Mental Status Exam
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What information should we obtain during the initial nursing assessment?
Education level
Legal status
marital history
Social History
Support systems
Insight into diagnosis and medication
Value system (including spiritual)
Special needs (including cultural)
Discharge goals
What is the mental status exam?
State-related exam
Information is based on the client’s current functioning and the mental status can and does change frequently
Represents a cross-section of the client’s psychological life at a given moment in time
Mental status exam: Appearance
Apparent age
Manner of dress
Cleanliness
Posture
Gait
Facial expressions
Eye contact (may vary depending on culture)
Changes in pupillary reaction
General state of health and nutrition
Mental status exam: Speech
Rate: rapid or slow
Volume: loud or soft
Amount: paucity, muteness, pressured speech
Characteristics: stuttering, slurring of words, unusual accents
Mental status exam: Motor Activity
Level of activity: lethargic, tense, restless, agitated
Type of activity: tics, grimaces, tremors
Unusual gestures or mannerisms
Compulsions
Mental status exam: Interaction during the interview
Is the client:
Friendly/hostile
Cooperative/uncooperative
Irritable
Guarded/suspicious/defensive
Apathetic
Seductive
Mental status exam: Mood
Mood is the client’s self-report of their:
Prevailing emotional state and reflection on current life situation
Ask the patient, “How are you feeling today,”
Examples: sad, fearful, hopeless, euphoric, anxious
Ask the patient to rate his/her mood on a scale of 1-10
Address suicidal/homicidal thoughts and plans
Mental status exam: Affect
Affect is the client’s apparent emotional tone, as observed by the nurse.
Range: does the client show a broad range of affect or does she/he have a blunted or flat affect
Duration: lability
Intensity: blunted or flat
Appropriateness: congruent, incongruent
Mental status exam: Delusions
False beliefs that are held despite a lack of evidence to support them
Most common involve persecutory, paranoid, grandiose, or religious ideas
Example: someone who has poor self-esteem may think that he is God, possibly driven by a need to feel important or powerful

Mental status exam: Perceptual disturbances
Illusions
Depersonalization (altered perception of self)
Derealization (altered perception of the environment)
Illusions
Errors in the perception of sensory stimuli
A confused person may mistake folds in the blanket for white rates or the cord of a window blind for a snake
A stimulus is a real object in the environment, but the person misinterprets it
Unlike delusions or hallucinations, you can explain and clarify illusions for the individual
Hallucinations
False sensory stimulation (can be auditory, visual, tactile (touch), olfactory (smell), or gustatory (taste))
Patient can see bugs crawling on or under the ir bodies
May be aware that something is wrong
Persecutory delusion
Believing that one is being singled out for harm or preventing from making progress by others

Referential delusion
A belief that events or circumstances that have no connection to you are somehow related to you

Grandiose delusions
Believing that one is a powerful or important person

Erotomanic delusions
Believing that another person desires you romantically

Nihilistic delusions
The conviction that a major catastrophe will occur

Somatic delusions
Believing that the body is changing in unusual ways

Control delusions
Believing that another person, group, or external force controls your thoughts, feelings, impulses, or behavior

Mental status exam: Thought content
Assess the patient’s thought content (delusions, obsessions) and these other things:
Thought broadcasting
Thought insertion
Depersonalization
Hypochondriasis
Ideas of reference
Magical thinking
Obsession
Phobia
Mental status exam: Thought processes (form of thought)
Circumstantial
Flight of ideas
Loose associations
Neologisms
Preservation
Tangential
Thought blocking
Word salad
Concrete thinking (taking things literally)
Clang associationns
Echolalia
Mutism
Poverty of speech
Ability to concentrate
Attention span
Mental status exam: Level of consciousness (LOC)
Confusion
Sedated
Stuporous
Orientation to time, place, and person
Mental status exam: Memory
Remote memory: recall of events, people, and information from the distant past
Recent memory: recall of events and information, and people from the past week or so
Immediate memory: recall of information to which a person was just exposed
Mental status exam: Impulse control
Aggression
Hostility
Fear
Guild
Affection
Sexual feelings
Mental status exam: Judgement and insight
Ability to problem solve
Ability to make decisions
Knowledge of self (limitations, consequences of actions, awareness of illness)
Adaptive/maladaptive use of coping mechanisms and ego defense mechanisms
Are they engaged in dangerous or illegal activities?
Destructive relationships?
“What would you do if you found a stamped addressed envelope lying on the ground?”
What is the nursing process in psychiatric mental health nursing?
Assessment
Nursing diagnosis
Outcomes identification
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
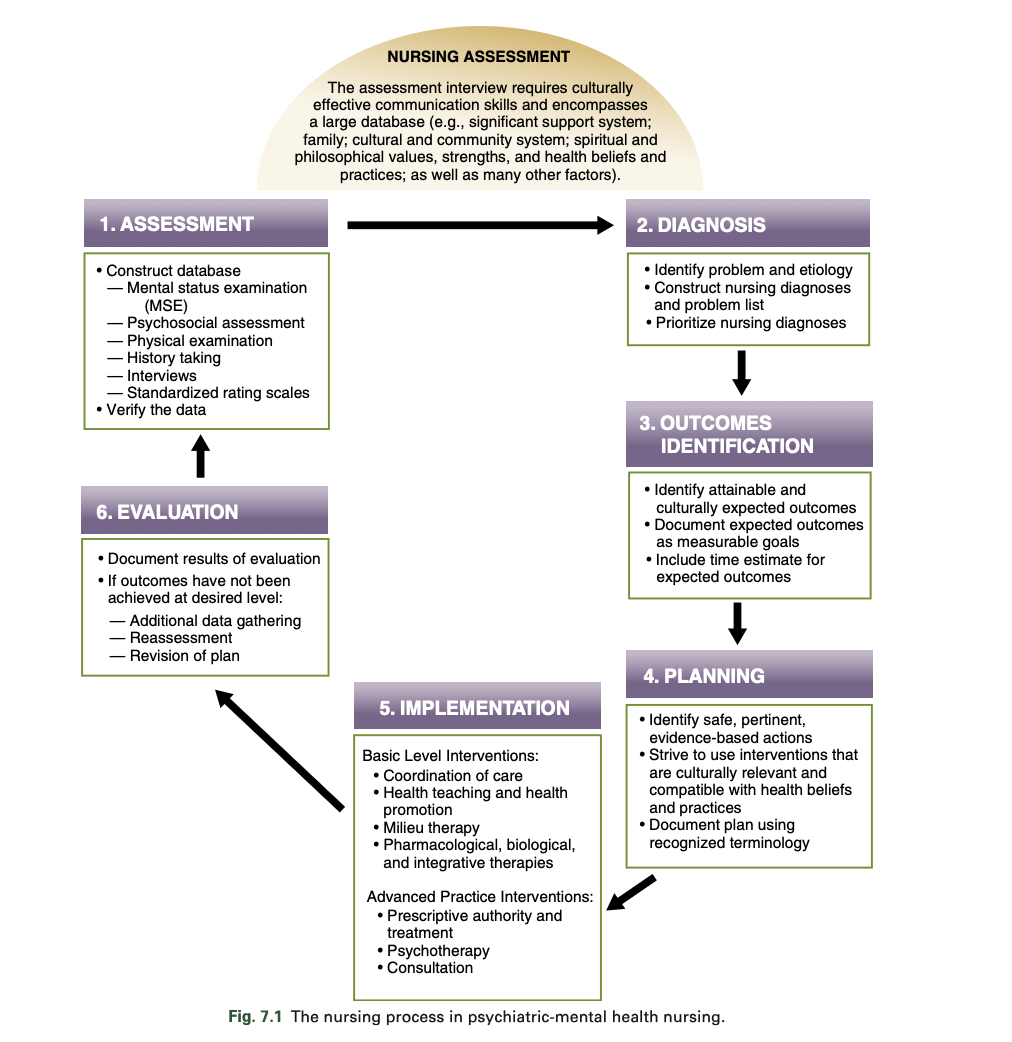
What are the three parts of a nursing diagnosis?
Nursing problem
Etiology factors (related to)
Defining characteristics, specific to patient (AEB)
How do we determine the outcomes identification?
Identify attainable and culturally expected outcomes
Document expected outcomes as measurable goals
Include time estimate
Usually the opposite, positive aspect of the nursing diagnosis
A 19-year-old college freshman visits the college nurse and reports that he has recently had two “anxiety attacks.” He says that he cannot predict when these attacks are coming.
What questions should the nurse ask to assess the extent of his current problem?
The young man reveals that he is afraid of losing his mind. What observations should the nurse make and document?
“What are you doing before these attacks happen?”
“Tell me more. What does losing your mind mean to you?”