Rates of reaction
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is needed for a collision to be successful
Correct orientation and particles must have activation energy
Activation energy definition
The minimum energy required for a reaction to take place
How does rate of reaction change during a reaction
Starts at its quickest, and the rate gradually slows down
What factors can alter rate of reaction
Concentration/pressure
Temperate
Catalyst
Surface area
How does conc/pressure effect ror
Particles are closer together so particle collisions are more frequent collisions so more effective collisions
How to measure ror experimentally (2 ways)
Measuring the decrease in mass using a balance during a reaction or measuring the volume of gas produced
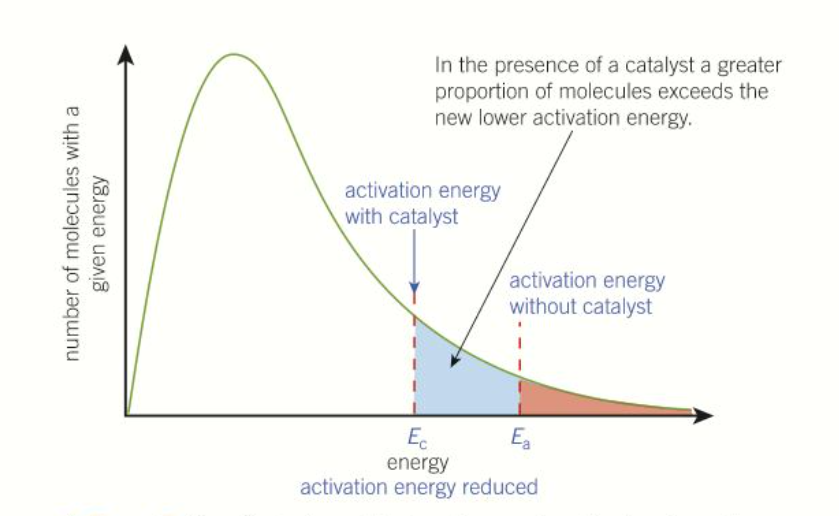
Catalyst definition
When a substance isn’t used up in a reaction and decreases the activation energy
Homogeneous catalyst
Catalyst thats in the same physical state as the reactants
Heterogeneous catalyst
Catalyst thats a different physical state as the reactants (usually solids with gaseous reactants)
How do catalysts work
Reactants are adsorbed onto the surface of the catalyst, where the reaction happens, then the products are desorbed
Benefits of using a catalyst
Lower cost than increasing temp/pressure
Reduces energy needed without being used up
Less CO2 produced as less energy needed
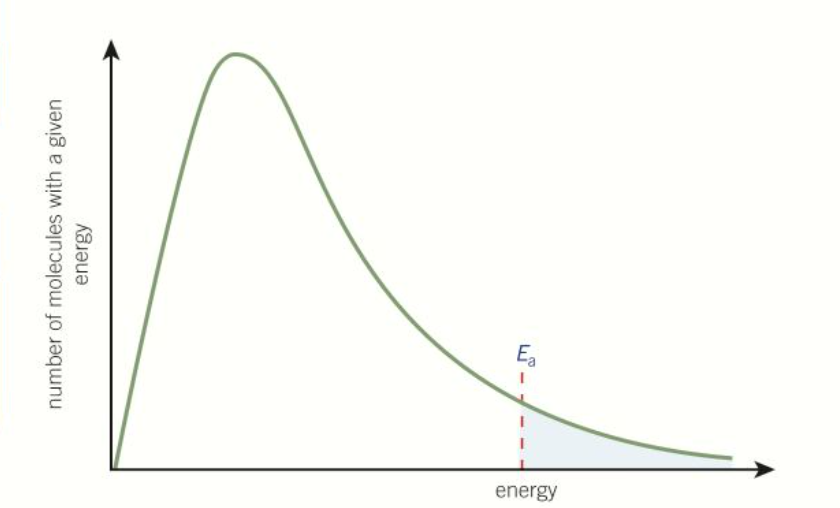
What does the boltzmann distribution look like
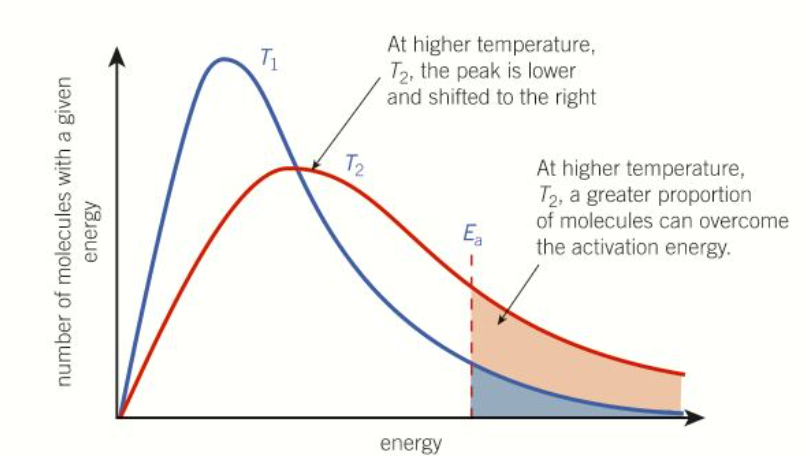
How does boltzmann distribution change with temperature
T2 = higher temp
What does the area under the boltzmann distribution represent
The number of molecules
How does a catalyst affect the boltzmann distribution
What makes a system in dynamic equilibrium
When the products are being made at the same rate as reactants are being made in a closed system and the concentrations do not change
What is le Chatelier’s principle
The equilibrium will move to minimise an external change
How does changing concentration affect equilibrium
An increase to one of the sides will shift the equilibrium to the opposite side, and a decrease to one of the sides will shift the equilibrium to that side
How does changing temperature affect equilibrium
Decreasing temperature will shift the equilibrium in the exothermic direction, increasing temperature will shift the equilibrium in the endothermic direction
How does changing pressure affect equilibrium
If pressure is increased, the equilibrium will shift to the direction with less gaseous moles and if pressure is decreased, the equilibrium will shift to the direction with more gaseous moles
Equation for Kc
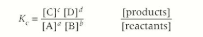
What does the value of Kc tell us about the equilibrium
Greater than 1: Shifted to the right (products)
1: in the middle
Less than 1: shifted to the left (reactants)
Benefits of a homogeneous catalyst
Increases reaction rate more than hetero because its mixed in with the reactants
Benefits of a heterogeneous catalyst
Easier to remove the catalyst from the reaction mixture
How does surface area affect the rate of reaction
Increasing the surface area will increase the number of molecules that can collide which will increase the frequency of collisions, hence frequency of successful collisions