Computational Thinking Midterm
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
What data type is always returned by input()?
string
What will be the output of print(5)?
5
Which of the following best describes comments in python?
They are ignored by Python and written for humans.
When do you use elif
When you have a case with multiple conditions, use elif to denote additional outcome.
if, elif conditional formatting
if
elif
elif
else
What will 12 % 5 evaluate to?
2
What is the result of round (15.6)?
16
Which operator returns the remainder after division?
%
After importing date time as dt, which line correctly retrieves the current date and time?
dt.datetime.now()
which of the following correctly imports the date time module with an alias?
Import date time as dt
Which function from the math module always rounds a number up?
ciel()
Which of the following is the correct way to import the sqrt function from the math module?
from math import sqrt
What is the result of the expression 7//2?
3
Literal
Fixed value that you write directly in your code - they represent themselves exactly. A number in an equation.
Expressions
Combinations of literals, variable, and operators that python can evaluate to produce a value. What comes after the equal sign in an equation.
Statement
Complete instructions that Python can execute. The entire equation.
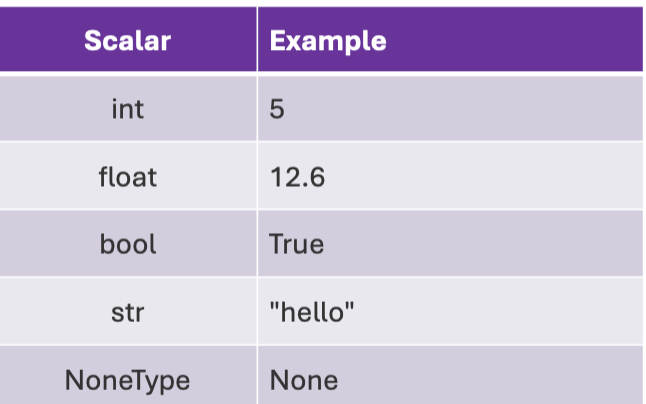
Data objects
Objects have a type that defines the kinds of things programs can do to them. They are scalar, they cannot be subdivided or they can be non-scalar, they have an internal structure that can be accessed.
Scalar Objects Example
Look at the image.
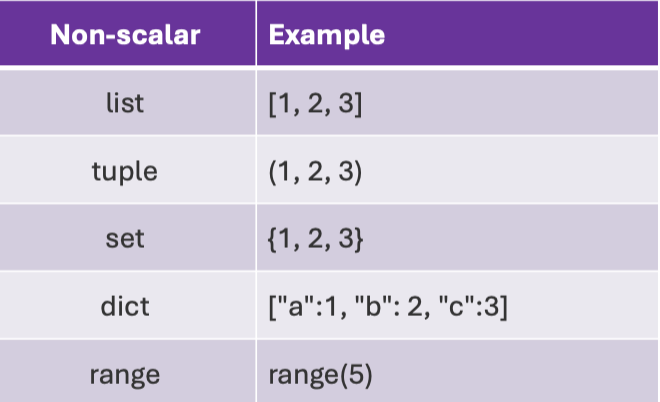
Non-scalar objects example
Look at the image.
type casting hierarchy
int>float>str
What does // produce
how many times a number can go in another one, 5//3 = 1
What does % produce
the remainder after division, 5%3 =2
What does ** produce1
Exponents / to the power of
How do you import as an alias?
import matplotlib as plt which would be used as plt.plot([1,2,3,4])
Math module
ciel = round up, floor = round down, round = normal rounding.
What does the not operator do?
Negates a boolean value
What will be the result of the expression 10 != 5
True
Which operator is used to require at least one condition to be True?
or
Which scenario best demonstrates the use of the compound logical expressions?
Determining if a student passed based on grade and attendence
What keyword is used in a multi-way decision
elif
Which of these is an example of boundary testing in an age classifier
Age = 12, 13, 17, 18
Which keyword begins a one-way decision in python?
if
Why does the operator != do
Not Equa;
What does the operator == mean
Equal to
What does a not operator do
used to negate a boolean expression
Which type of loop runs when you don’t know in advance how many times it will execute?
While loop
What does the iteration variable do in a for loop?
Holds each item in the sequence being processed.
What keyword ends a loop immediately?
break
What will this code print?
for i in range(1, 6):
if i % 2 == 0:
continue
print(i)1 3 5
Which python statements correctly increment the counter event_count?
even_count += 1
even_count = even_count + 1
What is the output of
for i in range(2, 6):
print(i)2 3 4 5
What does the operator += mean
Add and reassign
Which of the following loops is definite?
for i in range(5):
What keyword skips the rest of the current iteration but continues the loop?
continue
What is an indefinite loop?
a loop that keeps running until a specific condition is met. Will execute forever because the condition never becomes false.
What is a while loop
It evaluates the condition, and proceeds to test the conditions until it is false.
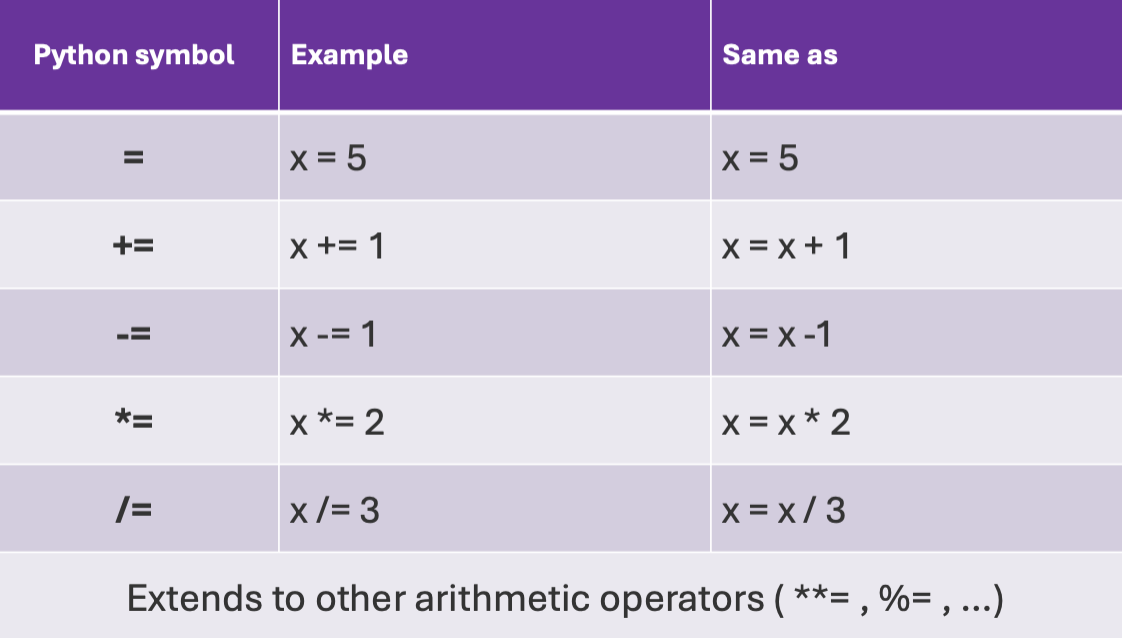
More assignment operators
Look at the image
What is a definite loop
A loop that runs a known number of times, you do know how many times it will repeat running it.
Iteration variables
For loops that explicit iteration variables that change each time through a loop. These iteration variables move through a sequence or set.
Range arguments
range(start, stop, step)
start - first number in the sequence
stop - upper limit
step - by how much it counts up or down
Lists
fruits = [“apple”, “banana”, “cherry”] , lists are mutable, they can be changed. duplicates are allowed, and allows mixed data types.
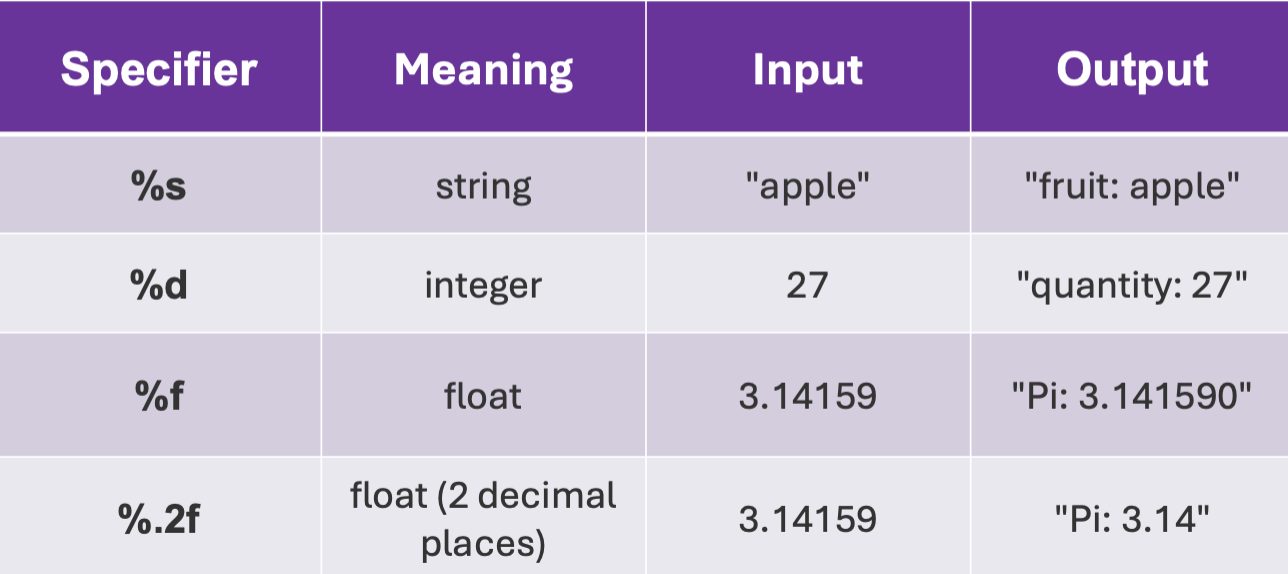
String formatting with modulo %
placeholders

Format specifiers for modulo
Look at image
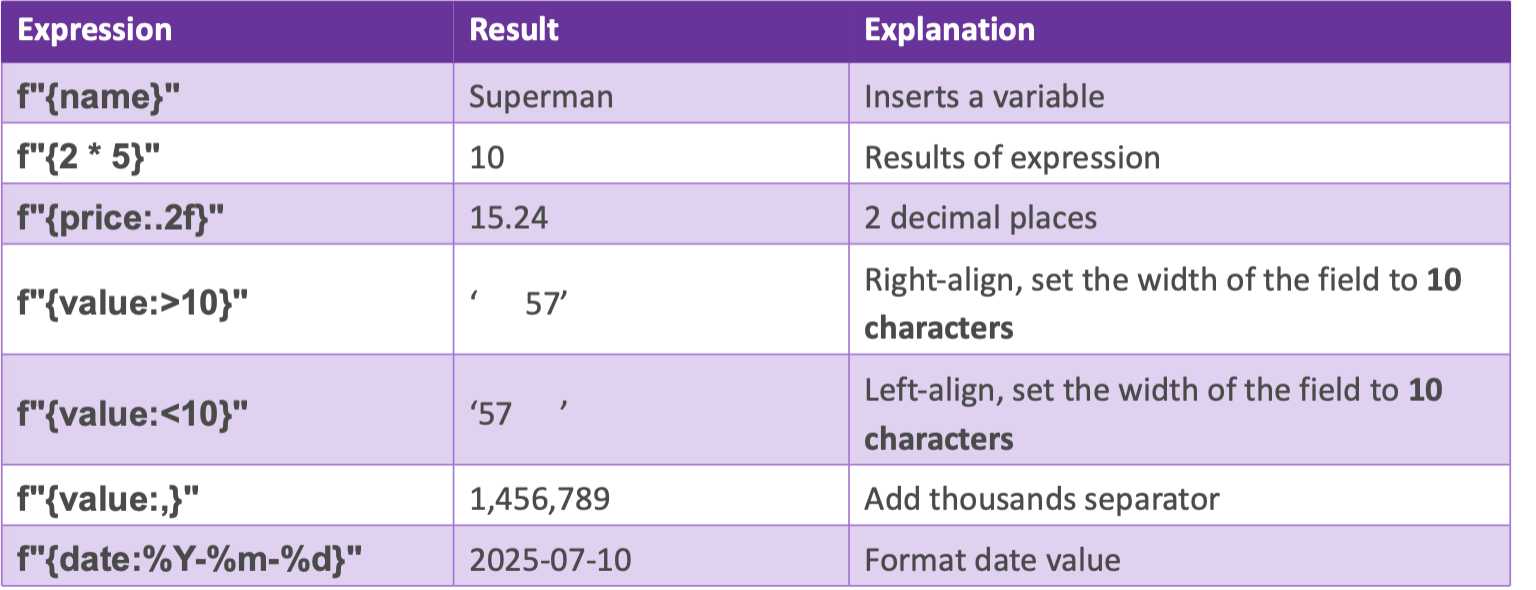
F string formatting
f"Hello, {name}! You’re {age} years old.”
You put the variables inside of the curly brackets
Important formatting instructions
Look at the image
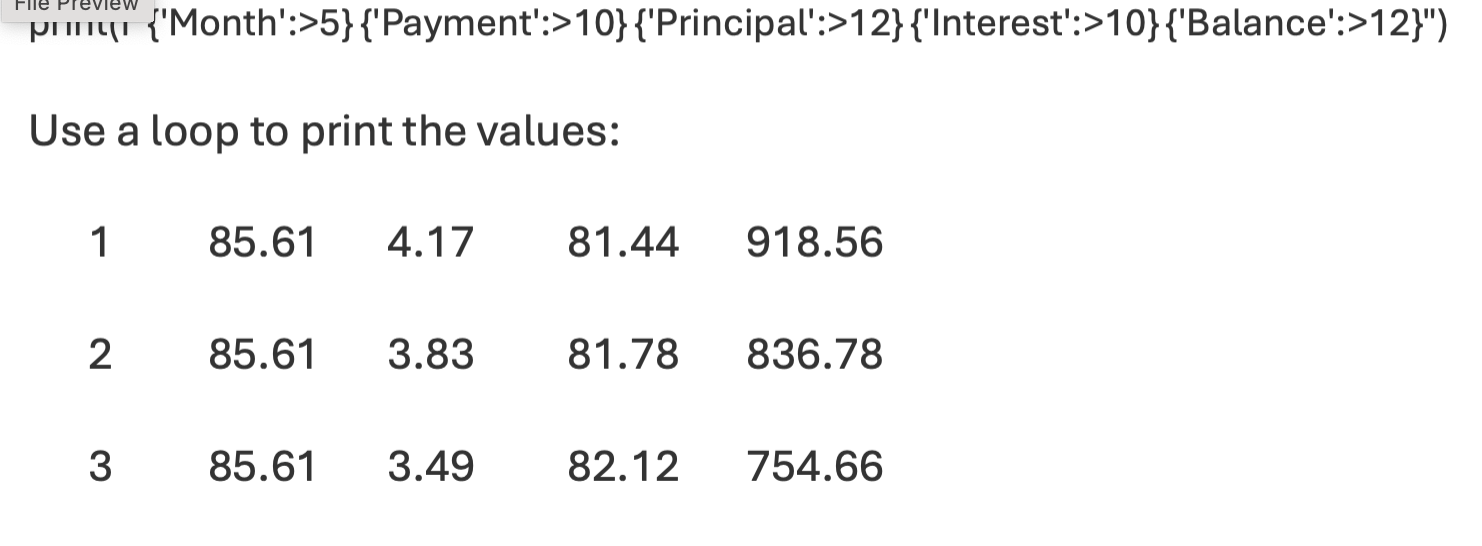
Formatting tables using f strings
print(f"{'Month':>5} {'Payment':>10} {'Principal':>12} {'Interest':>10} {'Balance':>12}")
What does print(fruit[1]) output when the word banana is there
a
Using open()
fh = open(“mbox.txt”, “r”)
Closing open files using close()
fh.close()
read the lines into a list
lines = fh.readlines()
Read the whole file into one string
content = fh.read()
Using the with statement
with open(“box.txt”, “r”) as fh:
content = fh.read(),
the with command automatically closes the file after its done reading
repr()
A build in function that return the representation of an object

len()
gives us the length of a string
.lower()
converts to lowercase
.upper()
converts to uppercase
.casefold()
“Aggressive” lowercase, works with unicode, converts it all to one readable text.
.strip()
removes leading and trailing whitespace, can insert a specific character into the parenthesis to specify what to strip.
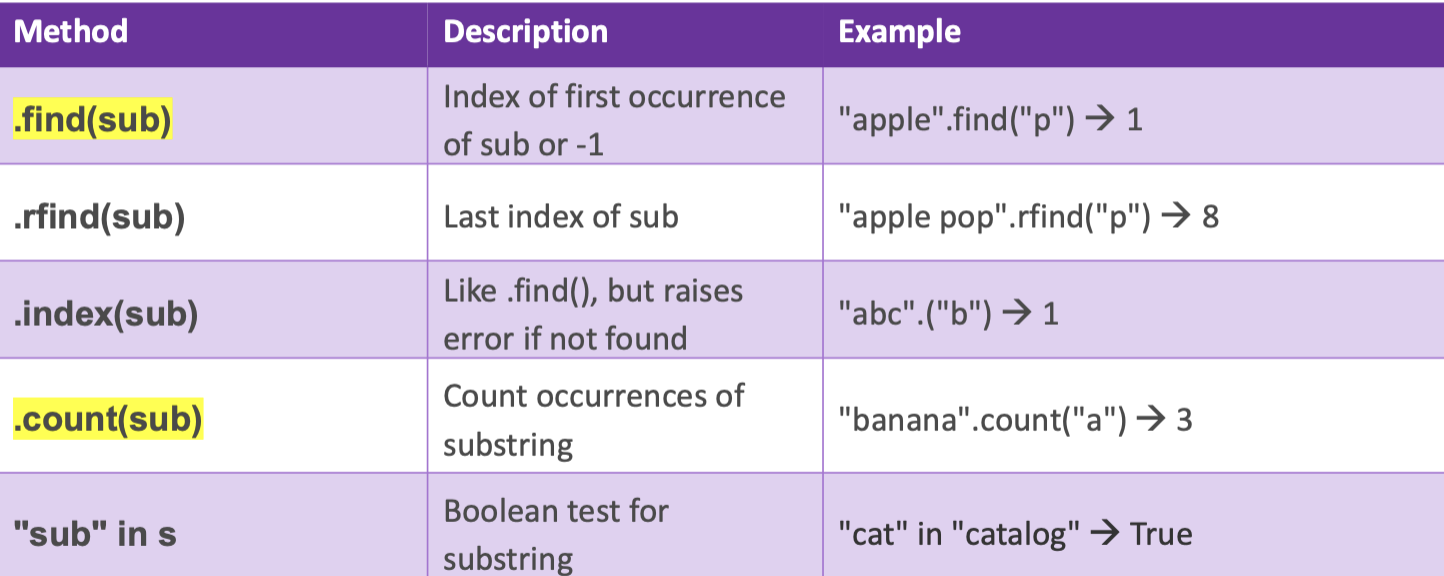
More search and count functions
Look at the image
.split()
splits on whitespace by default, can insert characters to split by
open, “a”
append, will append to the end of the file
open “w”
write, if a file doesn’t exist, python will create a new file otherwise it will overwrite any existing content
open “x”
write, if a file exists, python gives error, otherwise this will create a new file to which python can write content.
What is a list?
A list is a kind of collection, allows us to put many values in a single “variable”.
friends = [ 'Joseph', 'Glenn', 'Sally' ]
always in closed square brackets. mutable and each part can be induced to each part.
Negative Indices
Look at this image

.append()
we can add elements using the append method, the list stays in order and new elements are added at the end of the list.
deleting a list
del(fruit)
print(fruit), will be empty
.index()
returns the position of the first occurrence of an element in the list
.pop()
remove and return the last element in the list
.sort()
sorts elements in the list in ascending order, .sort(reverse=True) sorts in descending order
.deepcopy()
executes a deep copy, must import the copy module first. creates a second copy of the list. must attach to a new list.
Dictionaries
A mutable data structure that stores data as key-value pairs. ]
scores = { 'Chuck' : 61, 'Fred' : 83, 'Jan': 99 }
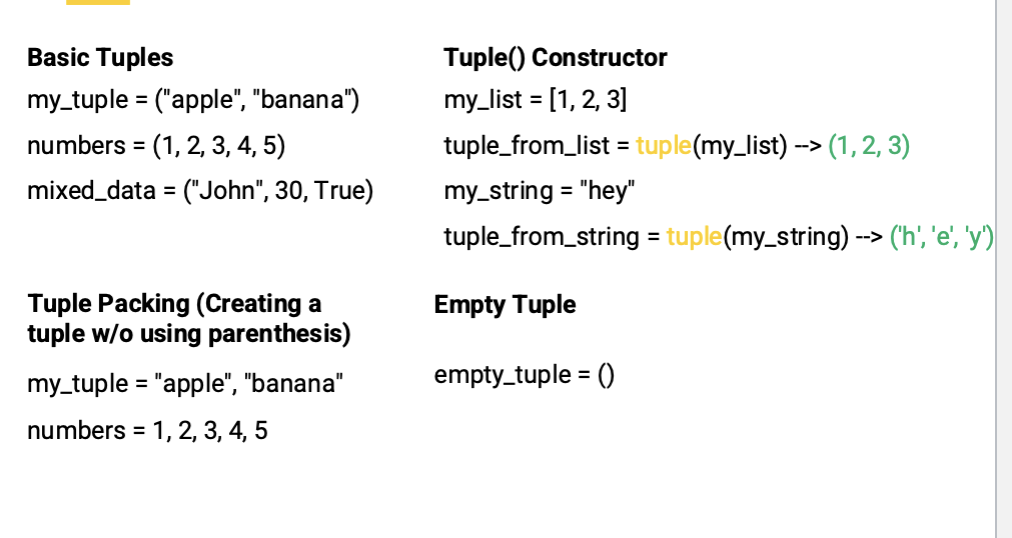
Tuple
A read only list, immutable, cannot be changed after it's created. In parenthesis.
What is a set?
A set is a collection of unique items that are unordered and unindexed. You cannot access elements using an index number. Inside curly brackets.

What does the difference method do for sets?
Returns items in one set but not the other
Which of the following creates a set correctly?
team = {“Alice”, “Bob”}
Which operations gives all elements that are in a or b (or both)?
a | b
What happens if you try to modify a tuple element?
Raises a TypeError
Which method removes a specific key from a dictionary and returns its value?
pop()
Why are tuples used instead of lists in some cases?
Tuples are faster and immutable
What does this code print?
a = {1, 2, 3} b = {3, 4, 5} print(a & b)
{3}
Given info = {"name": "Alice", "age": 30}, what does info.update({"age": 31}) do?
Updates “age” to 31
What will this code print?
prices = {"apple": 1.5, "banana": 0.9}
print(prices["banana"])0.9
What happens if you add a duplicate element to a set?
The duplicate is ignored.
Which module is needed to perform a deep copy of a list in python
import copy
If sales = [100, 200, 300], what is the output of sales * 2?
[100, 200, 300, 100, 200, 300]
If inventory = [50, 20, 70, 30], what does inventory.sort() produce?
[20,30,50,70]
Which of the following correctly creates a list in Python?
list = [1,2,3]
What does negative indexing allow you to do in a list?
Access items from the end of a list
Which of the following correctly copies a list without linking it to the original?
b =a.copy()