Lab 7 - Axial Muscles
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Parallel
The fascicles are parallel to the long axis of the muscle. They are long, strap-like muscles that can generate force. The strongest of these muscles are fusiform in shape; they are wide in the middle and taper at each end.
Convergent
These are fan-like muscles. The fascicles are broad at the origin and taper to a narrow insertion. This arrangement functions to concentrate the force of the muscle contraction into a small area.
Pennate
The fascicles are attached to a tendon in a feather-like manner. The tendon is the shaft of the feather and the fascicles are the vane.
Unipennate
Bipennate
Multipennate
the fascicles are attached to one side of the tendon
the fascicles are attached to both sides to the tendon
the fascicles converge on a branching tendon
Circular
These are sphincter muscles. The fascicles surround an opening. The action of the muscle increases or decreases the diameter of the opening.
Gliding
Movement back-and-forth or side-to-side, with no rotation or angular motion.
Flexion
Movement that draws bones toward each other, or decreases the angle of the joint to the bone.
Extension
Movement that separates bones from one another, or increases the angle of the joint to the bone.
Abduction
Moving part of the body away from the midline of body. (For fingers and toes, it is relative to midline of hand or foot.)
Adduction
Moving a part toward the midline of the body.
Rotation
The movement of a bone around its own axis, with no other simultaneous motion.
Circumduction
Motion where the proximal end of a bone is stable and the distal end moves in the form of a cone.
Pronation
A motion of the forearm that turns the palm backward or downward from the elbow. It does not rotate the humerus.
Supination
A motion of the forearm that turns the palm forward or upward from the elbow. It does not rotate the humerus.
Protraction
Movement of a bone forward or anteriorly parallel to the ground
Retraction
Movement of a bone backward or posteriorly parallel to the ground.
Elevation
A movement that raises a bone vertically, or upward.
Depression
A movement that lowers a bone vertically.
Inversion
Moves sole of foot inward towards the opposite foot at the ankle.
Eversion
Moves sole of foot outward at ankle, away from the other foot.
Dorsiflexion
Flexing the foot upward at the ankle.
Plantar flexion
Flexing the foot downward at the ankle.
Frontalis
When the occipitalis is contracted, it raises the eyebrows and wrinkles the skin of the forehead. When the occipitalis is relaxed, it draws the skin anteriorly.
Occipitalis
Pulls the skin of the head posteriorly.
Sternocleidomastoid
Together, they flex the head by flexing the cervical portion of the vertebral column. Alone they turn the head in the direction opposite of the contraction.
Temporalis
Acts with the masseter to raise and pull back the mandible.
Masseter
Raises and pulls back the lower mandible, closes the mouth, and clenches the teeth. It also may move the mandible from side to side.
Orbicularis oris
Closes and protrudes the lips. Pulls the lips back against the teeth.
Orbicularis oculi
Located around the eye and lies beneath the eyelid. It causes the eye to close or blink.
Nasalis
A sphincter-like muscle on the nose that functions to flare or dilate the nostrils.
Zygomaticus minor
A small cheek muscle that is involved in the expression of emotion, like smiling.
Zygomaticus major
A cheek muscle that extends down to the mouth. It draws the mouth upward and backward when laughing.
Levator scapulae
Elevates and draws the scapula medially. It also extends and / or flexes the head.
Splenius capitis
Extends the head when contracting together, and rotates the head when contracting singly.
Pectoralis minor
Depresses and abducts the scapula, rotates it down, and stabilizes it.
Pectoralis major
Adducts, flexes, and medially rotates the humerus inward.
Serratus anterior
Abducts the scapula and rotates it upward. It also lifts the ribs when the scapula is fixed.
Internal oblique
Compresses the abdomen and can rotate the vertebral column
Rectus abdominis
Flexes the lumbar region of the vertebral column and compresses the abdomen.
Trapezius
Elevates and/or adducts the scapula, rotates the scapula up or down, and draws the head back when the shoulders are fixed.
Rhomboideus minor & major
Elevates and helps the scapula rotate when adducting the arm.
Supraspinatus
Aids the deltoid when abducting the arm at the humerus.
Infraspinatus
Laterally rotates and abducts the arm at the shoulder.
Teres minor
Laterally rotates, extends, and adducts the humerus at the shoulder and stabilizes the elbow joint.
Teres major
Assists the extension of the humerus, medially rotates the humerus, and helps rotate the scapula downward.
Latissimus dorsi
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the arm at the shoulder. Also draws the arm inferiorly and posteriorly.
Lumbodorsal fascia
Connective tissue that acts as the origin for muscles of the lower back.
Levator scapulae
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is A?
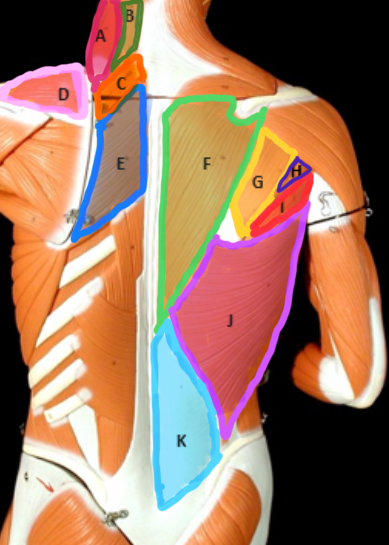
Splenius Capitis
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is B?
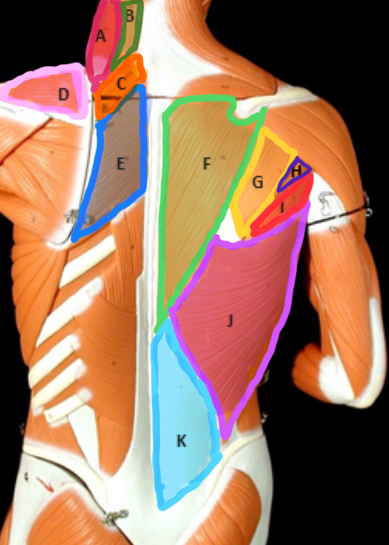
Rhomboideus Minor
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is C?
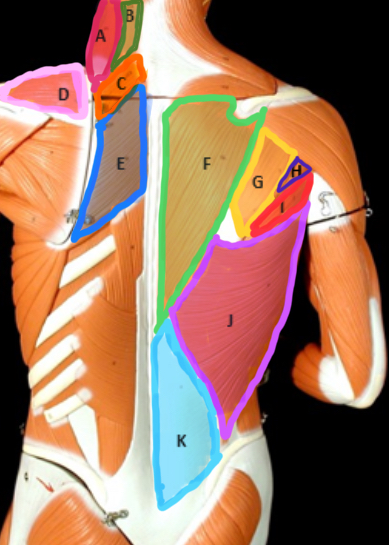
Supraspinatus
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is D?
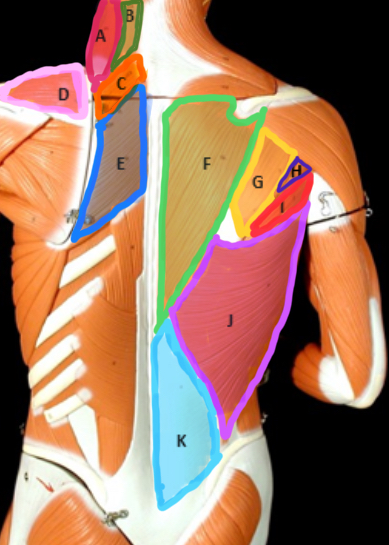
Rhomboideus Major
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is E?
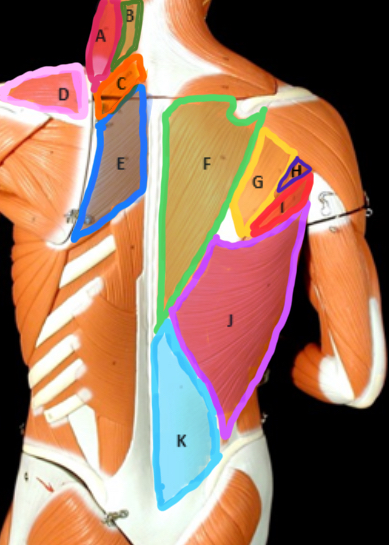
Trapezius
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is F?
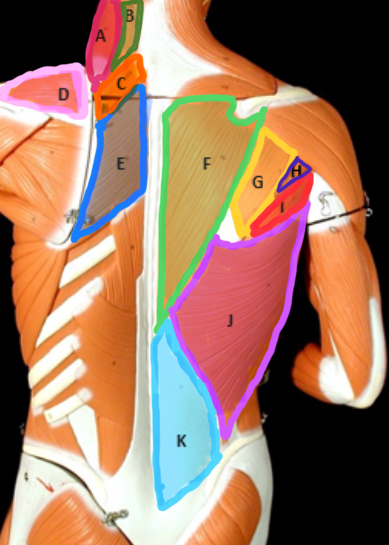
Infraspinatus
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is G?
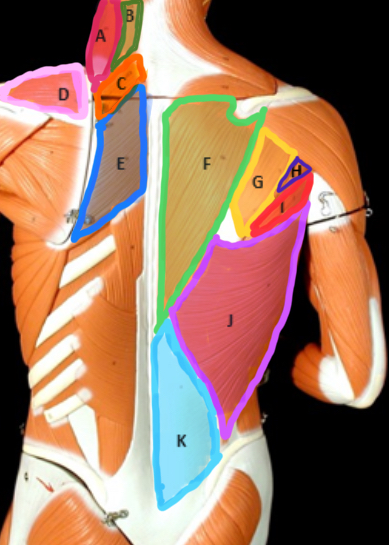
Teres Minor
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is H?
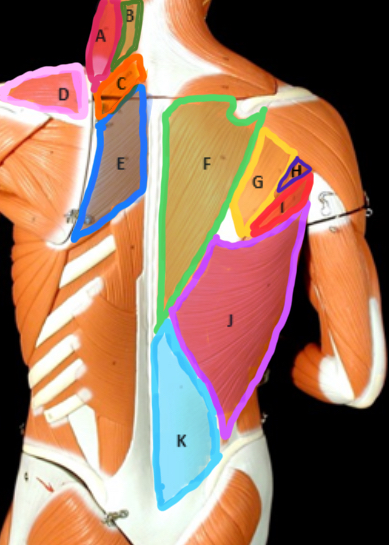
Teres Major
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is I?
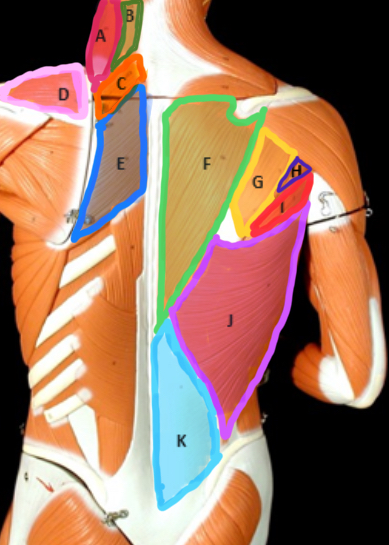
Latissimus dorsi
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is J?
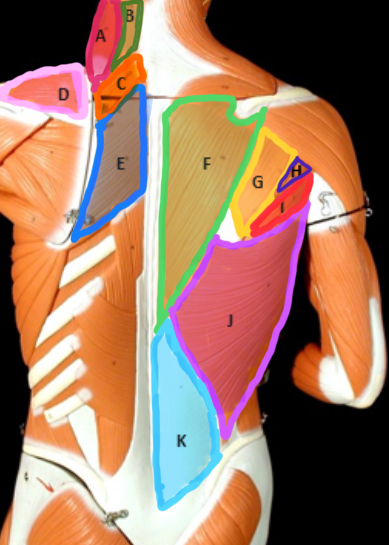
Lumbodorsal facisa
Type of Muscle: Thorax (posterior view)
What is K?
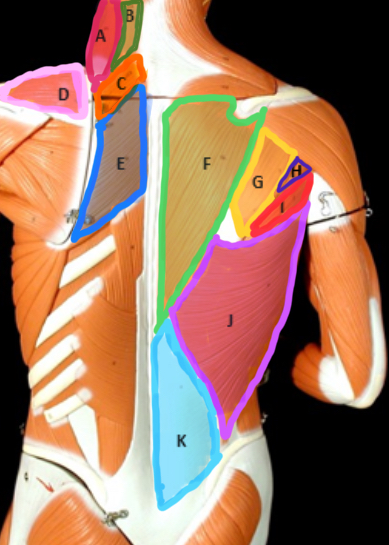
Pectoralis Minor
Type of muscle: Thorax (anterior view)
What is A?
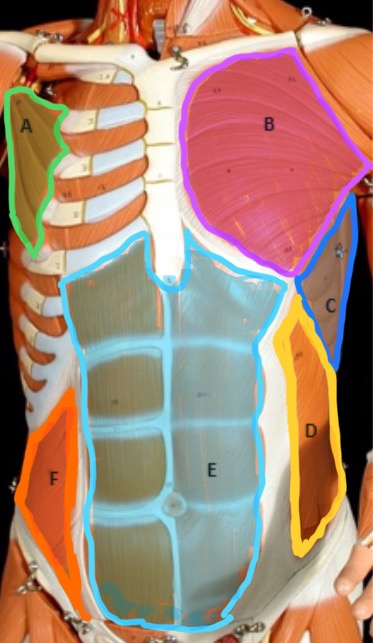
Pectoralis Major
Type of muscle: Thorax (anterior view)
What is B?
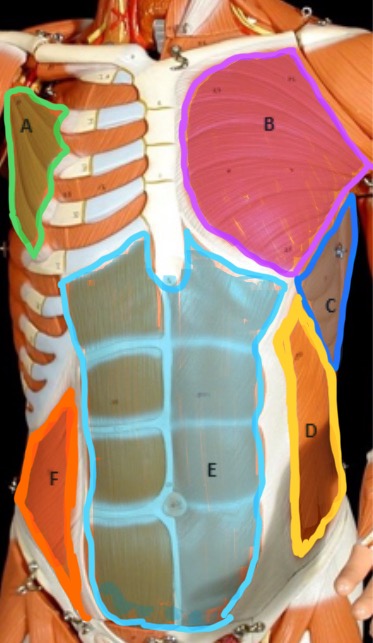
Serratus Anterior
Type of muscle: Thorax (anterior view)
What is C?
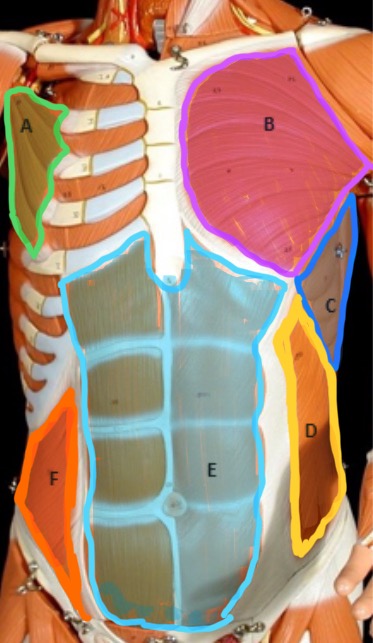
External Oblique
Type of muscle: Thorax (anterior view)
What is D?
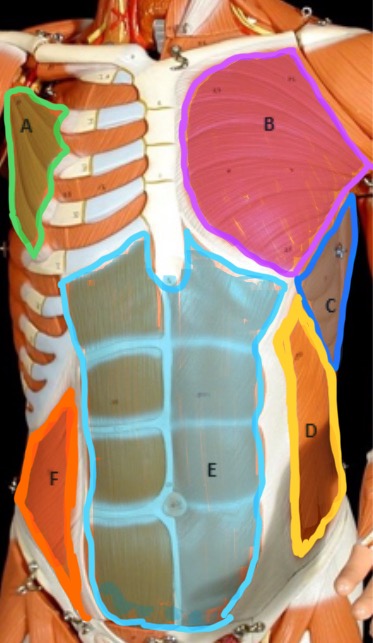
Rectus Abdominis
Type of muscle: Thorax (anterior view)
What is E?
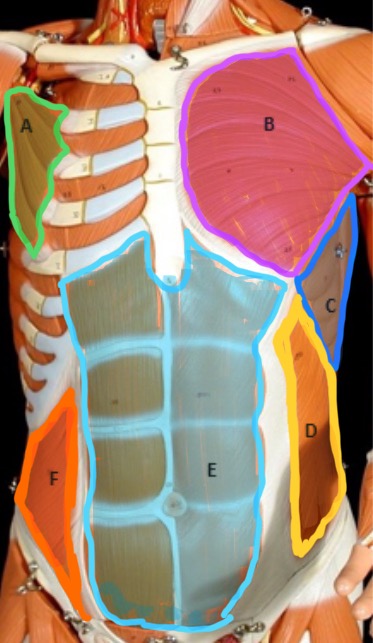
Internal Oblique
Type of muscle: Thorax (anterior view)
What is F?
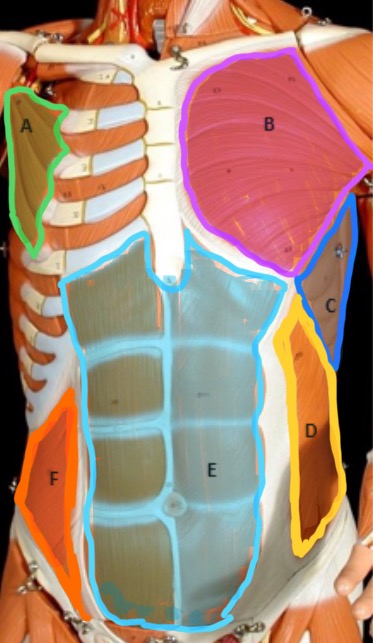
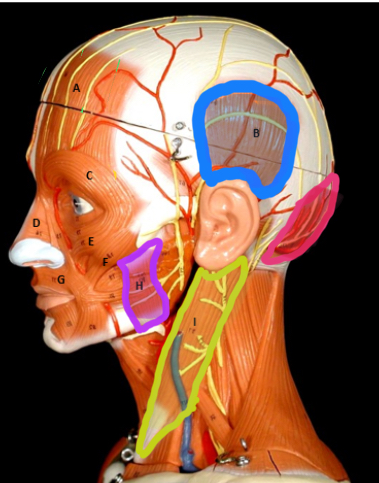
Frontalis
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Frontal View)
What is A?
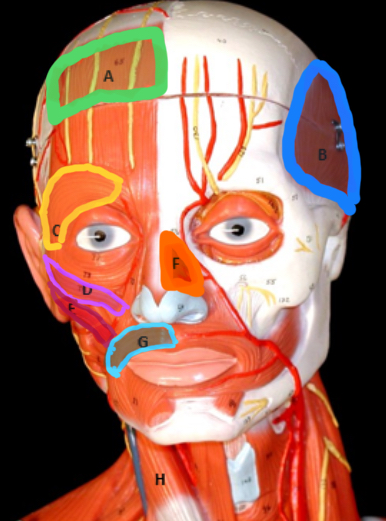
Temporalis
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Frontal View)
What is B?
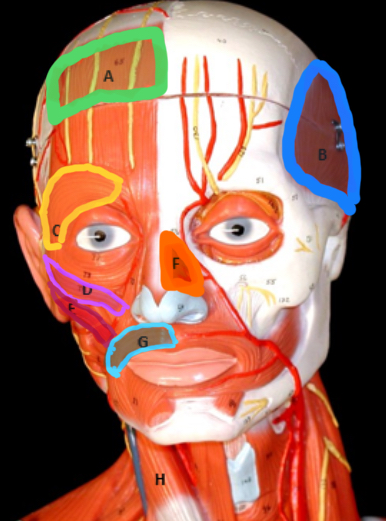
Orbicularis Oculi
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Frontal View)
What is C?
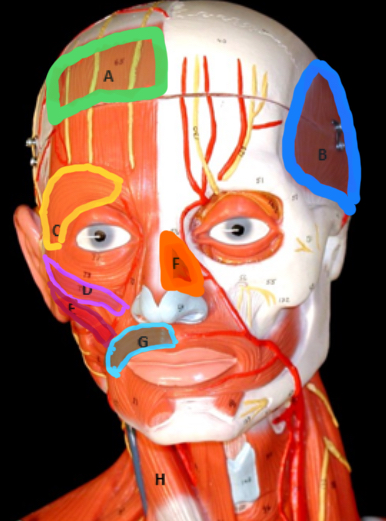
Zygomaticus Minor
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Frontal View)
What is D?
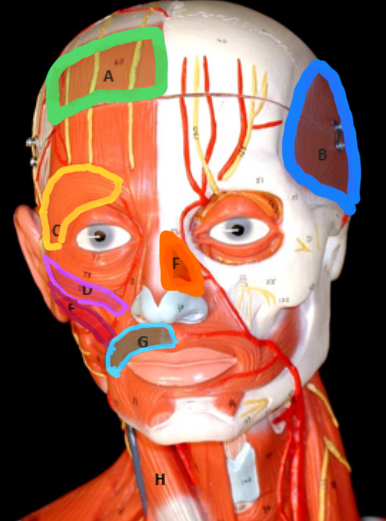
Zygomaticus Major
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Frontal View)
What is E?
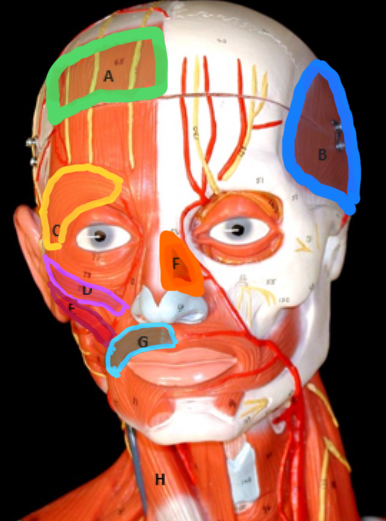
Nasalis
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Frontal View)
What is F?
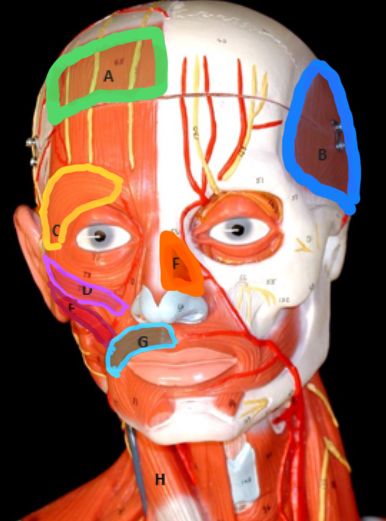
Orbicularis Oris
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Frontal View)
What is G?
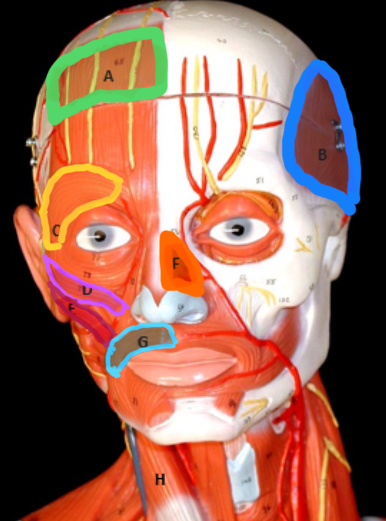
Masseter
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Lateral View)
What is H?
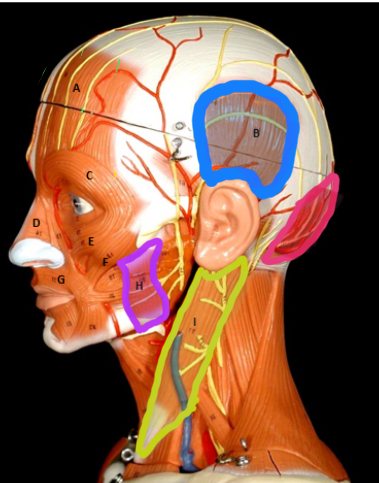
Sternocleiodomastoid
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Lateral View)
What is I?
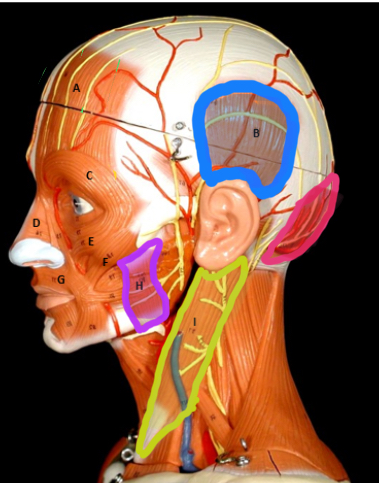
Occipitalis
Type of muscle: Head and Neck (Lateral View)
What is J?