Social Psychology & Abnormal Psych
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
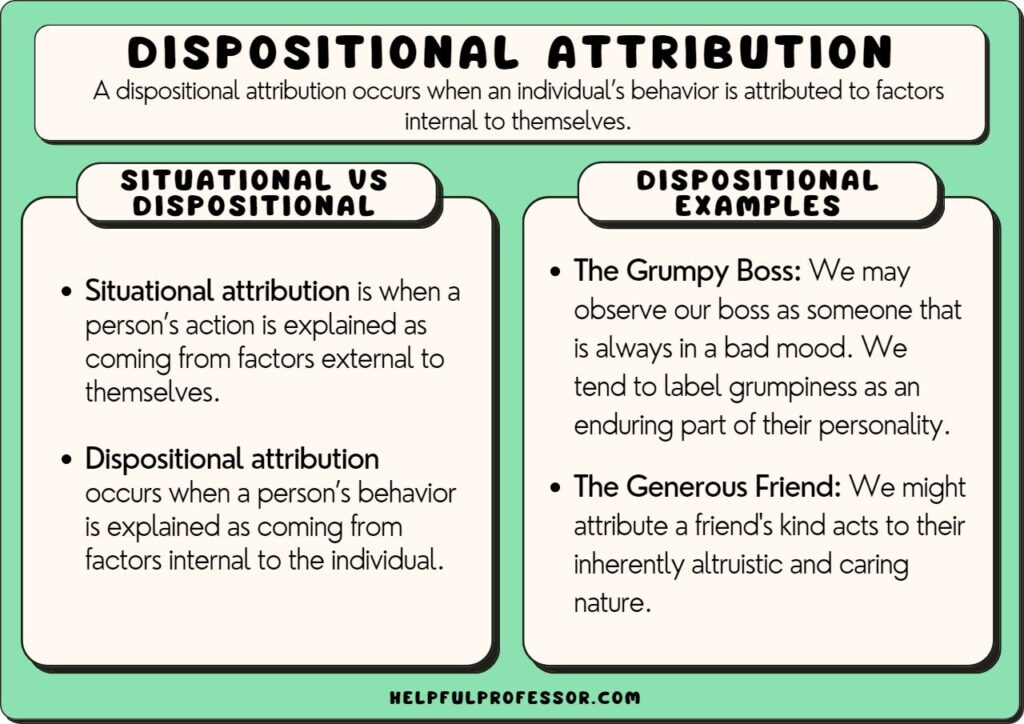
attribution: dispositional
explains behavior by attributing it to a person's internal traits, abilities, or personality
situational
the primary focus is on how the environment and external factors influence an individual's behavior, rather than internal traits or personal characteristics
fundamental attribution error
an individual's tendency to attribute another's actions to their character or personality, while attributing their behavior to external situational factors outside of their control
self-serving bias
a psychological concept where individuals tend to attribute successes to their own abilities and efforts, while blaming external factors for failures
social norms
the unwritten rules and expectations that guide behavior within a group or society
social influence theory
explores how individuals' attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors are shaped by social interactions and the presence of others
normative social influence
describes the phenomenon where people conform to group behaviors and beliefs to gain acceptance or avoid social disapproval
informational social influence
a type of conformity where individuals change their behavior or beliefs to align with others because they believe those others possess accurate information or knowledge
conformity
the act of modifying one's behavior or beliefs to align with those of a group, even if it means deviating from one's own judgment
altruism
the unselfish concern for the well-being of others, with a focus on acting to benefit someone else, even at a potential cost or risk to oneself
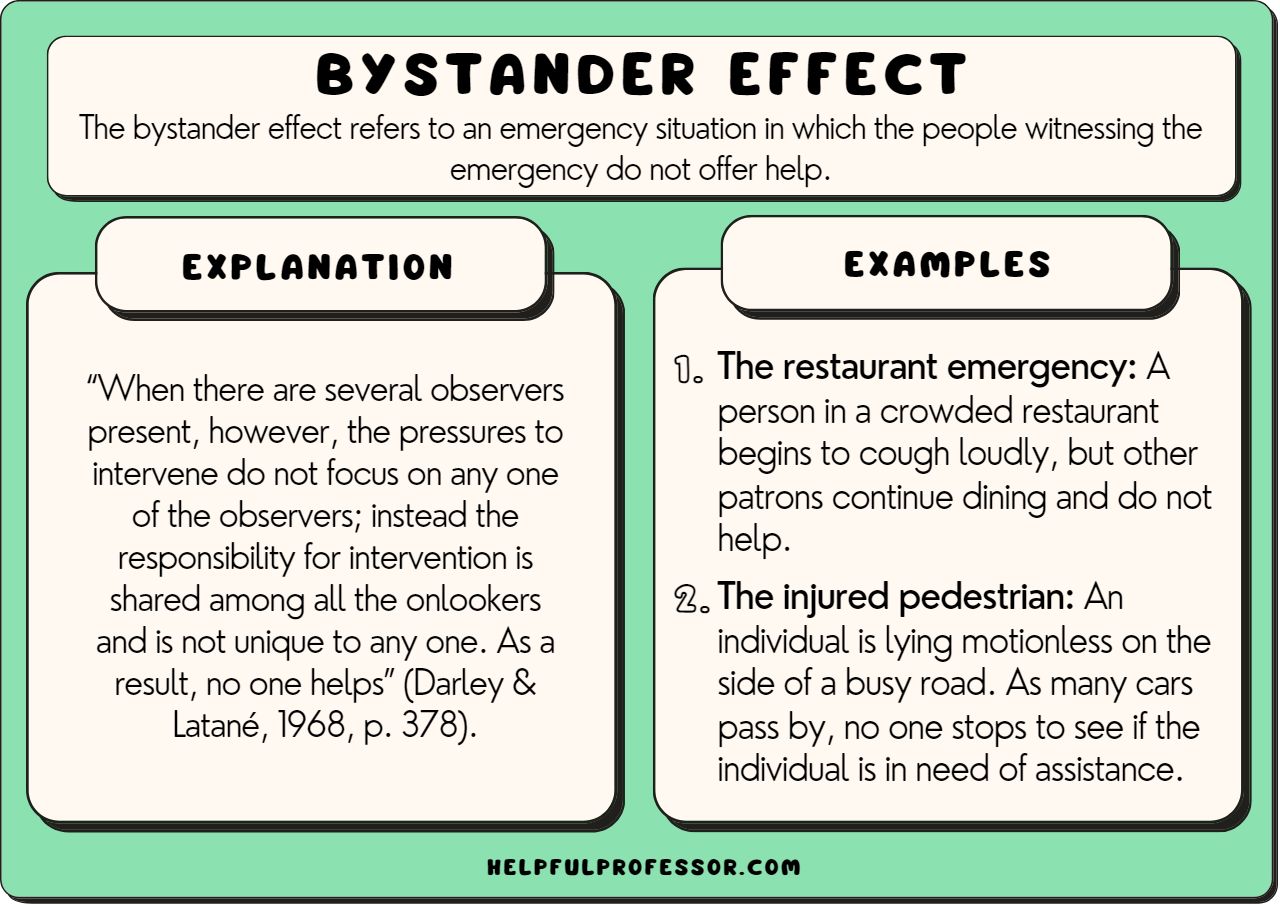
diffusion of responsibility (bystander effect/social loafing)
individuals in a group feel less personally responsible for taking action or helping when others are present
social exchange theory
a sociological and psychological theory that views social interactions as a process of individuals weighing the costs and benefits of their actions within relationships
reciprocity norm
a social expectation that when someone does something for you, you should return the favor in kind
social responsibility norm
a widely accepted belief that individuals have a moral obligation to assist others in need, even without the expectation of personal gain or repayment
just world phenomenon
a cognitive bias where people believe that the world is fair and that people get what they deserve, and vice versa
halo effect
a cognitive bias where a positive impression in one area positively influences our overall opinion of a person, product, or concept
social trap
a situation where individuals or a group pursue actions that seem beneficial in the short term but ultimately lead to negative consequences for everyone involved
foot-in-the door technique
a psychological strategy where a person is asked to agree to a small request first, making them more likely to agree to a larger request later
door-in-the-face technique
a compliance strategy where a large, unreasonable request is initially made, followed by a smaller, more reasonable request
deindividuation
a psychological phenomenon where individuals in a group lose their sense of personal identity and self-awareness, leading to behaviors they might not typically engage in
group polarization
a psychological phenomenon where a group's beliefs or attitudes become more extreme than the individual beliefs held by members before the group discussion
groupthink
a psychological phenomenon in which people strive for consensus within a group. In many cases, people will set aside their own personal beliefs or adopt the opinions of the rest of the group
prejudice
a preconceived judgment or opinion, often negative, about a person or group based on their perceived characteristics, even without sufficient knowledge or justification
discriminate
the differential treatment of individuals or groups based on their group membership, often leading to negative or unfair outcomes
stereotype
a widely held, fixed, and often oversimplified belief about a group of people
ingroup
a group to which an individual feels a sense of belonging and emotional attachment
outgroup
a group of people that an individual does not identify with or belong to, in contrast to their ingroup
ingroup bias
the tendency to favor one's own group (ingroup) and its members, while simultaneously disliking or devaluing other groups (outgroups)
outgroup homogeneity
a psychological phenomenon where individuals perceive members of groups they don't belong to (outgroups) as more similar to each other than members of their own group (ingroup)
group polarization
the tendency for a group to adopt more extreme positions on issues than individuals would hold on their own, after group discussion
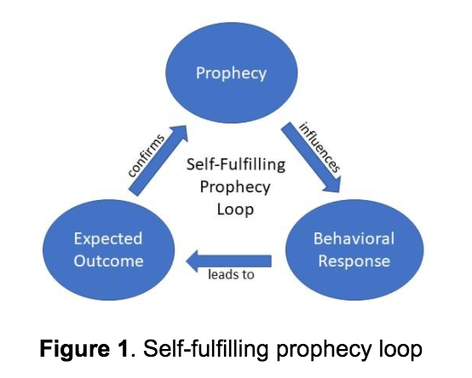
self-fulfilling prophecy
a situation where a belief or expectation leads to actions that cause the belief or expectation to become true