pth_as 2201/2203 exam 2 mizzou
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
Functions of the skeletal system
support, protection, movement, energy and mineral reserves, blood cell production
appendicular skeleton bones
pectoral girdle, upper limbs, pelvic girdle, lower limbs
axial skeleton bones
skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
3 types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
hyaline cartilage
most common type of cartilage, has tint collagen fibers (fibrilis), and is found in the ends of long bones, costal cartilages, respiratory structures and fetal skeletons
Elastic cartilage
similar to hyaline, but lots of elastic fibers, very resilient and flexible and tolerate repeated bending. found in pinna and epiglottis
fibrocartilage
has little ground substance and the matrix has thick, dense collagen fibers, resists strong compression. found in intervertebral discs, knee joints, and pubic symphysis
spongy bone
inside of bones
better at shock absoprtion
compact bones
smooth, dense external portion of bones
strong and rigid
made up of osteons
osteoclasts
cells that consume bone
osteoblast
cells that build new bone
osteocytes
mature bone cells
long bones
bones longer than they are wide, humerus and femur
short bones
bones that are the same width and length, carpals and tarsals
irregular bones
bones of the vertebrae and face
flat bones
bones of the ribs, shoulder blades, pelvis, and skull
parts of the long bone
epiphysis, epiphyseal line, diaphysis, compact bone, spongy bone, periosteum, endosteum, medullary cavity, nutrient arteries, and articular cartilage
endochondral ossification
formation of most bones
1. bones begin as hyaline cartilage
2. bone replaces cartilage
3. epiphyseal plates ossify
ex. femur and ribs
intramembranous ossification
bones that grow within a membrane, forms many flat bones as well as maxialle, zygomatic mandible and center of clavicle
epiphyseal plate
growth plates
pectoral girdle
bones that connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton
- clavicle and scapula
major part and processes of the scapula
glenoid cavity- articulates with hummerus
subscapular foss- anterior site for muscle attachment
coracoid process- attachment point of bicep
acromion- articulates with acromial end of clavicle
upper limb bones
humerus, radius, ulna, 27 hand bones (carpals, metacarpal, phalanges)
major parts of the hummerus
head- articulates with scapula
distal end- articulates with radius and ulna
tubercles- sites for muscle attachment
deltoid tuberostity- attachment for deltoid
trochlea- articulates with trochlear nottch of ulna
Phalanges and carpals
8 carpals: Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Trapezium, Trapzoid, Capitate, Hamate
digits 2-5 have 3 phalanges & pollex has 2
pelvic bones
ilium, pubis, ischium, acetabulum, public symphysis, sacrum, and coccyx
pelvic bone articulation
ilium
superior ridge of the bone, houses greater sciatic notch
ischium
ischial tuberosities are "sit bones"
pubis
contributes of obturator foramen
pelvic inlet and outlet
inlet: space between pelvic and abdonimal cavities
outlet: inferior opening defined by ischial tuberosities
brim: edge of inlet
major features of the femur/articulations
- head: carried on a neck that angles laterally to join shaft
- greater trochanter: sites for muscle attachment
- medial and lateral condyle: articulate with tibia
-linea aspera: ridge along the posterior diaphysis
- patella articulate with femur at patellar surface
tibia vs. fibula
tibia is larger and more sturdy, medially located
tibia articulates with femur and talus
tarsals and phalanges
7 tarsal bones, 5 metatarsals and 14 phalanges, 3 per foot (proximal, middle, distal), hallux has no middle
hallux = big toe
calcaneus
heel
achilles tendon
attaches posterior surface and enables extension of foot
types of joints
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
fibrous joints
connected by fibrous tissue, i.e sutures
synovial joints
connected at a joint cavity within a capsule, i.e ball-socket (shoulder)
cartilageinous Joints
connected by cartilage tissue, i.e pubic symphsis
plane joint
allows articulating bones to glide past each other between tarsals and carpals
hinge joints
allows flexion and extension, i.e elbow and knee
pivot joint
allows rotation, i.e radius and ulna
condylar joints
one bone is convex and the other is concave, i.e knuckles
ball and socket joint
allows flexion/extension, adduction/abduction and roation, i.e hip and shoulder
synchondrosis
an almost immovable joint between bones bound by a layer of cartilage, as in the vertebrae.
Symphysis
A type of joint that has grown together forming a very stable connection.
knee bones
femur, tibia, fibula, patella
knee ligaments
ACL and PCL: deep within capusle, connects femur and tibia
LCL: connects femur and fibula
MCL: connects tibia and femur
menisci: stabilizes joint, provides side to side rocking of femur on tibia
temporomandibular joint
connection on either side of the head between the temporal bone of the skull and mandibular bone of the jaw
elbow bones and ligaments
hinge joint, annulnar ligament forms pibor at proximal radioulnar joint
- annulnar ligament attaches to ulna medially and laterally
hip (coxal) joint
femur and os coxae, ball and socket joint
- acetabulum is where the head of the femur sits
ligeamentum teres extends from acetabulum of fovea capitus
glenohumeral joint
joint of the scapular and humerus, ball and socket joint
Flexion/extension
bending and extension of a limb
Pronation/supination
turning the hand to a palm down or palm up position
Eversion/inversion
turning outward, turning inward
Abduction/adduction
movement away/towards from midline
Lateral rotation/medial rotation
→ left leg rotates counterclockwise
→ left leg rotates clockwise
Dorsiflexion/plantarflexion
up and down movement of the foot
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
Opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the fingertips
Protraction/Retraction
anterior to posterior movement of scapula or mandible
Elevation/Depression
up and down
types of muscle tissue
smooth, cardiac, and skeletal
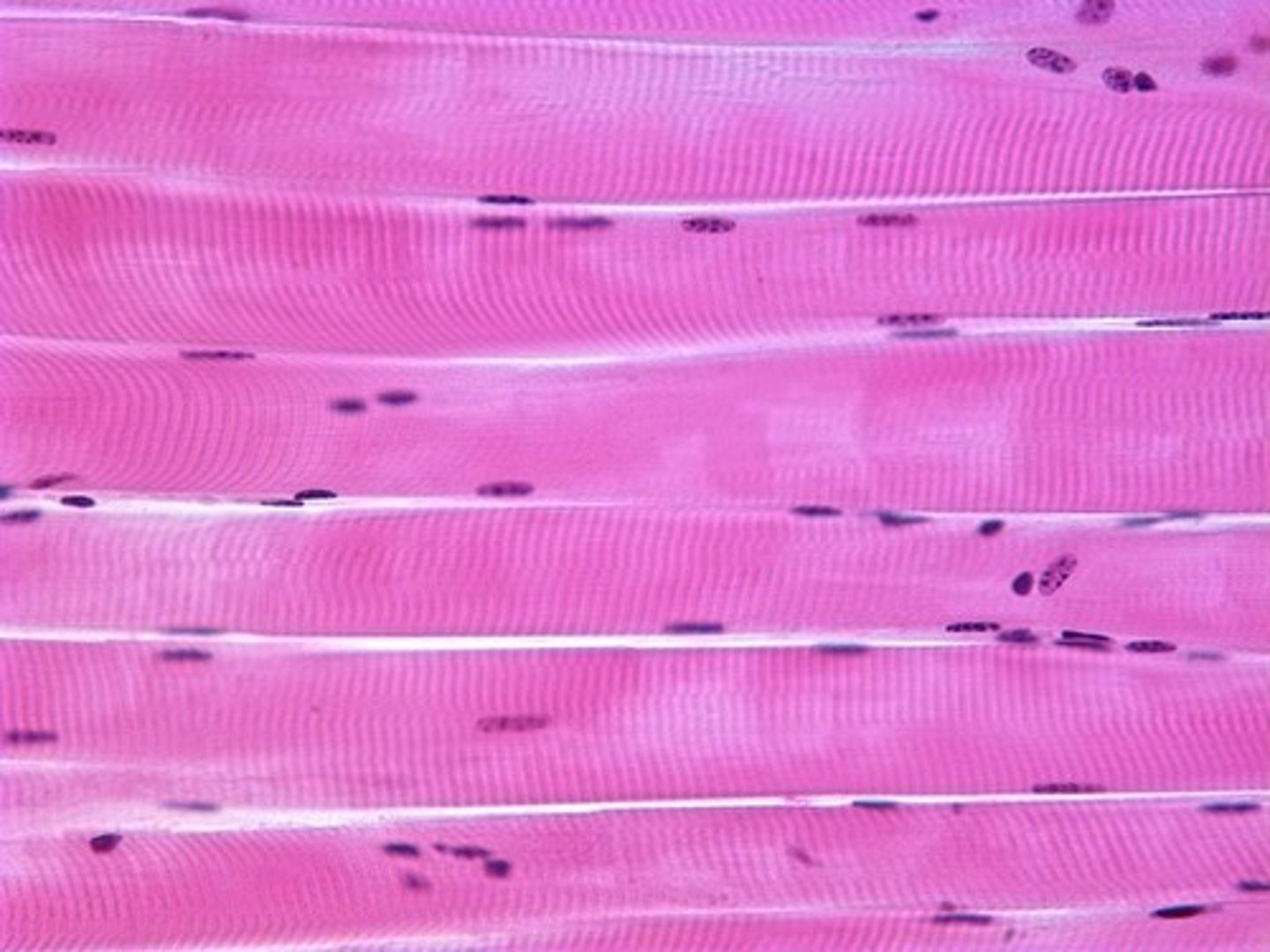
Skeletal muscle
pulls on muscles, striated and voluntary
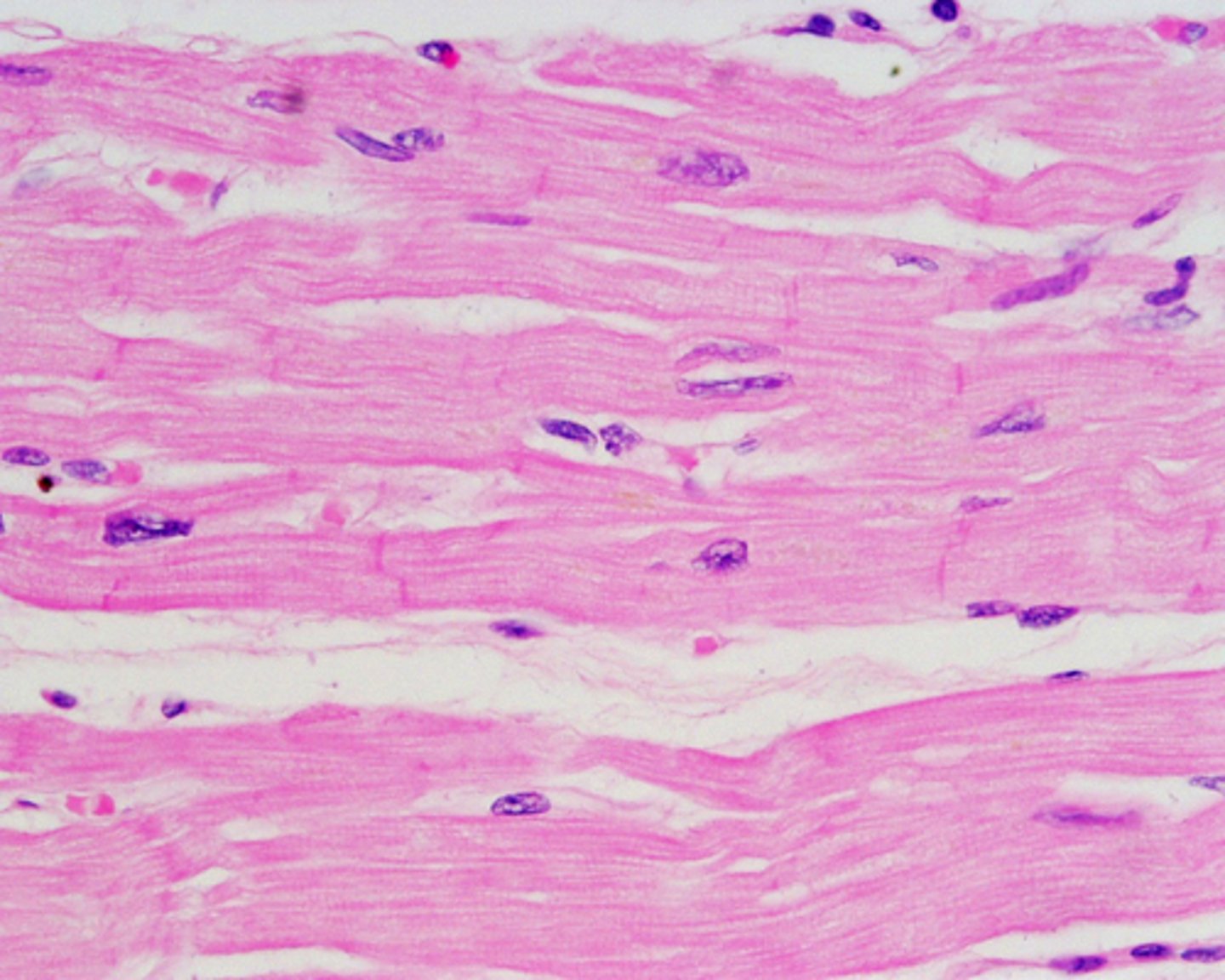
Cardiac muscle
only in the heart, striated, y-shaped and involuntary, has intercalated discs
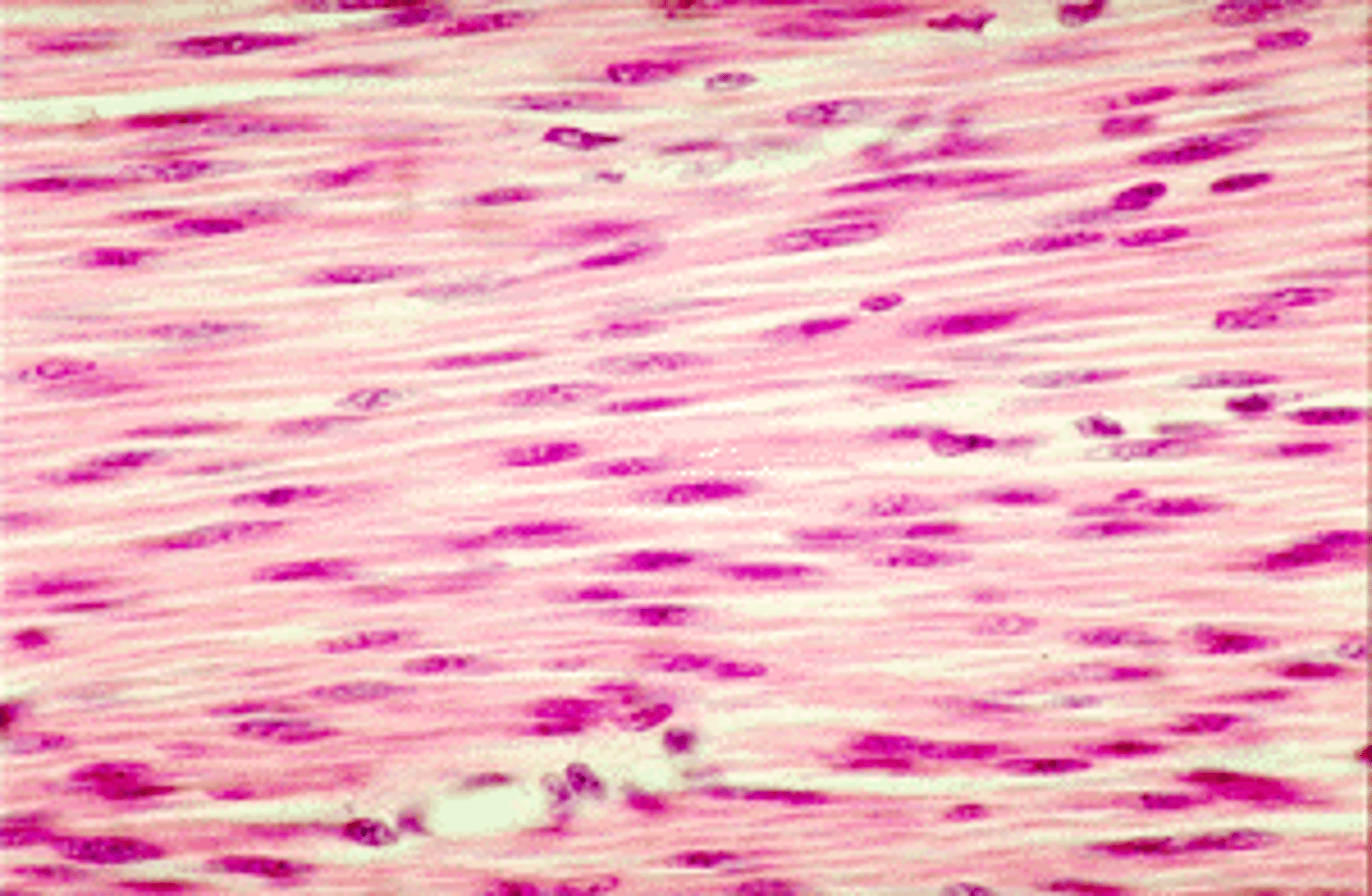
Smooth muscle
pushes fluid and solids along the digestive tract, regulates the diameters of small arteries, not striated and involuntary
Skeletal muscle properties
1. contractability
2. excitability
3. extensibility
4. elasticity
Skeletal muscle functions
produce movement, maintain posture, support, generate heat, and storage & movement of materials
layers of connective tissue
deep fascia, epiphysium, perimysium, and endomysium
deep fascia
surrounds individual muscle as well as muscle with the same action
epiphysium
surrouned entire muscle, separates individuals
perimysium
surrounds each fascia, divides skeletal muscle into compartments
endomysium
surrounds muscle fibers within a fascicle
sacromere
Contractile unit of muscle
circular muscles
sphincter, surround external body opening, i.e mouth
convergent muscles
broad area converges on attachment site (tendon, aponeurosis, or raphe); muscle fibers pull in different directions, depending on stimulation; ex: pectoralis muscles
parallel muscles
fascicles run paralelle to long axis of muscles, tapered at both ends, high endurance, i.e satorius
pennate muscles
feather shaped, short fascicles, attach obliquely, i.e deltoid
synergist
muscles with similar actions
antagonist
muscles with opposite actions
trapezius
Elevates, depresses, retracts, and rotates the scapula, attaches to C1-T12 vertebrae and scapular spine and clavicle
rhomboid major and minor
elevate anad retract scapula, ataches to vertebrae and medial border of scapula
serratus anterior
protracts and rotates scapula and holds it flat against the rib cage, attaches to scapula and anterior rib
pectoralis major
adducts, flexes, and medially rotates arm
attaches to sternum, clavicle, ribs and humerus
latissimus dorsi and teres major
adducts, extends, and medially rotates arm; LD attaches to lower back and humerus and TM attaches to scapula and humerus
deltoid
abducts, flexes, and extends arm, medially and laterally rotates arm; attaches to sternum, clavicle, ribs and humerus
Suprasinatus
initiates abduction of arm (first 15); attaches to supraspinous fossa of scapula and humeral tuberosities
infraspinatus
laterally rotates arm; attaches to infraspinous fossa of scapula and humeral tuberosities
teres minor
laterally rotates arm; attaches to infraspinous fossa of scapula and humeral tuberosities
subscapularis
medially rotates arm; attaches to subscapular fossa of scapula and humeral suberosities
Coracobrachialis
flexes and adducts arm; attaches to scapula and humerus
brachialis
flexes forearm; attaches to humerus and ulna
biceps brachii
long and short head; flexes and supinates arm; attaches to scapula and radial tuberosity
Brachioradialis
flexes forearm; attaches to posterior humerus and radius
triceps brachii
long, medial, and lateral heads; long extends forearm and arm, medial and lateral extend forearms; long attaches to scapula and ulna & medial/lateral attach to humerus and ulna
flexor muscles
flex wrist and digits; attaches to humerus medial epicondyle, forearm, wrist and digits
extensor muscles
extend wrist and fingers; attaches to humerus lateral epicondyle, forearm, wrist, and digits
iliopsas
illiacus + psoas major; attaches to ilium and femur; thigh and trunk flexion
gluteus maximus
extension and lateral rotation of thigh; attaches to ilium, sacrum and femur