DSA11 - Delayed Puberty, Precocious Puberty, and Galactorrhea
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Cortisol
Although Estrogen and Testosterone BOTH provide negative feedback on the HPG axis, which of the 3 HPA hormones is the ONLY hormone to provide negative feedback?
Precocious (FEMALE)
Is this Precocious, Normal, or Delayed puberty in FEMALES?
> Thelarche/Hair (Pubic & Axillary) < 8 y/o
> Menarche < 10 y/o
Normal (FEMALE)
Is this Precocious, Normal, or Delayed puberty in FEMALES?
> Thelarche/Hair (Pubic & Axillary) = 10 y/o
> Menarche = 12.5 y/o
Delayed (FEMALE)
Is this Precocious, Normal, or Delayed puberty in FEMALES?
> Thelarche/Hair (Pubic & Axillary) > 12 y/o
> Menarche > 15 y/o
Precocious (MALE)
Is this Precocious, Normal, or Delayed puberty in MALES?
> Testicular Enlargement < 9 y/o
> Pubic/Axillary Hair < 10 y/o
Normal (MALE)
Is this Precocious, Normal, or Delayed puberty in MALES?
> Testicular Enlargement = 11.5 y/o
> Pubic/Axillary Hair = 12 y/o
Delayed (MALE)
Is this Precocious, Normal, or Delayed puberty in MALES?
> Testicular Enlargement > 14 y/o
> Pubic/Axillary Hair > 14.5 y/o
Gonadal Injury
Define Condition:
Type of PRIMARY Puberty condition - An insult to the testicles or ovaries, resulting in the gonads being unable to produce testosterone or estrogen
-Hx:
> Vascular Insufficiency
> Chemo
> Radiation
> Autoimmune
> Trauma
-Path:
> Adrenal gland still produce DHEA-S and AS --> Axillary/Pubic hair, Body Odor, Acne still appear
> Characteristics that need Sex Hormones don't appear (M = Deep voice, facial hair, MSK develop; F = Breast develop, menarche)
-Sx/PE:
MEN
> Fatigue
> Low Libido
> Low muscle mass
> Gynecomastia
> Infertility
WOMEN
> Amenorrhea/Oligomenorrhea
> Hot flashes
> Vaginal dryness
-Dx:
Labs
> FSH/LH = HIGH
> Est/Test = LOW
-Tx: Replacement of Testosterone/Estrogen/Progesterone
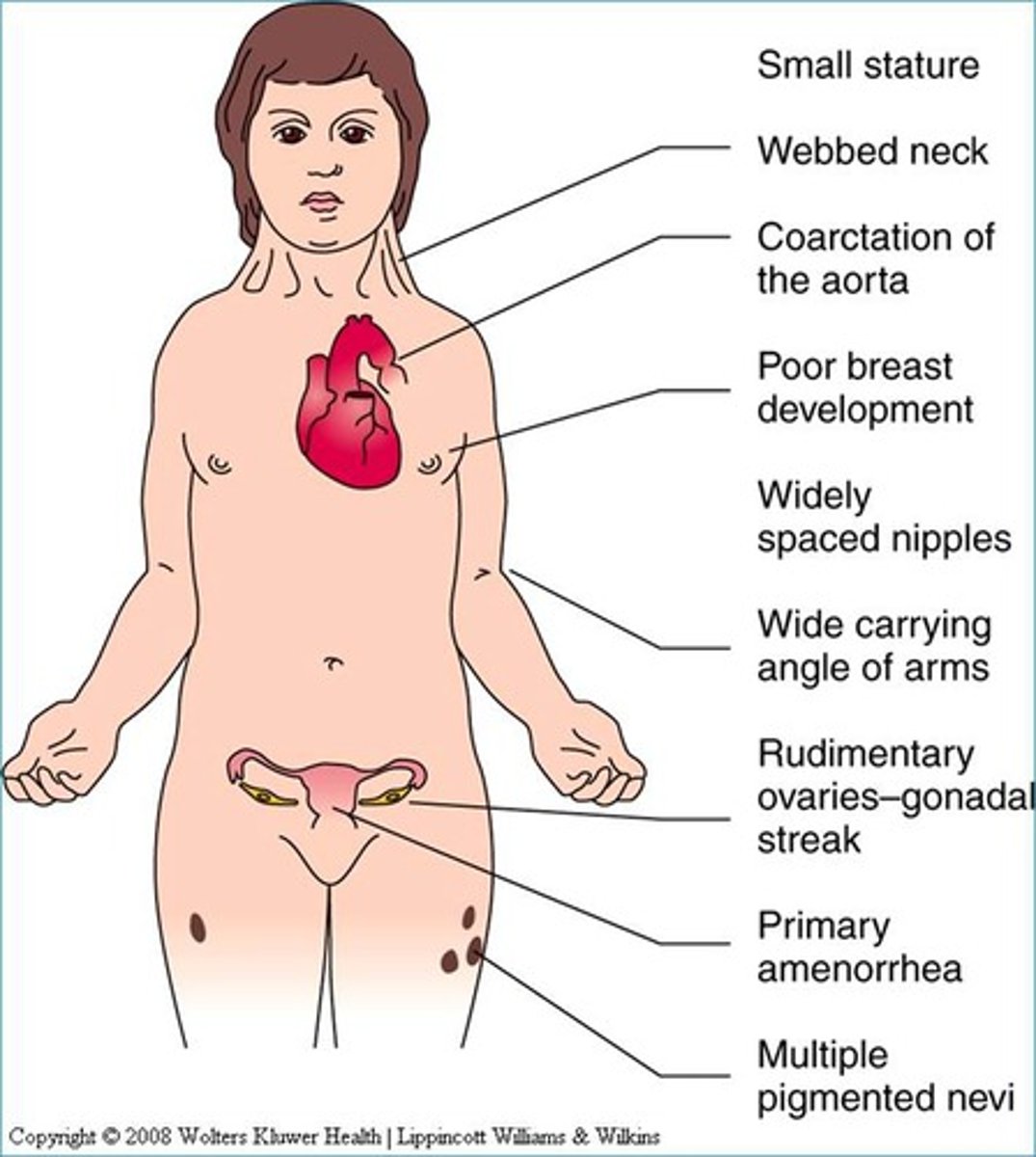
Turner Syndrome
Define Condition:
Type of PRIMARY Puberty condition - chromosomal disorder in which female is born w/ single X chromosome
-Hx: Affects 1 n 2,000 live female births
-Sx/PE:
> Gonadal dysgenesis = streak gonads (Small amts of connective tissue and paucity of absence of follicles)
> Short Stature
> Cardiac Malformations involving aortic arch (BICUSPID AORTIC VALVE, Coarctation of Aorta)
> Structural renal anomalies
> Low posterior hairline
> Webbed neck
> Shield chest
> Short 4th metacarpal bone
-Dx:
Karyotype = CONFIRM
Labs
> FSH/LH = HIGH
> Estrogen = LOW
-Tx: Estrogen/Progestrone Replacement +/- Growth Hormone
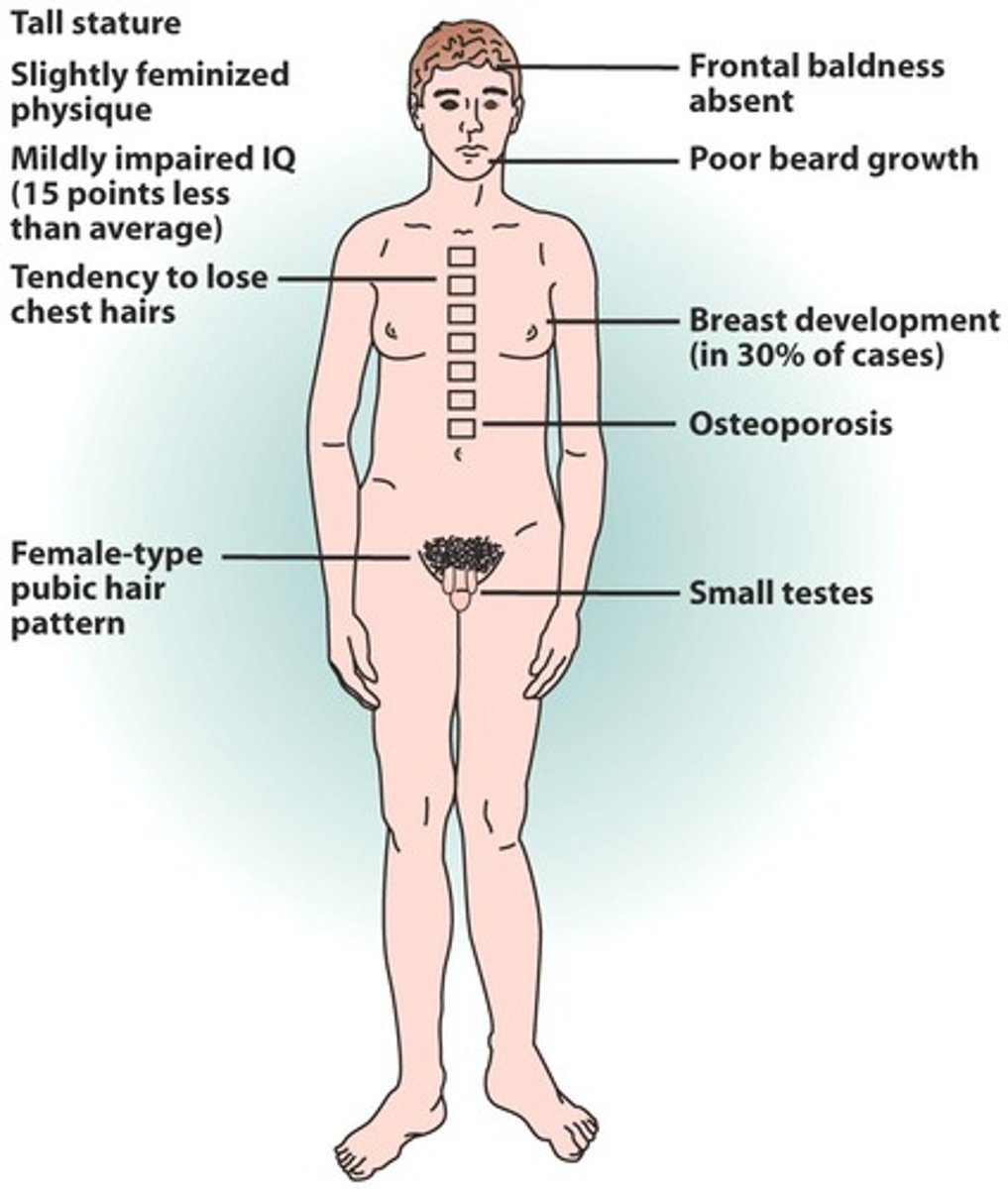
Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY)
Define Condition:
Type of PRIMARY Puberty condition - chromosomal abnormality in which a male is born with two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome
-Hx: 1 in 600 males
-Sx/PE:
> Primary Gonadal Insufficiency
> Small Testes
> TALL STATURE
> Eunuchoid Habitus (arms and legs are disproportionately long relative to the torso)
> Gynecomastia
> Learning Disabilities
-Dx:
Karyotype = CONFIRM
Labs
> FSH/LH = HIGH
> Test = Low(ish)
-Tx: Testosterone Replacement
-Prog:
> Infertility
> Breast cancer
> Mediastinal germ cell. tumors
Constitutional delay of growth and puberty ("Late Bloomer")
Define Condition:
Type of SECONDARY Puberty condition - NOT pathologic, but variant of normal
-Hx: FHx of Late Puberty
-Sx/PE: Healthy
-Dx:
Labs
> FSH/LH = LOW
> Test/Est = LOW
Bone Age = DELAYED
-Tx: Reassurance, Testosterone in Boys (jump start)
Kallmann Syndrome
Define Condition:
Type of SECONDARY Puberty condition - genetic condition notable for abnormal migration/development of GnRH-releasing neurons and olfactory neurons
-Sx/PE:
> Delayed/Incomplete/Absent Puberty
> HYPOGONADISM in Adulthood (if UnTx)
> Anosmia (60%)
-Dx:
Molecular Genetic Analysis
Labs
> FSH/LH = LOW
> Test/Est = LOW
MRI = Hypoplasia or Aplasia of Olfactory bulbs/sulci/tracts
-Tx: Replacement of testosterone or estrogen/progesterone
Hypopituitarism
Define Condition:
Type of SECONDARY Puberty condition - diminished hormone secretion from pituitary gland
-Hx:
> Congenital: Mutations
> Acquired:
>> Trauma
>> Radiation
>> CNS Infex
>> Neurosurgical Injury
>> Sellar Tumors
-Path:
-Sx/PE:
-Dx:
Labs
> FSH/LH = LOW
> Test/Est = LOW
MRI (Brain/Pituitary) = Compromised Pituitary gland
-Tx: Replacement of testosterone or estrogen/progesterone + Any other compromised pituitary hormones as well
Sheehan Syndrome
Define Condition:
Type of SECONDARY Puberty condition (Cause of ADULT Hypogonadism) - clinical scenario occurring in response to vascular insufficiency of the pituitary gland that occurs in the early post-partum timeframe
-Path: Pituitary gland enlarged during pregnancy --> more susceptible to vascular insufficiency
-Prog: From Excessive Post-Partum Bleeding
> Hypovolemic Shock
> Inadequate Perfusion of Pituitary Gland
Chronic illness, Undernutrition, Excessive exercise causing "Functional Hypothalamic Hypogonadism)
Define Condition:
Type of SECONDARY Puberty condition - GnRH secretion is diminished, perhaps as a physiologic adaptation, in the setting of illness or an otherwise compromised state of overall health
-Hx:
> YOUNG WOMEN
> High-level of exercise OR Caloric Restriction
-Path: Evolutionary adaptation to prevent pregnancy and conserve energy
-Sx/PE: Amenorrhea (if insult doesn't occur after puberty)
-Dx: DX OF EXCLUSION
Labs
> FSH/LH = LOW
> Test/Est = LOW
Bone Density = Compromised
-Tx: Estrogen replacement
Central Precocious Puberty (CPP)
Define Condition:
When GnRH secretion simply “turns on” ahead of schedule
-Hx:
> Female = IDIOPATHIC (85%)
> Male = Idiopathic (25-60%)
> Non-Idio = CNS LESIONS
>> Hypothalamic Hamartoma (a/w "gelastic seizures" - seizures manifesting w/ laughing/Other CNS Tumors)
>> Radiation
>> Trauma
>> Structural Abnormalities
-Sx/PE:
> Boys = LARGER TESTICLES for age
-Dx:
Bone Age = ADVANCED
Labs
> FSH/LH = HIGH for age (normal for those old enough for puberty)
> Test/Est = HIGH for age (normal for those old enough for puberty)
MRI = Look for CNS lesion
-Tx: CONSTANT GnRH receptor agonist (Leuprolide injection, Histrelin Implant)
-Prog:
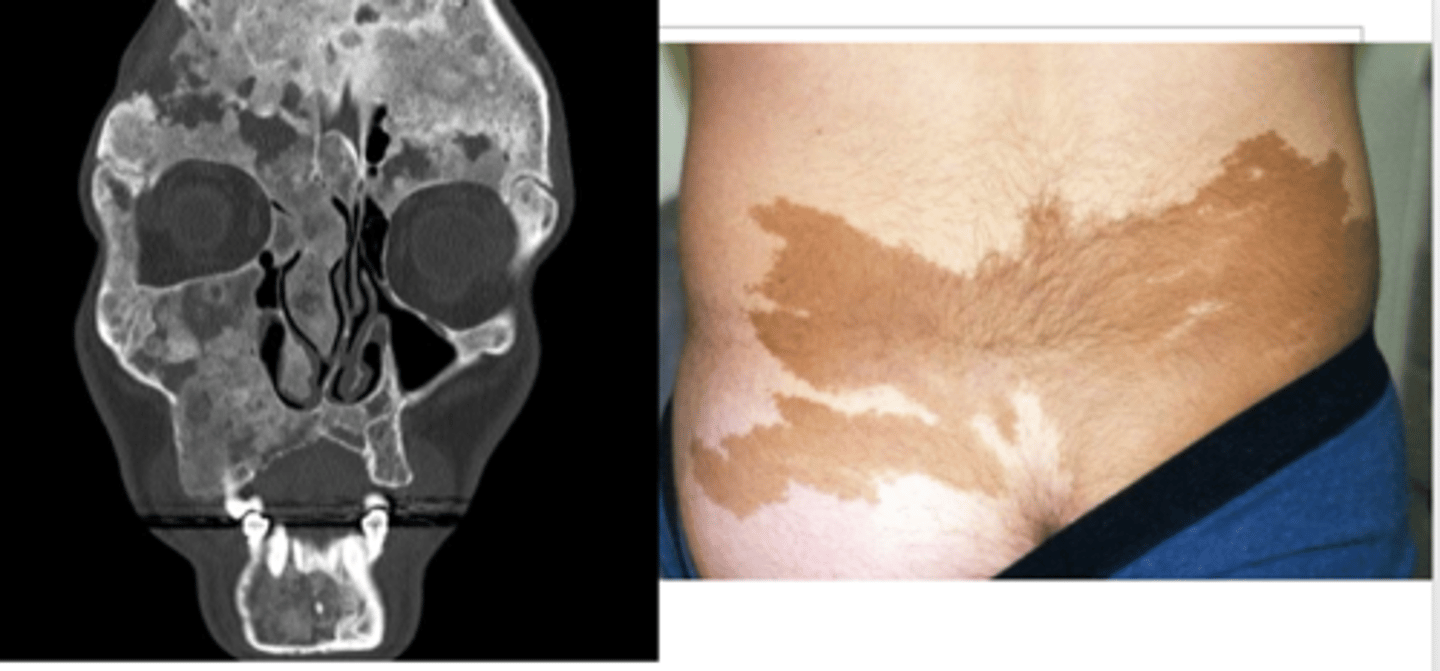
McCune Albright Syndrome
Define Condition:
Activating mutation to the GNAS gene results in constant activation of (potentially) several G protein-coupled hormone receptors
-Path:
> Affects FSH & LH receptors --> inappropriate secretion of Testosterone or Estrogen
> TSH/GHRH/ACTH receptor activation --> Hyperthyroidism, GH Excess, Cortisol Excess
-Sx/PE:
> Precocious Puberty
>> Larger Testicles for age
> Cafe-au-lait patches w/ irregular borders (Coast of Maine borders) that "respect the midline"
> Fibrous dysplasia (normal bones replaced by fibrous connective tissue and poorly formed trabecular bone) affecting multiple bones
-Dx:
Labs
> FSH/LH = LOW (constant and abnormal state of activation b/c of negative feedback)
> Test/Est = HIGH
Bone Age = ADVANCED
Molecular DNA Analysis
-Tx: For PUBERTY Issue
> Girls = Aromatase inhibitors, Estrogen Blockage
> Boys = Aromatase inhibitors, Antiandrogens
-Prog:
Hormone-secreting Tumor
Define Condition:
A tumor is autonomously secreting testosterone or estrogen, resulting in secondary sexual characteristics
-Path:
> Girls = Granulosa cell tumor (in ovary)
> Boys = Leydig cell tumor (in testicle)
-Sx/PE:
> Palpable mass on testicular exam (boys) or on abdominal exam (girls)
>> Other gonad (w/o tumor) will be SMALLER (no FSH/LH to stimulate)
-Dx:
Labs
> FSH/LH = LOW
> Test/Est = HIGH
Imaging (US, CT) = Mass
-Tx: Surgical excision
-Prog:
Exogenous exposure
Define Condition:
Child exposed to substance that causes pubertal development
-Hx/Path:
> Test/Est Topical Applications
> Lavender/Tea Tree Oil (Weak Estrogen activity --> Breast Development)
-Dx:
Labs
> FSH/LH = LOW
> Test/Est (if offending agent) = HIGH
-Tx: Remove offending agents
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
Define Condition:
-Path: Causes androgenic pubertal features
-Sx/PE:
> Axillary Hair
> Pubic Hair
> Acne
> Deep voice
Galactorrhea
Define Condition:
Excessive or inappropriate discharge of milk from the nipple
-Hx:
> Idiopathic (Normal Prolactin Concentration)
> Secondary (Hyperprolactinemia)
>> Pregnancy
>> Lactotroph adenoma (Prolactinoma)
>> Hypothyroidism
>> Medication induced
Pregnancy
Define Cause of Galactorrhea:
When PL increases physiologically during this period and may also be INCREASED d/t increased Estrogen levels
-Path: Placenta is primary source of estrogen biosynthesis during pregnancy
-Dx: Urine Pregnancy Test
Lactotroph adenoma (prolactinoma)
Define Cause of Galactorrhea:
Uncontrolled expansion of prolactin secreting cell in pituitary --> Functional Adenoma that secretes EXCESSIVE prolactin
-Hx: WOMEN from 20-40 y/o (also males, any age)
-Path: PL Suppresses GnRH secretion --> Suppress Estrogen and Testosterone
-Sx/PE:
> Headaches
> Visual Impairment (compression of optic chiasm --> Bitemporal Hemianopsia)
> Premeno Females =
>> Oligomenorrhea/Amenorrhea
>> Inferility
>> Hot Flashes
>> Vaginal Dryness
>> Low Bone Density
>> GALACTORRHEA
> Postmeno Females = No Consequences (stopped making estrogen anyway)
>> GALACTORRHEA
> Men =
>> Impotence
>> Infertility
>> Fatigue
>> Gynecomastia
>> Diminished libido
>> (+/-) GALACTORRHEA
-Dx: MRI of Brain
-Tx:
> 1st = Dopamine Agonist (Cabergoline or Bromocriptine)
>> Activation of the dopamine receptor on the lactotroph cell inhibits PL release and reduces the size of the adenoma
>> Efficacy = 90%
>> Adenoma may shrink enough to d/c Treatment
> 2nd = Transphenoidal Surgery
>> If no response/no tolerance to D2 Agonist
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1)
Define Cause of Galactorrhea:
A condition caused by a AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT mutation to the gene on a tumor suppressor on chromosome 11, associated with several endocrine tumors
-Hx: 1 to 10 per 100,000 individuals
-Hx/Path:
> Pituitary Adenoma = PLoma (20%), GH adenoma (5%)
> Parathyroid Adenoma = By Age 50 in 100%
> Pancreatic Tumors = Gastrinoma (30-40%), Insulinomas (100%), Glucagonomas (3%), Somatostatinomas (<1%)
-Dx:
Criteria
> TWO of classic tumors
> FHx of Condition + ONE of classic tumors
GENE TESTING
-Tx:
> Periodic Screening
> Tx of Tumor
Hypothyroidism
Define Cause of Galactorrhea:
-Path: Low T3/T4 --> High TRH (feedback) ==> PL Secretion
-Hx: Uncommon
-Sx/PE:
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
> ENLARGED THYROID GLAND (High TSH stimulates growth)
-Dx:
Labs
> T3/T4 = LOW
> PL = HIGH
-Tx: TH Replacement
Medication-Induced Hyperprolactinemia
Define Condition:
-Hx/Path: Use of...
> D2 Agonists (Antipsychotics, Metoclopramide) = Blocks Dopamine receptor on pituitary gland --> Can't inhibit PL secretion
> TCAs
> Verapamil
-Dx:
Labs
> PL = HIGH (Not High enough to induce Galactorrhea
-Tx: Remove offending agent
Idiopathic Galactorrhea
Define Cause of Galactorrhea:
-Dx:
Labs
> PL = Normal
-Tx: Reassurance or D2 Agonist (if bothersome)