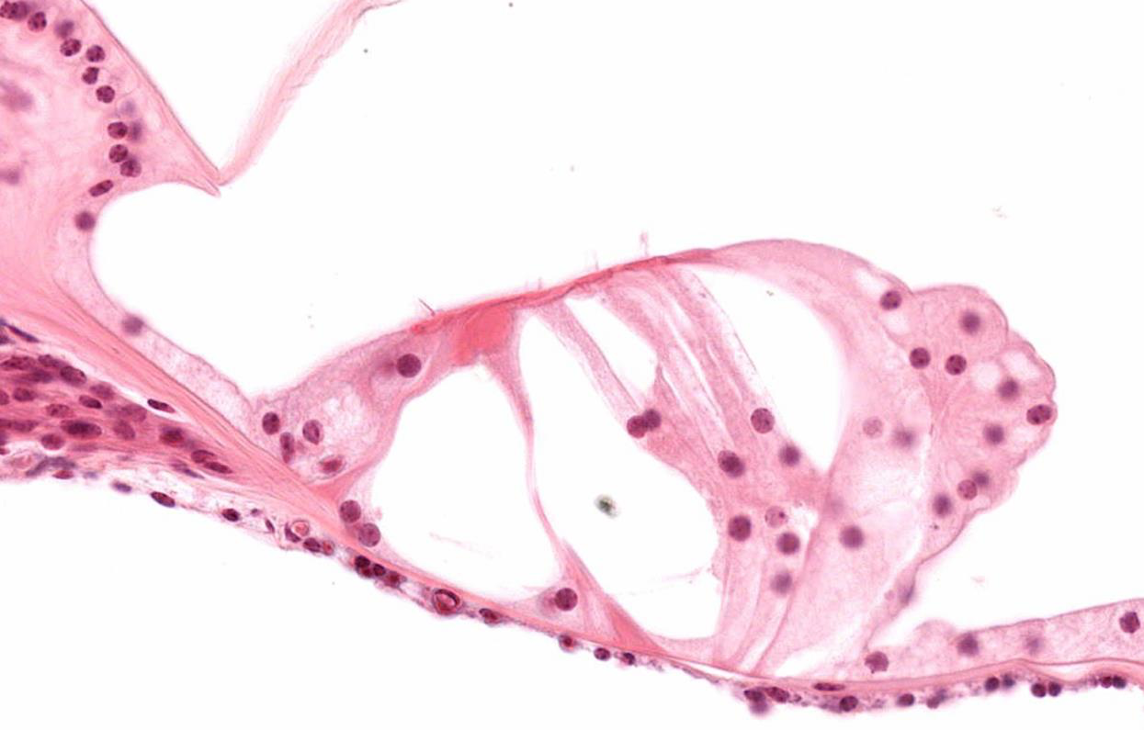
Identify!
Cochlear Hair Cells
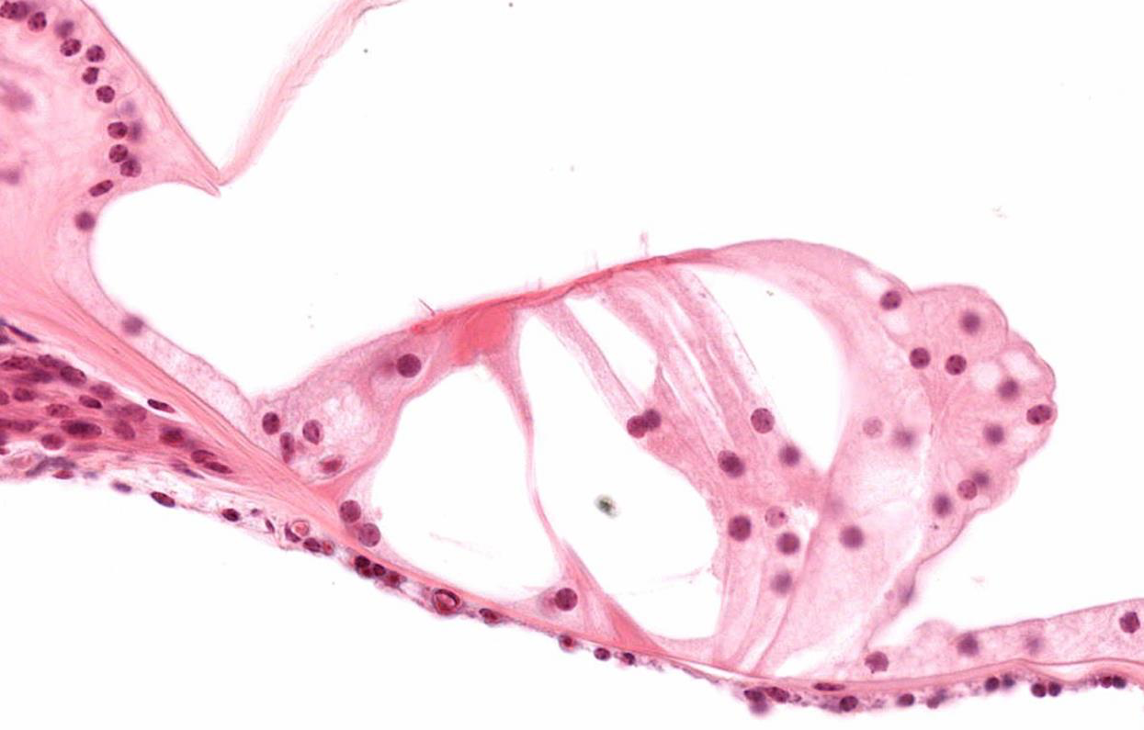
Identify!
Gut microvilli
Lateral Domain Terminal Bar, Junctional Complex
Occluding/Tight junctions/zonula occludens
Anchoring junctions
Communicating junctions (gap junctions)
Occluding/Tight junctions/zonula occludens
Linked to actin
Separates cellular and tissue compartments
Three major transmembrane proteins of Occluding/Tight junctions/zonula occludens
Occludin
Claudins
Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM)
Anchoring junctions
Linked to actin and intermediate filaments
Zonula adherens → actin
Macula adherens (desmosome) → intermediate filaments
Lateral folds
folds of plasma membrane
increasing surface area
The Basal Domain
Involved in cell-to-matrix adhesion.
Basement membrane
Cell-to-ECM junctions
Focal adhesions → actin
Hemidesmosome → intermediate filaments
Basal cell membrane infoldings
Epithelial Secretory Mechanisms
exocrine glands
endocrine glands
exocrine glands
unicellular or multicellular (glands)
Release product on epithelium surface
Histological Types of Endocrine Glands
Release product into blood
Cord and clump
Follicle
Cord and Clump
most common
cells are arranged in interconnecting cords and clumps between dilated blood capillaries
store hormone intracellularly
Follicle
group of cells forms a vesicle enclosing a central cavity in which hormone is stored
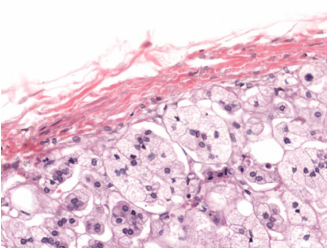
Identify!
cord and clump
endocrine
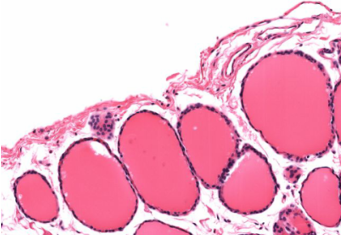
Identify!
follicle
endocrine
Types of Multicellular Glands
simple tubular
simple coiled tubular
simple tubular branched
simple acinar/alveolar
branched tubular
branched acinar/alveolar
branched tubuloacinar
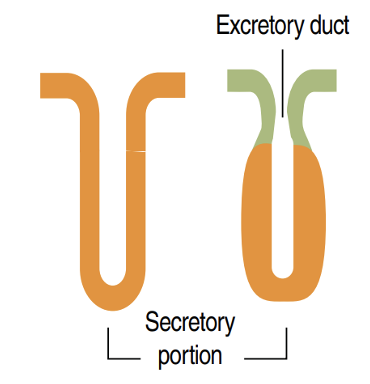
Identify!
simple tubular gland
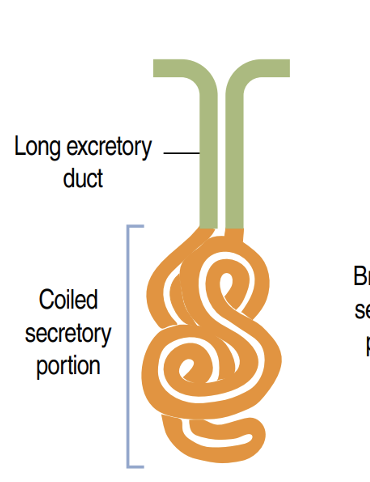
Identify!
Simple coiled tubular gland
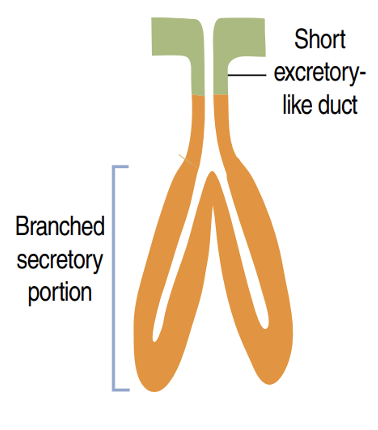
Identify!
Simple tubular branched gland
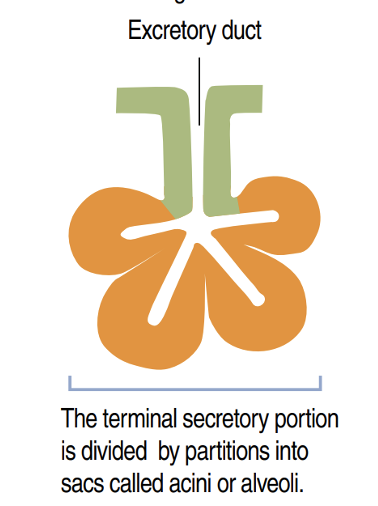
Identify!
Simple acinar/alveolar gland
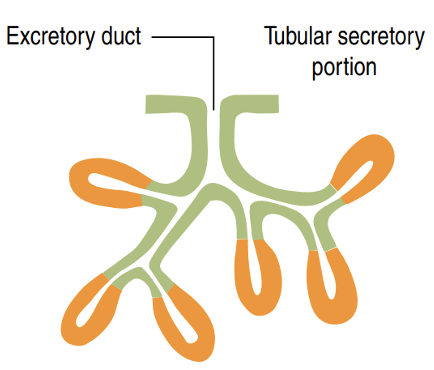
Identify!
Branched tubular gland
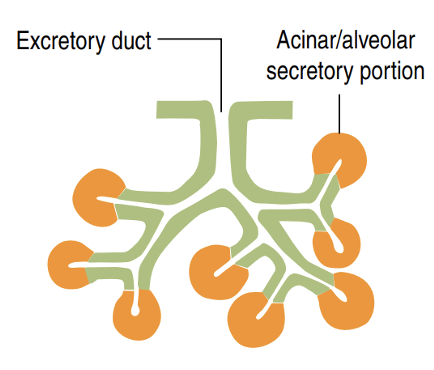
Identify!
Branched acinar/alveolar gland
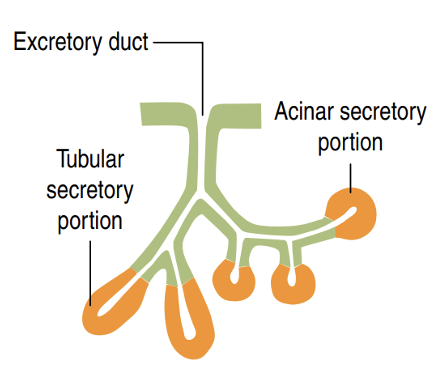
Identify!
Branched tubuloacinar gland
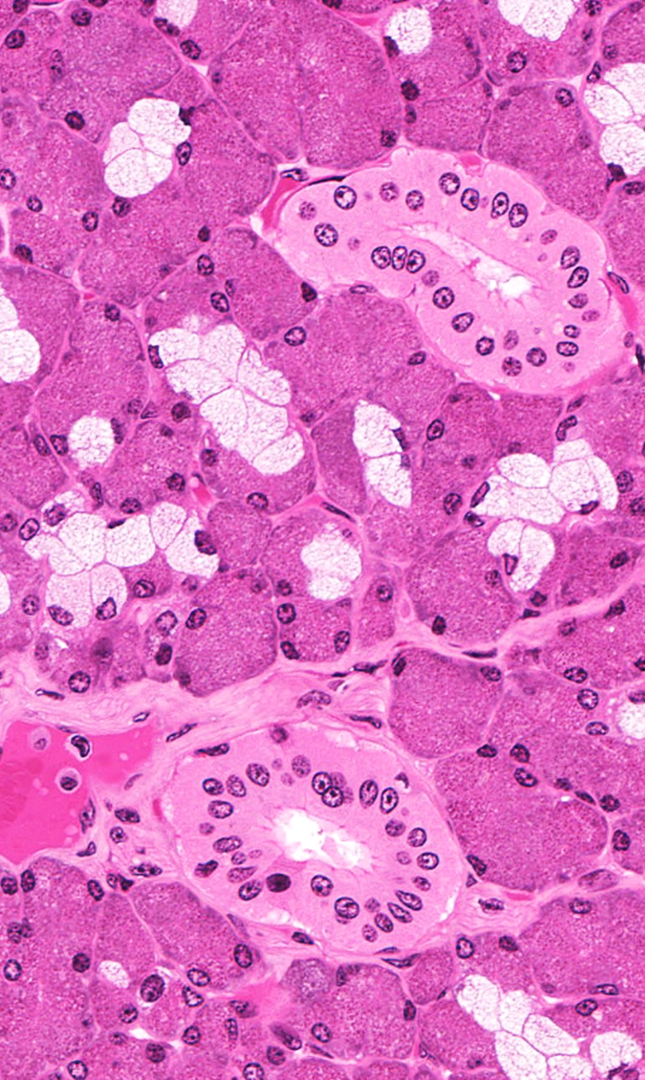
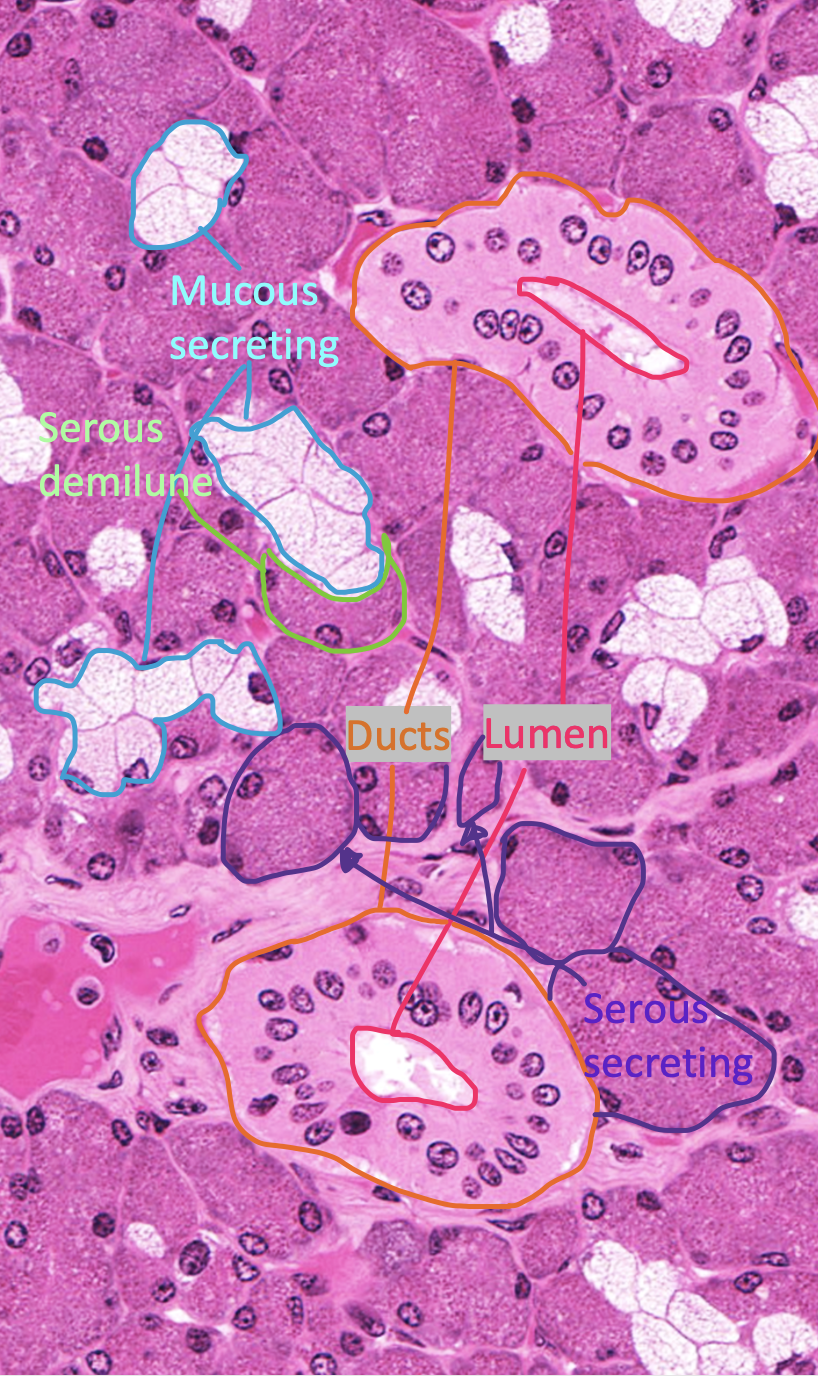
Identify!
ducts
lumen
mucous secreting (stain pale with H&E)
serous secreting
serous demilune
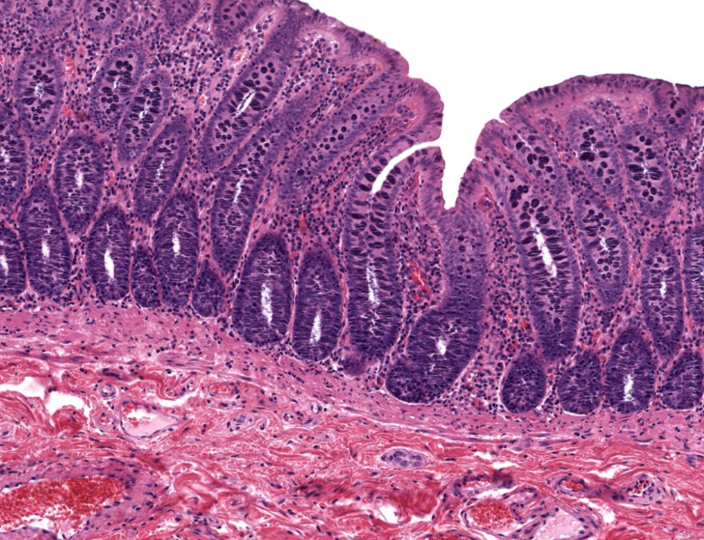
Identify!
simple tubular gland
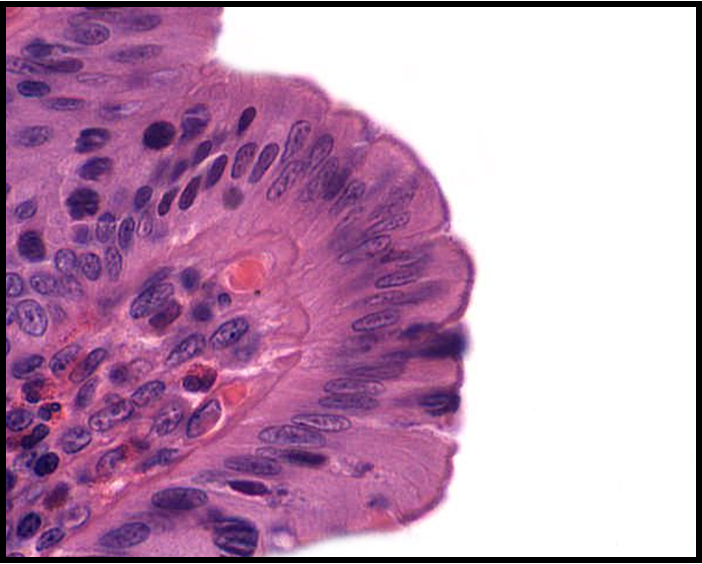
Identify!
simple columnar