Gait Deviations
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are primary gait deviations?
Gait deviations directly caused by an impairment
What are examples of causes of primary gait deviations?
Deformity
Weakness
Impaired motor control
Pain
What are secondary gait deviations?
Deviations caused by
abnormal posture or
abnormal movement at an adjacent joint
What are examples of secondary gait deviations?
Forefoot contact at IC due to inadequate knee extension during TSw
Excessive DF during MSt due to a knee flexion contracture (primary issue)
What are compensatory gait deviations?
Deviations that accommodate for an impairment rather than being a direct result of it
What are examples of a compensatory gait deviations?
Ipsilateral trunk lean during stance to compensate for weak hip abductors
Excessive hip flexion during MSw to compensate for weak DFs
What types of disorders can cause compensatory gait deviations?
Musculoskeletal (MSK)
Central Nervous System (CNS) disorders
What causes toe drag during initial swing?
Insufficient knee flexion to clear the foot
What causes toe drag during mid-swing
Insufficient DF to clear the toes
How does the medial longitudinal arch behave during the gait cycle?
It flattens during LR,
and rises again during late MSt into TSt
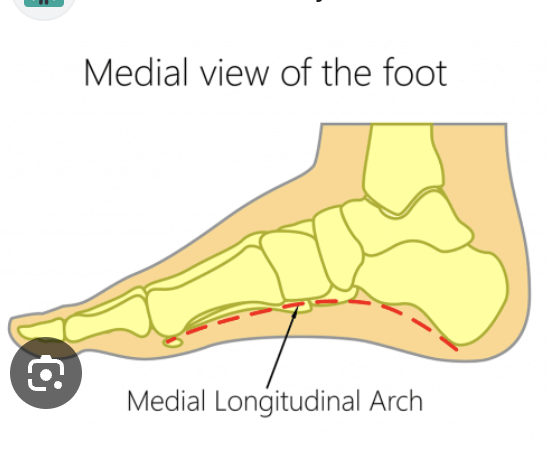
What happens to the medial arch during loading response (LR)?
It flattens as body weight is accepted
What muscle controls the lowering of the medial arch during LR?
posterior tibialis
How does the posterior tibialis act during LR?
Eccentrically, to control the lowering of the medial arch
What happens to the medial arch during late mid-stance to terminal stance?
It rises to prepare for push-off
How does the posterior tibialis act during late mid-stance to terminal stance?
Concentric contraction to raise the medial arch
How does an AFO help prevent genu recurvatum during stance phase?
By fixing the foot in DF, which encourages knee flexion
What effect does dorsiflexion from an AFO have on knee motion?
It promotes knee flexion during stance phase
How does an AFO influence the heel rocker?
It accentuates the heel rocker action,
which naturally promotes knee flexion
During which phases of gait does the AFO help maintain knee flexion?
Mid-stance and terminal stance
Hip during Loading Response (LR)
Impairment: Gluteus maximus weakness
Deviation/Compensation: Gluteus maximus gait — trunk leans backward to lock hip into extension

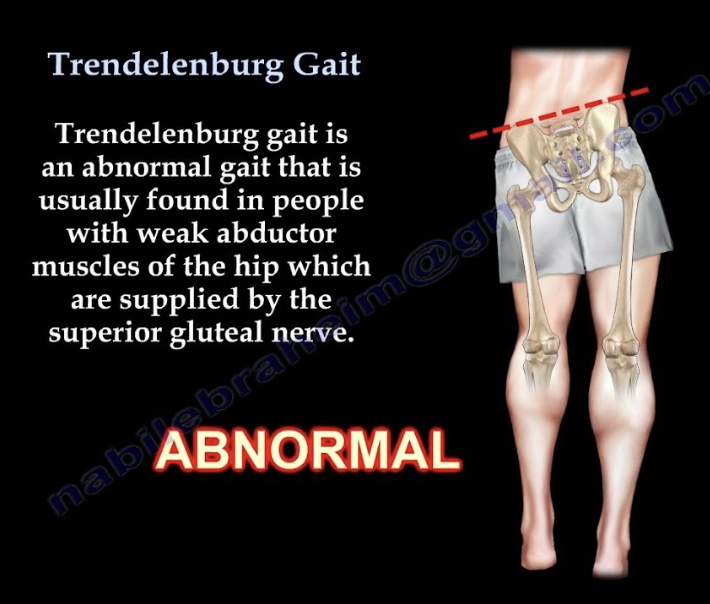
Hip during Mid-Stance (MSt)
Impairment: Gluteus medius weakness of the stance leg
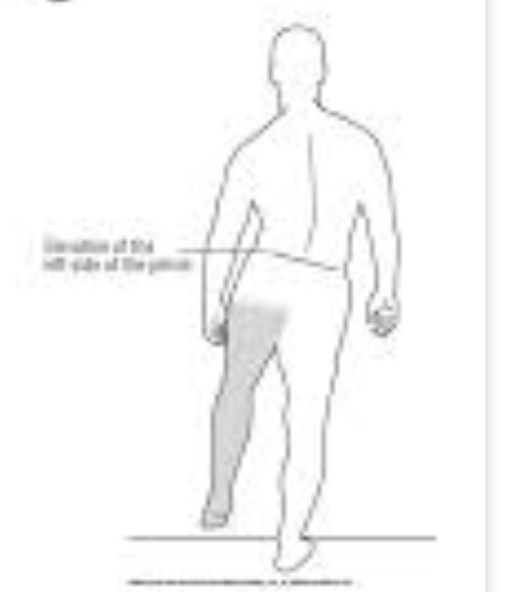
Deviation/Compensation: Trendelenburg gait — contralateral pelvis drops
Hip during Mid-Stance (MSt)
Impairment: Gluteus medius weakness
Deviation/Compensation: Compensatory Trendelenburg gait — trunk leans over stance limb to prevent pelvic drop
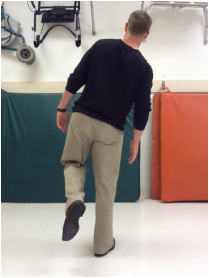
Hip during Mid-Stance (MSt)
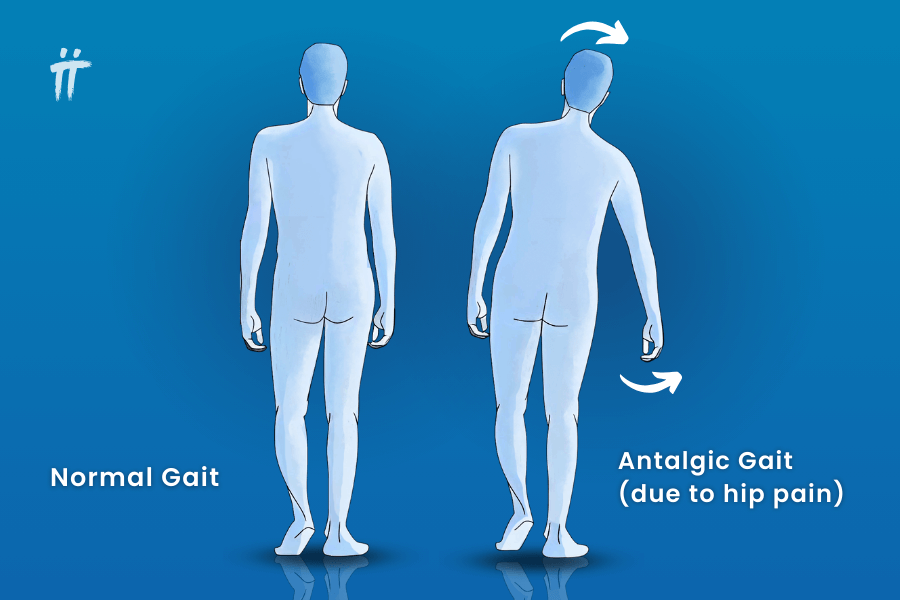
Impairment: Pain in the stance limb
Deviation/Compensation: Antalgic gait — reduced stance time on painful leg, shortened opposite step length
ant = against
-algic = pain
Ex: Jandro quickly shifts weight off the painful R leg, so the L leg swings earlier, making the L step shorter
Hip during Mid-Stance (MSt) — Deviation/Compensation
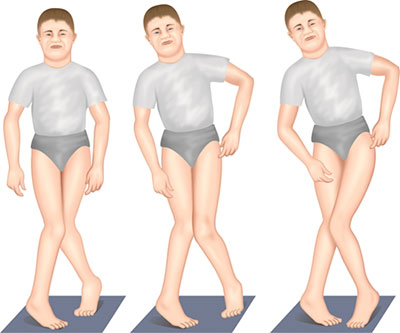
Impairment:
Skeletal deformity
Hip hypomobility
Adduction contractures
Abnormal adductor muscle activity
Deviation/Compensation: Scissoring gait — thighs cross midline and may touch
Hip during Terminal Stance (TSt)
Impairment:
Hip flexion contracture
Joint hypomobility
Pain or
Joint effusion
Deviation/Compensation: Excessive Backward Rotation of the pelvis during TSt
Hip during Swing Phase
Impairment: Inadequate hip flexion or DF
Deviation/Compensation: Circumduction — swing leg moves laterally in a circular motion to clear the foot
Hip during Mid-Swing (MSw)
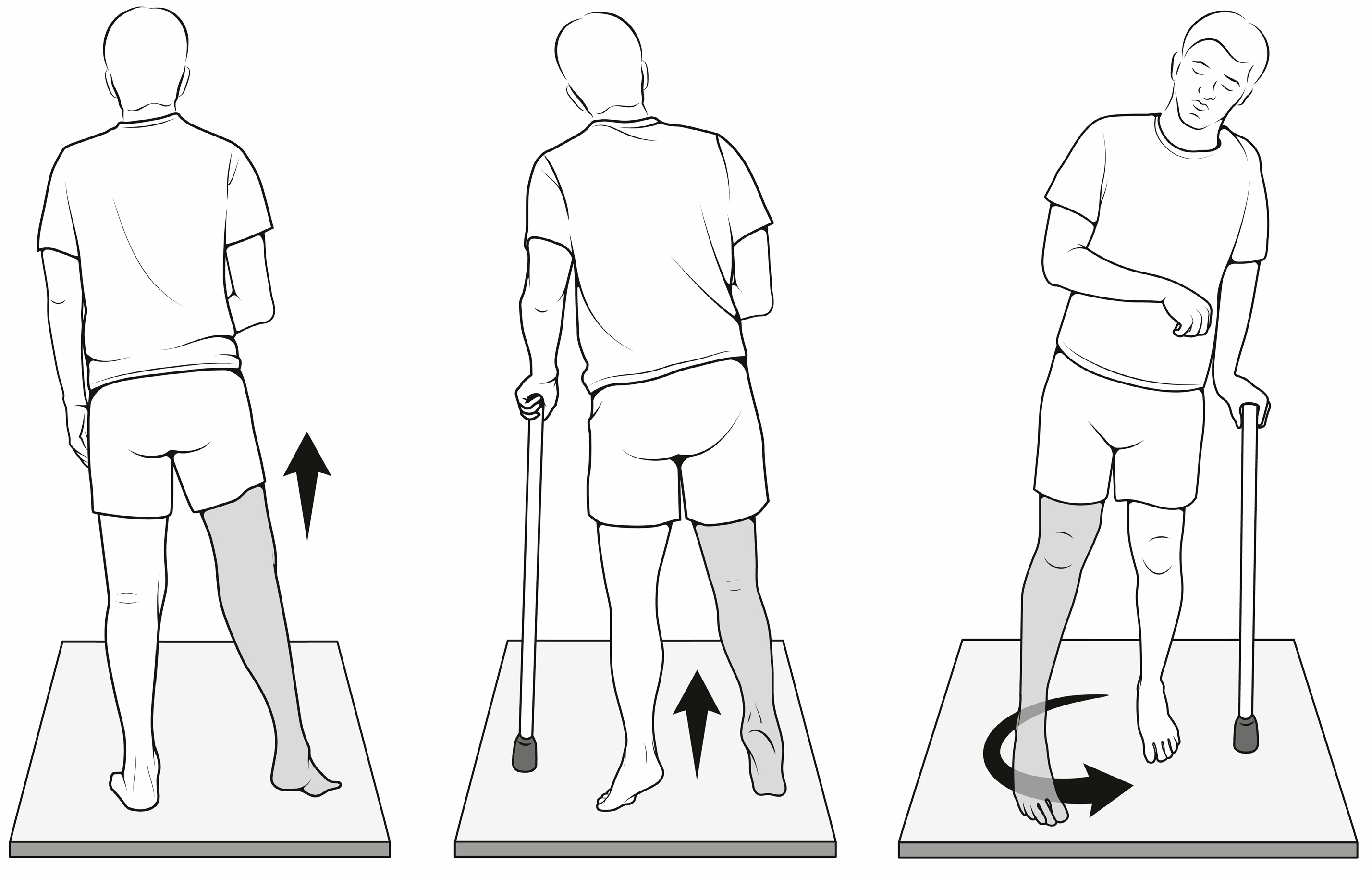
Impairment:
Inadequate knee flexion
Insufficient DF
Longer swing limb
Flexed stance knee
Deviation/Compensation: Steppage gait — excessive hip flexion resembling marching
Knee during Initial Contact (IC)
Impairment: Quadriceps weakness or spasticity (often upper motor neuron lesion)
Deviation/Compensation: Extensor thrust — knee suddenly jerks into extension
Knee during Loading Response (LR)
Impairment: Quadriceps weakness
Deviation/Compensation: Quadriceps gait — trunk leans forward to shift LoG anterior to knee, creating external extension moment
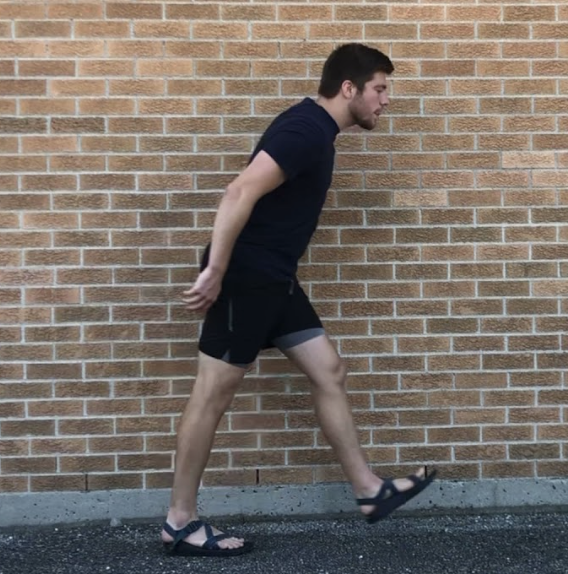

Knee during Loading Response (LR)
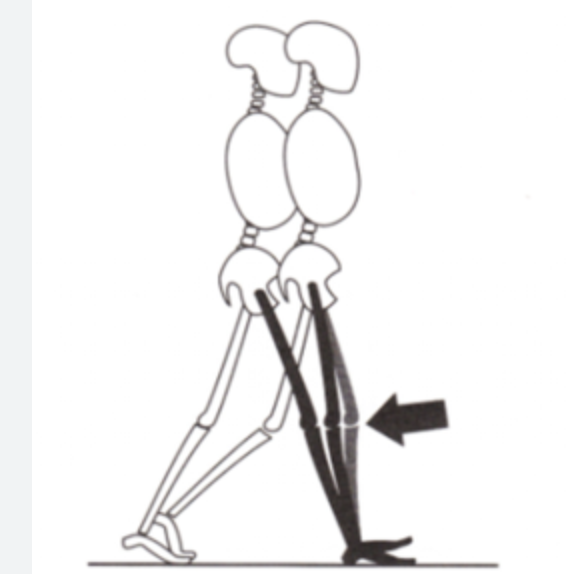
Impairment: Skeletal deformity or ligament instability
Deviation/Compensation: Thrust — sudden uncontrolled varus or valgus movement on weight acceptance
Varus Thrust in photo
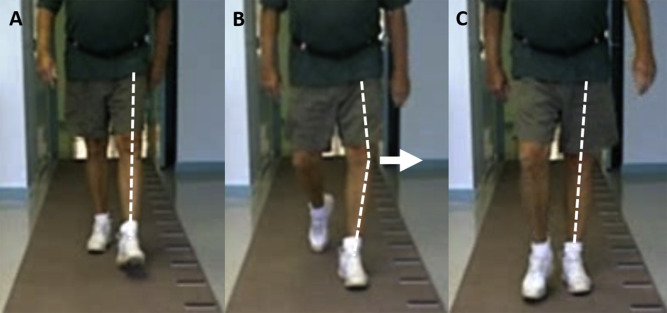
Knee during Mid-Stance (MSt)
Impairment: Quadriceps weakness, tight PFS or hamstrings
Deviation/Compensation: Genu recurvatum — knee hyperextension
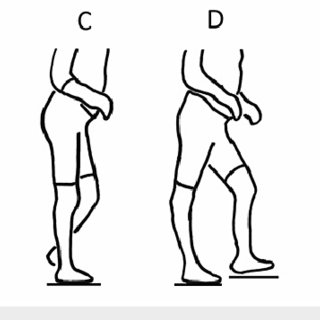
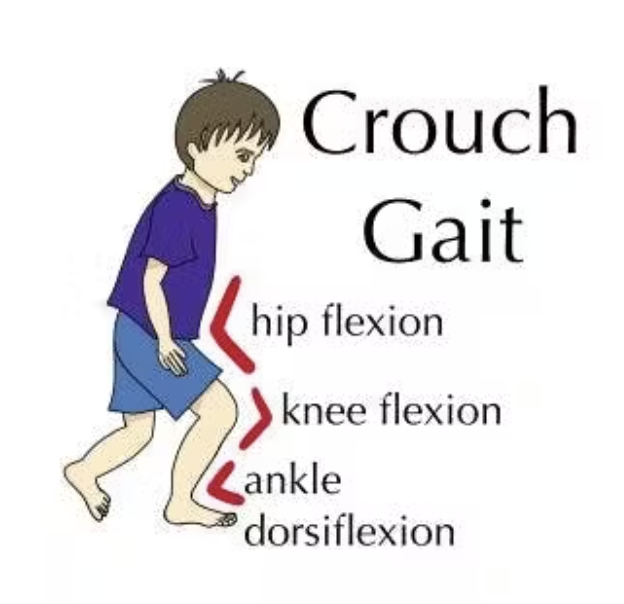
Knee during Mid-Stance (MSt)
Impairment:
Knee flexion contracture
hamstring tightness or spasticity
Deviation/Compensation: Crouch gait — knee remains excessively flexed
Knee during Initial Swing (ISw)
Impairment:
Knee extension contracture
Spasticity of knee extensors
Deviation/Compensation: Inadequate knee flexion causing toe drag

Knee during Mid-Swing (MSw)
Impairment:
Impaired motor control of hip/knee flexors,
Inadequate ankle DFs
Short stance limb
Deviation/Compensation: Excessive knee flexion during MSw
Knee during Terminal Swing (TSw)v
Impairment:
Knee flexion contracture
Hamstring overactivity
Joint pain/effusion
Deviation/Compensation: Inadequate knee extension causing instability in the next stance phase
Ankle & Foot during Initial Contact (IC)
Impairment:
DF weakness
PF contracture
talocrural joint hypomobility
impaired motor control
Deviation/Compensation: Foot flat — initial contact on forefoot or whole foot instead of just the heel
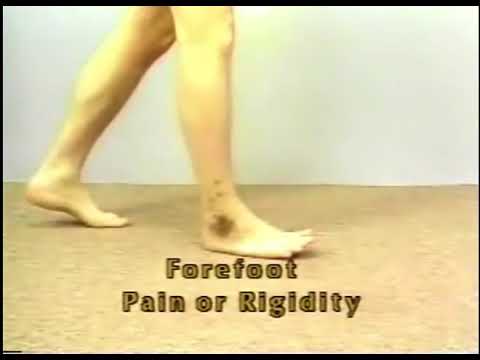
Ankle & Foot during Loading Response (LR)
Impairment: DF weakness
Deviation/Compensation:
Foot slap — forefoot rapidly plantarflexes uncontrollably

Ankle & Foot during Mid-Stance (MSt)
Impairment:
PF contracture
skeletal deformity
joint hypomobility
impaired PF control
Deviation/Compensation: Early heel off on stance leg
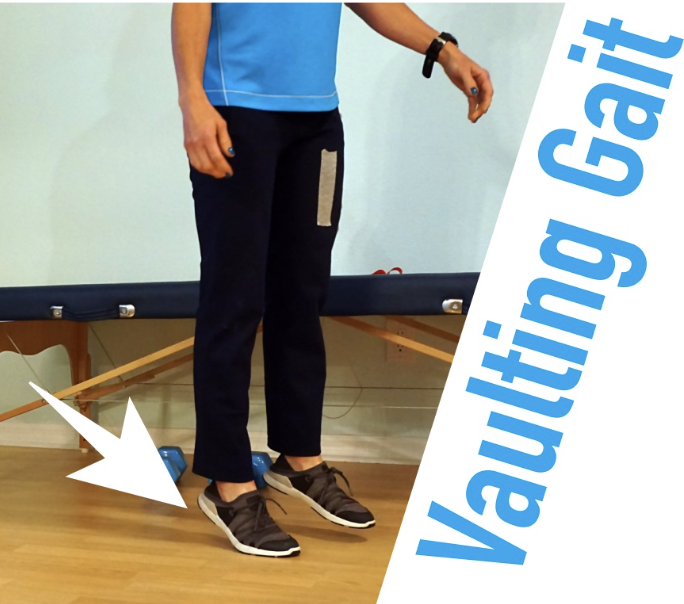
Ankle & Foot during Mid-Stance (MSt)
Impairment:
Inadequate knee flexion
insufficient DF
longer swing limb
Deviation/Compensation: Vaulting — premature heel rise on the unaffected limb to give the affected foot extra clearance and avoid tripping

Ankle & Foot during Terminal Stance (TSt)
Impairment:
Hindfoot valgus deformity
foot invertor weakness (Tibialis Ant + Post)
Deviation/Compensation: Excessive pronation
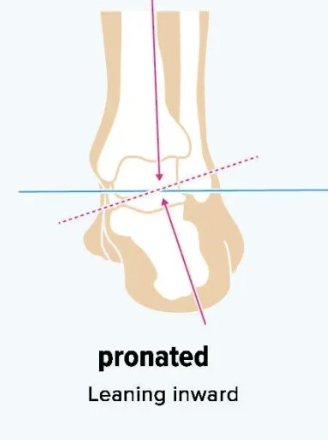
Ankle & Foot during Pre-Swing (PSw)
Impairment: Inadequate Hallux MTP extension
Deviation/Compensation:
Reduced push-off force
impaired toe rocker
shortened contralateral step length
Ankle & Foot during Initial Swing (ISw)
Impairment: Inadequate knee flexion
Deviation/Compensation:
Toe drag — toes fail to clear the ground; compensates with:
vaulting (premature heel rise on opposite limb) AND
circumduction (lateral circular motion of swing leg) to clear foot
not sure if its the best pic →
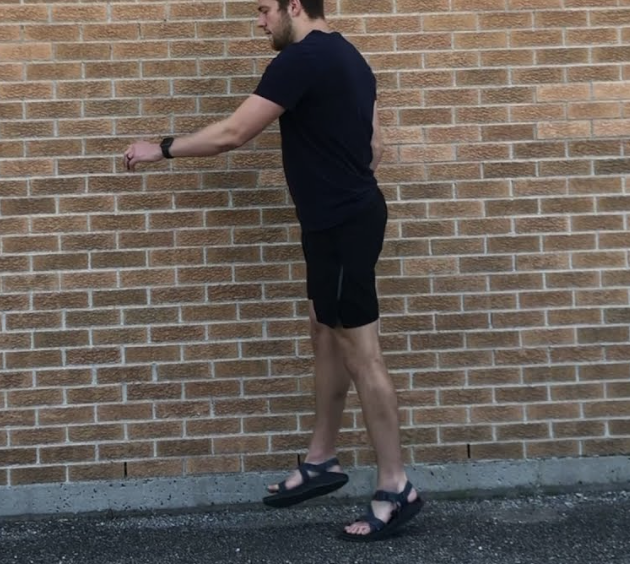

Ankle & Foot during Mid-Swing (MSw)
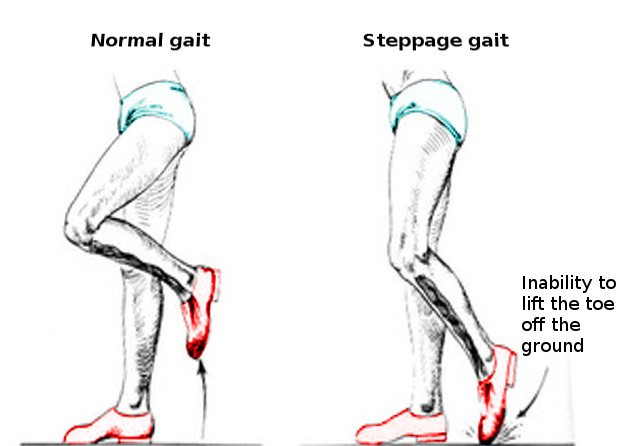
Impairment:
DF weakness
deep fibular nerve injury
Pes Equinus (PF contracture) deformity
Deviation/Compensation:
Foot drop — ankle remains plantarflexed, compromising toe clearance and increasing fall risk;
Compensates with hip hiking or circumduction to clear the foot
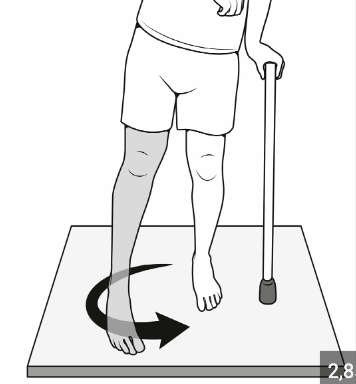
Ankle & Foot during Mid-Swing (MSw)
Impairment: DF weakness
Deviation/Compensation:
Hip hiking or circumduction to clear the foot