Unit 2: Matter & Temperature (Ch.10-12)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Endothermic
energy transfers into an object
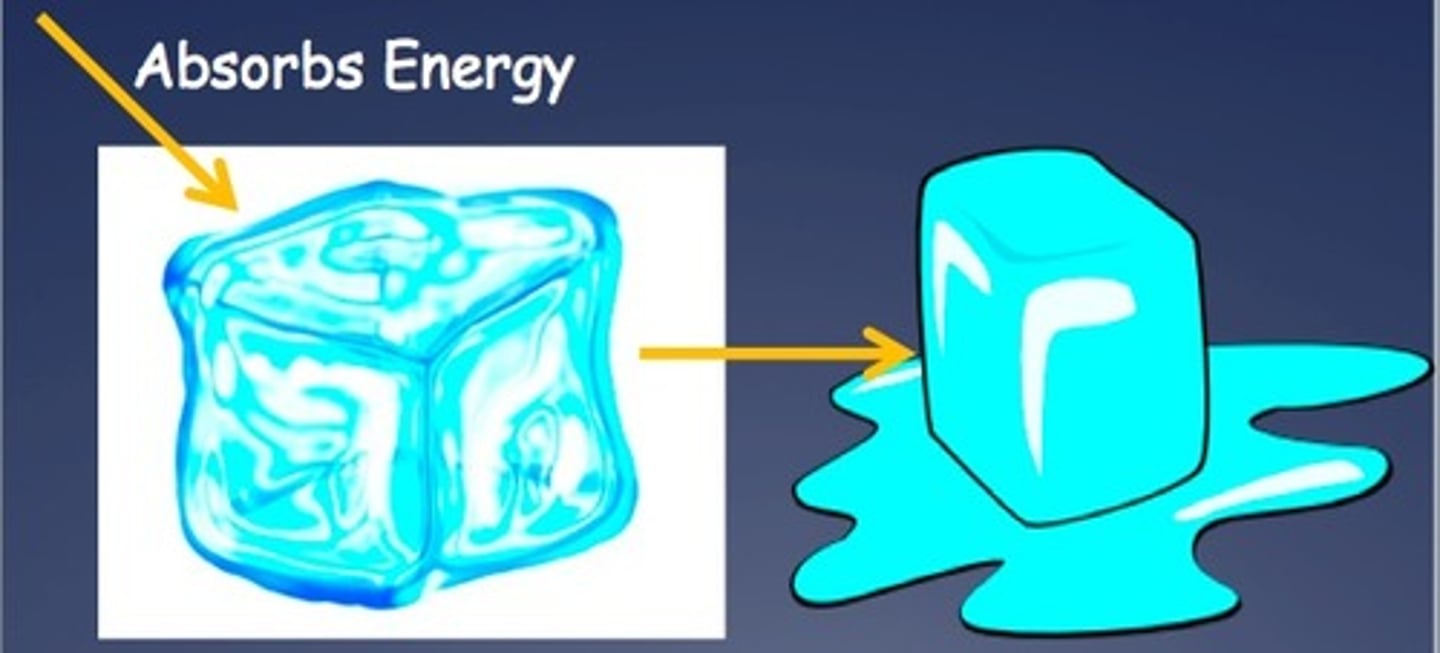
Exothermic
energy transfers out of an object

Absolute Zero
0°K
-273.15°C
-459.67°F
coldest temperature limit that can NEVER be reached

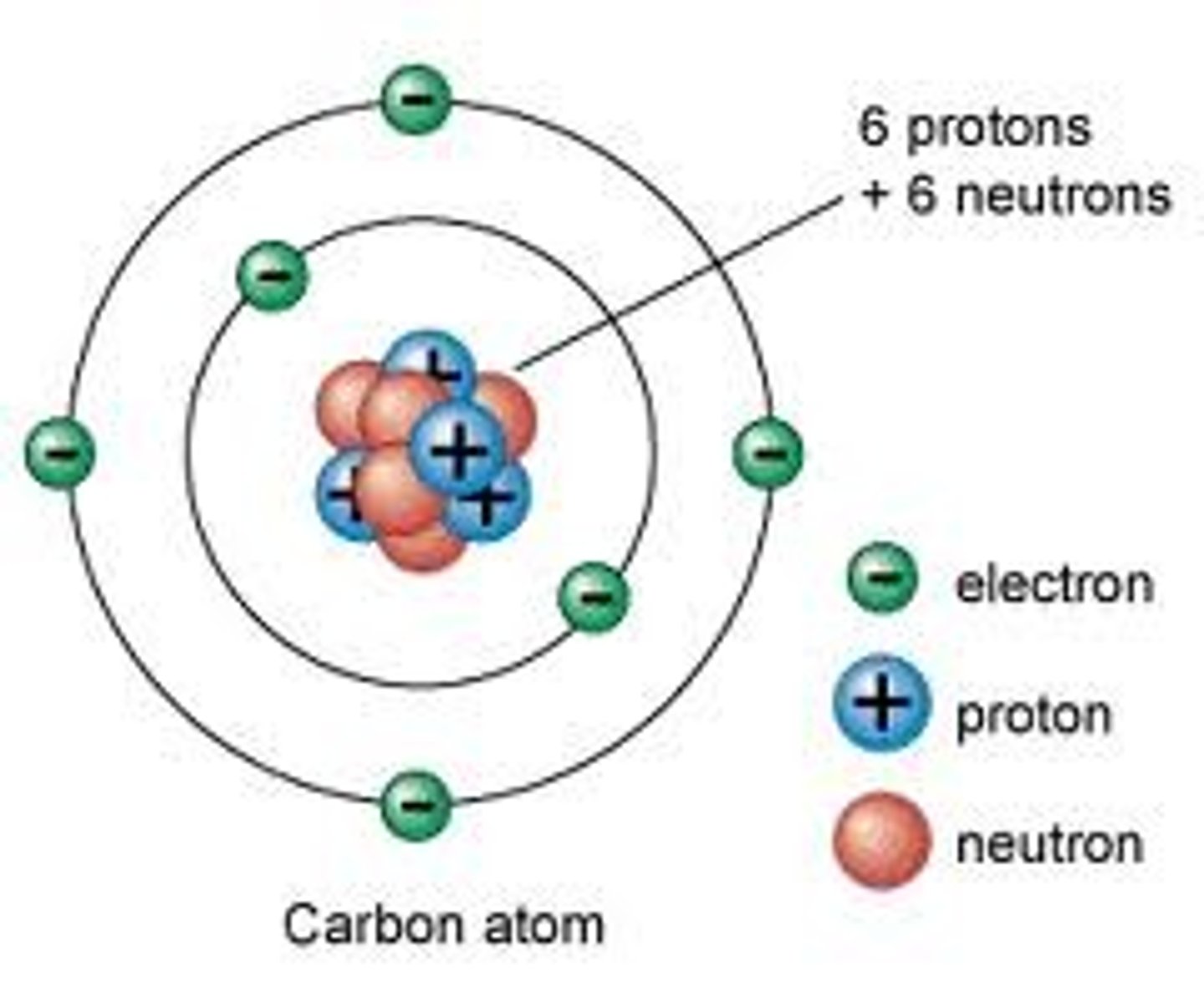
Atom
the basic unit of a chemical element
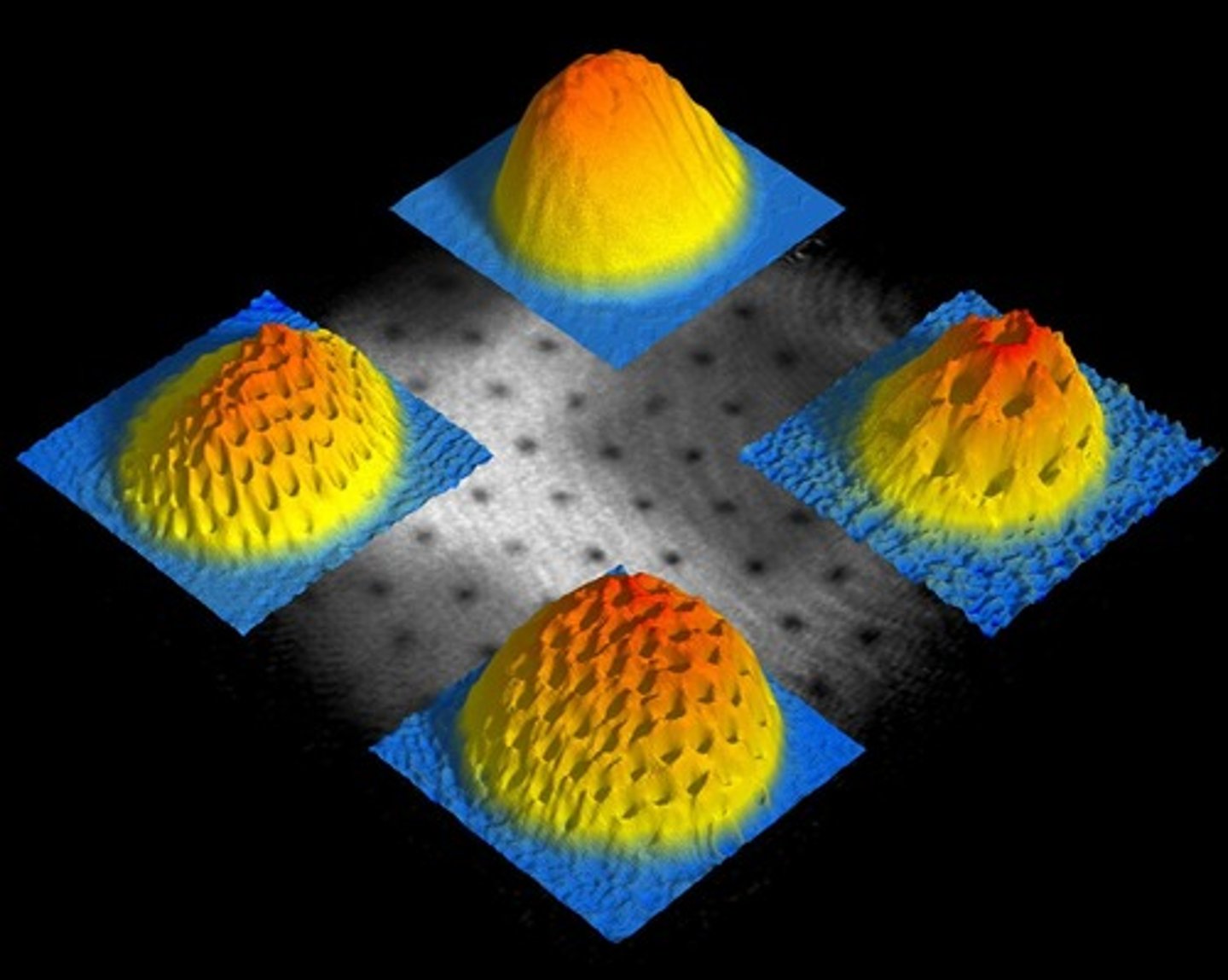
Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC)
a state of matter in which separate atoms or subatomic particles, cooled to NEAR absolute zero where atoms begin to lose their identity and act like a wave
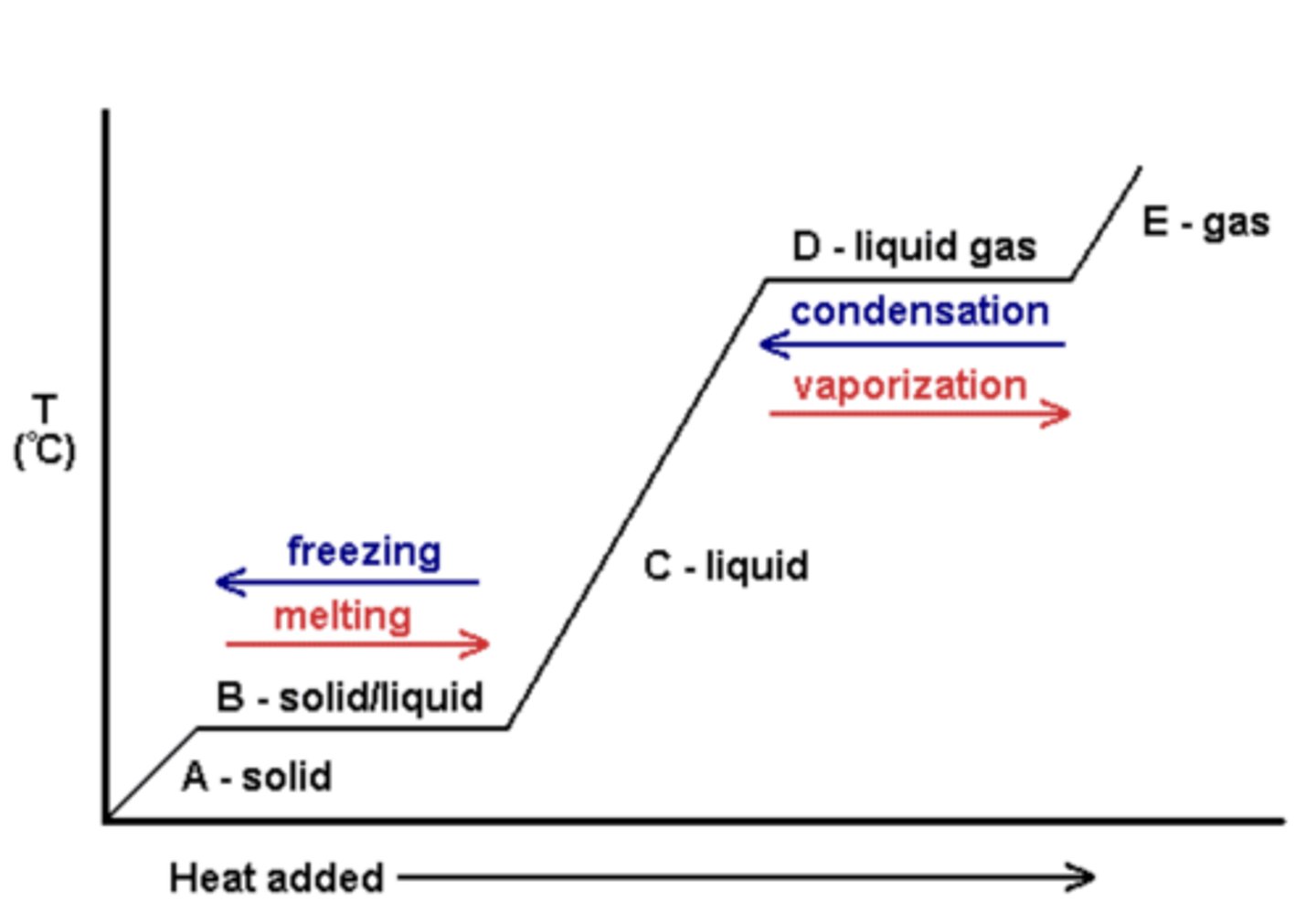
Boiling, Vaporization, Evaporation
a phase change where a liquid changes into a gas
endothermic

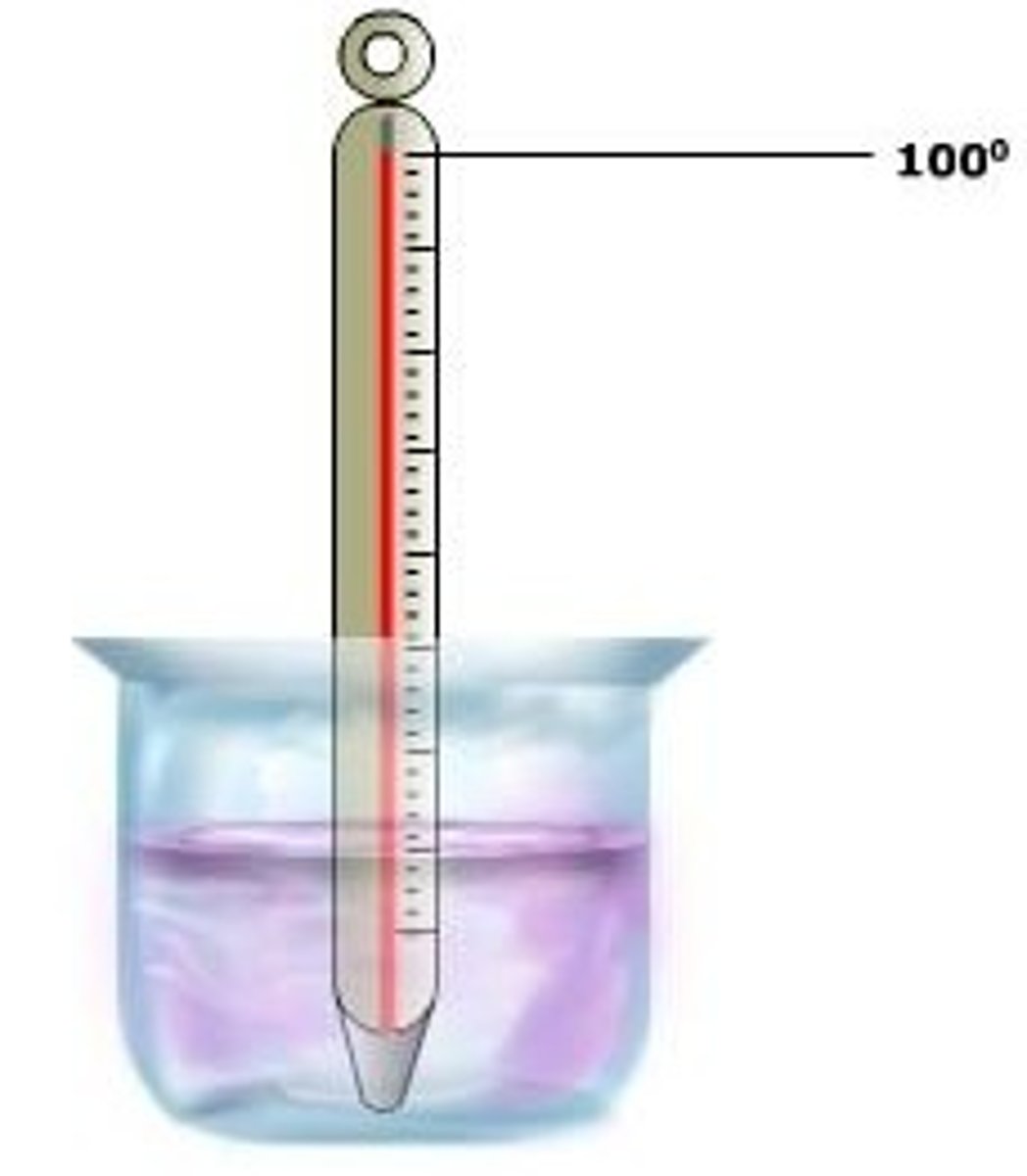
Boiling Point
for water...
100°C (at sea level)
212°F (at sea level)
373°K (at sea level)
the temperature where a liquid turns into a gas
Celsius (°C)
temperature scale where water at sea level freezes at 0° and boils at 100°

Compound
a substance that contains two or more elements chemically joined together and has the same composition throughout (NaCl)
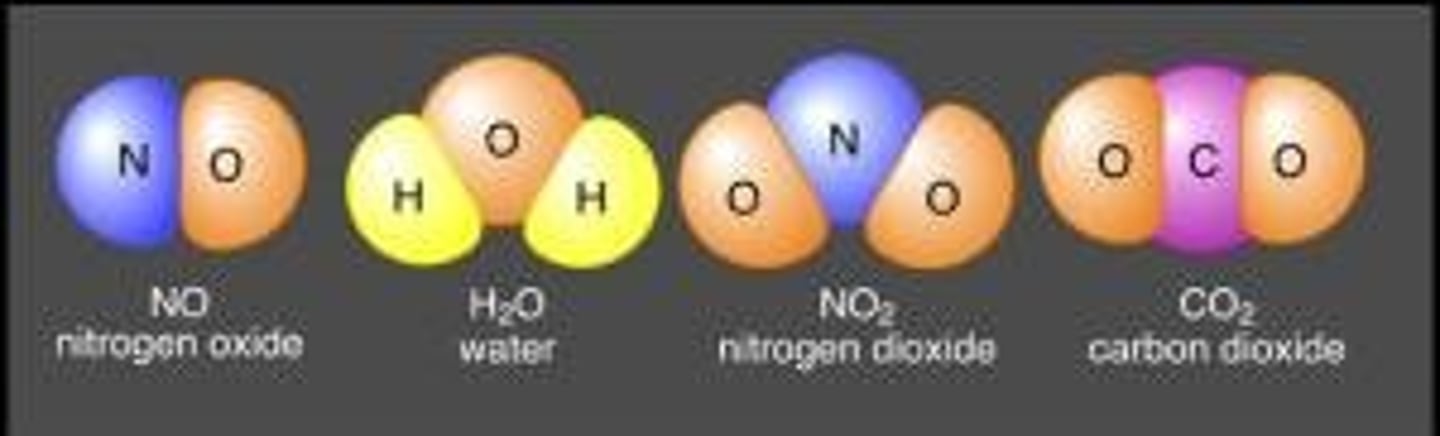
Condensation
a phase change from a gas to a liquid
exothermic

Deposition
a phase change from a gas to a solid
exothermic

Element
pure substances
cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical or physical means
Freezing
a phase change from a liquid to a solid
exothermic

Fahrenheit (°F)
a temperature scale where water freezes at 32° and boils at 212°

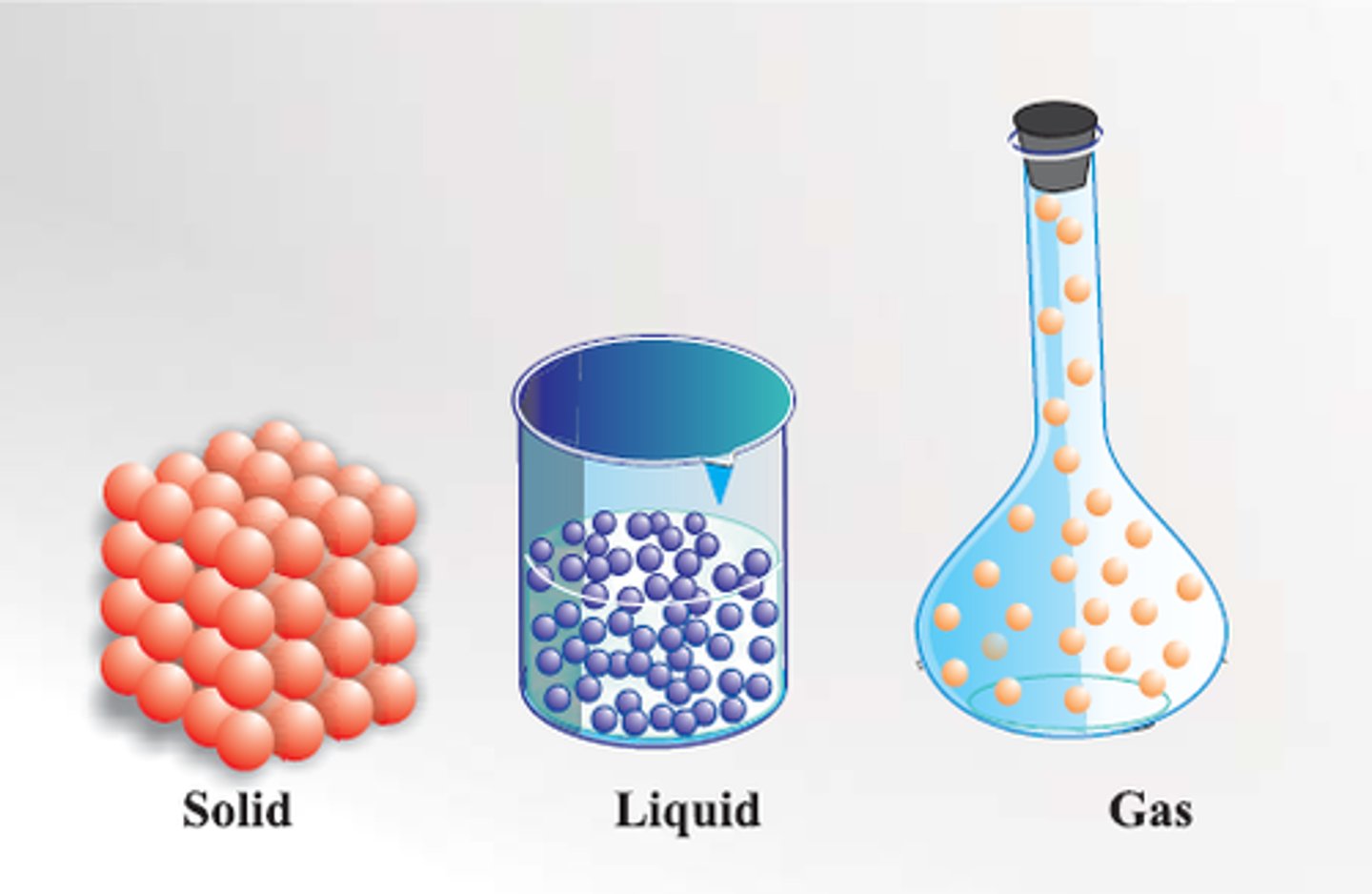
Gas
more kinetic energy than a liquid
less kinetic energy than a plasma
fills up the volume and takes the shape of a container
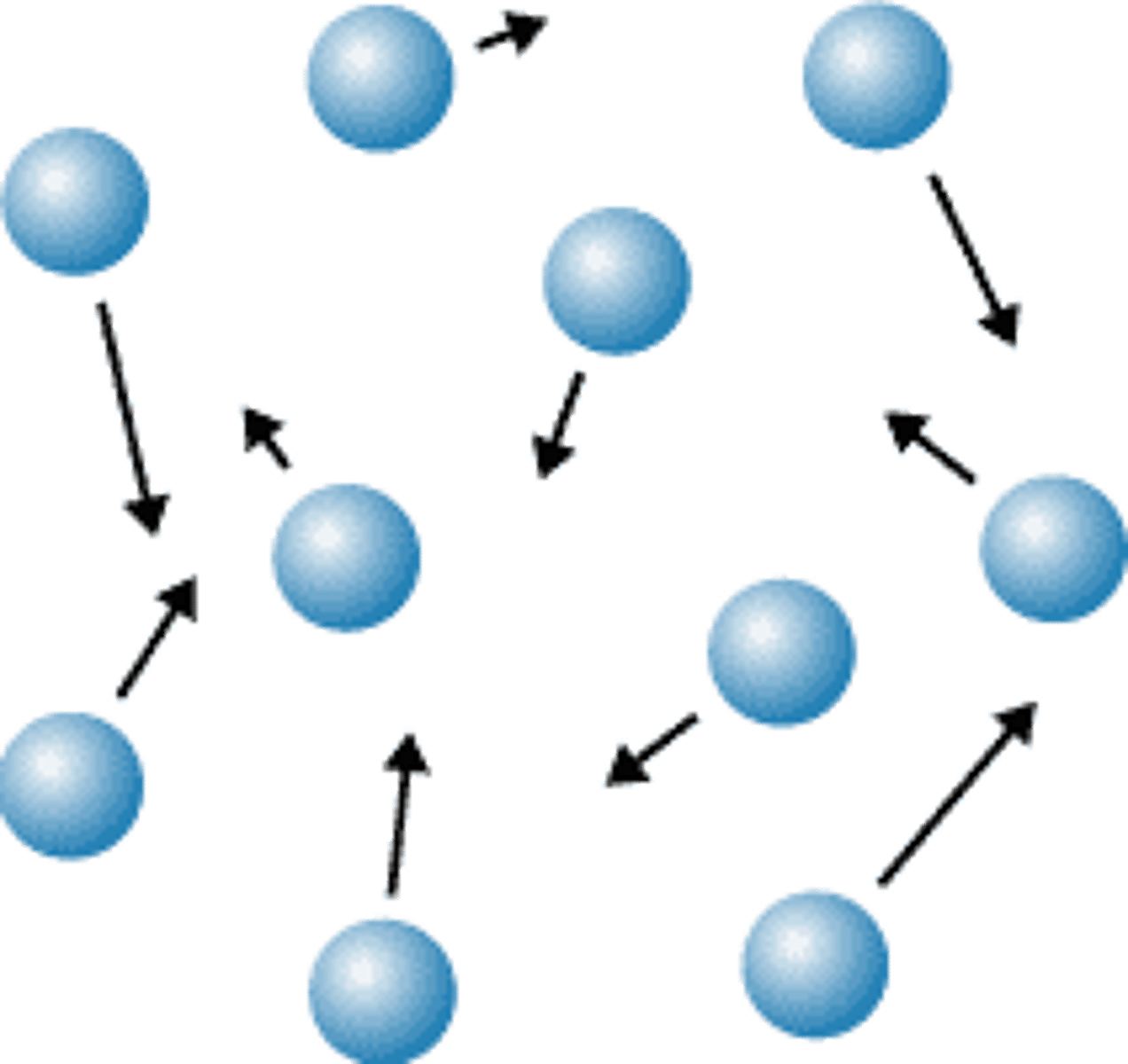
Heterogenous
a mixture where the particles are large enough to be picked out by eye

Homogeneous
a mixture where the particles are too small to be picked out by eye

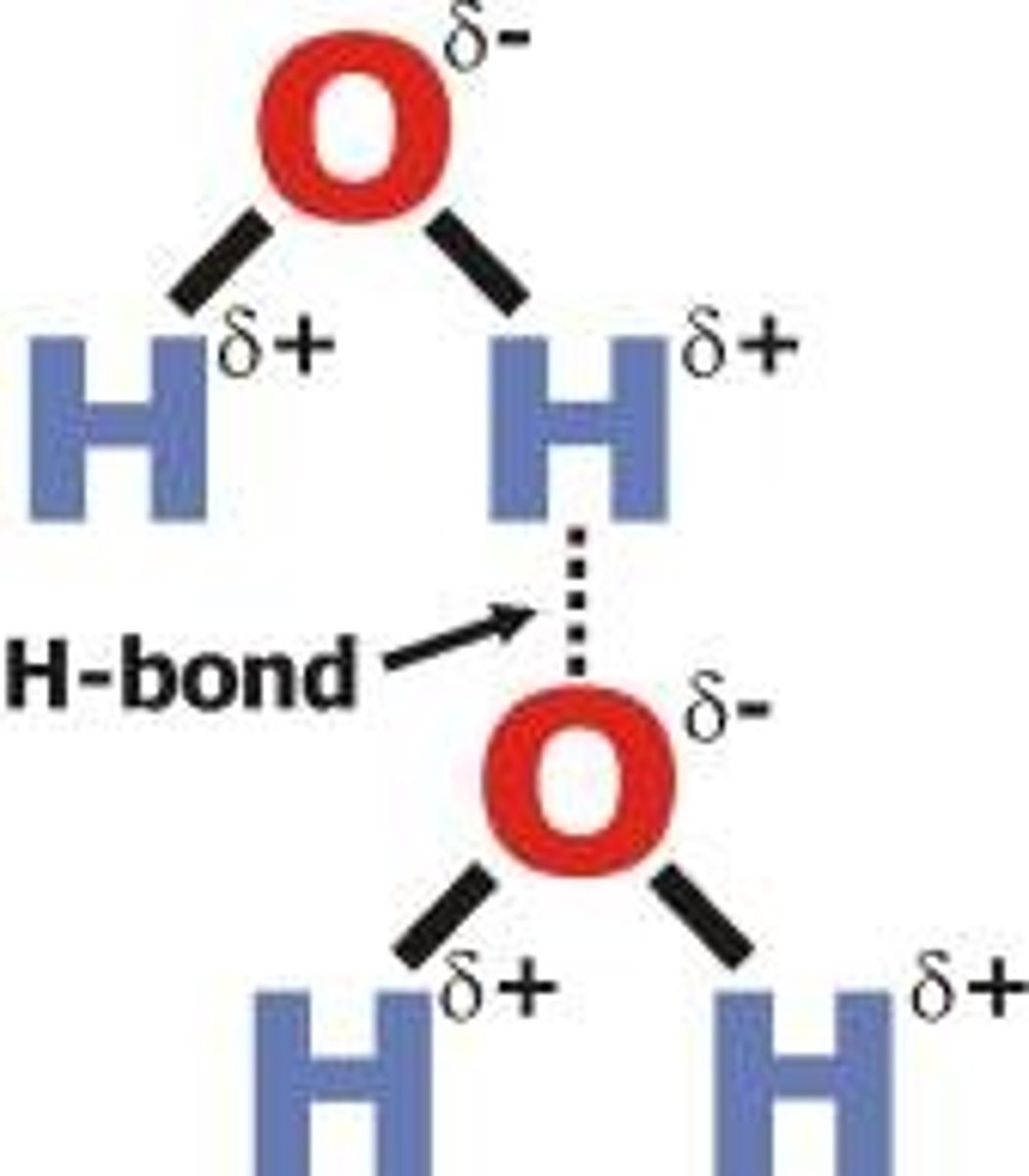
Intermolecular Forces
attractive or repulsive forces between neighboring particles (atoms, ions, molecules)
Kelvin (°K)
a temperature scale where water freezes at 273.15° and boils at 373.15°
0° is the coldest limit for temperature, that can NEVER be reached

Kinetic Energy (Ek)
energy of movement

Liquid
fills the shape of a container, but not the volume
more kinetic energy than a solid
less kinetic energy than a gas

Matter
takes up mass and has volume
Melting
a phase change from a solid to a liquid
endothermic

Melting Point
for water...
0°C (at sea level)
32°F (at sea level)
273.15°K (at sea level)
the point where a solid changes to a liquid
Mixture
a combination of different elements and/or compounds that CAN be separated by physical means

Molecule
a group of 2 or more atoms joined together by a chemical bond (H₂0, C0₂) can be the same atom, covalent bond

Phase Change
A change from one state (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition, no temperature change takes place.
Heat energy changes the position of the particles relative to each other (potential energy).
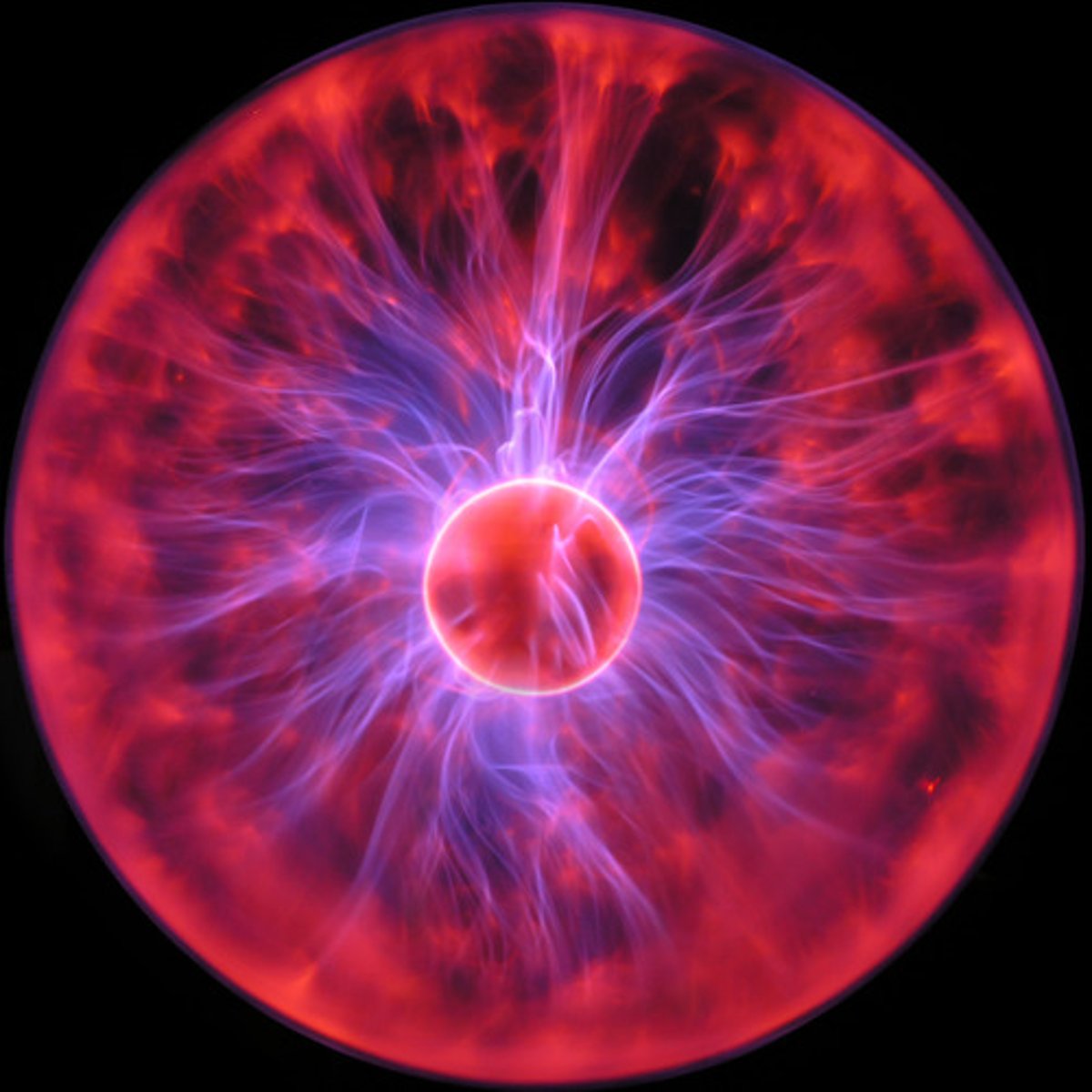
Plasma
the atoms have two much energy to hold onto their electrons
more kinetic energy than a gas
Potential Energy (Ep)
energy due to position or stored energy

Pure Substance
CANNOT be separated by physical means
elements & compounds / molecules
Solid
has a definite volume and shape
more kinetic energy than BEC
less kinetic energy than a liquid
Sublimation
a phase change from a solid to a gas
endothermic

Temperature (T)
the AVERAGE particle motion
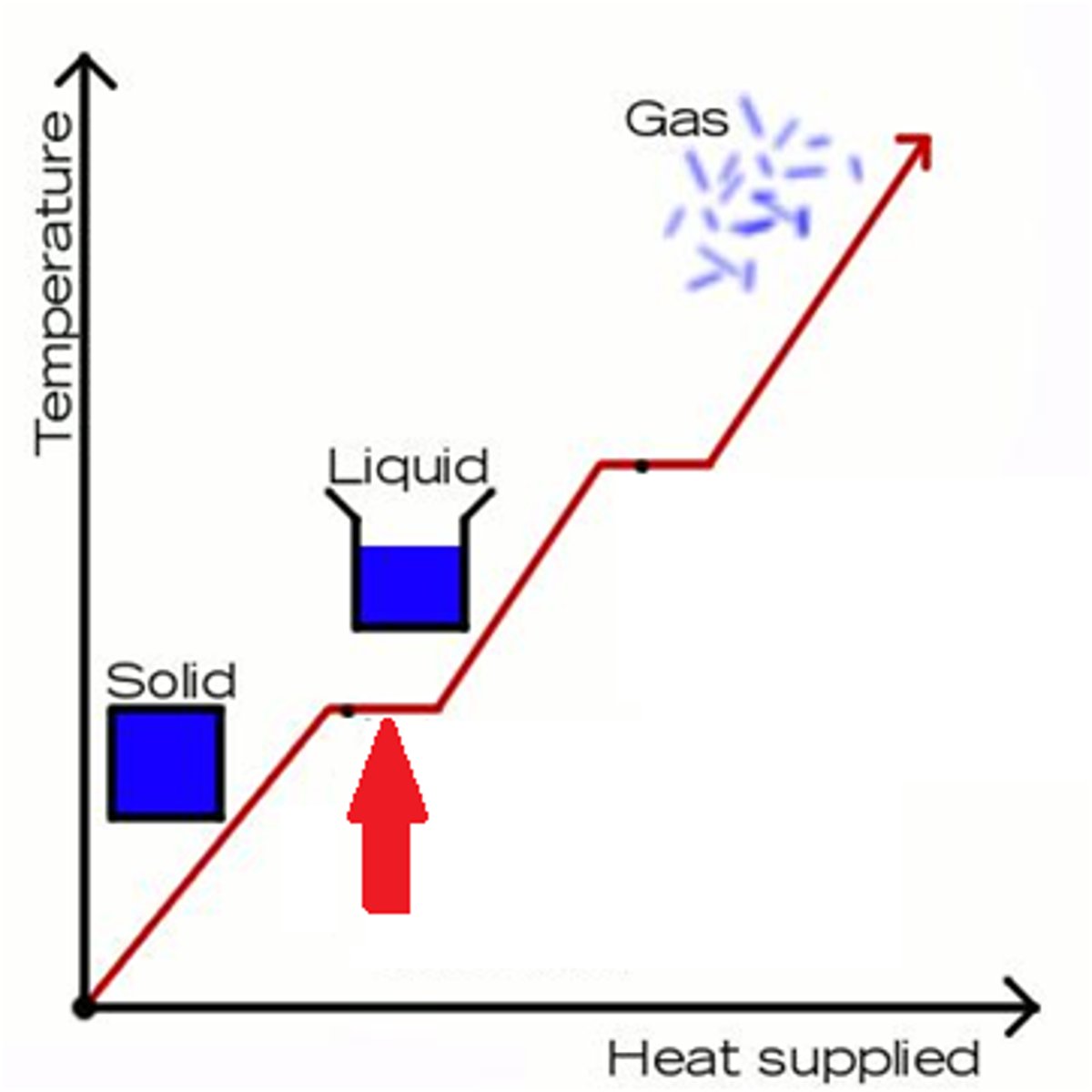
Heat of Fusion
energy required to change a gram of a substance from the solid to the liquid state without changing its temperature (melting)
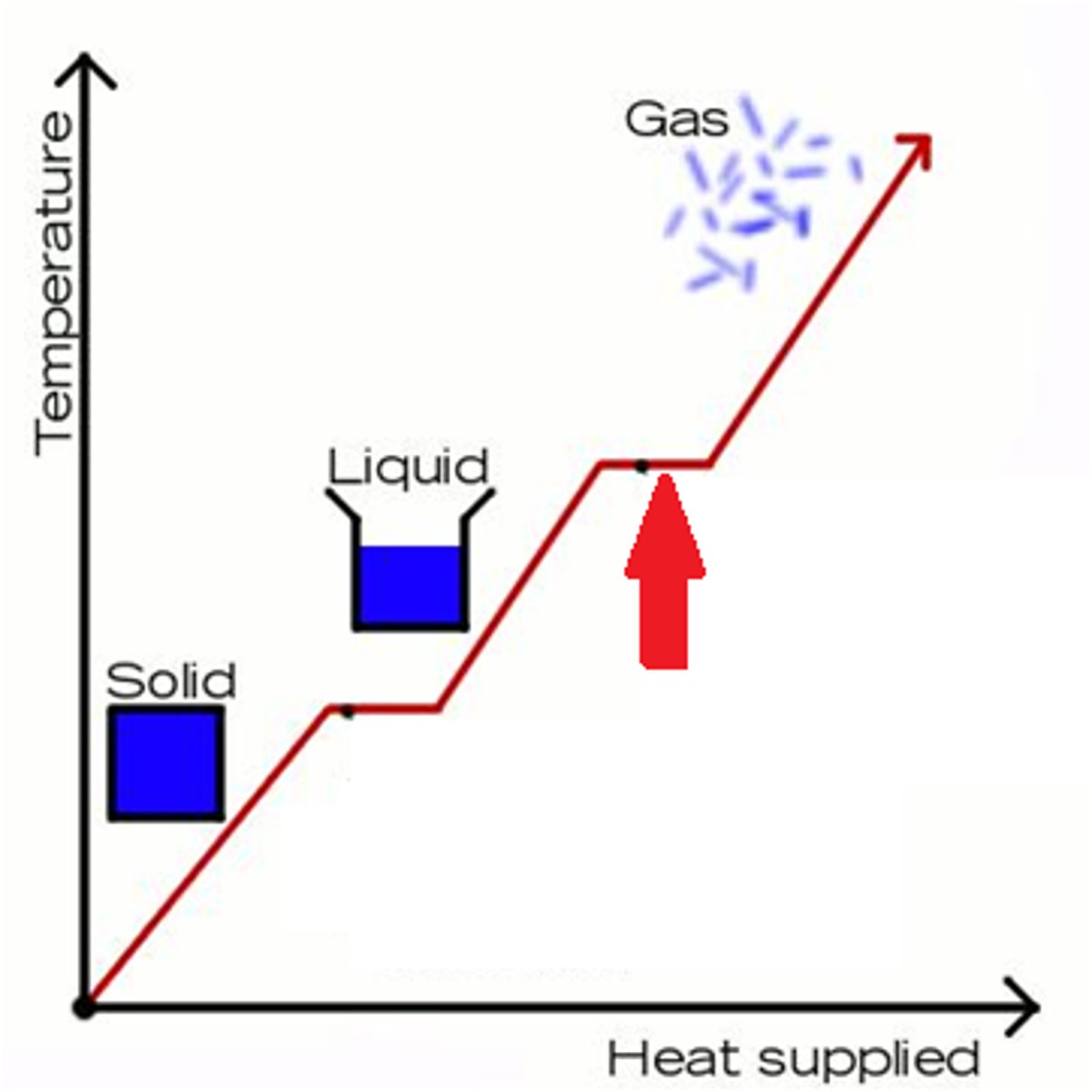
Heat of Vaporization
the quantity of heat that must be absorbed if a certain quantity of liquid is vaporized at a constant temperature
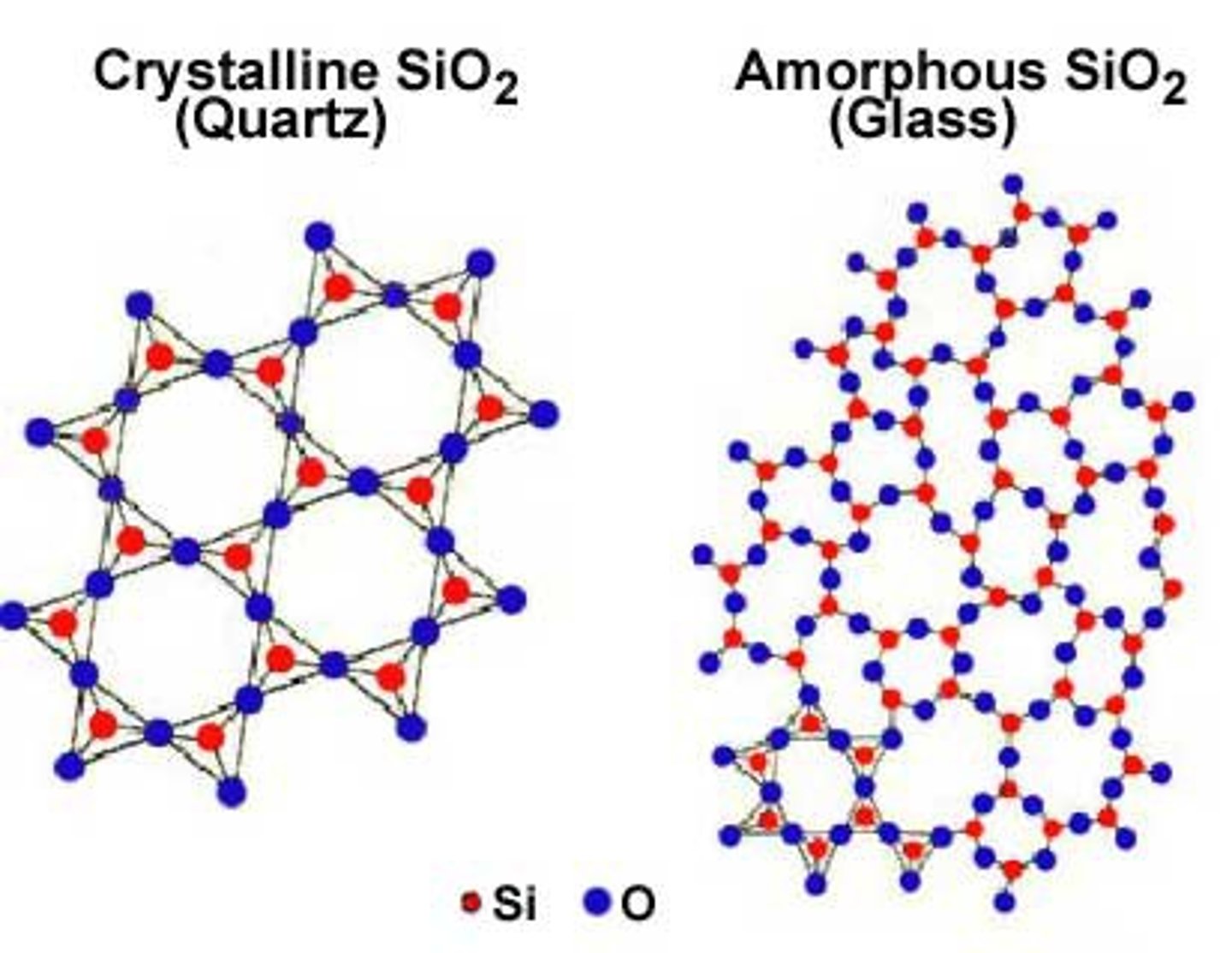
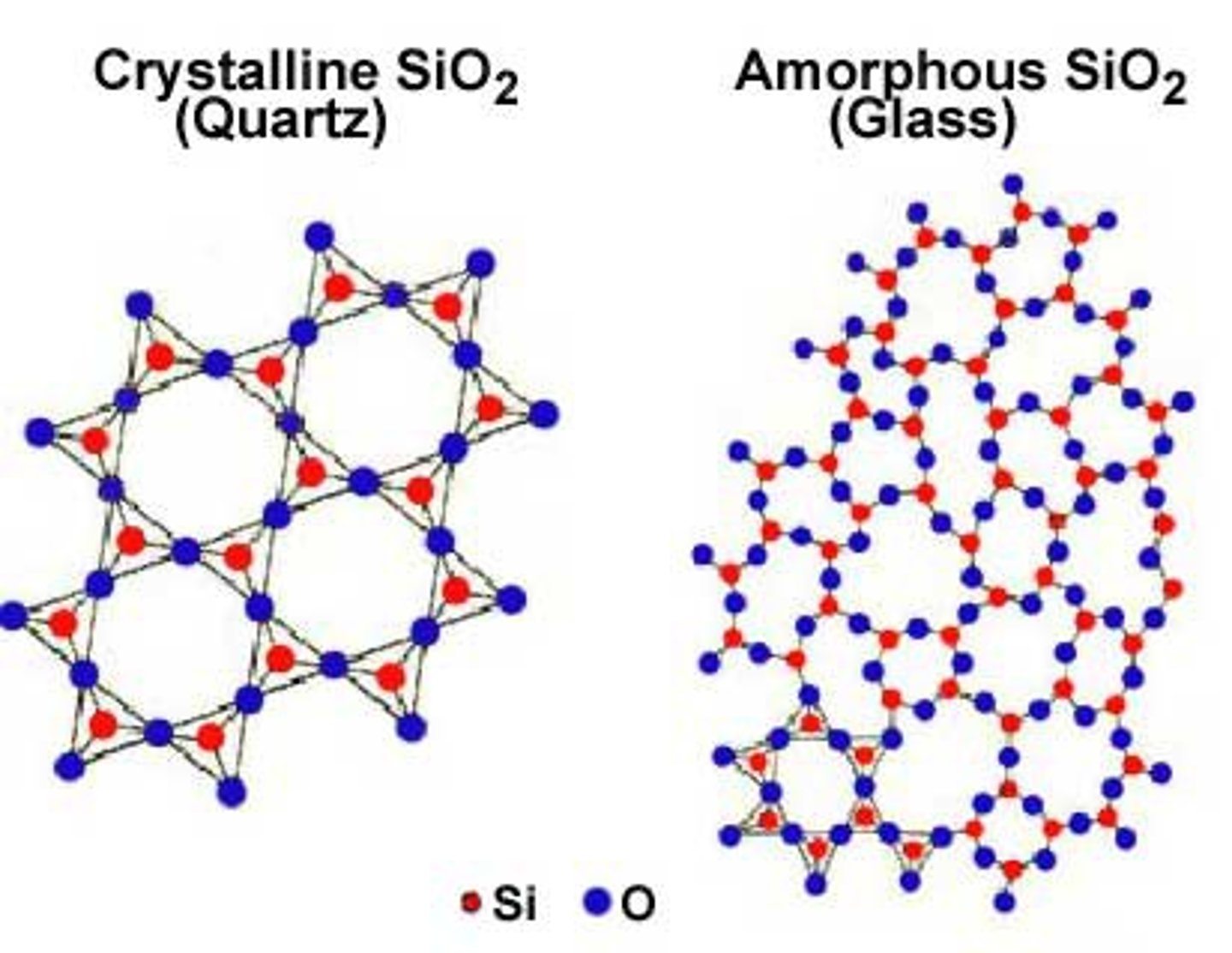
Amorphous
a non-crystalline solid that has no definite patterns or structure
Brittle
likely to break, snap, or crack when pressure is applied

Calorie
the amount of heat required at a pressure of 1 standard atmosphere to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1° Celsius

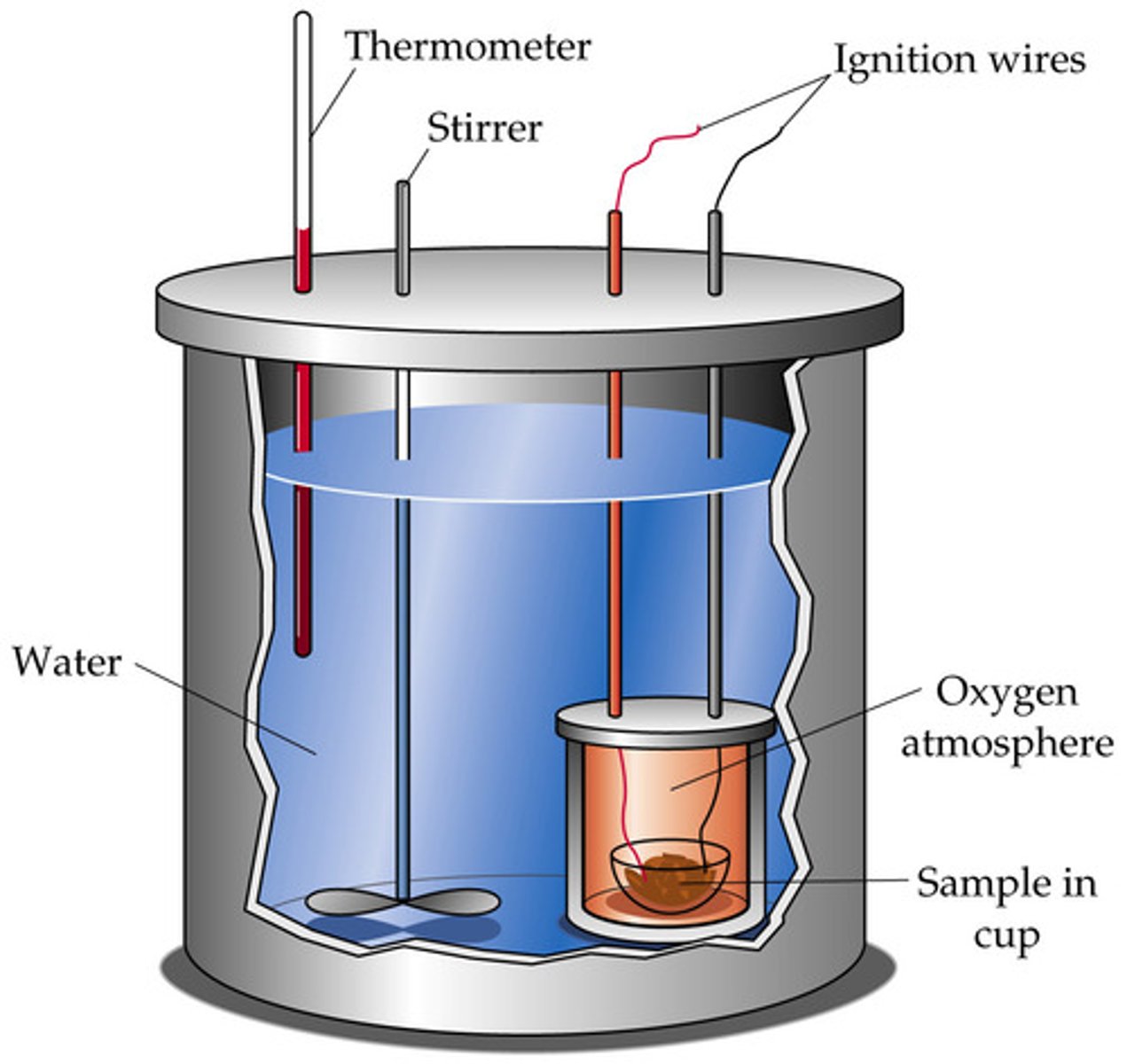
Calorimeter
deviced used to contain heat energy so the specific heat of an unknown object can be calculated
Chemical Change
a change that results in NEW chemical substances

Chemical Property
any of a material's properties that is evident during or after a chemical change
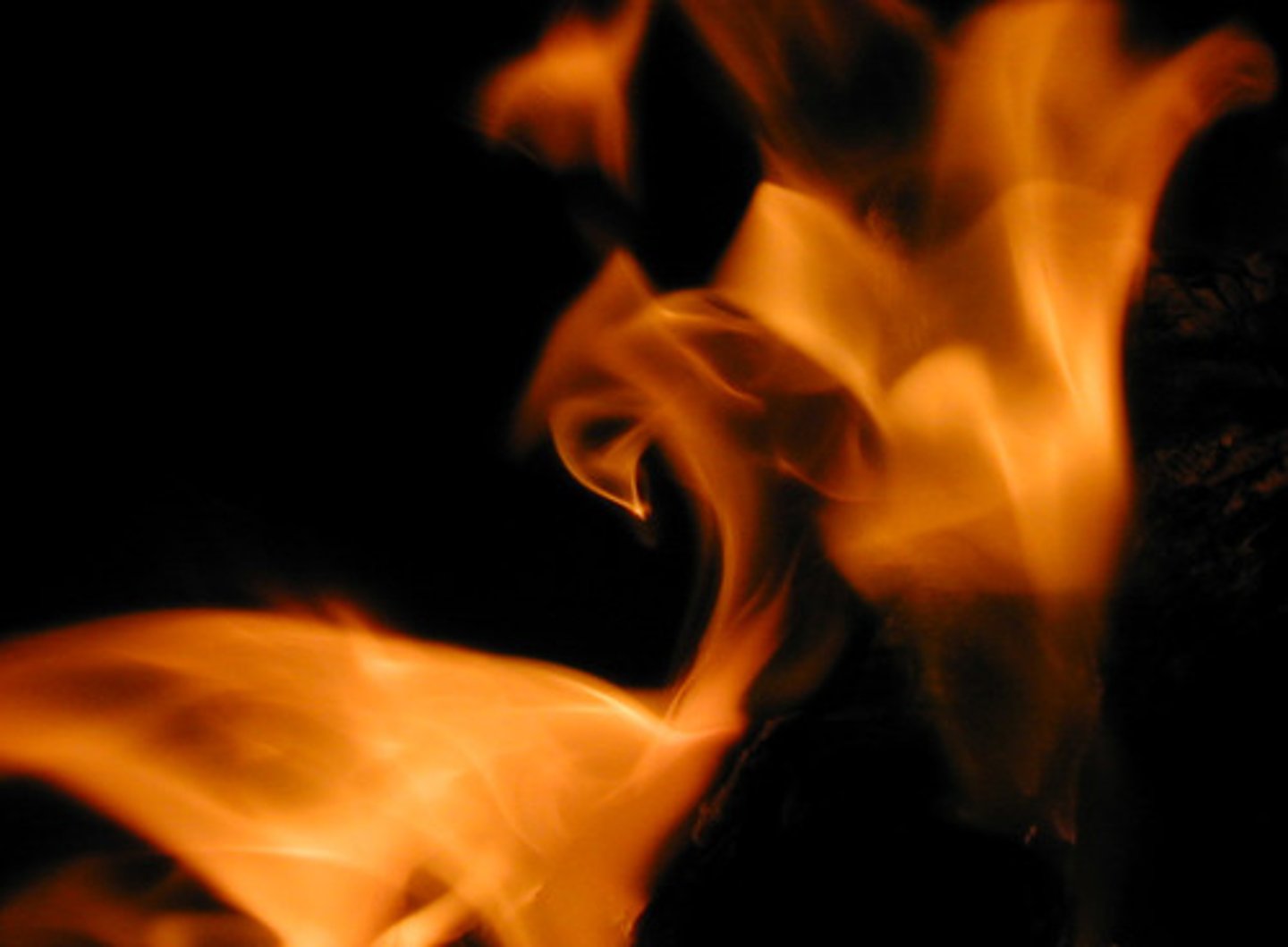

Chemical Reaction
a reaction where bonds are broken and formed resulting in the creation of new substances
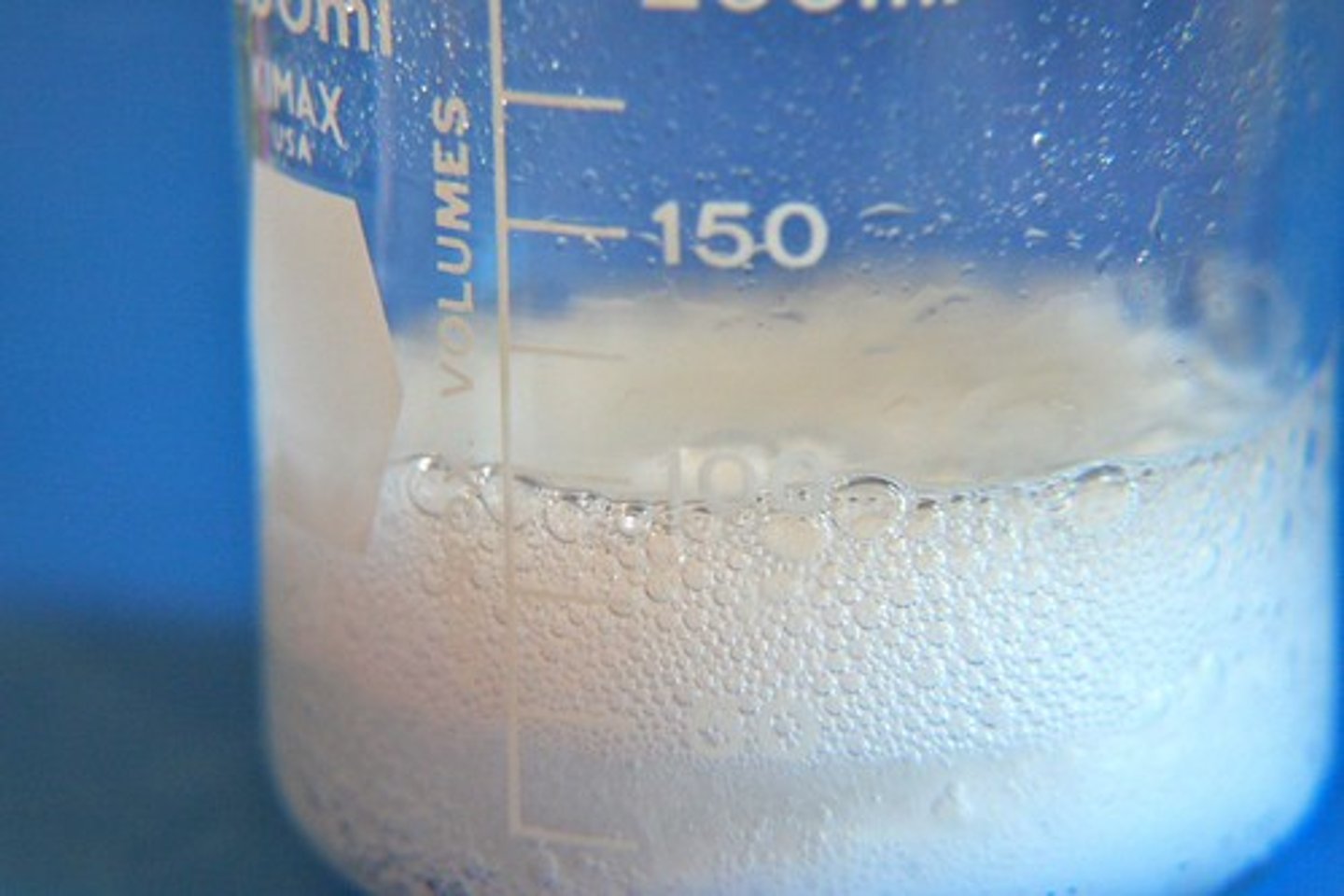

Physical Change
a change that results in the SAME chemical substance

Physical Property
used to observe and describe matter without changing its composition

Crystalline
a solid with a regular arrangement of atoms in a lattice pattern
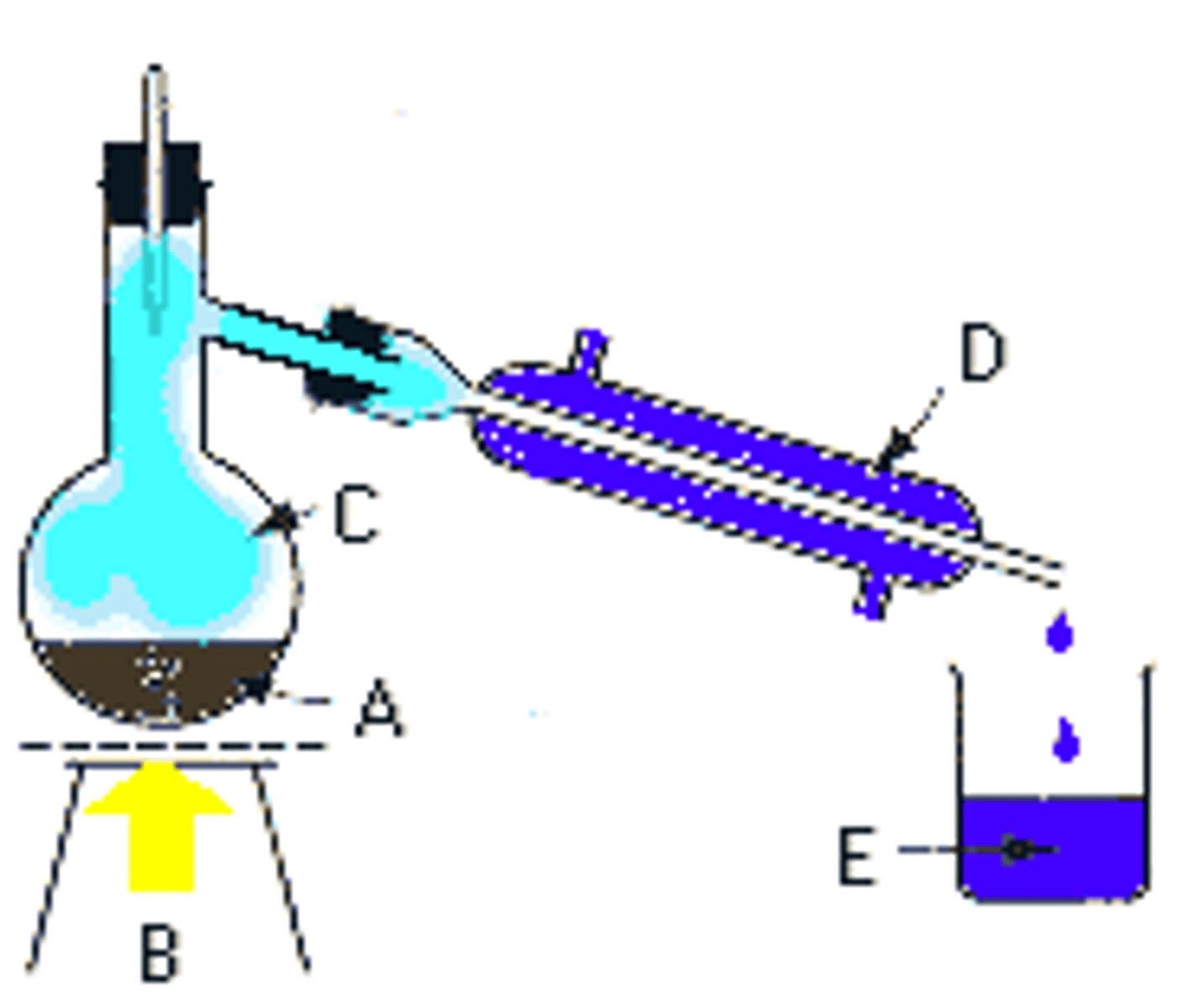
Distillation
separating substances in a liquid by using evaporation and condensation
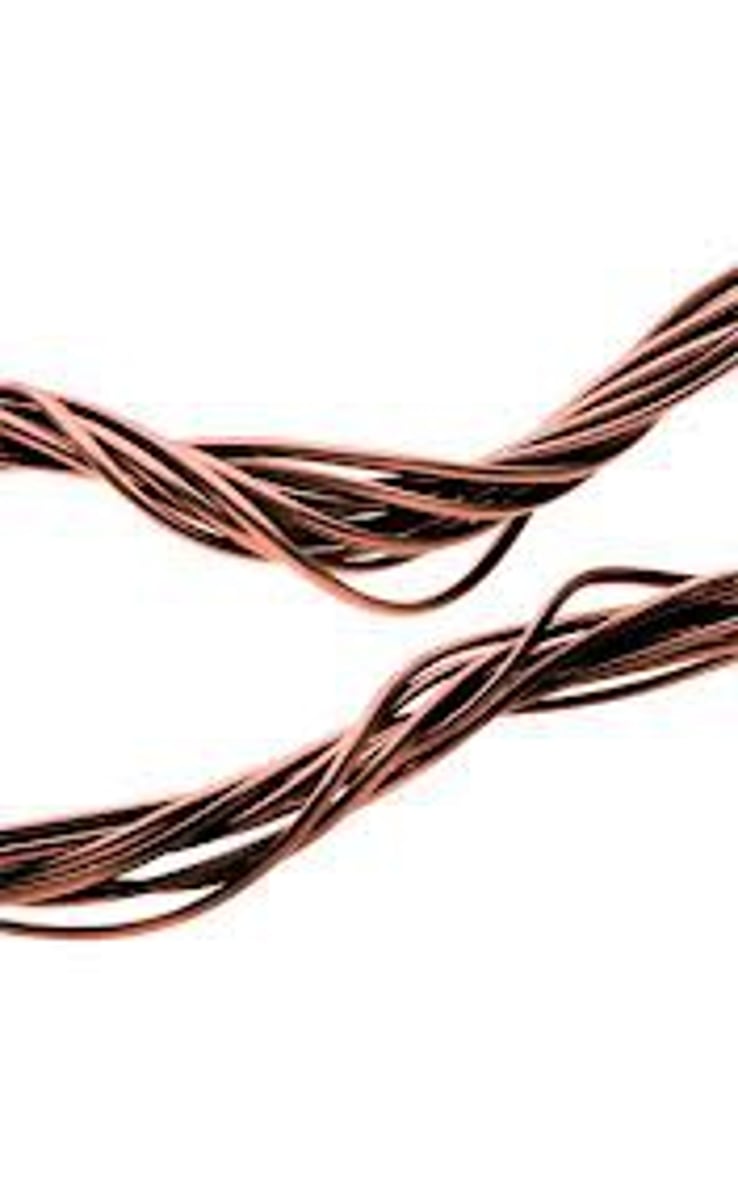
Ductility
the ability to be drawn into a wire without breaking (tensile strength).

Filtration
separating a suspended solid from a liquid by passing it through the pores of some substance

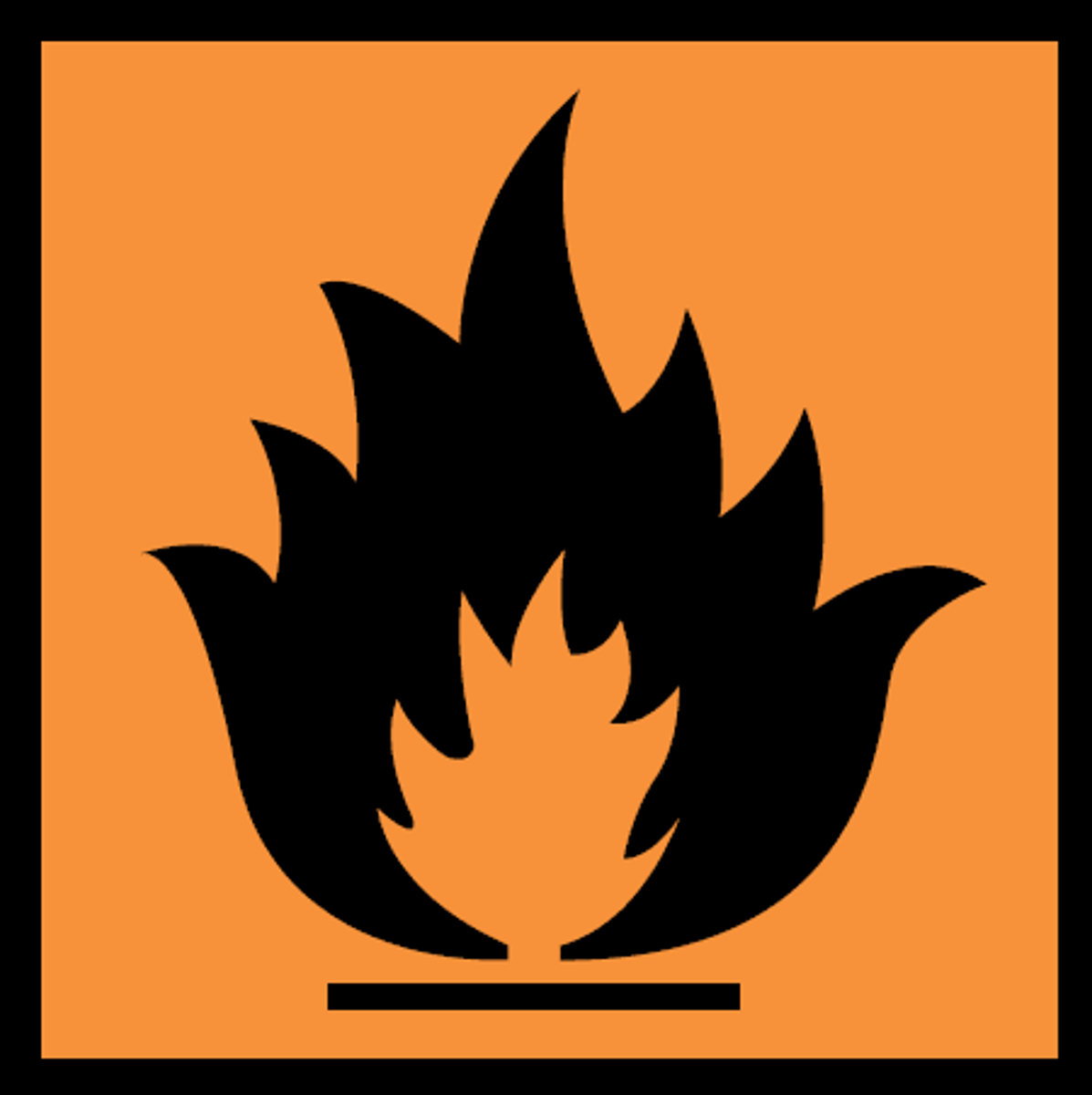
Flammability
the ability to burn or ignite

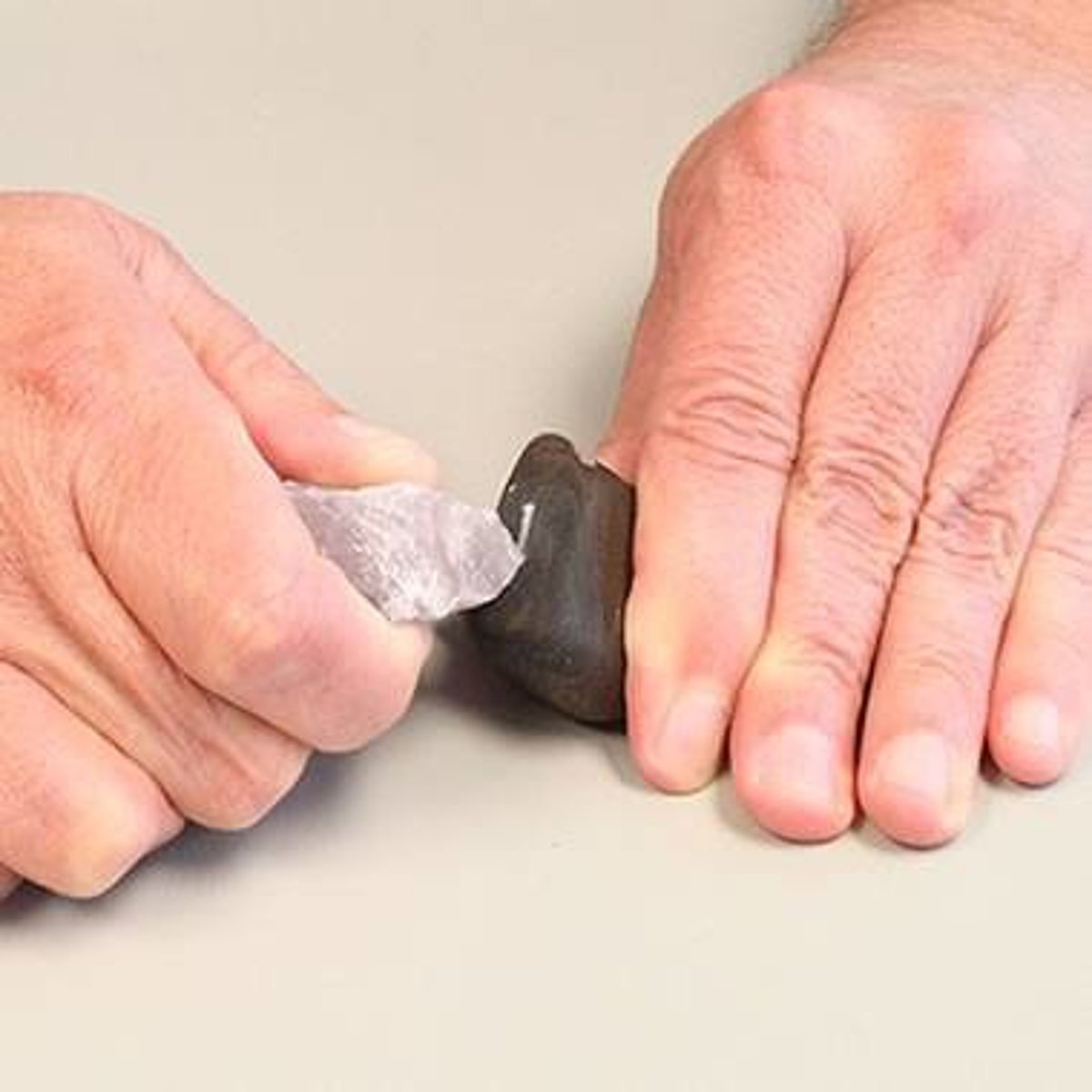
Hardness
the ability of a material to resist plastic deformation (be scratched)

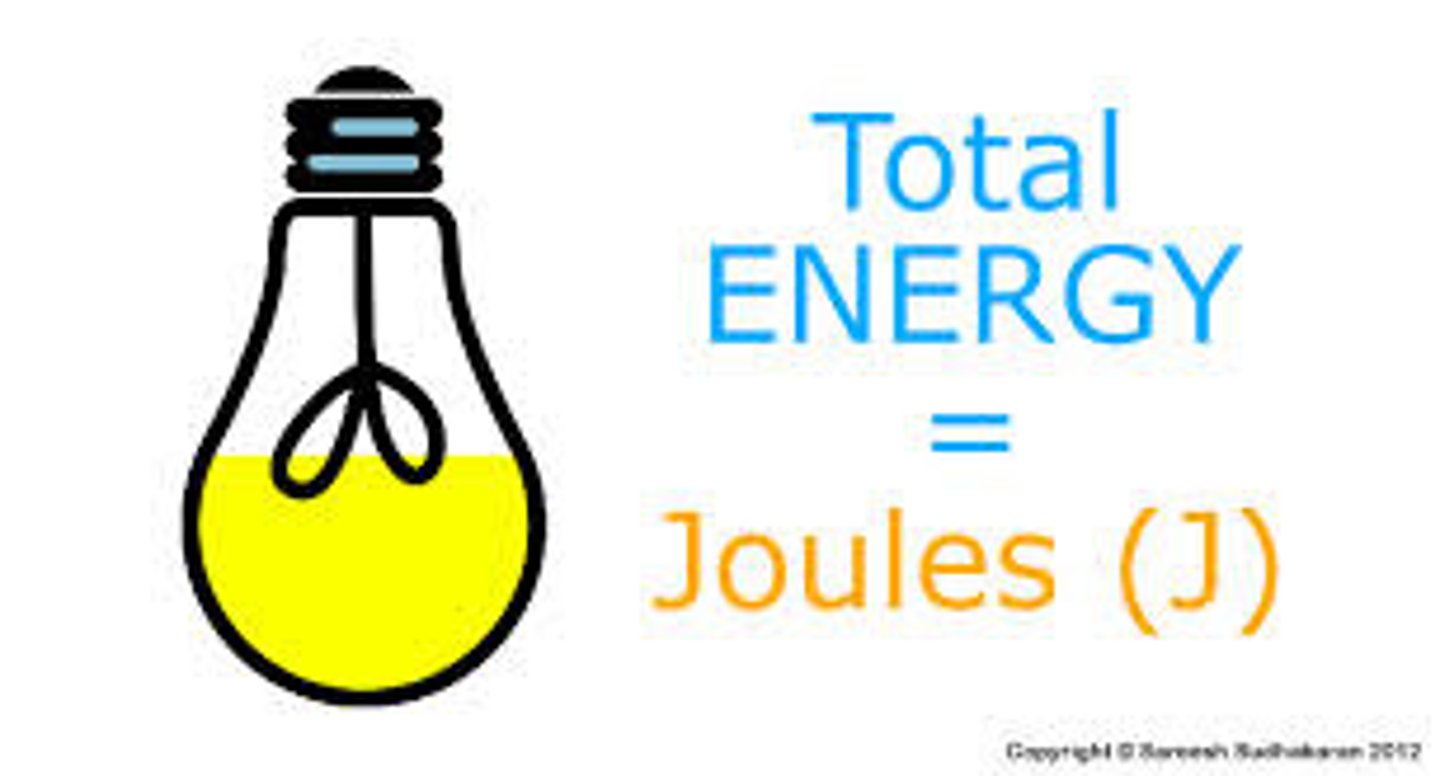
Joule (J)
SI unit of work or energy
Malleability
the ability of a solid to bend or be hammered into other shapes without breaking

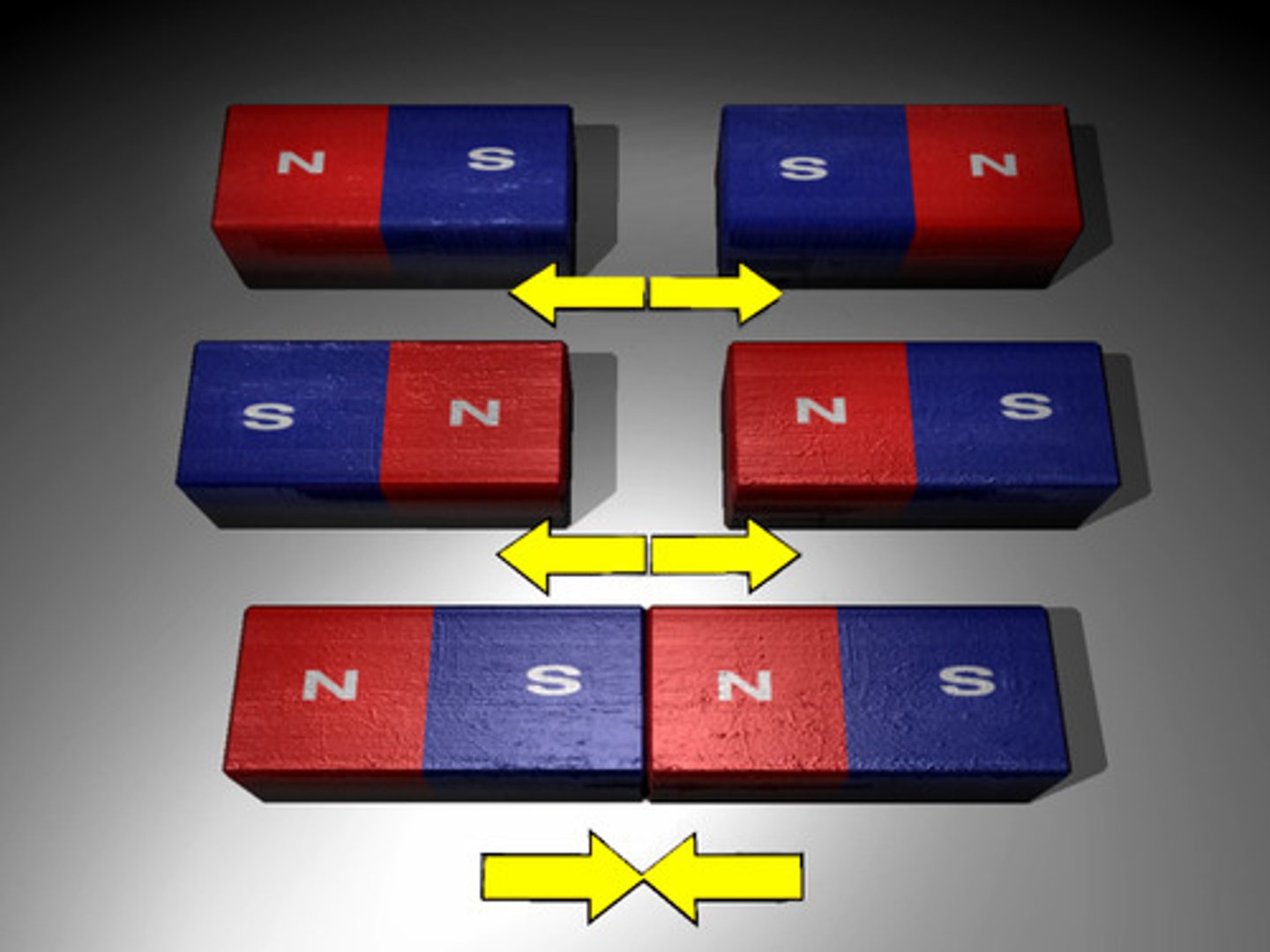
Magnetism
the motion of electric charges creates a field that attracts or repels other fields
Mass (m)
the amount of matter an object contains
measured in grams

Specific Heat (Cp)
the rate an object changes temperature
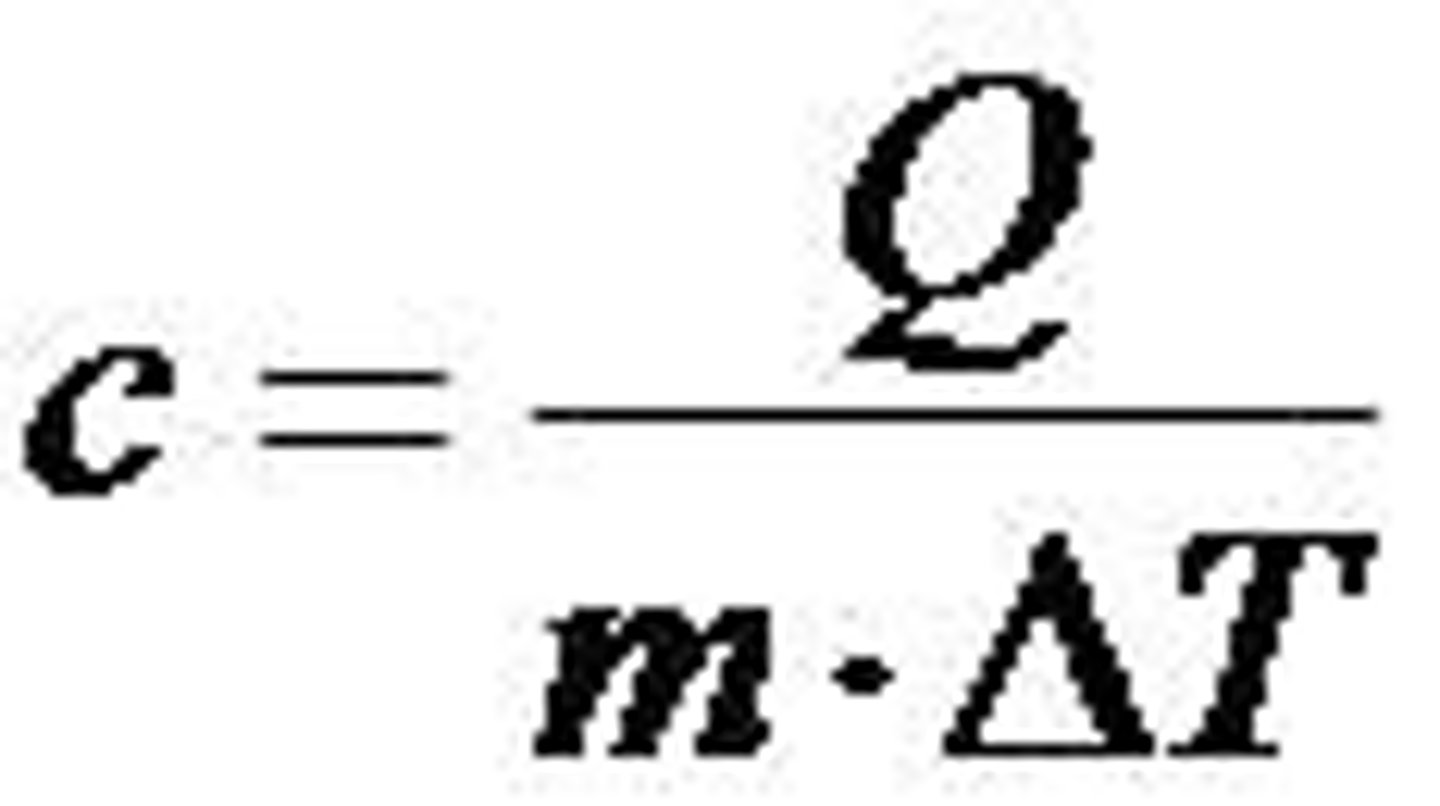
Tensile Strength
the force required to pull or stretch an object

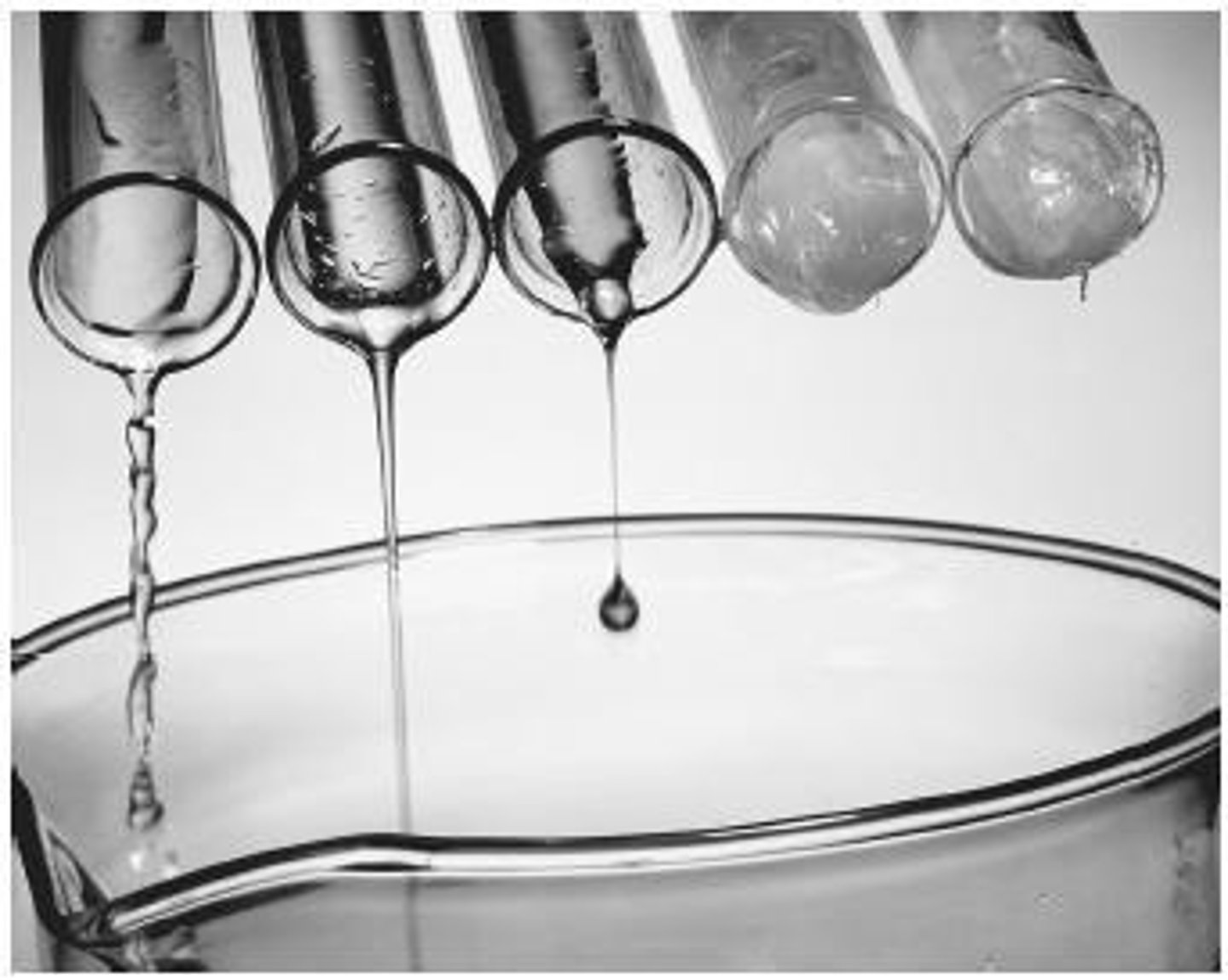
Viscosity
the thickness, or resistance of a liquid to flow

Thermal Expansion
how an object enlarges when heat is applied
