BP - F2022 - States of Mind (Sleep & Happiness Mlcls)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
1
New cards
consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment
2
New cards
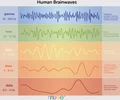
gamma
continuous in nearly all brain states; denotes heightened cognitive processing related to perception, learning, and problem solving (32-100 Hz)
3
New cards
beta
awake, alert consciousness, thinking analytically (13-32 Hz)
4
New cards
alpha
associated with physical and mental relaxation and with light/N1 and REM sleep (8-13 Hz)
5
New cards
theta
associated with creativity, insight, deep states, deep meditation, reduced consciousness, N2 sleep; can be enhanced by repetitive activities like running (4-8 Hz)
6
New cards
delta
deep sleep; loss of bodily awareness; repair
7
New cards
electroencephalograph
EEG, measures the brain's electrical activity
8
New cards
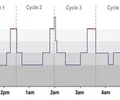
sleep hypnogram
graph that represents the stages of sleep as a function of time
9
New cards
sleep cycle
typically 90-minutes long; 4-5 per night; identified by brain-wave patterns and behavioral changes
10
New cards
circadian rhythm
the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle
11
New cards
REM
paradoxical sleep because it is associated with alpha waves typical of wakefulness; vivid dreams; motor cortex is very active but the brain stem is blocking messages so you're not moving
12
New cards
non-REM 1
light sleep; characterized by alpha & theta waves
13
New cards
non-REM 2
characterized by theta waves; includes sleep spindles and k-complexes which indicate brief bursts of activity
14
New cards
non-REM 3
characterized by slow-rolling delta waves; deep sleep; brain is unresponsive to external stimuli, more difficult to awaken individual
15
New cards
neurotransmitter
chemical messenger released from an axon terminal of a neuron in response to an action potential; it crosses the gap to the receptors on dendrites of adjacent neurons
16
New cards
endocrine system
set of glands that secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells
17
New cards
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, it regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
18
New cards
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion; produces oxytocin
19
New cards
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress
20
New cards
hormone
chemical messengers released directly into the blood by the endocrine system; in particular, neurochemicals are released by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
21
New cards
anandamide
The Bliss Molecule; also known as an endocannabinoid; increases naturally with prolonged aerobic exercise and increased Omega 3 in diet; neurotransmitter
22
New cards
dopamine
The Reward Molecule; increases naturally by setting goals and achieving them; neurotransmitter
23
New cards
oxytocin vasopressin
The Bonding Molecules; hormones that increase bonding with others; increases naturally with hugs or petting animals
24
New cards
endorphin
The Pain-Killing Molecule; hormone & neurotransmitter; produced by the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus; increase naturally through strenuous exercise, eating chocolate, smiling and laughing, meditating, singing, and listening to music
25
New cards
GABA
The Anti-Anxiety Molecule; slows down the firing of neurons and creates a sense of calmness; increases naturally with yoga and meditation; neurotransmitter
26
New cards
serotonin
The Confidence Molecule; makes you less sensitive to rejection; bolsters self-esteem; to increase, aerobic exercise, bright light, eat high-protein foods with tryptophan (turkey, salmon) with healthy carbs; produced in intestines and brain, so hormone and neurotransmitter
27
New cards
adrenaline
The Energy Molecule; also called epinephrine; released from adrenal glands, making it a hormone, but a small amount is produced in neurons of the medulla oblongata, making it also a neurotransmitter; plays role in fight or flight mechanism; creates exhilaration and a surge of energy and alertness, and an increase in heart rate and blood pressure; used in Epi-Pens to treat acute allergic reactions; increase naturally through a high-intensity workout
28
New cards
amygdala
source of raw emotions; located in the limbic system; hyper-stimulated by love; also associated with fight or flight responses to stimuli, memory, making decisions, and processing emotions and perceiving the emotions of others
29
New cards
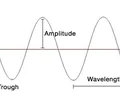
wave
a disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another
30
New cards
brainwave
a pattern of electrical current in the brain caused by neurons communicating, visually represented as a wave
31
New cards
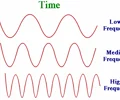
frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
32
New cards
love molecules
dopamine, serotonin, adrenaline/epinephrine
33
New cards
depressants
drugs that reduce neural activity and speed up body functions (ex: alcohol)
34
New cards
stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions (ex: caffeine)
35
New cards
resistance
increased by using the strategy of distraction
36
New cards
Hertz
the unit of frequency; equal to 1 cycle per second; abbrev.: Hz
37
New cards
sleep strategies
exercise (but not right before bed); avoid caffeine in the afternoon/evening; avoid eating close to your bedtime; avoid blue light emitting devices (backlit black & white reading devices are OK)