Population Ecology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is a population?
a group of individuals from the same species that live in the same area at the same time
what is population ecology
study of how and why the number of individuals in a population changes over time
The number of individuals present in a population depends on what four processes?
birth, death, immigration, and emigration
populations grow due to
birth and immigration when individuals enter a population by moving from another population
populations decline due to
deaths and emigration which occurs when individuals leave a population to join another population
Demography
the study of factors that determine the size and structure of populations through time
If a population consists primarily of young individuals with a high survival rate and reproductive rate… the population size should?
increase over time
Life table
summarizes the probability that an individual will survive and reproduce in any time during its lifetime
survivorship
the probability of an individual in a population surviving to a specific age
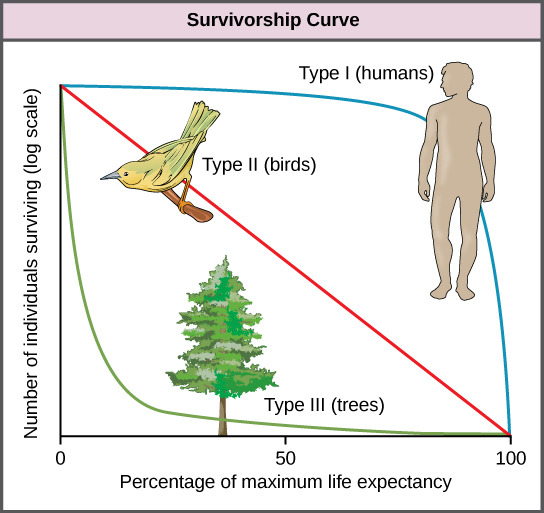
The survivorship curve
plot of the logarithm of the number of survivors vs age
Type 1 survivorship curve
survivorship throughout life is high, and most individuals approach the maximum life span (humans)
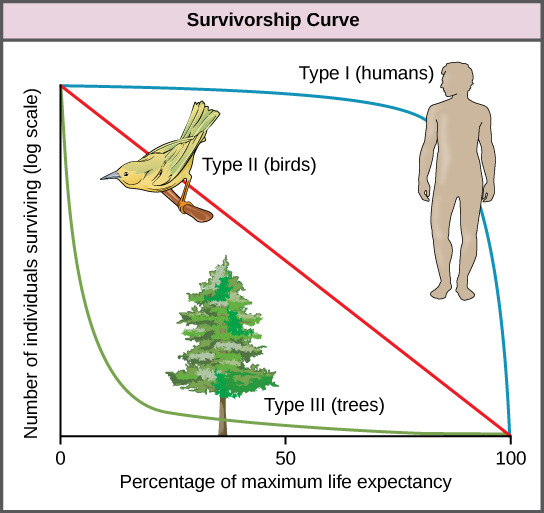
Type 2 survivorship curve
most individuals experience relatively constant survivorship over time ex. songbirds
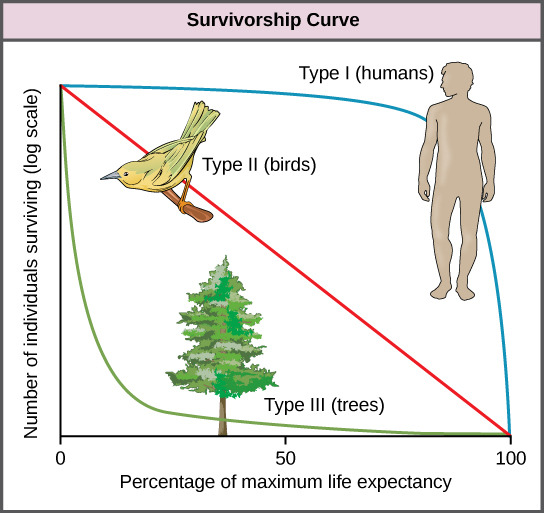
Type 3 survivorship curve
high death rates early in life, with high survivorship after maturity ex. plants
Fecundity
number of female offspring produced by each female in the population
Age-specific fecundity
average number of female offspring produced by a female in a given age class
what does data on survivorship and fecundity allow researchers to calculate?
the growth rate of a population
Fitness trade-off
occur because every individual has a restricted amount of time and energy at its disposal
a female can…
maximize fecundity, maximize survival, or balance between the two
life history
describes how an organism allocates it resources to growth, reproduction and activities related to survival
aspects of an organism’s life history
survivorship, age-specific fecundity, age at first reproduction, and growth rate
organisms with high fecundity tend to…
grow quickly, reach sexual maturity at a young age, produce many small eggs or seeds
organisms with high survivorship tend to
grow slowly and invest their energy and time into traits that reduce damage from enemies and increase their ability to compete for resources
A population’s growth rate is the…
change in the number of individuals in the population per unit of time
if no immigration or emigration is occurring
growth rate = N (number of individuals in a population) x r (per-capita rate of increase)
Per-capita rate of increase (r)
is the difference between the birthrate and death rate per individual r= b-d
If the per-capita birthrate is greater than the per-capita death rate then…
r is positive and the population is growing
intrinsic rate of increase
when birthrates per individual are as high as possible and death rates per individual are as low as possible r reaches this
intrinsic rate of increase equation
N/t = rmax x N
exponential population growth occurs when…
r does not change over time and is density independent (does not depend on the number of individuals in the population)
two circumstances of exponential growth
a few individuals found a new population in a new habitat
a population has been devastated and beings to recover, starting with a few surviving individuals
population density
the number of individuals per unit area
what happens when population density gets very high?
the population’s per-capital birthrate should decrease and the per-capita death rate increase, causing r to decline (density dependent)
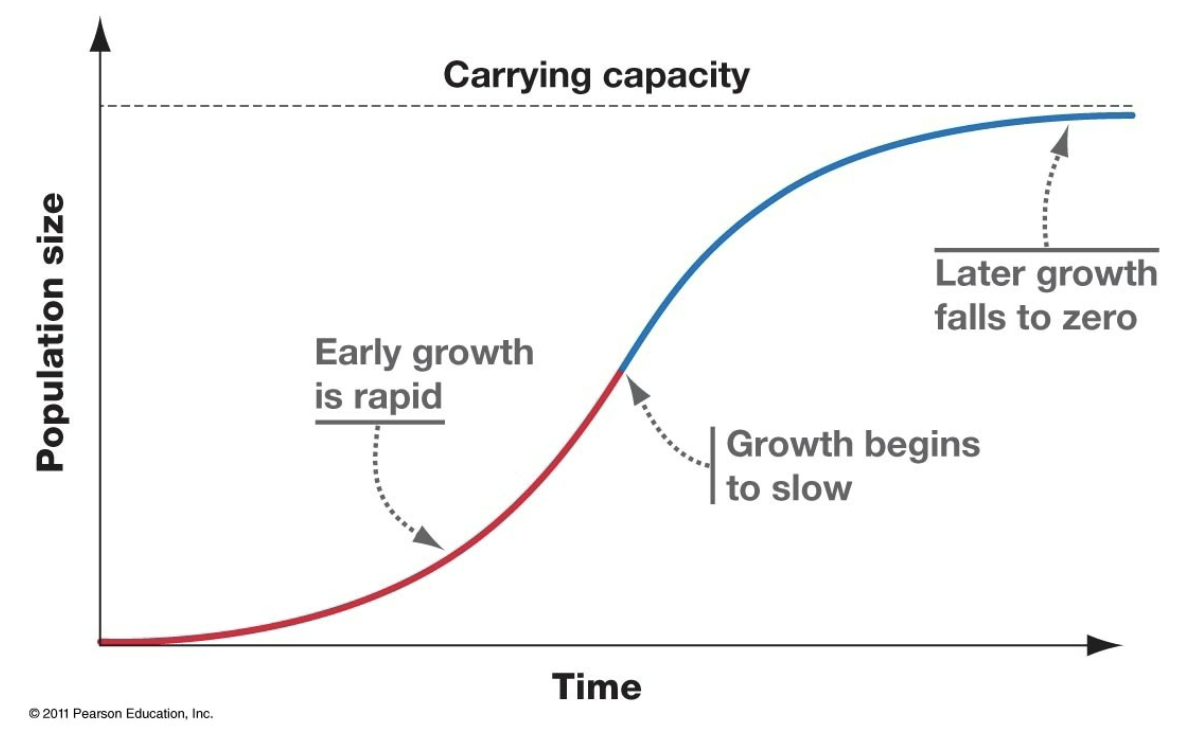
Carrying capacity (K)
the maximum number of individuals in a population that can be supported in a particular habitat over a sustained period of time
carrying capacity of a habitat depends on what factors
food, space, water, soil quality, resting/nesting sites
If a population size of N is below carrying capacity K…
the population should continue to grow and a populations growth rate should be proportional to (K-N)/K
logistic growth equation
ΔN / Δt = rmax N((K-N)/K)
the logistic growth equation describes…
logistic population growth- population growth where the growth rate slows down as the population size approaches carrying capacity
logistic growth is density depended which means
as a population approaches a habitat’s carrying capacity, its growth rate should slow
three distinct stages of density-dependent growth
Initially, growth is exponential (r is constant)
Growth rate begins to decline (N increases) when competition for density-dependent factors begins to occur
Growth rate reaches 0 at the carry capacity ( N vs. t is flat)
Density dependence graph
density independent factors such as _____ are ____. They change _____
variation in weather patterns, abiotic, birthrates and death rates regardless of population size
density dependent factors such as _____ are usually ___ change ______
increased predation when a deer population increases, biotic, in intensity as a function of population size
density-dependent changes in survivorship and fecundity cause
logistic population growth
population cycles
regular fluctuations in size
hypotheses for population cycles
depends on density depended factors. Predation, disease, or food shortages intensify at high population density and cause population numbers to crash
age structure of a population tends to be…
uniformed in developed countries and bottom-heavy in developing countries
population momentum
increase survivorship and many young women still have children even though fecundity is lower
in 2021, the world population is estimated at
over 7.8 billion, and 79 million people are added each year
worldwide growth rate
1.2%
replacement rate
each woman producing exactly enough offspring to replace herself and her offspring’s father
when the replacement rate is sustained for a generation…
zero population growth
the future of the human population relies on
fertility rates and how many children each woman living decides to have