Lab 7 Demography data collection and analysis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Pseudoreplication
counting an individual more than once violates a major assumption of statistical analysis
How was pseudoreplication avoided (AT CEMETERY)
students were to be vary careful not to count the headstones that another group had already done
(thats why recording each headstone was useful)
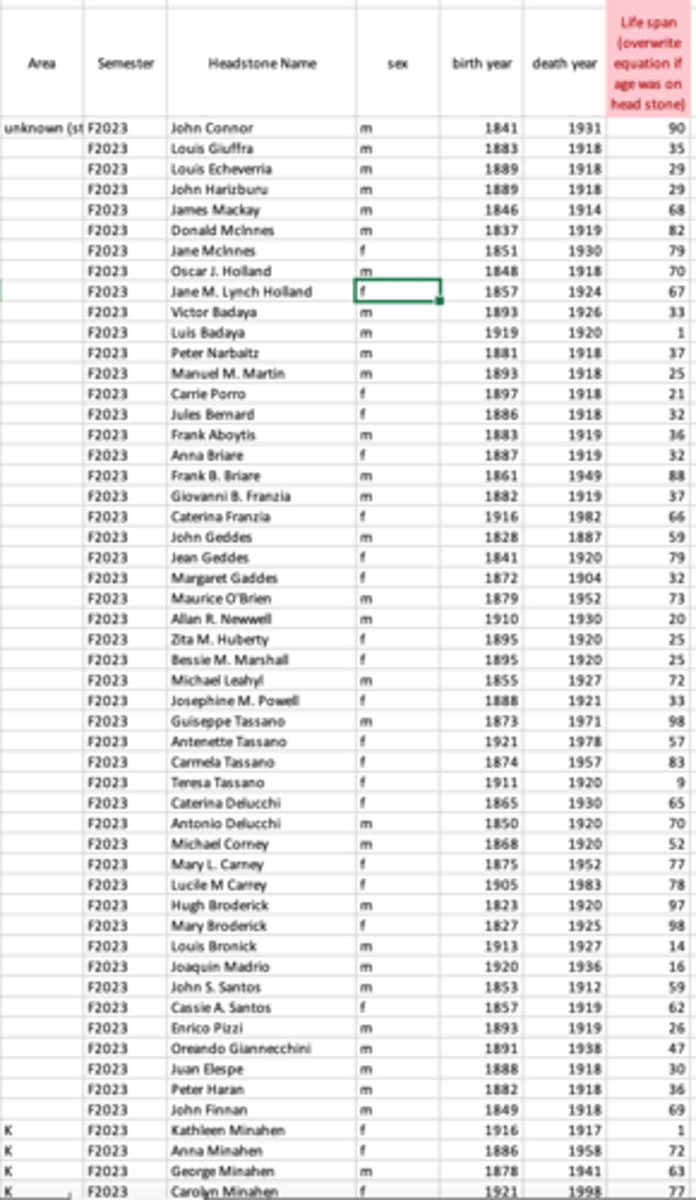
Data collection methodology
1.) students were put into groups and were assigned a specific row at the cemetery
2) each student collected 50-75 data points (headstones)
3) Each data point recorded the name, inferred sex, birth year, and death year
Headstones were only skipped if
- the name or gender wasn't able to be determined
- if the headstone did not contain the necessary information
- the deceased person was less than 1 year old
How was the data standardized (PT 2 DEMO)
POSSIBLE ERRORS
- any cells that contained ages that were less than or equal to zero were deleted
- any calls that were ages that were greater than 110 were deleted
How was data standardized (PT 1 DEMO)
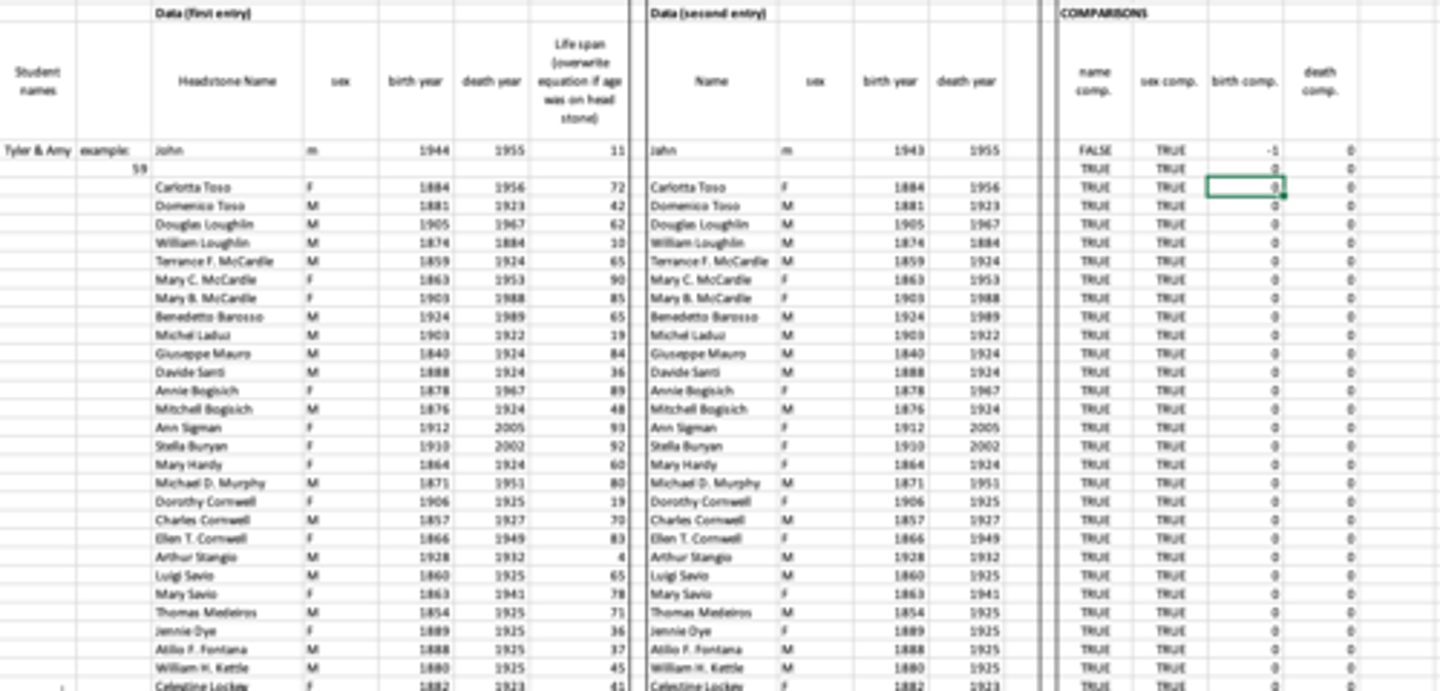
AFTER CEMETERY
1) each student wrote there recorded data on an excel sheet twice
2) Both data sets were compared on the comparison chart
--------------
POSSIBLE OUTCOMES FROM THE COMPARISON CHART:
True = name and/or inferred sex was written correctly
False = name and/ or inferred sex was incorrect
+# or -# = Birth comp/death comp = difference in birth/deat year was either above or below actual age
0 birth/death comp = the difference in birth or death years was 0 (meaning data was inputted correctly
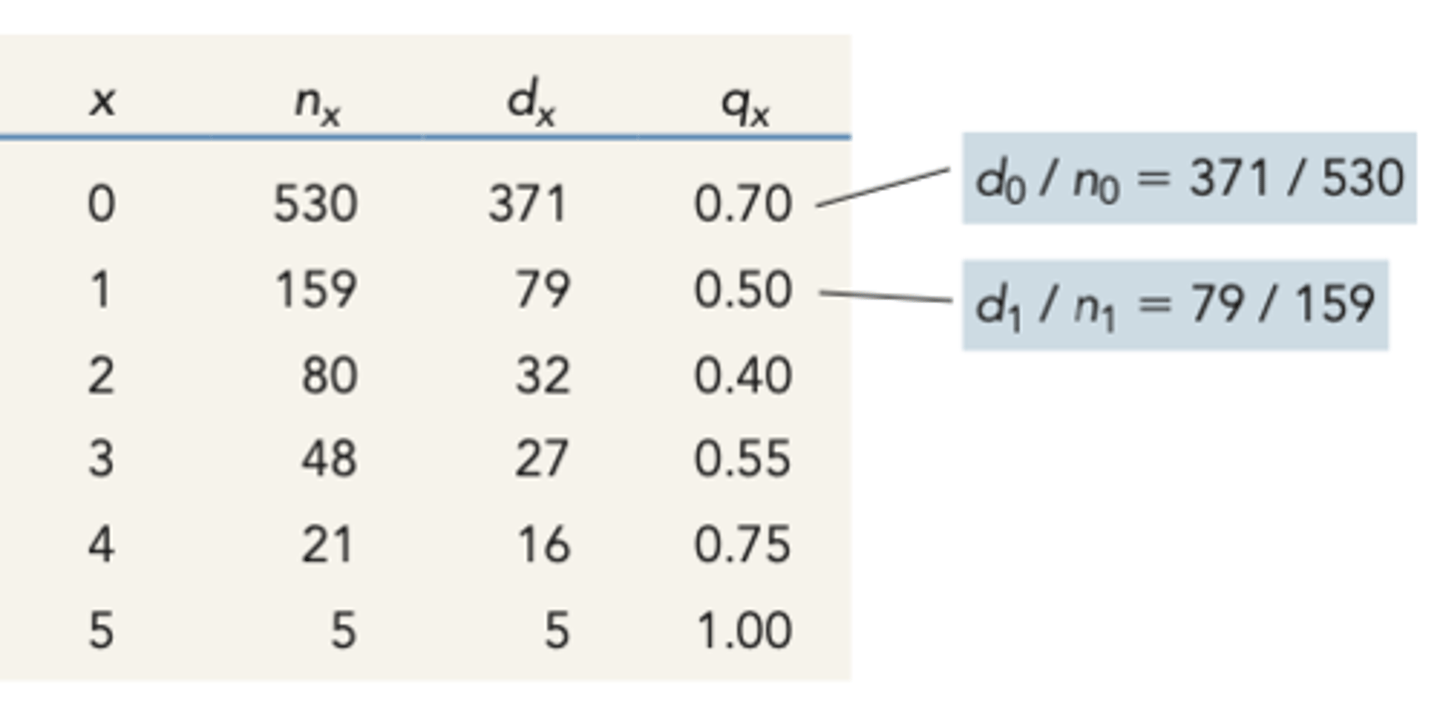
life tables
Age-specific summaries of survival patterns of a population
--------------
WHAT LABELS DOES IT INCLUDE
- x
- nx
- lx
- dx
- qx
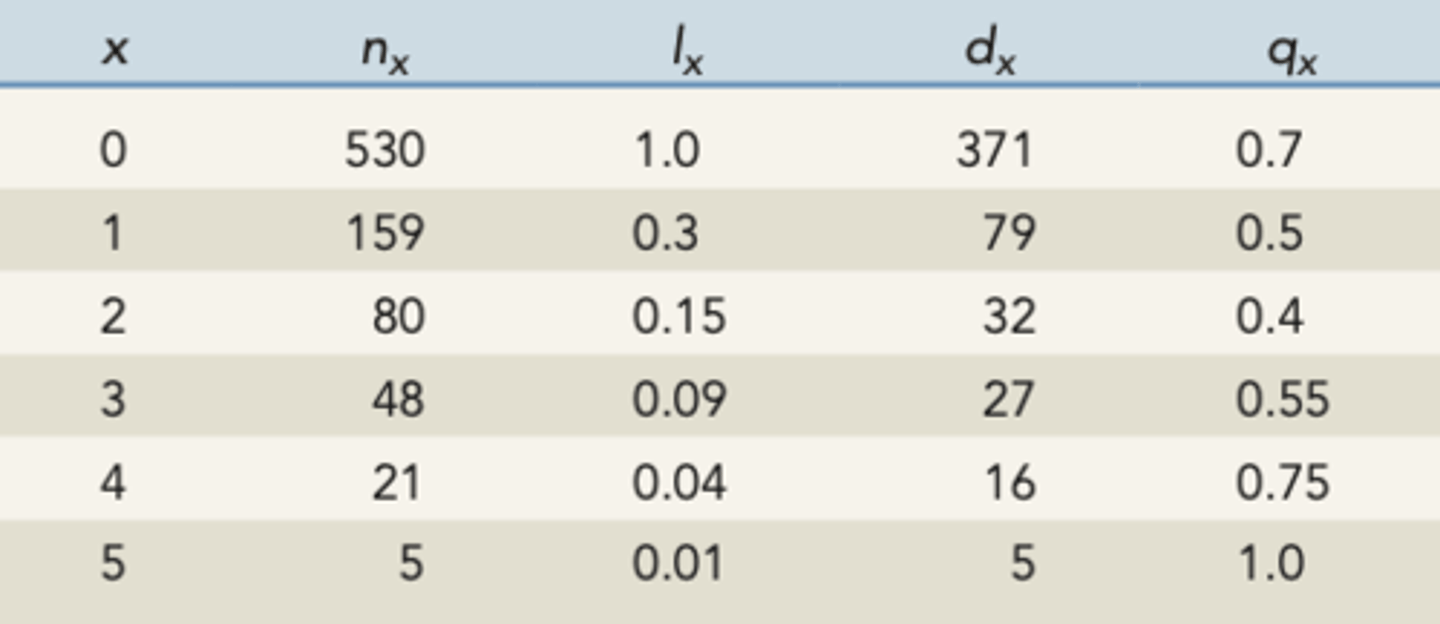
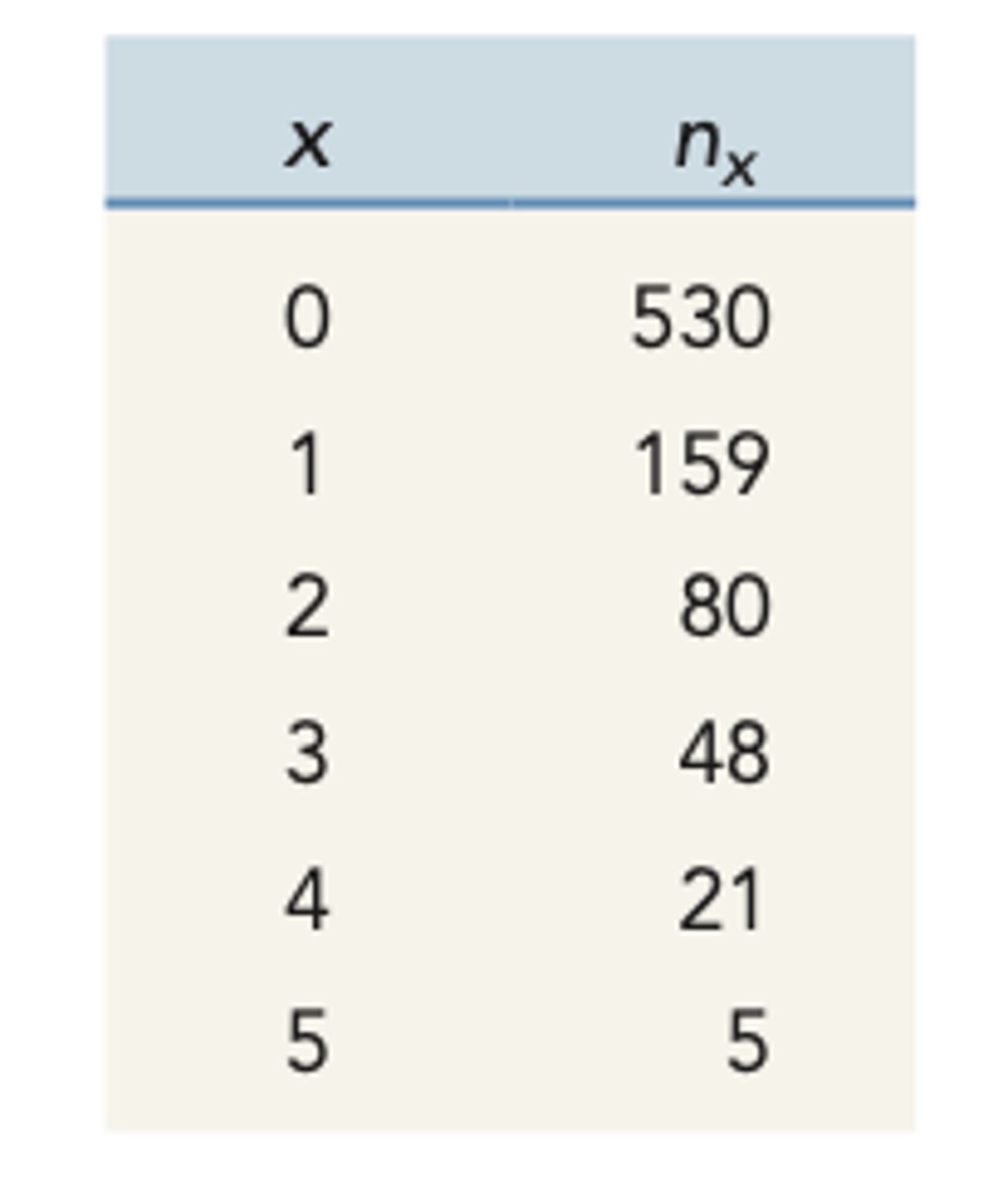
x (life table)
age class
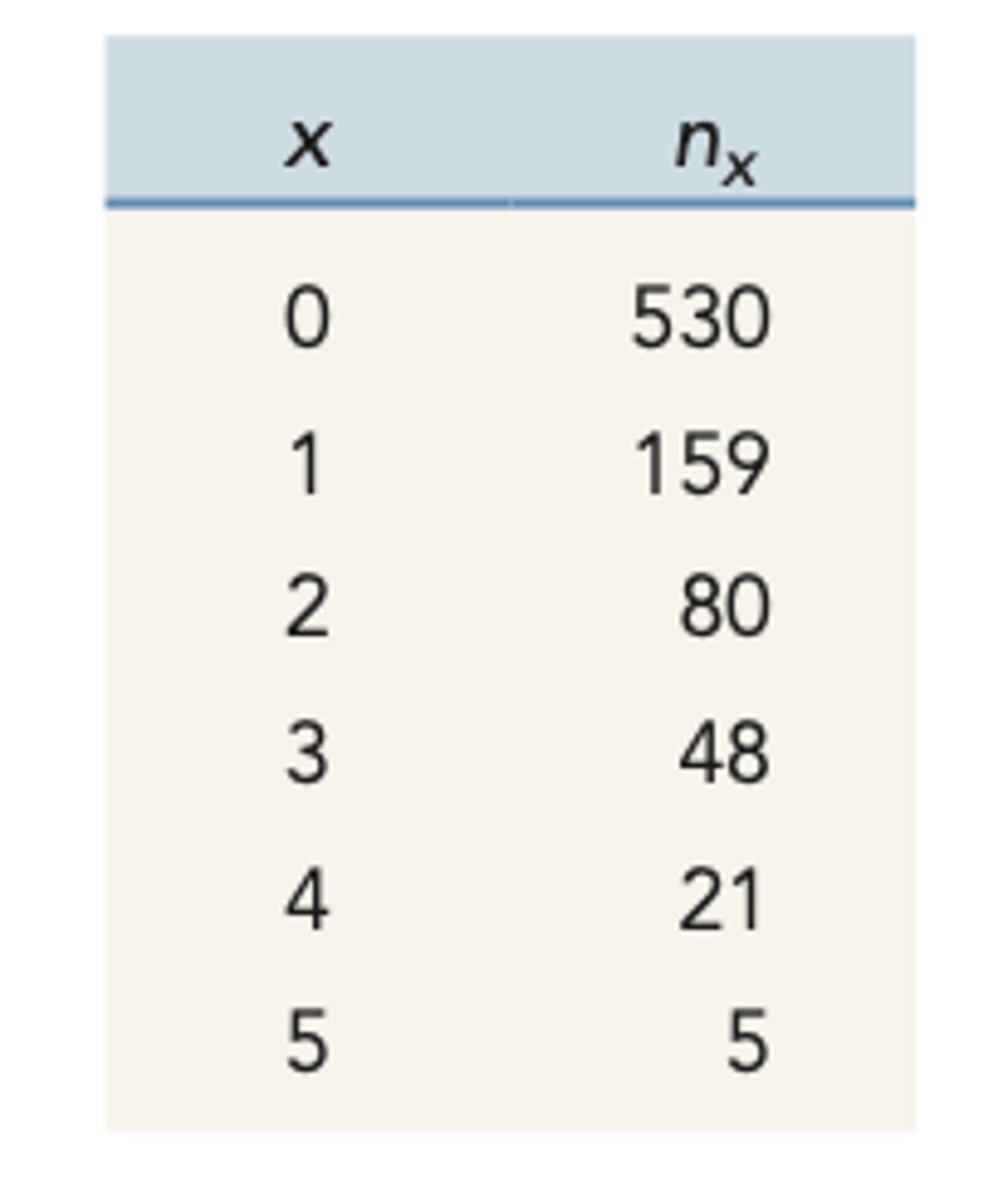
nx (life table)
number of individuals alive at beginning of age x
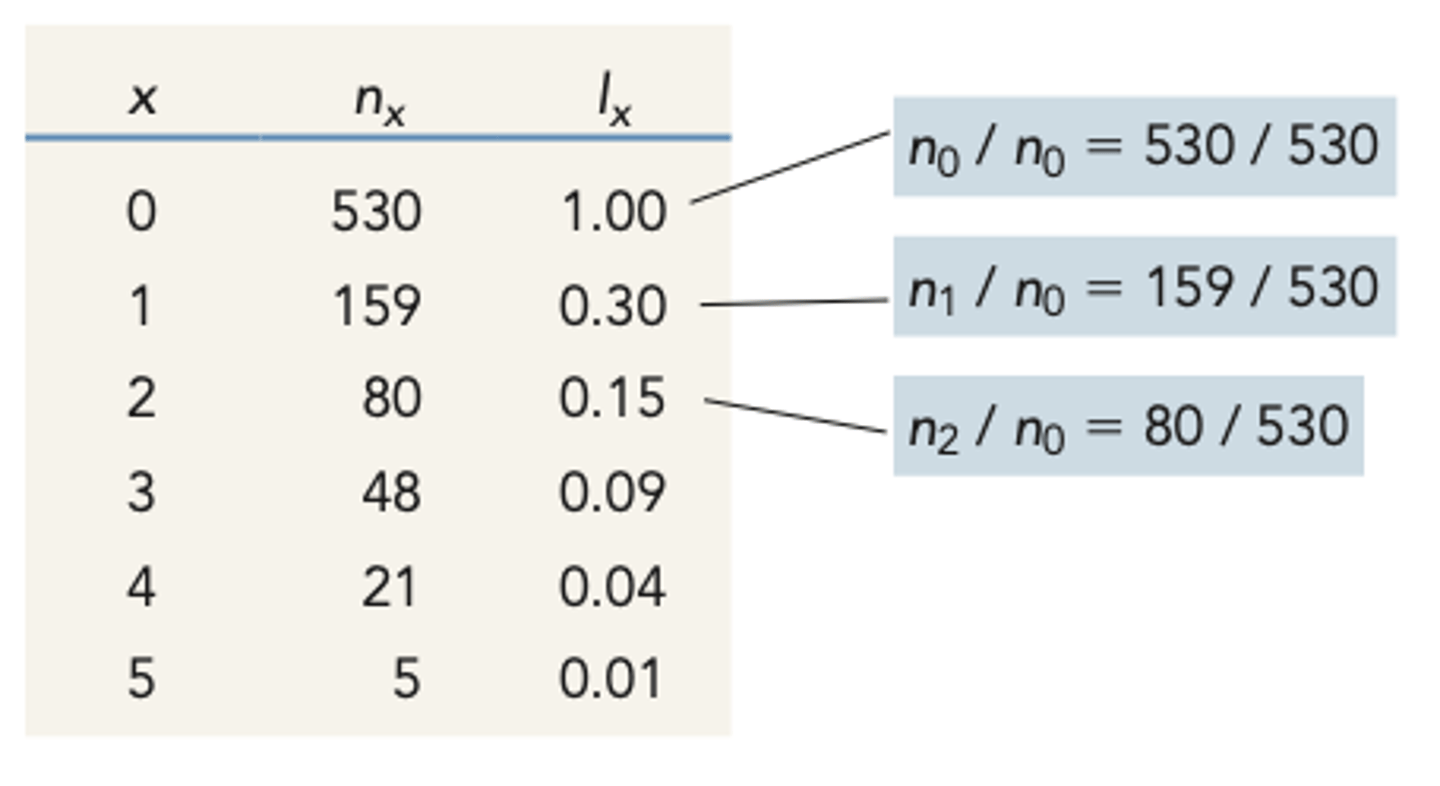
Lx (life table)
TEXTBOOK DEF
- survivorship, represents the probability at birth of surviving to any given age (x)
--------------
EQUATION
(Nx/N0)
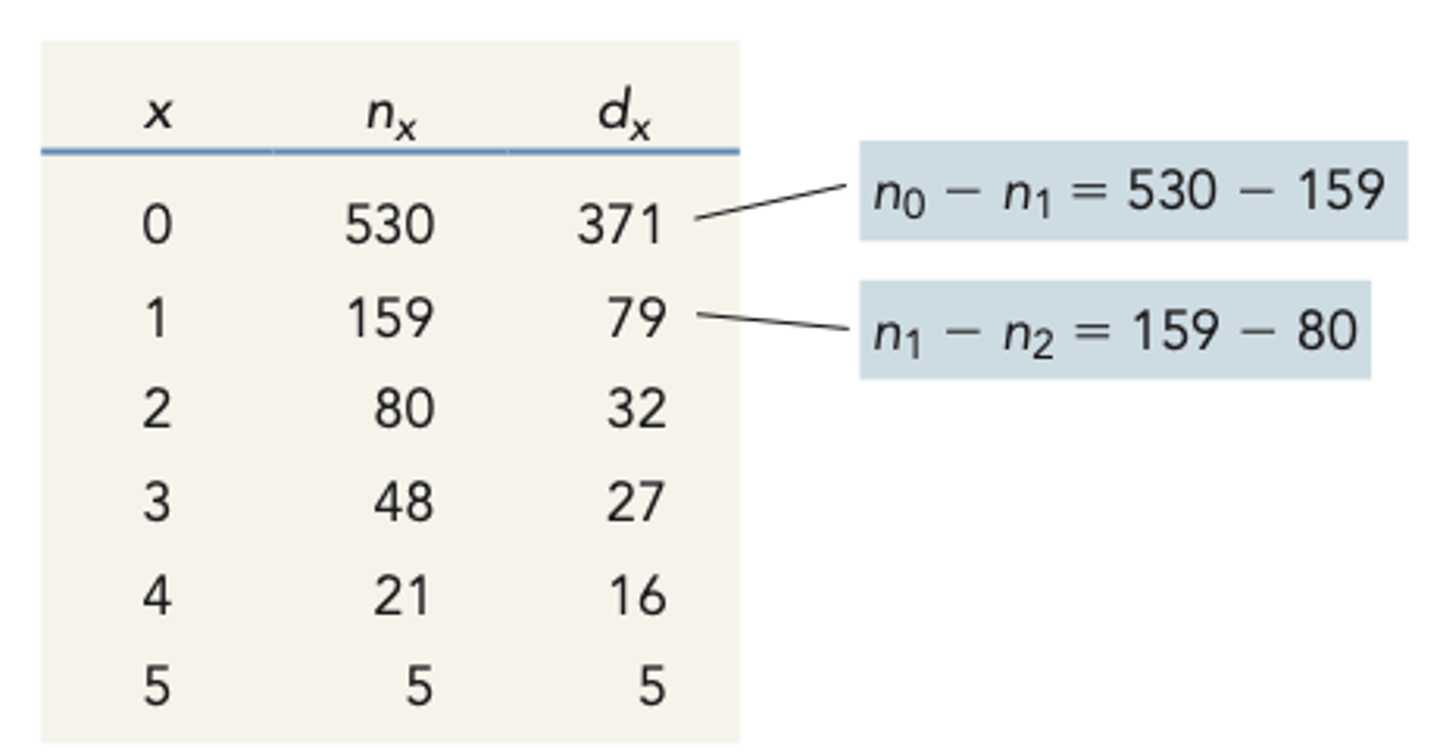
dx (life table)
measure of age-specific mortality during time interval
--------------
HOW IS IT MEASURED
- subtracting the number of individuals alive for any age class and the next older age class
--------------
EQUATION
nx - (nx+1)
qx (life table)
age specific mortality rate
- number of individuals that died during any given interval (dx) divided by the number of alive individuals at the beginning of that interval (nx)
--------------
EQUATION
(dx/nx)
cohort approach (life tables)
Studies a group of individuals from birth to death
Static approach (life tables)
"snapshot in time"
- samples a group of individuals over a single time period
--------------
WHAT DOES IT ASSUME
- each age class is proportionately sampled an that age-specific mortality rates (and birth rates) remained constant over the time period
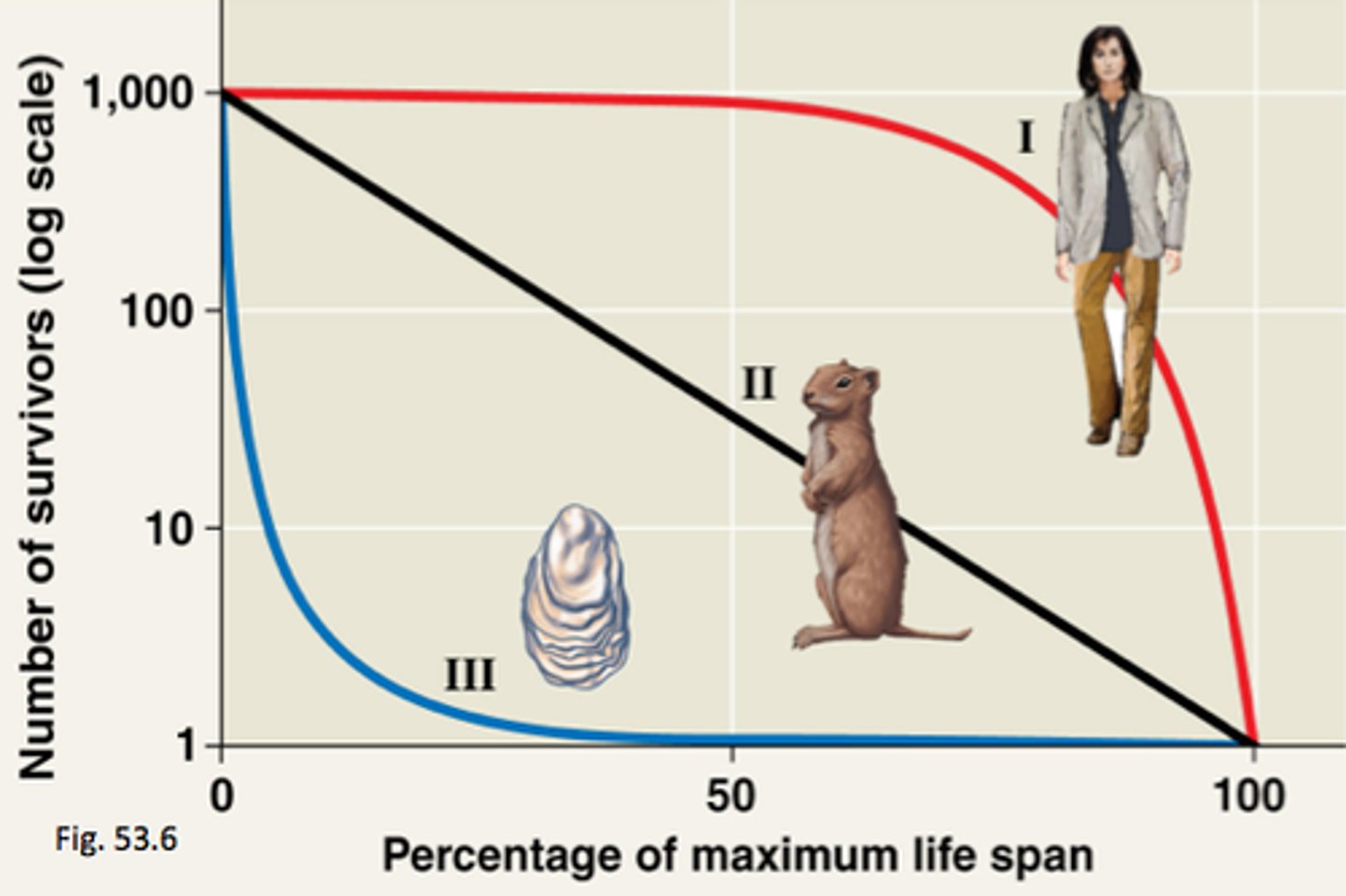
survivorship curve
Graph showing the number of survivors in different age groups for a particular species.
- is based on the lx column on life table
--------------
TYPES OF SURVIVORSHIP CURVES
- type 1
- type 2
- type 3
Axis of surviorship curve
X axis = age (years) (or % of maximum life span)
Y axis = Survivorship (lx) (# of individuals surviving in log10 scale)
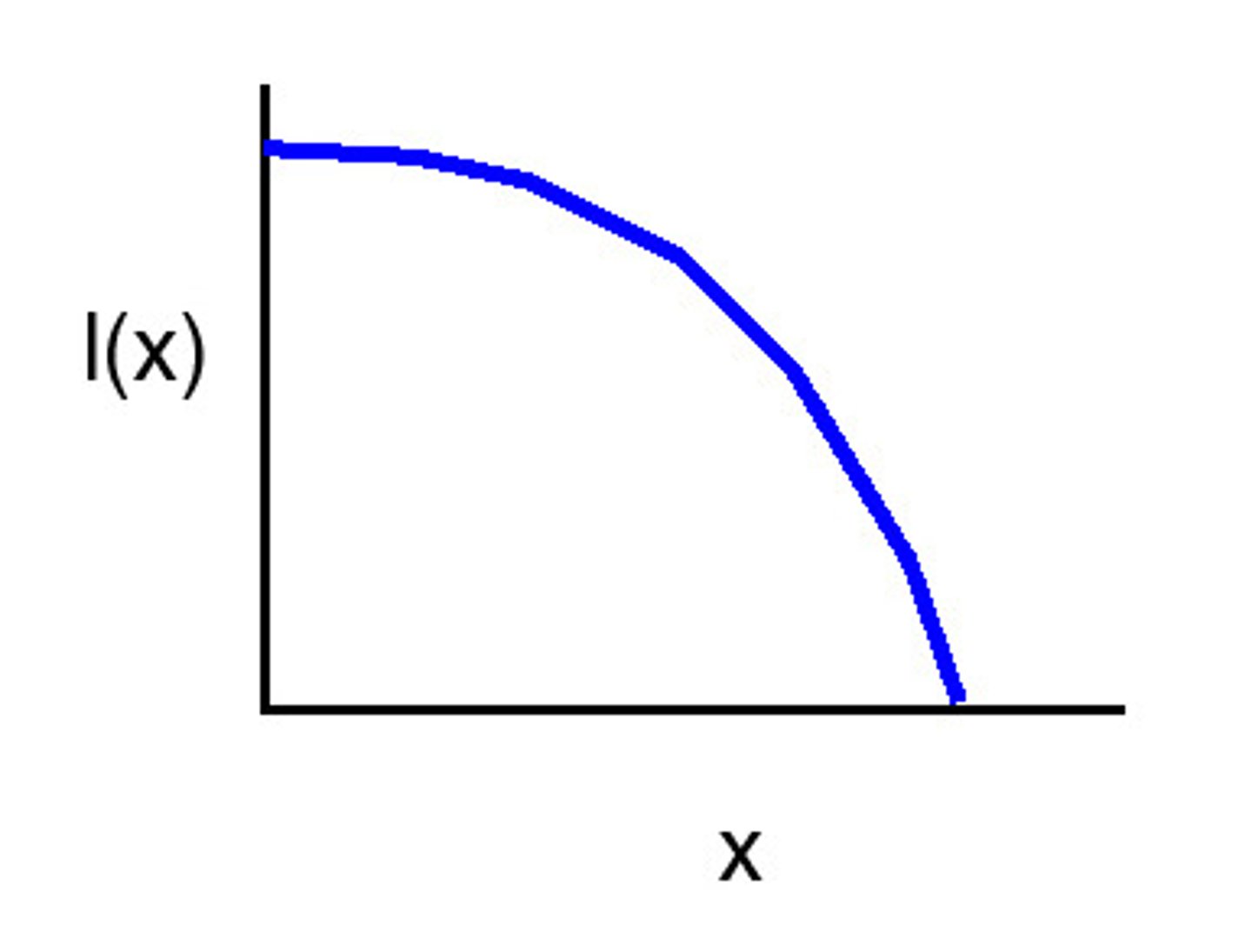
Why Log scale (Survivorship curve)
"hides the early mortality in the dataset"
Type 1 survivorship curve
- low death rates during early and middle-age groups
- high death rates among older age groups
--------------
IS COMMON FOR HUMANS
Type 2 survivorship curve
fairly constant death rate at all ages
- constant rate of survival across all age classes (except oldest)
--------------
IS COMMON FOR SMALL MAMMALS AND LARGE BIRDS
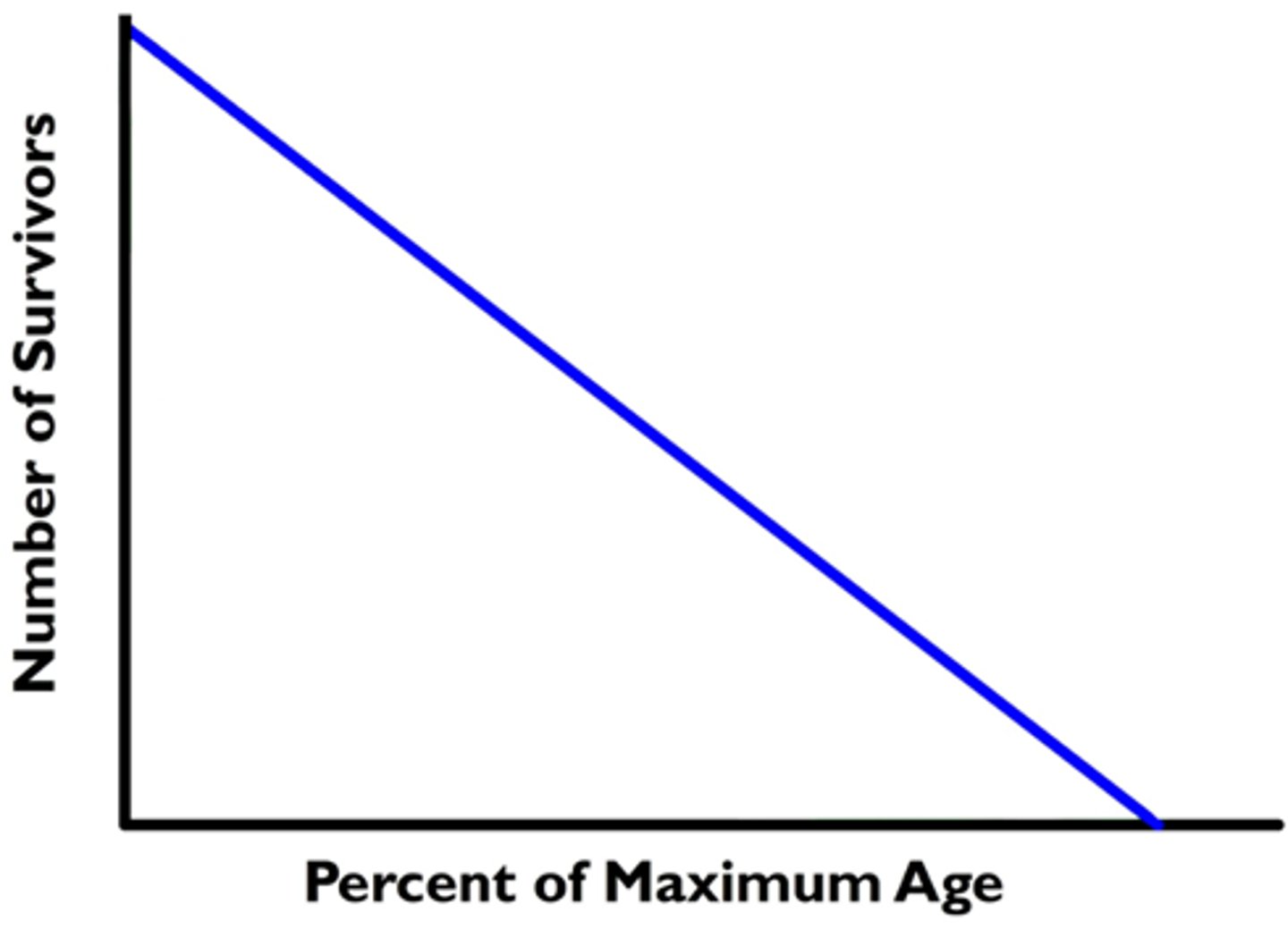
type 3 survivorship curve
- high death rates for the young age groups
- low death rate for older/surviving age groups
- slope of middle age class indicates most individuals that survive youth make it to old age
--------------
COMMON FOR:
- oysters
- fish
- vertebrates
- plant species
- trees
Average (Excel Eqautions)
Average <1950
Average >=1950
Average Life span Male or female
=Average(data:range)
Life span (Excel equations)
life span <1950
life span >=1950
Life span male
life span female
<1950
=IF(death year, <1950, lifespan age,'''')
--------------
>=1950
=IF(death year, >=1950, lifespan age,'''')
--------------
Male
=IF(sex="M",lifespan age,"")
--------------
Female
=IF(sex="F",lifespan age,"")
Count (Excel Equation)
=count(Data:range)
Average Life span for male and female
(Excel equation)
Male <1950
Female <1950
Male >=1950
Female >=1950
Male <1950
=AVERAGEIFS(lifespan age,sex,"M",death year,"<1950"
--------------
Female <1950
=AVERAGEIFS(lifespan age,sex,"F",death year,"<1950"
--------------
Male >=1950
=AVERAGEIFS(lifespan age,sex,"M",death year,">=1950"
--------------
Female >=1950
=AVERAGEIFS(lifespan age,sex,"F",death year,">=1950"
dx (Excel equation)
dx <1950
dx >=1950
<1950
=COUNTIF($I$4:$I$2152,">="&O4)-COUNTIF($I$4:$I$2152,">="&O5)
--------------
>=1950
=COUNTIF($J$4:$J$2152,">="&O4)-COUNTIF($J$4:$J$2152,">="&O5)
Sum (Excel equation)
Sum <1950
sum >=1950
=SUM(data:range)
%dx (Excel equation)
% dx <1950
% dx >=1950
=(dx/total dx) * 100
--------------
EXAMPLE:
=(P4/P$17)*100
% of total male and female deaths (Excel equation)
FOR AGE PYRAMID
(# of sex within age group / $ total # of sex for all age groups) * 100
--------------
EXAMPLE
=AC4/AC$17*100
--------------
FOR MALES VALUES SHOULD BE NEGATIVE
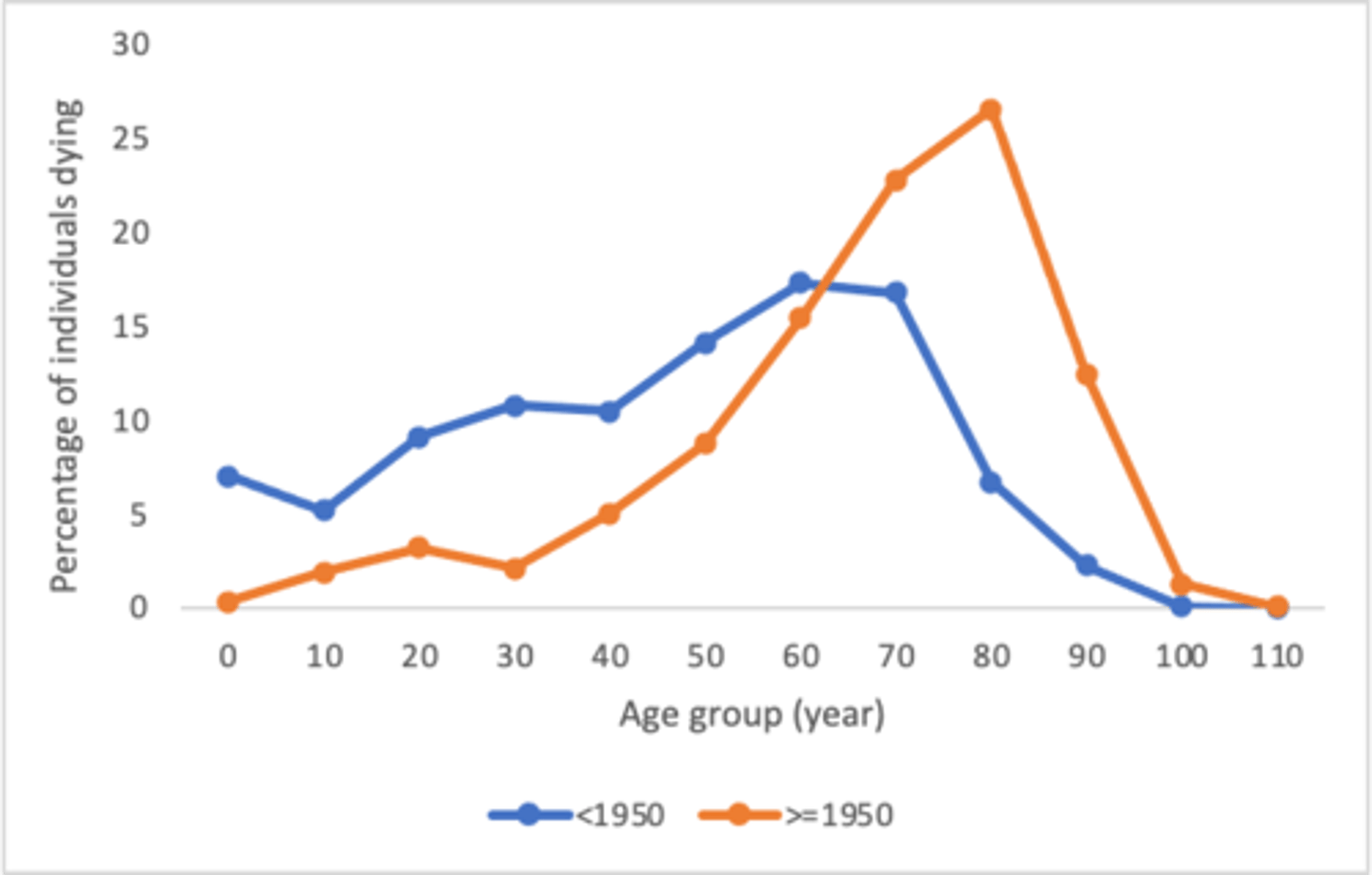
percentage of individuals dying graph
X-axis = age group (years)
Y-axis = percentage of individuals dying
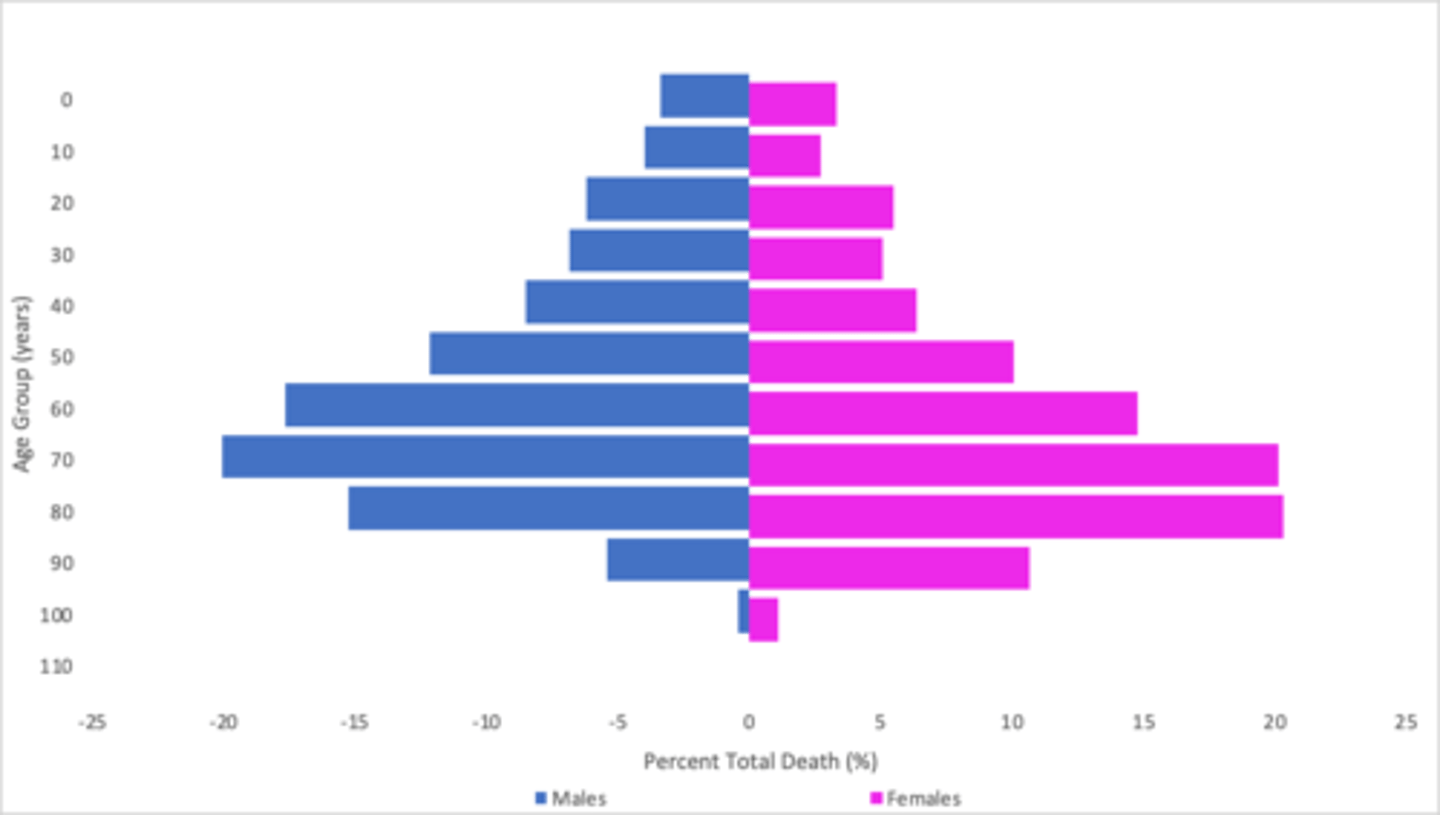
age pyramids
graphs with horizontal bars representing the numbers of males and females of each age group
--------------
AXIS
- X-axis = percent total deaths (%)
- Y-axis = Age group (years)