A&P unit 2 - bones
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
compact bone
-”dense cortical bone”
-hard bone
-on outside of bones
-80% of bone mass
spongy bone
-”trabecular bone”
-soft/spongy
-inside of compact bone
-20% of bone mass
hyaline cartilage
-most common cart.
-growth plates, precursor to bone
-on ends of bones
→ ribs to sternum, nose, throat
fibrocartilage
-support & absorb shock
→ in between vertebrae, btwn knee
compare ligaments vs tendons
-both are dense regular connective tissue
ligaments = bone to bone
tendons = bone to muscle
functions of bone
-support, protection
-levers for movement
-storage of calcium and phosphate
-hemopoiesis = produce blood cells
4 bone types
long bone, short bone, flat bone, irregular bone
long bone
-longer than they are wide
-bigger on ends
→ femur, humerus
short bone
-long as they are wide
-support, not movement
→ tarsals, carpals
flat bone
-flat
-for protection
→ skull
irregular bone
-doesn’t fit into the other bone types
→ vertebrae
red bone marrow vs yellow bone marrow
yellow = fat storage
red = hemopoiesis → make blood cells from stem cells
where is red bone marrow found children vs adults
children = in spongy bone and medullary cavity of long bones
adults = axial skeleton only
what kind of tissue is bone
connective tissue
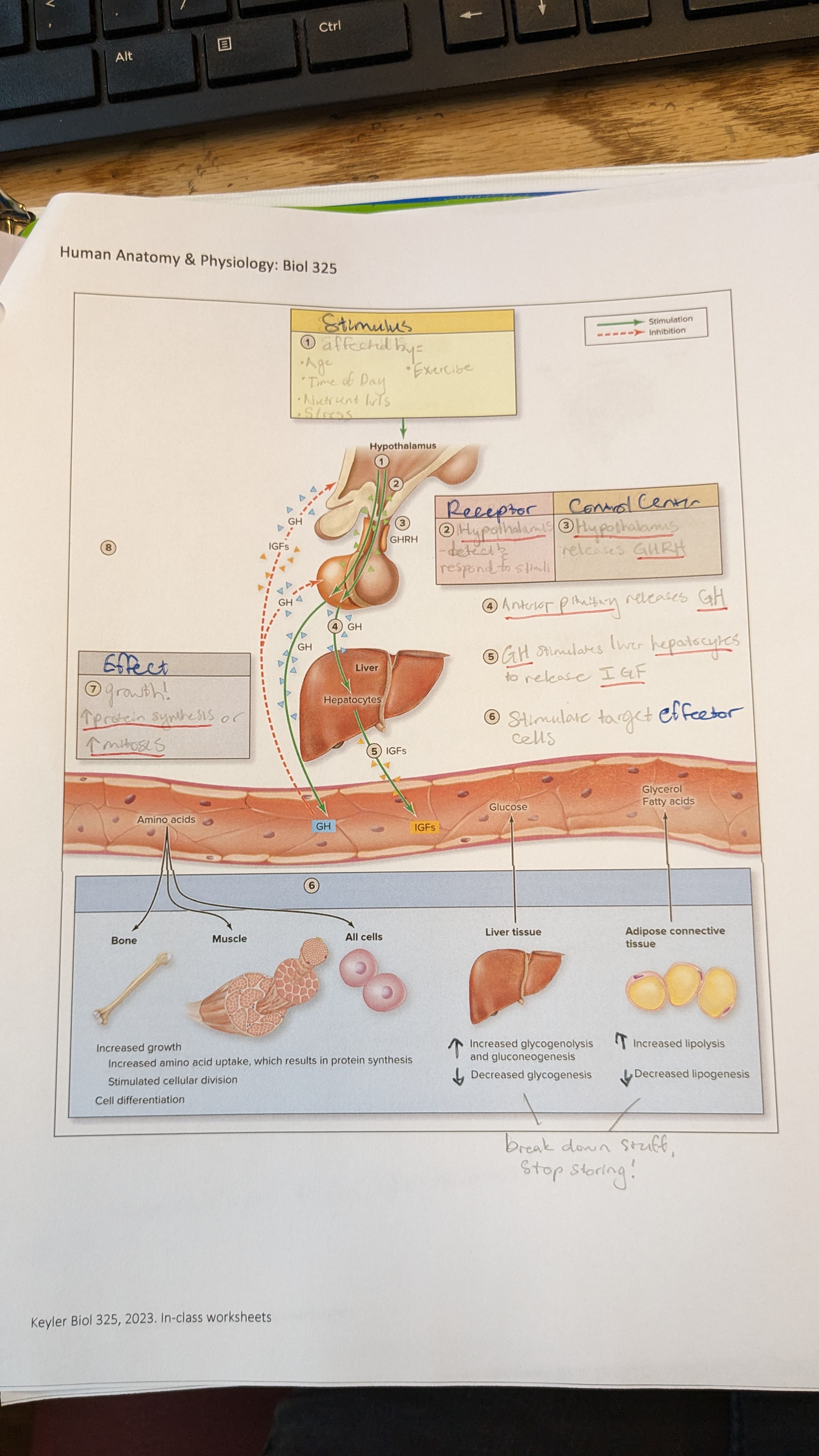
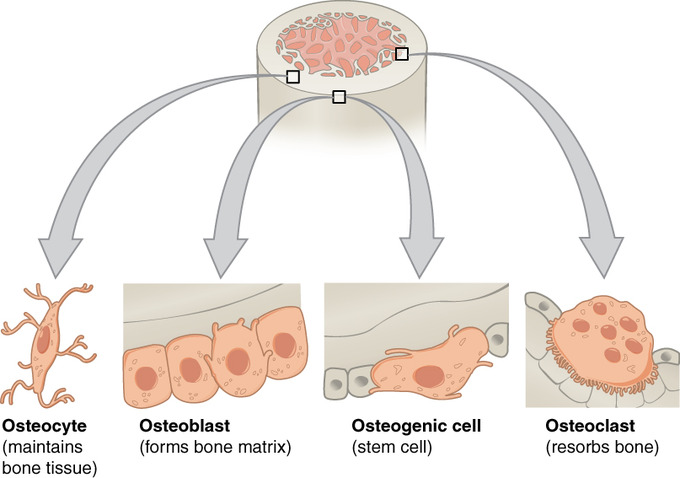
osteogenic/osteoprogenitor cells
-stem cells
-hemopoiesis
-in periosteum and endosteum
-matures to become osteoblast
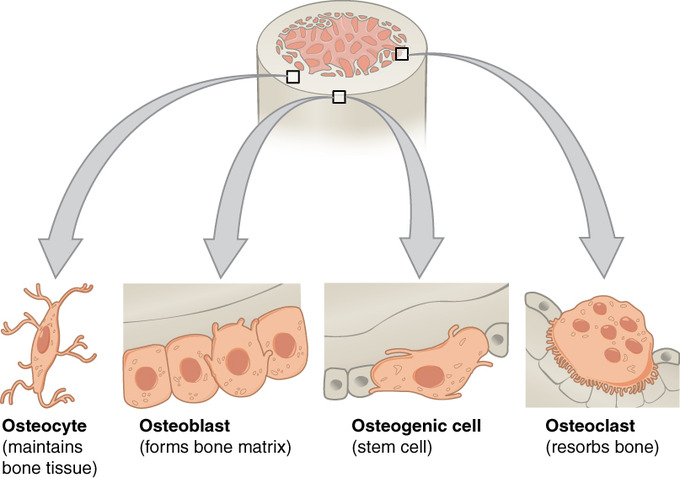
osteoblast
-bone matrix, hard bone
-from osteogenic cells
-synthesize osteoid
-differentiate into ostecytes
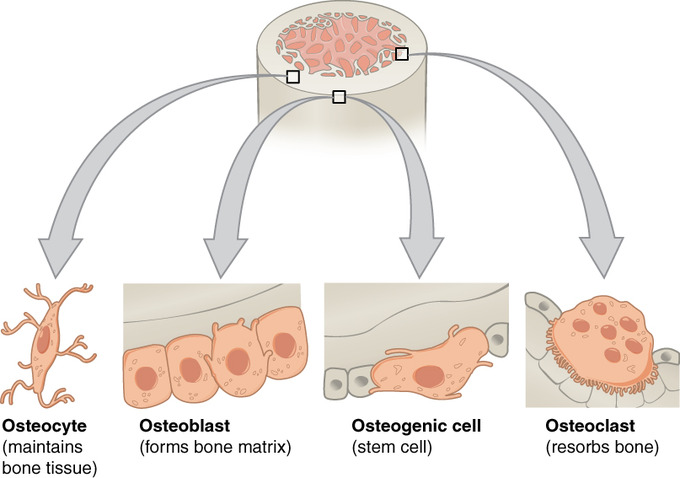
osteocyte
-maintain bone tissue
-mature bone cell derived from osteoblasts
-detect stress on bone & trigger new bone formation
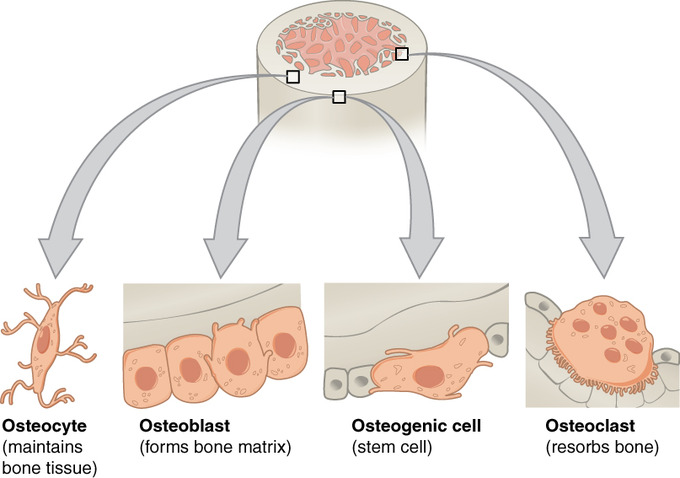
osteoclast
-break down & reabsorb bone
-phagocytic → ruffled border = large surface area, more efficient
-derived from fused bone marrow cells
-make reabsorption lacuna in depression of bone surface
organic parts of bone
-make bone bendy
-osteoblast secrete osteoid
-osteoid = collagen & glycoprotein
→ it will calcify
inorganic parts of bone
-make bone rigid
-salts, calcium, phosphate
-form hydroxyapatite crystals that deposit around osteoblast collagen fibers
bone formation brief overview
1) osteoblast secretes osteoid layer
2) osteoid layer calcifies & hardens
3) deposition of inorganic hydroxyapatite crystal
what materials are needed for basic bone formation
- vitamin D = help calcium absorption in gut
- vitamin C = needed to make collagen
- calcium and phosphate = needed for calcification
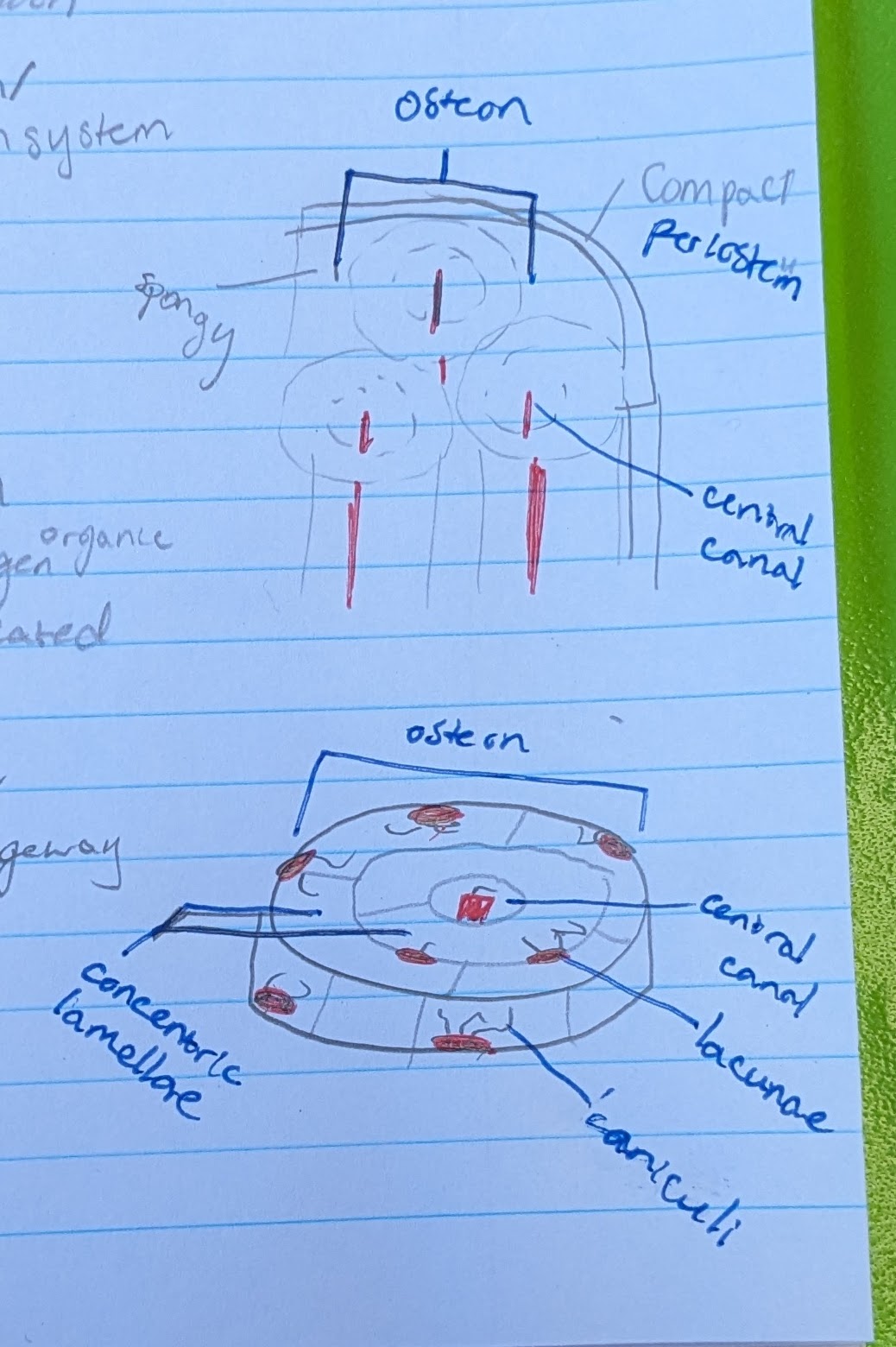
osteon
circular portion. total “system” of bone microscopic anatomy
**IN COMPACT BONE
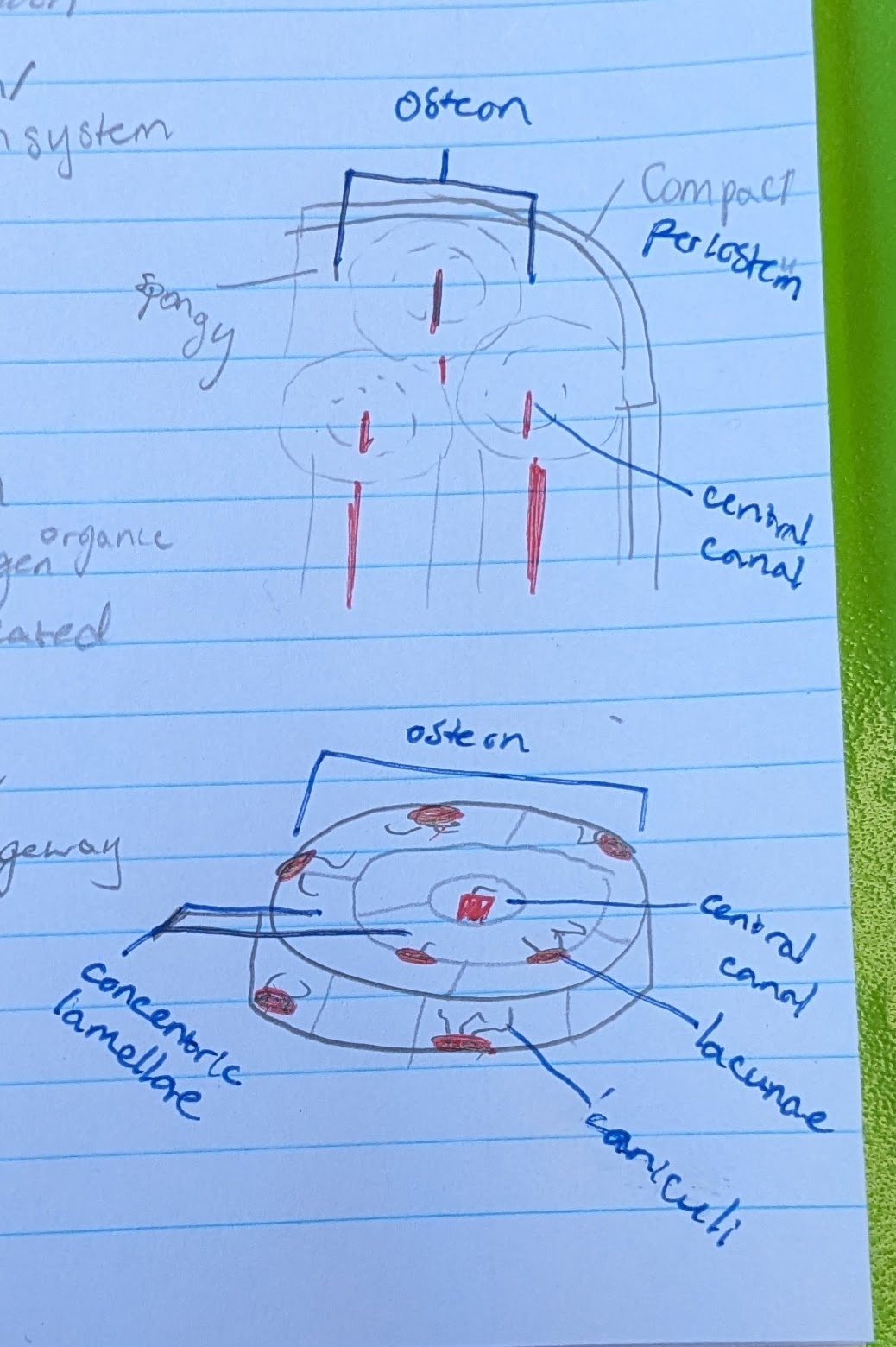
central canal
in center of each osteon
allows blood vessel and nerve
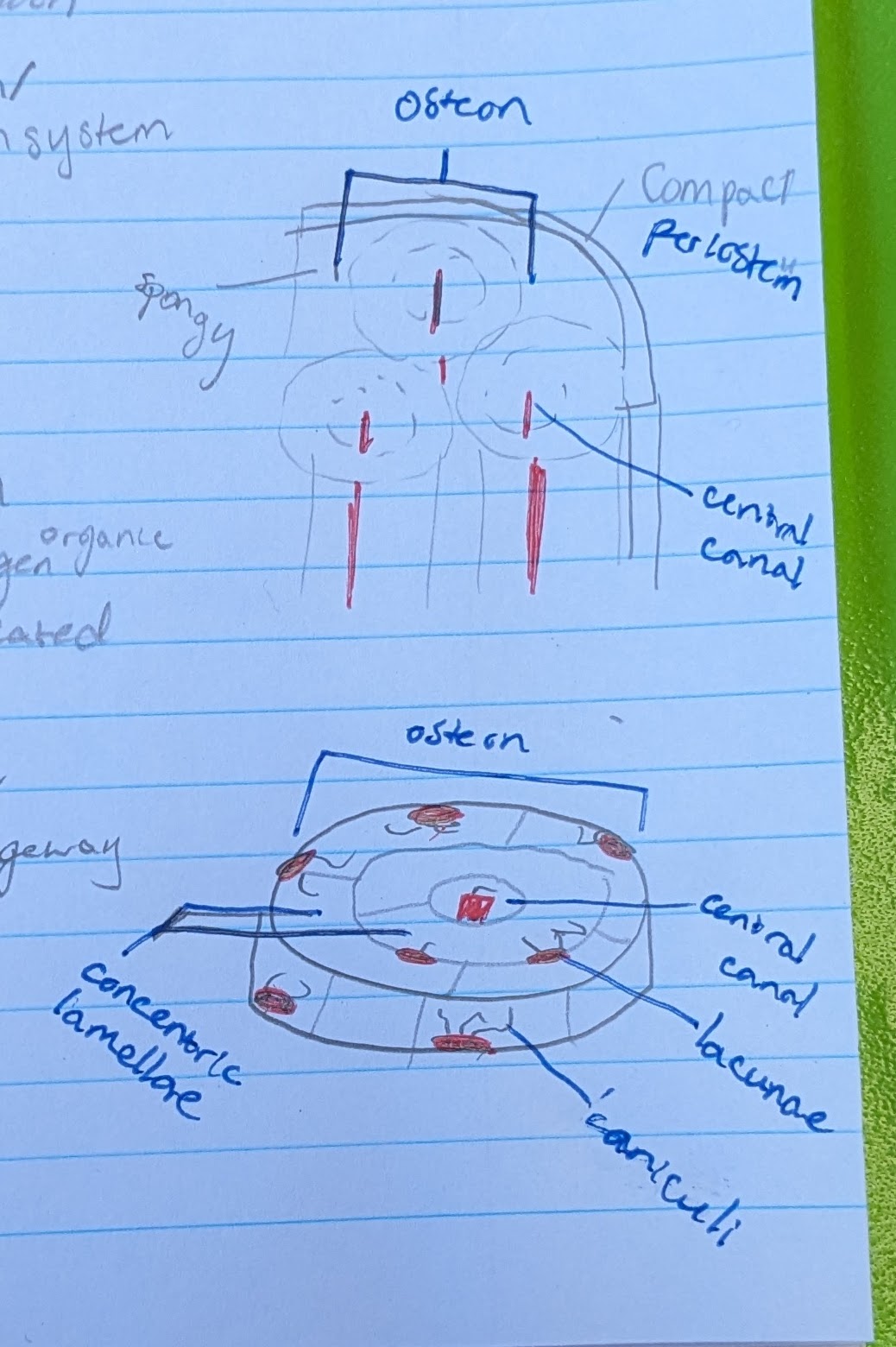
concentric lamellae
the circle layers in each osteon
made of calcified matrix, and organic collagen
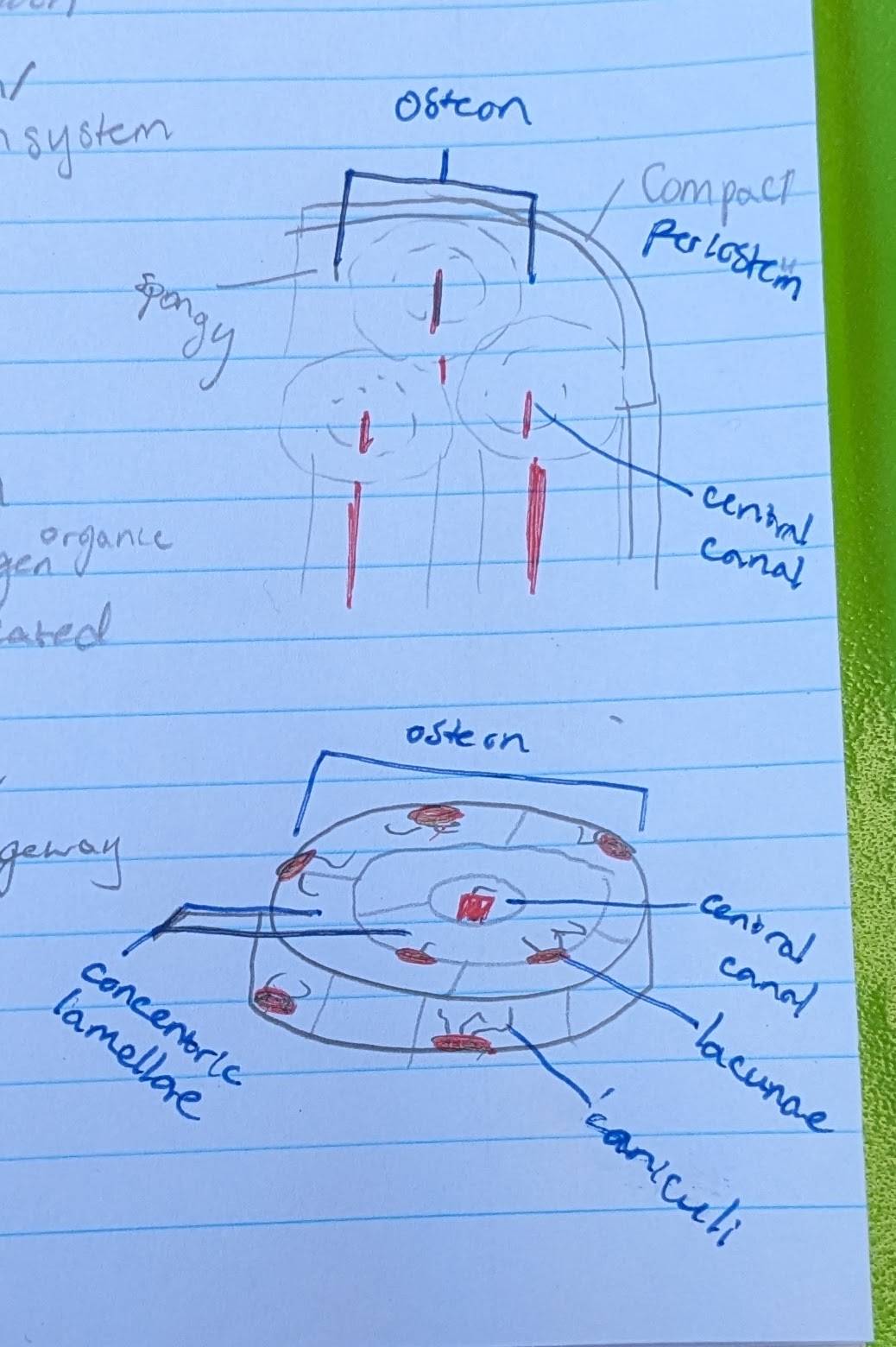
lacunae
pits where osteocytes are located
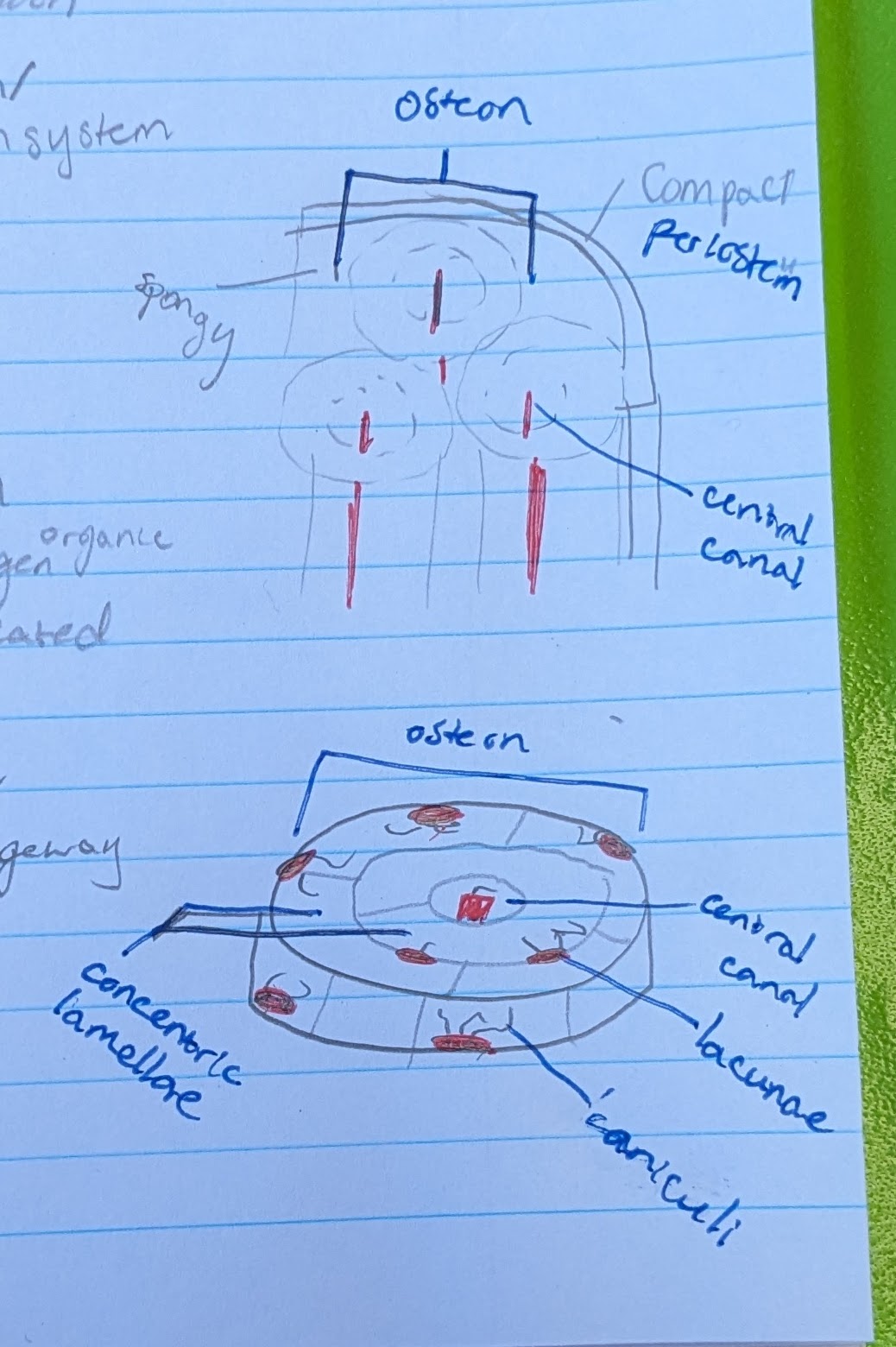
osteocytes (in osteon function)
located in a lacuna
maintain bone matrix
→ bone strength
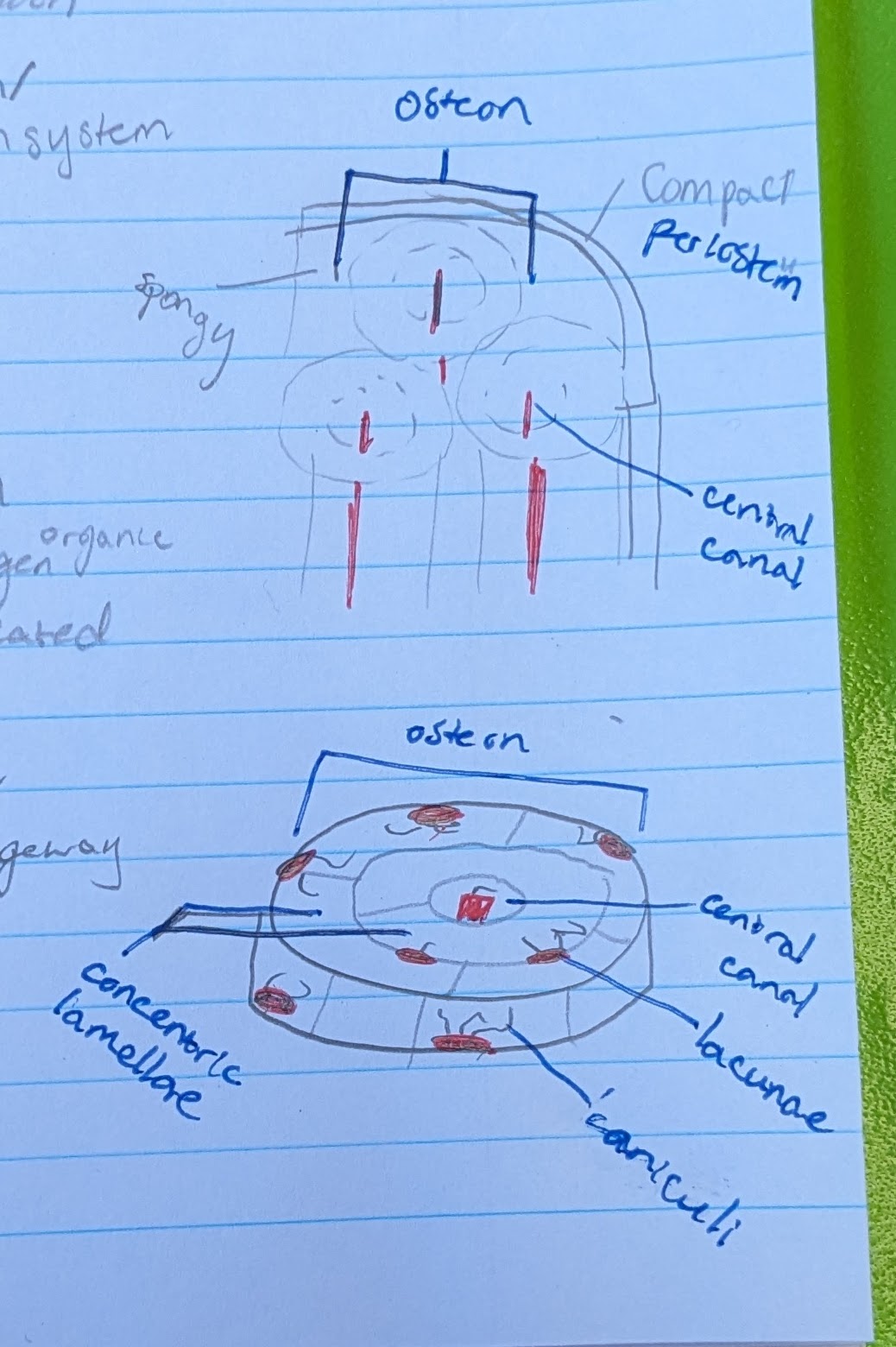
canaliculi
small canals reaching from each lacuna
for intercellular communication and nutrient passageway
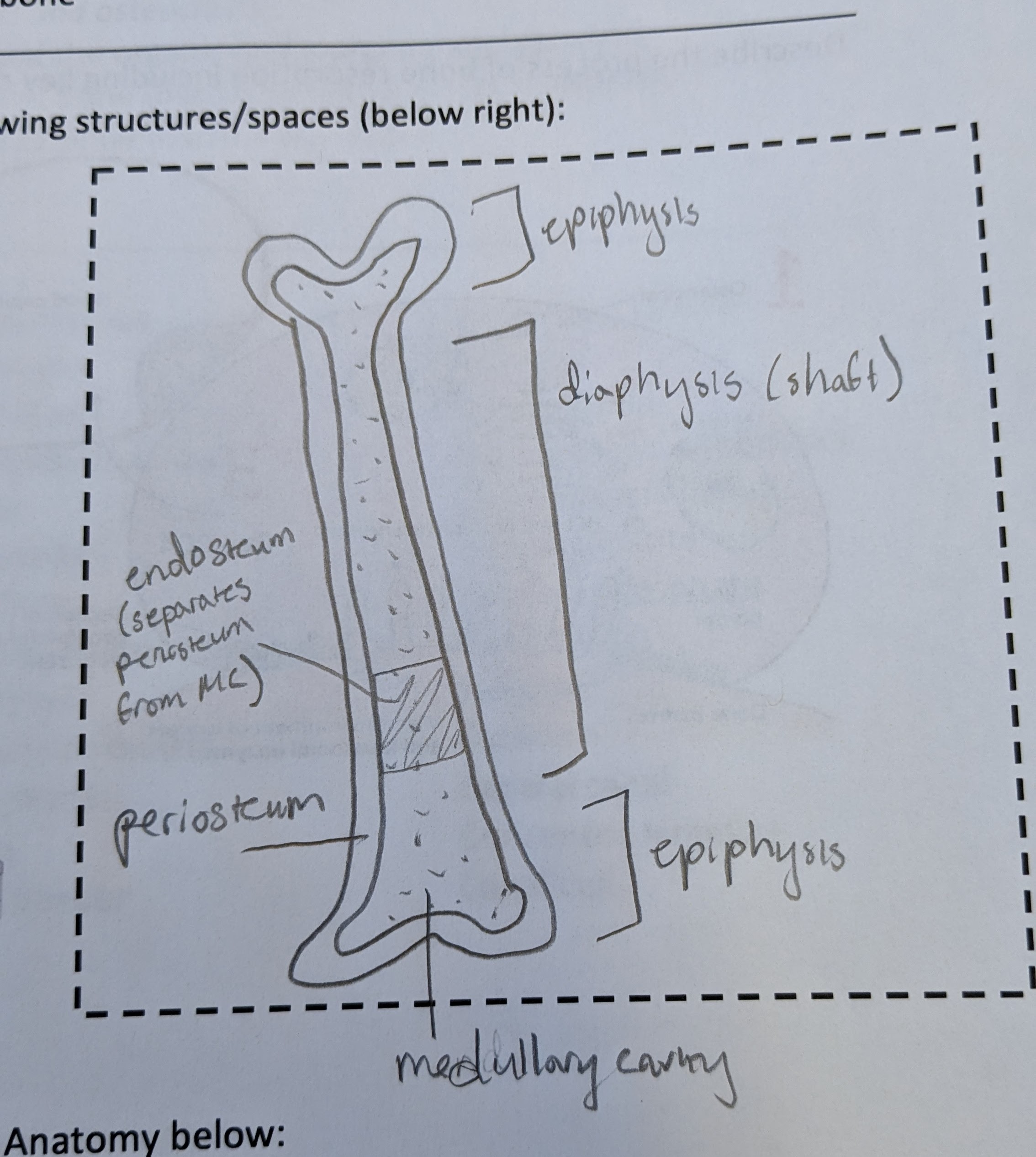
draw a long bone and identify
-diaphysis
-epiphysis
-medullary cavity
-periosteum
-endosteum
2 layers of periosteum
-fibrous layer → outer. made of collagen. for support and connection
-osteogenic layer → inner, closer to endosteum. house osteoblasts
what is bone remodeling and why is it important?
remove mineralized bone followed by formation of new bone
-calcium & phosphorus homeostasis
-maintain skeleton integrity w/o adding weight
-adds strength to stress lines
2 steps of bone remodeling
1) Resorption of old mineralized bone → osteoclasts
2) build new bone → osteoblasts secrete osteoid
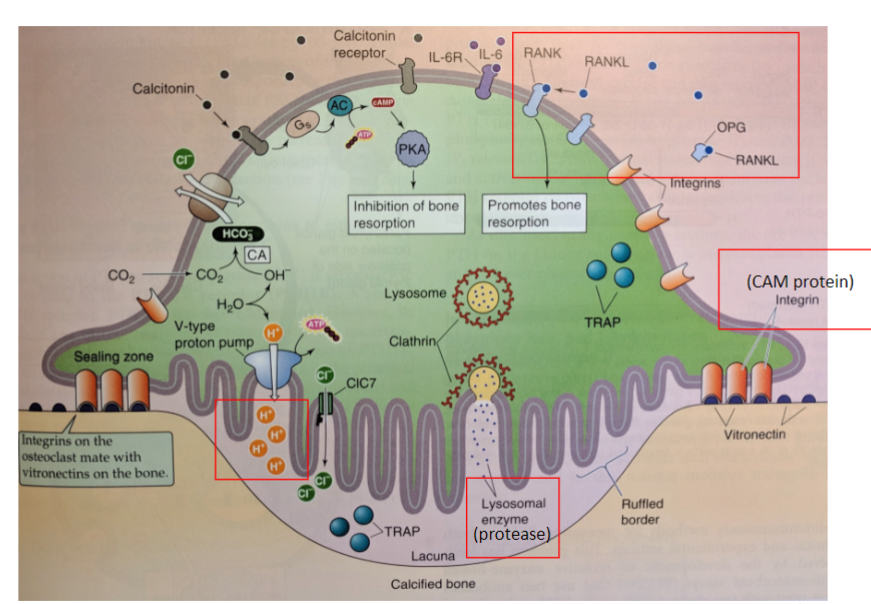
Resorption process
-osteoclasts adhere to bone and create seal via integrin proteins, form resorptive pit
-then secrete acid to dissolve calcium phosphate, and protease to dissolve organic osteod
-uses RANK, RANKL, OPG
-negative feedback, maintained by calcium levels
osteoclast picture
(need to know CAM/integrin, H-pump, lysosome, protease, RANK, RANKL, OPG)
osteopetrosis vs osteoporosis
osteopetrosis =overly dense bones. caused by too much OPG, or too little RANK
osteoporosis = too thin bones. caused by not enough OPG, or too much RANK
RANK and RANKL function
RANK = receptor protein
RANKL = receptor ligand. binds RANK. secreted by osteocytes
-stimulates osteoclast activation to break down bone
—> resorption & decrease bone mass
OPG function
OPG = osteoprotegin. decoy receptor for RANKL, stops breakdown of bone
-no osteoclasts activated so bone is not destroyed. osteoblast action
—> build new bone & increase bone mass
RANK, RANKL, OPG feedback loop (image)

basic multicellular unit (BMU)
title for osteoclast and blast ‘team’
-regulated by paracrine and endocrine communication
-located on surface of spongy bone, and in osteons (in cortical bone)
-5 steps = activation, resorption, reversal, formation, termination
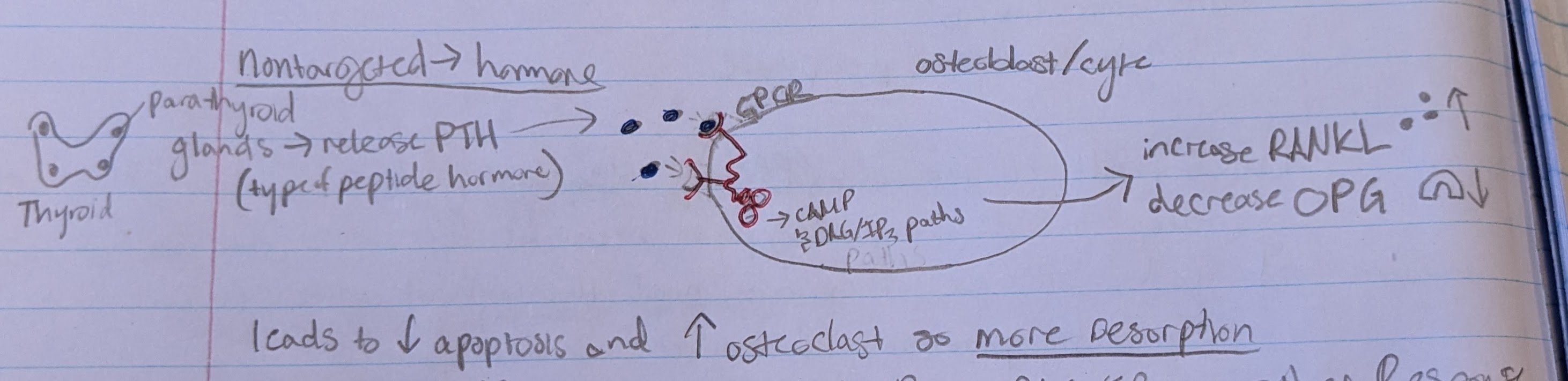
non-targeted remodeling vs targeted remodeling
non-targeted = happens everywhere in body. initiated by systemic hormone
targeted = specific regions. initiated by osteocytes
how does an osteocyte detect stress in bone?
-osteocyte is floating in plasma by bone
-stress causes plasma to move
-plasma moves cilia on osteocyte → detection
-osteocyte will activate B catenin → this will increase OPG and decrease RANKL to build bone
increasing OPG and decreasing RANKL leads to
more building of bone (osteoblast)
decreasing OPG and increasing RANKL leads to
more resorption of bone (osteoclast)
non-targeted resorption
-parathyroid glands release PTH
-PTH bind to GPCR pathway in osteoblast/cyte
-activate cAMP and DAG/IP3 pathway
-cell increase RANKL and decrease OPG → more resorption
what happens to your bones if there is no weight-bearing activity
bones will weaken
-osteocytes not activated → stop releasing OPG
-now there is nothing to stop RANKL so increased resorption
compare the 4 types of bone fractures
-stress fracture = thin break caused by phys activity
-pathologic fracture = occurs in bone weakened by disease
-simple fracture = bone break but does not penetrate skin
-compound fracture = bone break penetrates skin
step 1 of bone fracture repair
hematoma forms from fracture → blood clot
-BV torn within periosteum
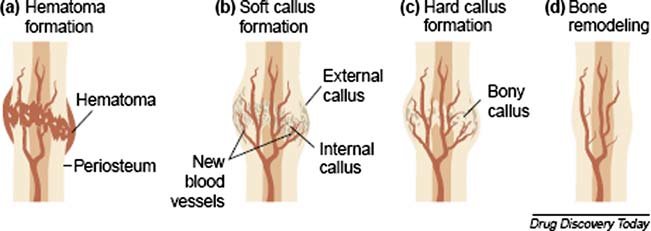
step 2 of bone fracture repair
form soft callus
-fibroblasts produce collagen
-hematoma is reorganized into connective tissue procallus
-chondroblasts form dense regular CT
-procallus becomes soft callus
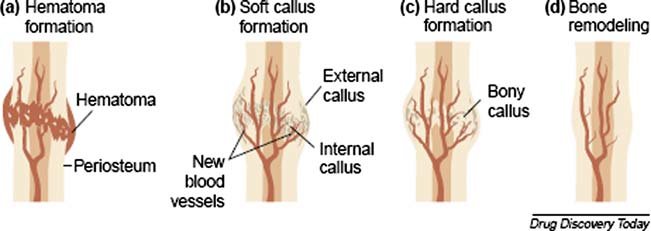
step 3 of bone fracture repair
form hard (bony) callus
-osteoblasts near soft callus produce trabeculae → replace soft callus
-form hard callus
-then callus continues to grow and thicken
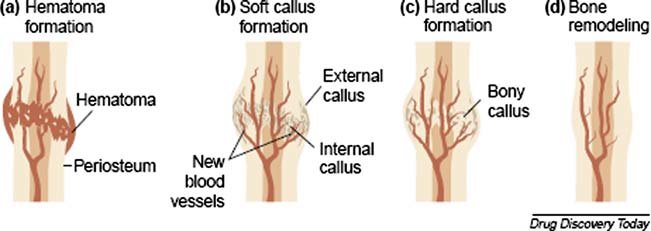
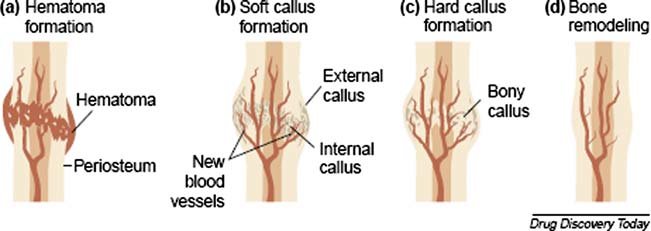
step 4 of bone fracture repair
bone is remodeled
-osteoclasts remove excess material
-compact bone replaces primary bone
-usually leaves slight thickening of bone
what are the 2 types of bone growth?
interstitial growth = get longer
appositional growth = get wider
interstitial growth depends on ______
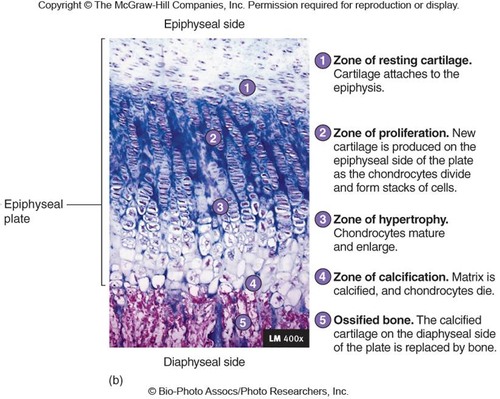
the epiphysial plate (5 zones)
zone 1 of epiphysial plate (interstitial growth)
zone of resting cartilage
-closest to epiphysis
-small chondrocytes → make cartilage
-secures epiphysis to epiphyseal plate
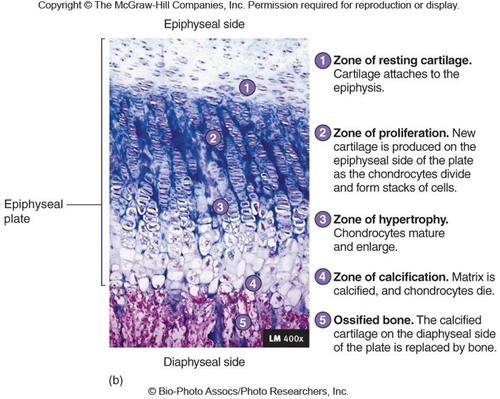
zone 2 of epiphysial plate (interstitial growth)
zone of proliferation
-chon. do mitosis
-then form columns → flattened lacunae
-columns are parallel to diaphysis of bone
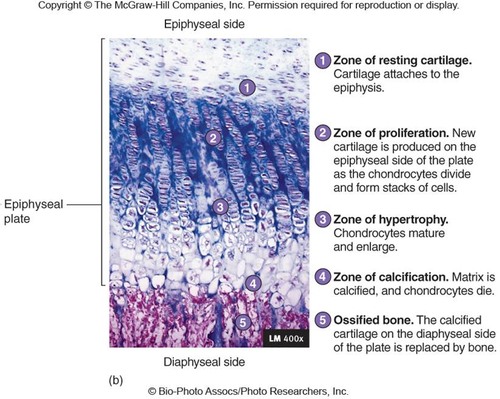
zone 3 of epiphysial plate (interstitial growth)
zone of hypertrophic cartilage
-chon. stop dividing
-do hypertrophy → the chon. get bigger
-walls of lacunae thin
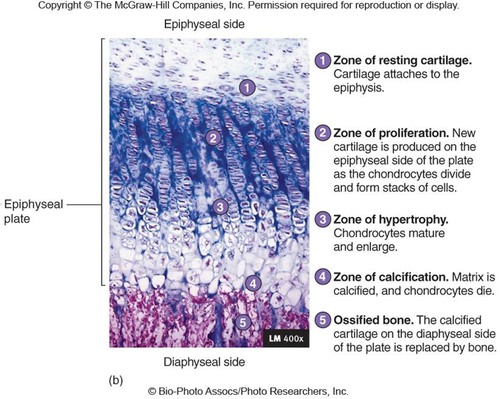
zone 4 of epiphysial plate (interstitial growth)
zone of calcification
-only 2-3 layers of chon.
-mineral deposition
-minerals destroy chondrocytes
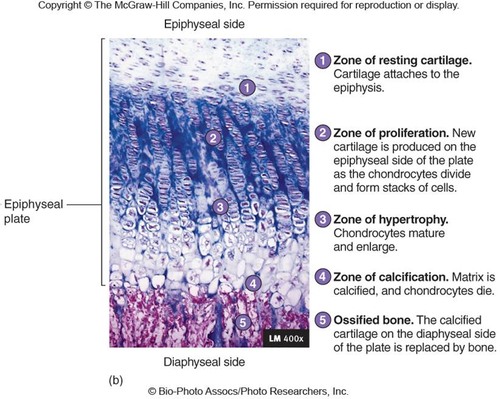
zone 5 of epiphysial plate (interstitial growth)
ossified bone
-walls of lacunae break down
-space invaded by osteoprogenitor cells
-new bone forms on top of calcified matrix
appositional growth process
-in periosteum
-bone matrix deposited within layers parallel to surface
-osteoclasts resorb inner/old bone to keep bone light
what is calcium required for?
-initiation of muscle contraction
-exocytosis
-blood clotting
-stimulation of heart by pacemaker cells
-calcium is part of mineral structure in bones
vitamin D production and activation (photo)
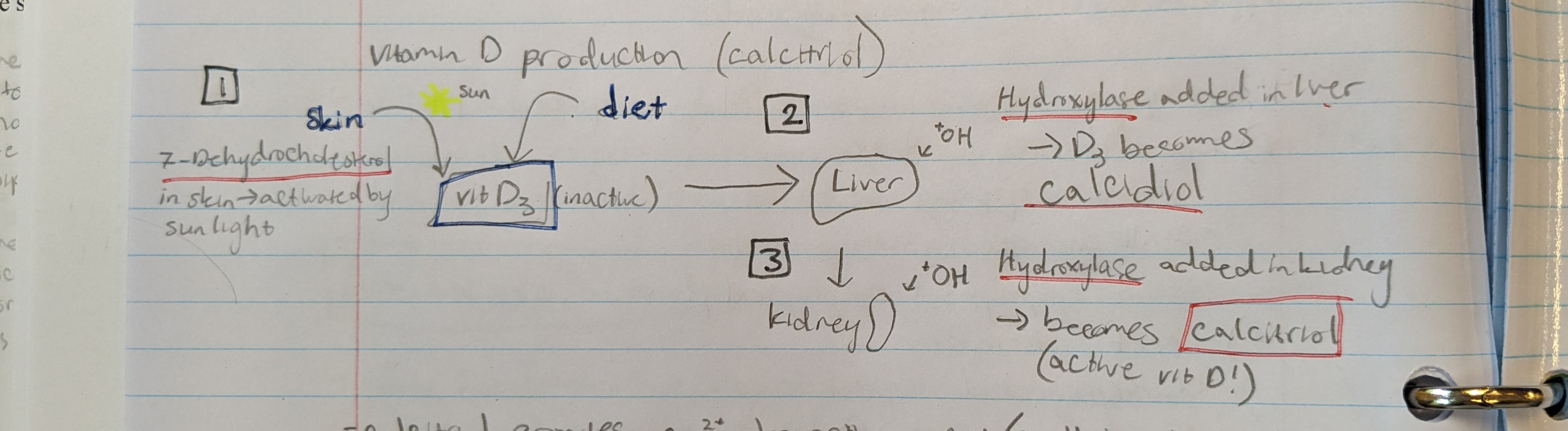
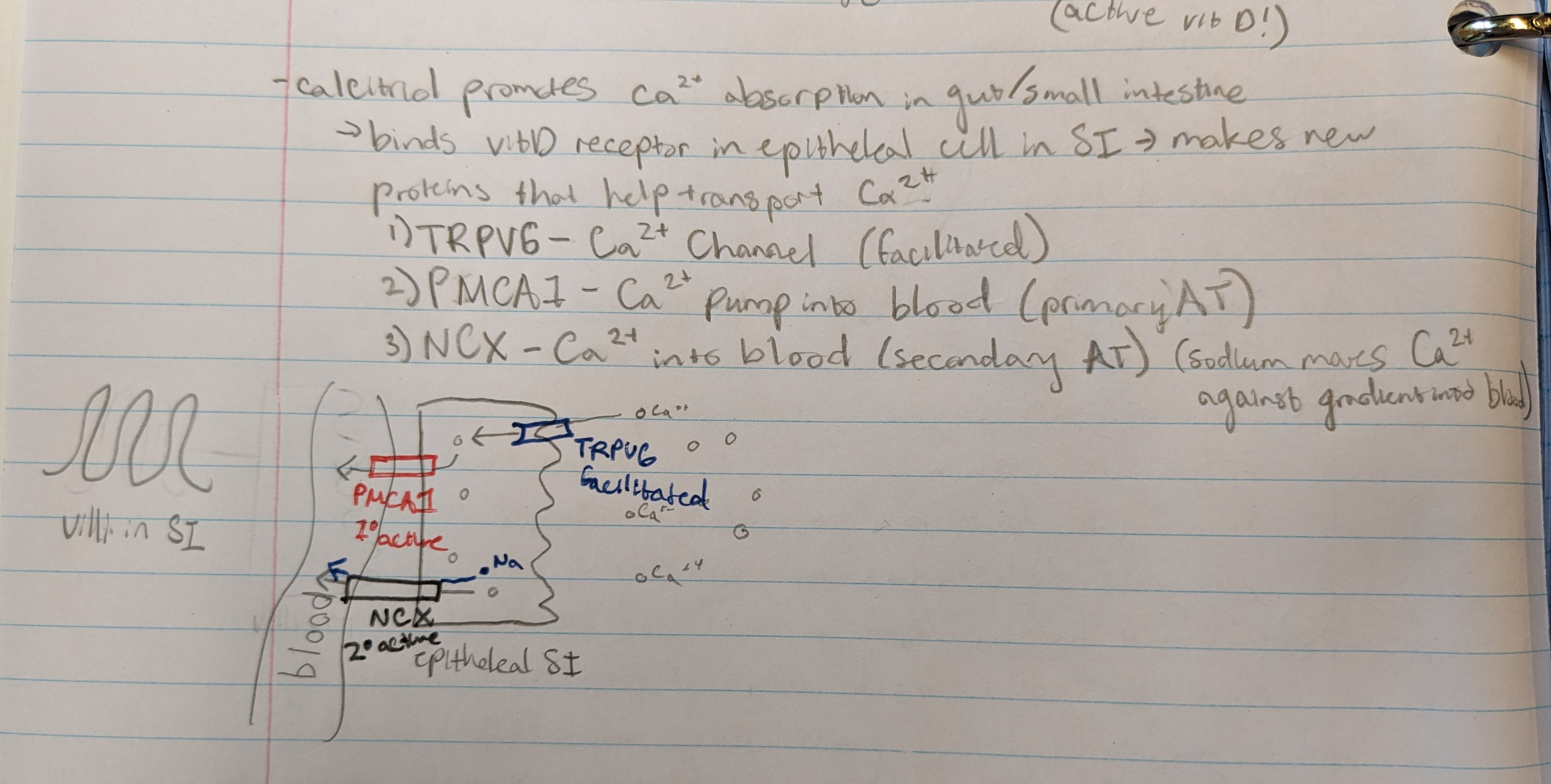
what does calcitriol do?
provides Ca2+ absorption in small intestine
→ binds vit D receptor in epithelial cell in SI → initiates creation of proteins that help transport Ca2+
Calcitriol protein channels
1) TRPV6 - Ca channel (facilitated)
2) PMCA1 - Ca pump into blood (primary active transport)
3) NCX - Ca pump into blood (secondary active transport) (sodium moves Ca against gradient into blood)
synergistic effect between PTH and vit D
they act together to increase concentration of calcium in blood
how does PTH affect kidney function related to calcium?
it stimulates kidney to excrete less Ca in urine → you hold onto more calcium, increase Ca lvl in blood
(opposite of calcitonin)
calcitonin
hormone produced by thyroid gland
-regulated blood calcium lvls by inhibiting Ca absorption
how does calcitonin affect kidney function related to calcium?
stimulate kidneys to excrete more Ca in urine → you lose more, meaning it decreases Ca blood lvls
(opposite of PTH)
How does aging affect bone?
lose tensile strength
-make less osteoblasts/collagen and more minerals → ↓ organic, ↑ inorganic = bones more brittle
-osteopenia = insufficient ossification. precursor to osteoporosis
-menopause means ↓ estrogen, which helps with OPG. ↓ OPG means nothing to stop RANKL binding
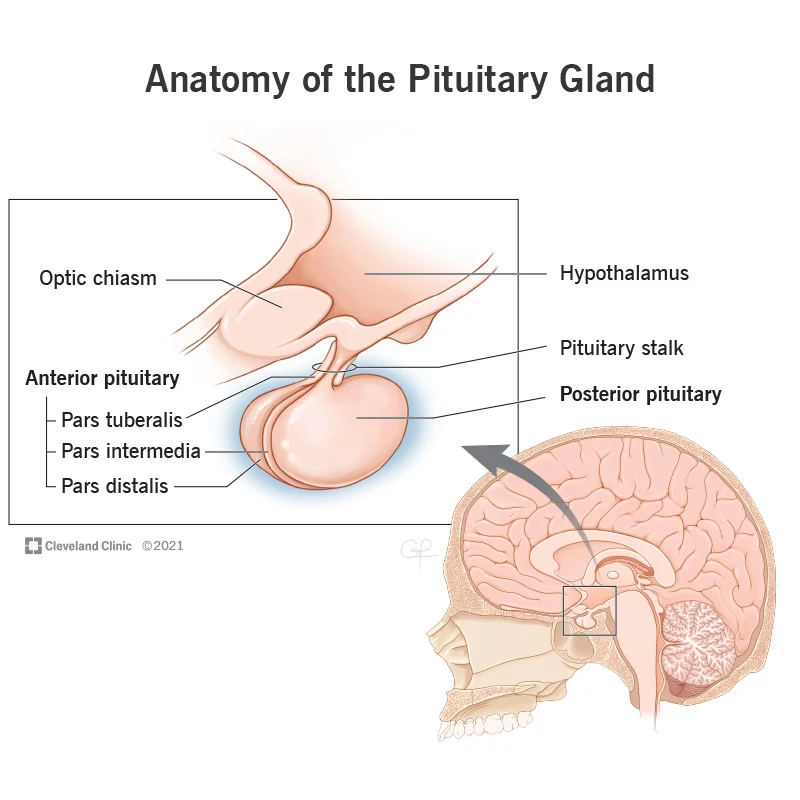
pituitary gland posterior vs anterior
PP - neural tissue → part of nervous system
AP - epithelial tissue → part of endocrine system
regulatory hormones
-hormones secreted by hypothalamus that go into AP gland
-releasing hormone = stimulate AP to release a hormone into blood (→ GHRH)
-inhibiting hormone = stimulate AP to stop releasing hormones into blood (→ GIH)
what are the hormones of the anterior pituitary gland?
TSH - Thyroid stimulating hormone
PRL - Prolactin
FSH - Follicle-Stimulating hormone
LH - Luteinizing Hormone
ACTH - Adrenocorticotropic hormone
GH - Growth hormone
**TP-FLAG acronym
Thyroid stimulating hormone
-TSH
-secreted by AP
-thyroid → control metabolism
Prolactin
-PRL
-secreted by AP
-females = breast dev. and milk production
*NOT a tropic hormone
Follicle-Stimulating hormone
-FSH
-secreted by AP
-females = ovary follicle growth, & estrogen prod.
-males = sperm prod.
Luteinizing Hormone
-LH
-secreted by AP
-females = ovulation
-males = testosterone secretion
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
-ACTH
-secreted by AP
-adrenal cortex → secrete cortisol
Growth hormone
-GH
-secreted by AP
-body growth
tropic hormones
hormones that tell another endocrine gland to secrete its own hormones
-most hormones from AP are tropic hormones
Posterior pituitary hormones
-PP does NOT make own hormones, instead 2 hormones from hypothalamus are stored there
-ADH/vasopressin = tell kidneys to store water, don’t pee
-oxytocin = uterine contraction during birth, milk ejection during breastfeeding
How do the hypothalamus and PP work together to release hormones?
-the hormones ADH/vasopressin and oxytocin are made in the hypothalamus
-they travel down axon to be stored in neural terminals in PP
-when neuron gets excited, the hormones are released from the terminals into BV for distribution thru the body
what does growth hormone release?
Insulin-like growth factor IGF from liver
-hepatocytes in liver secrete IGF
-IGF is like GH but has longer half-life
what kinds of cells do GH and IGF bind to?
ALL CELLS have receptors for GH, IGF, or both
→ when bound it stimulates growth
how do GH and IGF stimulate growth?
2 ways
-increase protein synthesis
-increase division/mitosis of cells
what are 3 results of GH?
-hyperplasia of chondrocytes → more mitosis
-linear growth @ epiphysis → bones grow
-increase amino acid uptake from muscle fibers
glycogenolysis
break glycogen into glucose (for energy)
→ stimulated by GH and IGF
gluconeogenesis
convert nutrients into glucose (storage)
→ inhibited by GH and IGF
glycogenesis
make glycogen (storage)
→ inhibited by GH and IGF
lipolysis
break down triglycerides (for energy)
→ stimulated by GH and IGF
lipogenesis
form triglycerides (storage)
→ inhibited by GH and IGF
Pituitary Dwarfism/GH deficiency
-present @ birth, but not seen until age 1
-decreased GH production
-short stature, low blood sugar
-Rx = GH injection over years
Pituitary Gigantism
-oversecretion of GH in childhood
-extremely tall, large organs, large tongue
-short life span, diabetes/hyperglycemia
Acromegaly
-excessive GH in adults
-no growth in height → epiphyseal plate closes in adolescence
-growth in appositional → face, jaw, hands, feet
-Rx = take synthetic form of GIH
hypothalamus/pituitary feedback loop (photo)