2.4 APUE07-10
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Including the initial parent process, the total number of the processes (in total) will be ____ after executing the code segment below.
if (pid=fork()) {fork();}
if (pid=fork()) {fork();}
if (pid=fork()) {fork();}
8
9
16
27
32
27
Including the initial parent process, the total number of the processes (in total) will be ____ after executing the code segment below.
if (fork()) {fork();}
1
2
3
4
0
3
After fork, the return value for the child is ___
-1
0
1
a new process ID for the child process
the process id of the parent process
0
By convention, UNIX System shells associate the file descriptor __ with the standard input of a process.
0
1
2
3
-1
0
After fork, the differences between the parent and child are ____.
The return values from fork
The process IDs
The different parent process IDs
All of the above
None of the above
All of the above
A file ___ is normally small non-negative integer that the kernel uses to identify the files accessed by a process.
buffer
table
descriptor
i-node
entry
descriptor
By convention, all shells in Unix open ___ file descriptors whenever a new program is run.
0
1
2
3
4
as many as needed
3
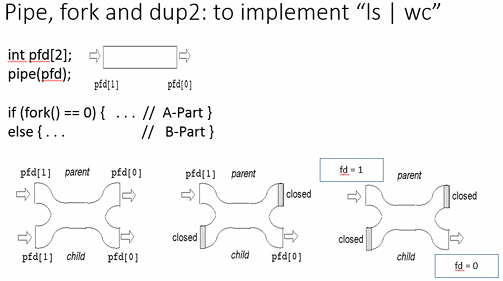
Consider a code segment for a pipe (e.g., to run "ls | wc") as we discussed in the classes, shown below.
What would it be the code segment using execlp for the "parent" process after setting the file descriptors for the pipe?
execlp("ls","ls",(char *)0);
execlp("wc","wc",(char *)0)
execlp("ls","wc",(char *)0)
execlp("wc","ls",(char *)0)
execlp("ls | wc",(char *)0)
execlp("ls","ls",(char *)0)
Signals provide a way of handling ___ events
asynchronous
If a process needs a child process to do some of its work, it will call ___ to make a copy of the current process.
dup
clone
thread
fork
dup
fork
After fork, the return value for the parent process is ___
-1
0
1
the child process id
the process id of the parent process
the child process id
What would be a proper way to set a signal handler (sig_int) for SIGINT?
SIGINT(sig_int);
sigint(SIGINT);
SIGINT(signal, sig_int);
signal(SIGINT, sig_int);
signal(sig_int, SIGINT);
signal(SIGINT, sig_int);
The new process created by fork is called the child process. This function is called once but returns ___.
none
once
twice
three times
as many as needed
twice
Given fork program as shown below, what would be the total number of processes at the end including the process running this program.
for (i=1; i < nprocs; i++) { childpid = fork(); }
When nprocs = 3, then the total number of processes after this code will be ____
1
2
4
8
16
4
For convenience, ___ call is used to execute a command string (e.g., "ls -la | wc") within a program.
thread
process
pipe
fork
system
system
Including the initial parent process, the total number of the processes (in total) will be ____ after executing the code segment below.
fork(); fork(); fork();
1
4
6
8
16
8
Including the initial parent process, the total number of the processes (in total) will be ____ after executing the code segment below.
if (fork() < 0) {fork();}
1
2
3
4
0
2
The new file descriptor returned by dup is guaranteed to be the ___ numbered available file descriptor
lowest
highest
fixed
stack
arbitrary
lowest
Including the initial parent process, the total number of the processes (in total) will be ____ after executing the code segment below.
if (pid=fork() && pid2 = fork()) {fork();}
if (pid=fork() && pid2 = fork()) {fork();}
if (pid=fork() && pid2 = fork()) {fork();}
16
27
32
48
64
64
Which API call completely replaces the current process with a new program (text, data, heap, stack)?
fork
system
exec
exec
The ____ contains all the information about the file: type, permissions, size, data pointers, etc.
v-node
i-node
file descriptor
superblock
directory
i-node
![<p>For a pipe (ls | wc), what does the parent do after fork but before exec?</p><div data-type="horizontalRule"><hr></div><ul><li><p><span>close(pfd[0]); dup2(pfd[1], 1); close(pfd[1]);</span></p></li><li><p><span>close(pfd[1]); dup2(pfd[0], 0); close(pfd[0]);</span></p></li><li><p><span>close(pfd[0]); dup2(pfd[0], 1); close(pfd[1]);</span></p></li><li><p><span>close(pfd[1]); dup2(pfd[1], 0); close(pfd[0]);</span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/92d47a43-de48-4fd0-9bc6-f6e77b2f95ac.png)
For a pipe (ls | wc), what does the parent do after fork but before exec?
close(pfd[0]); dup2(pfd[1], 1); close(pfd[1]);
close(pfd[1]); dup2(pfd[0], 0); close(pfd[0]);
close(pfd[0]); dup2(pfd[0], 1); close(pfd[1]);
close(pfd[1]); dup2(pfd[1], 0); close(pfd[0]);
close(pfd[0]); dup2(pfd[1], 1); close(pfd[1]);