Lecture 30 Cell Motility I
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
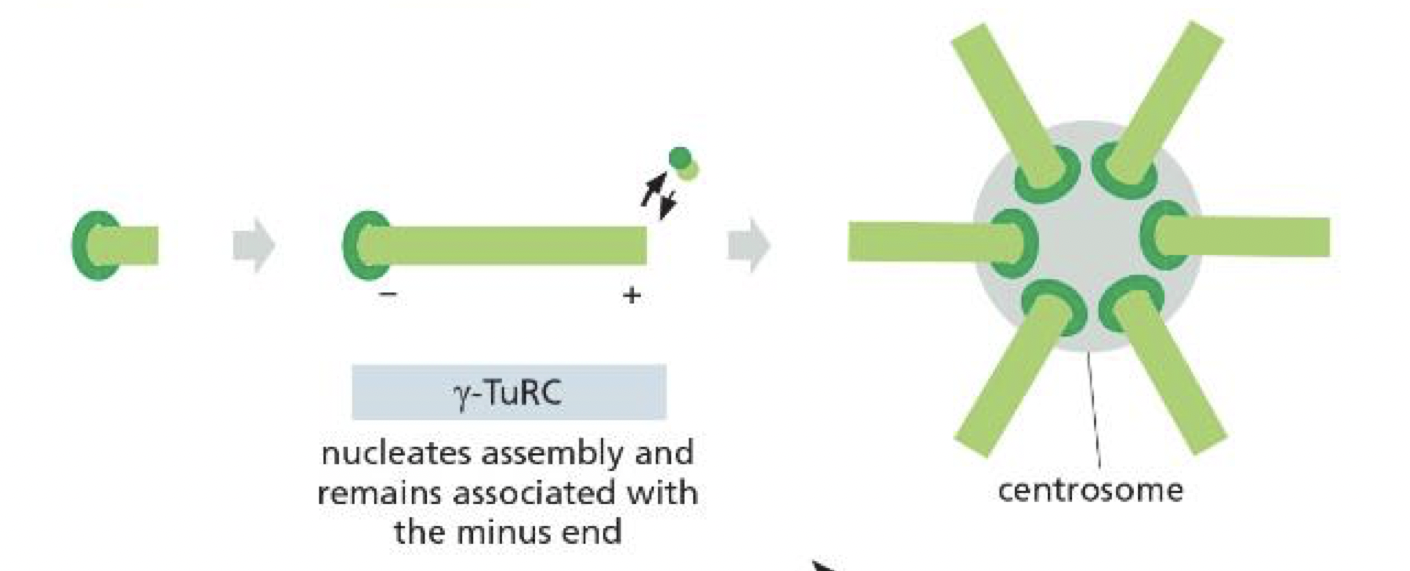
briefly, what does the gamma tubulin in the centrosome of micotubules do
nucleates them and protects the minus end
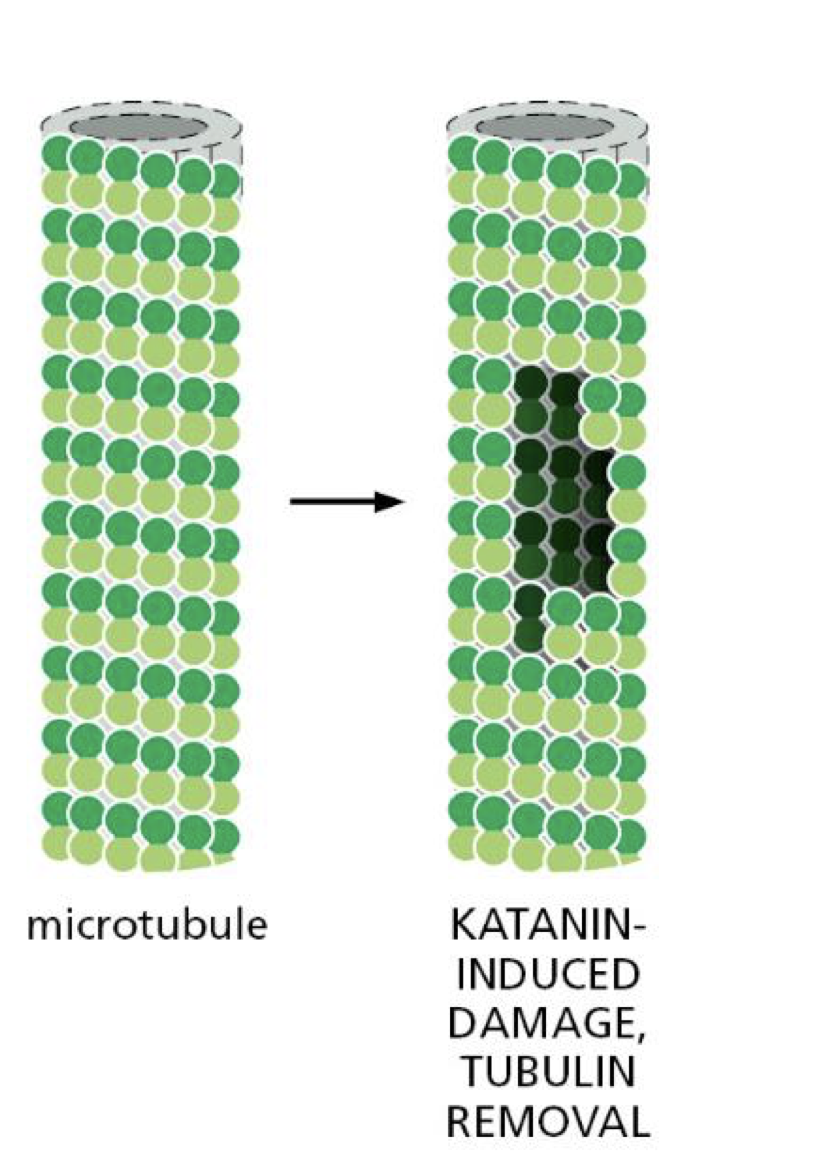
katanin
severs microtubule filaments
sits on wall of GDP tubulin and use ATP to extract tubulin subunit
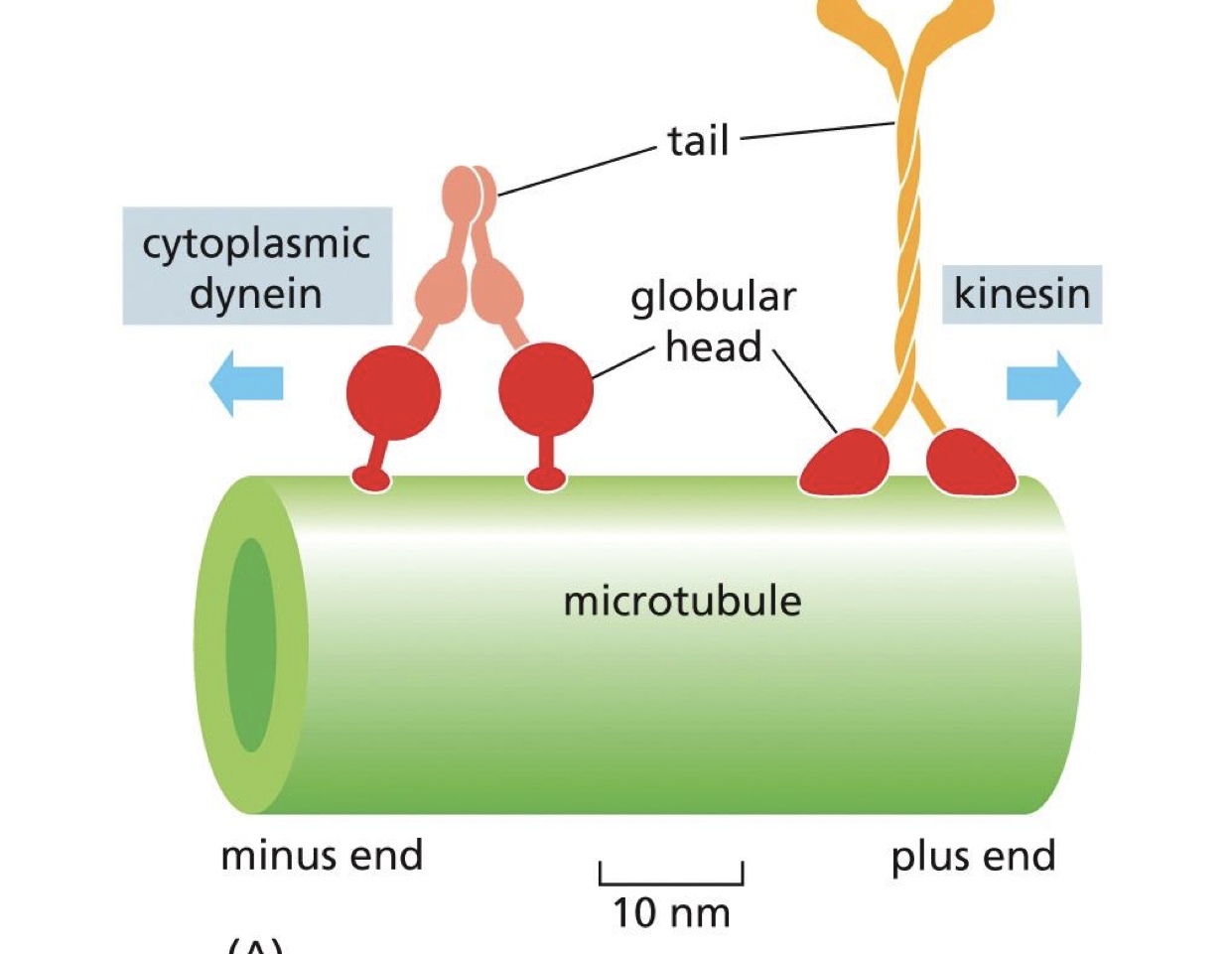
kinesis talk toward which end
plus end
dyne walk toward which end
minus end
what allows kinesin and dynein to walk in terms of their structure
the fact that they are dimers
what is the function of the head and tail of kinesin and dynein
head: binds and hydrolyze ATP to walk along microtubules
Tails: interact with cargo either directly or indirectly through adaptor proteins
dynein usually needs adaptor
how do kinesin help position organelles in eukaryotic cells
through anterograde trafficking (to plus end)
bind to ER as cargo and walk it out to plus end and stretch out ER network throughout cytoplasm
how do dynein help position organelles in eukaryotic cells
retrograde traffic to minus end
keep Golgi around minus end around centrosome
when are myosin heads in their highest/rigor state compared to when kinesin is in their highest/most rigor state
myosin in rigor state when there is NO NUCLEOTIDE BOUND / ADP bound
kinesin in most rigor state when there is either no nucleotide or when they are ATP bound
describe how the kinesin walks
one head encounters microtubule, binding tightly, causing ADP to be released and ATP binds to empty nucleotide binding site = tight bound
neck linker throws second head forward
first head hydrolysis ATP, releasing ADP and Pi, leading head no exchanges its ADP for ATP
kinesin moves processively step by step
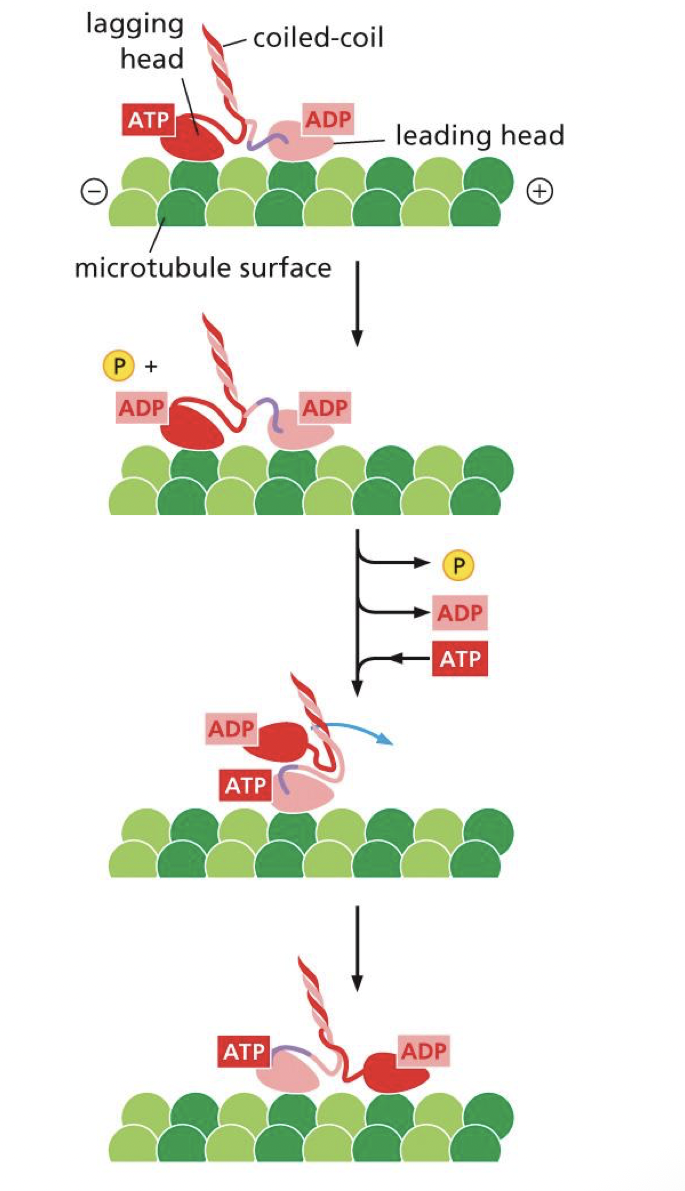
how does cytoplasmic dynein interact with cargo
through adaptor proteins
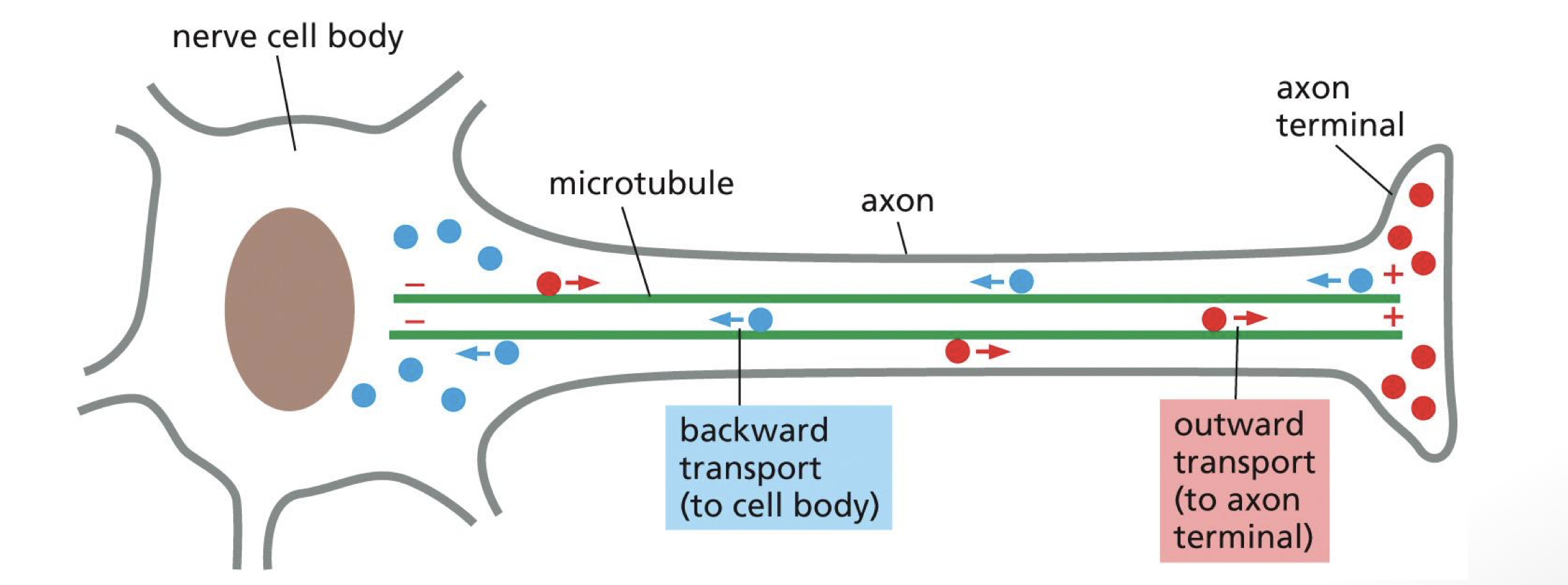
what allows for directional transport
microtubules pointing in the same direction
Summarize how fluorescent marker proteins and non-hydrolyzable ATP analogs can be used to study the activity of motor proteins such as kinesin or myosin.
we can see / track kinesin in space and time
see that kinesin moves progressively toward plus end
tail is usually tagged
Compare the functions and movements of cilia and flagella.
cilia moves fluid over cell surface due to dynein power stroke
flagella propels itself through liquid solution in wave form
both are extension of cell that are microtubule based inside
Describe the arrangement of microtubules inside a cilium or flagellum
the microtbule base structure inside cilia and flagella is called an axenin
two microtubule doublets with dynein dimers in between so that they can walk along adjacent doublets
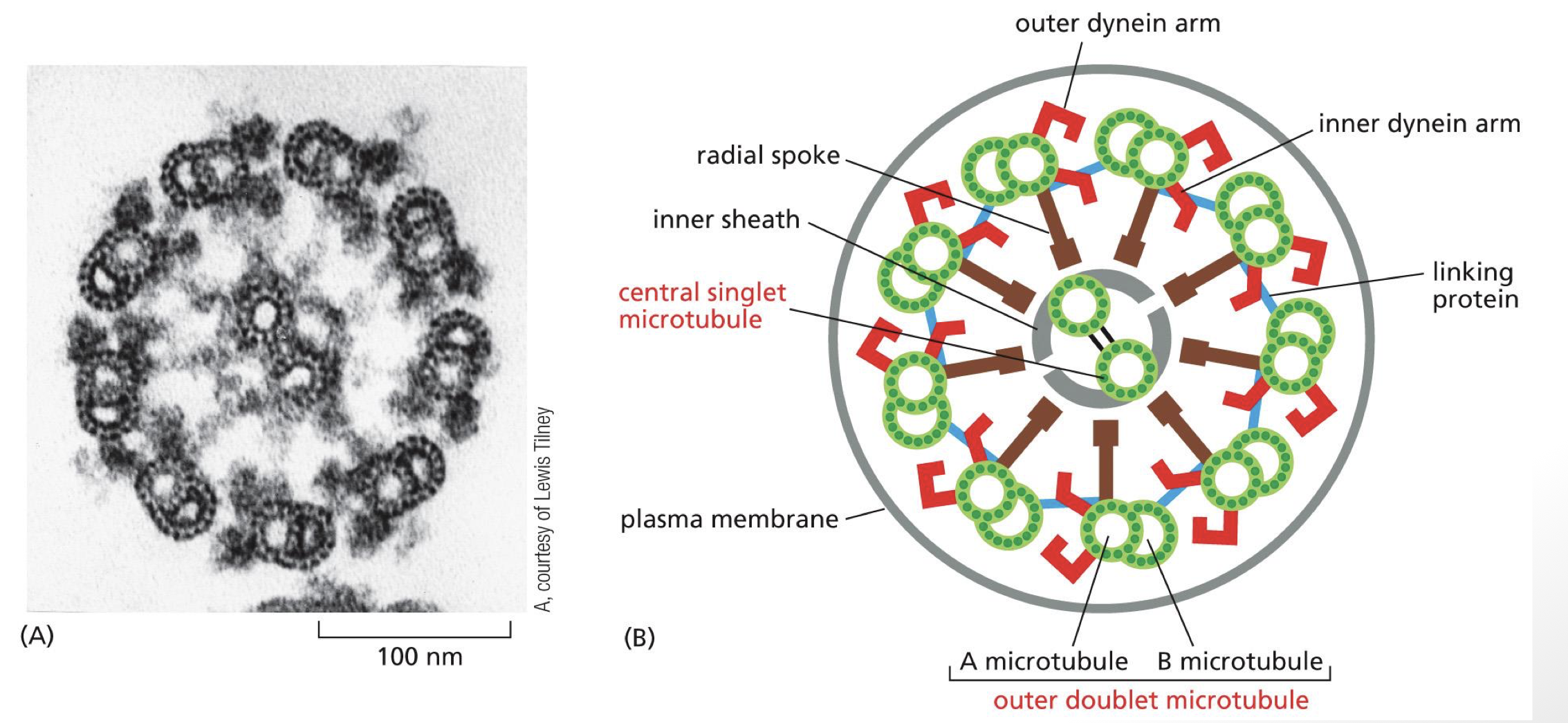
describe the arrangement of the axonem
9 + 2 arrangements
doublets have one A and one B microtubule
dynein associate with A microtubule on tail
dynein head walk on B microtubule on adjacent doublet
center 2 are important for stability / organization
what happens if we phosphorylate our microtubule associated proteins (MAP)
they will not be recruited to microtubules because MAPS have a positive charge and microtubule tails have a neg charge
allows us to repurpose our microtubules for things such as the mitotic spindle
result: MAPS not recruited to microtubules due to charge repel
name 2 functions of MT motors (K and D)
moving vesicles / directional transport
position organelle in eukaryotic cell
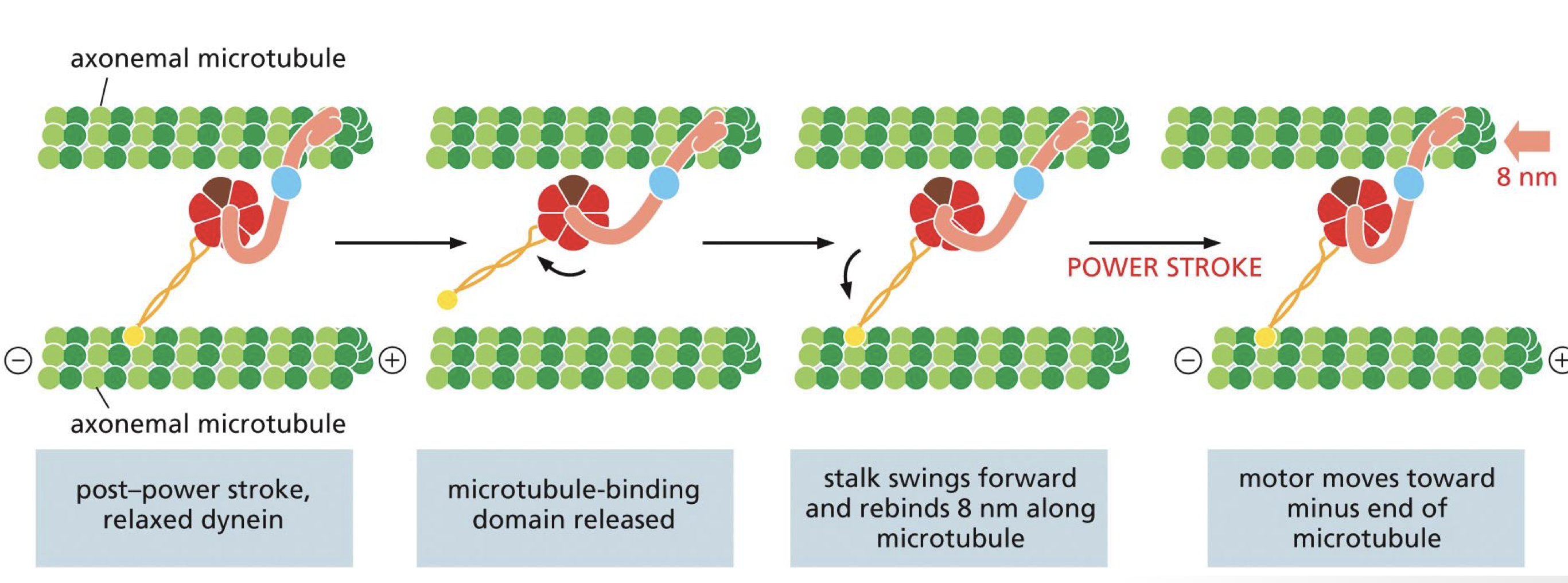
describe the dynein power stroke
dynein is stable when ATP bound
ATP hydrolysis releases microtubule binding domain and stalk swings forward, stretching the linker making it more reactive
motor moves toward minus end of microtubule
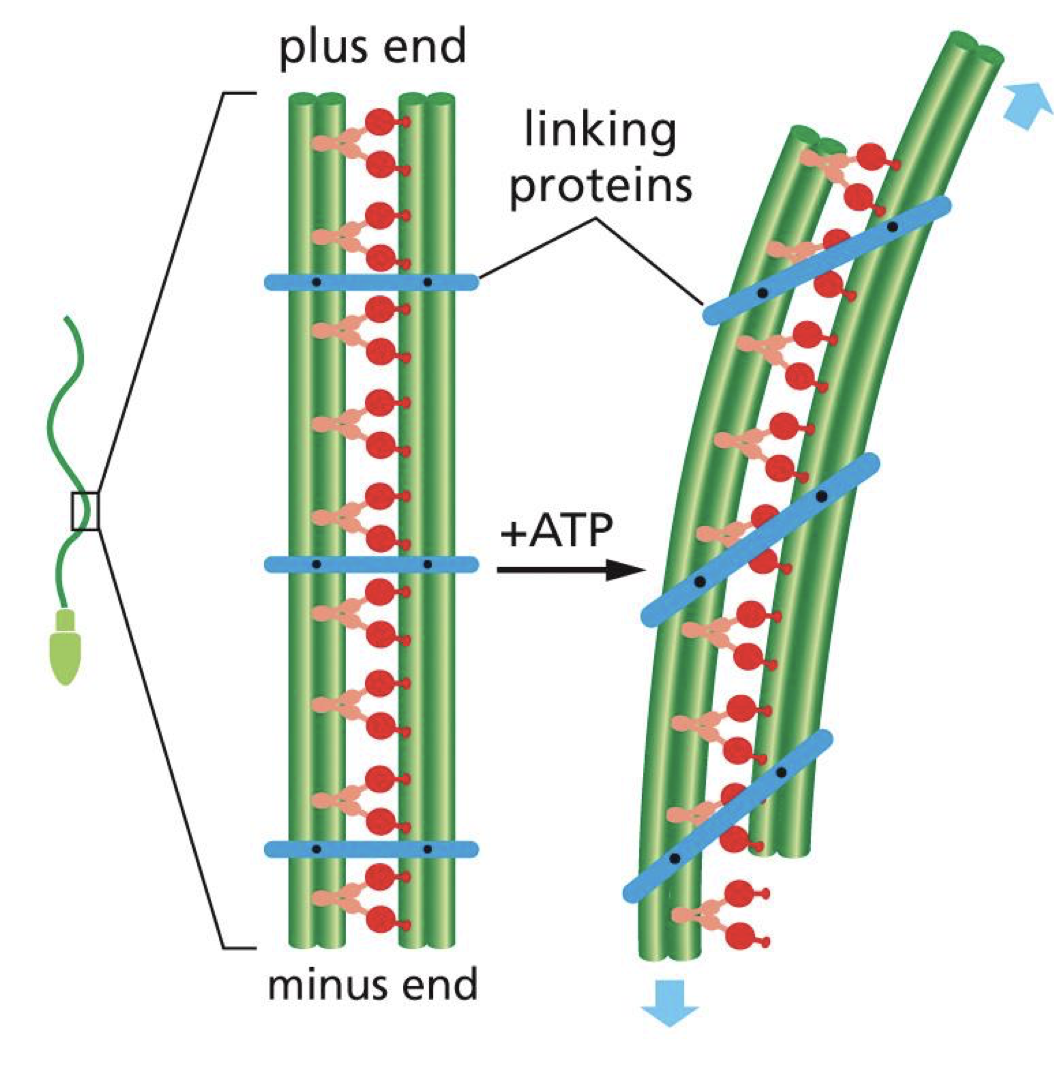
**dynein produces microtubule sliding
in flagellum, dynein cause microtubule bending