ch. 24, section 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
what are the general animal features?
heterotrophic eukaryotes, and multicellular
2
New cards
what does it mean that animals are heterotrophic?
they rely on ingesting other organisms as a food source for energy
3
New cards
how do animals feed?
dependent on their diet, they have specialized mouth functions which perform different functions
4
New cards
how do animals digest?
after obtaining the food they digest either in specialized cells or organs
5
New cards
majority of the animal species are what? and make up what percentage?
90-95% are invertebrates, (most under the category of insects)
6
New cards
invertebrates:
no backbones, have exoskeletons
7
New cards
exoskeletons:
hard or tough outer coverings
8
New cards
vertebrates:
have backbones and endoskeletons
9
New cards
endoskeletons:
internal support structure
10
New cards
what type of habitats are invertebrates and vertebrates found in?
terrestrial, marine, and freshwater ecosystems
11
New cards
describe the animal cell structure:
* no cell walls
* the cells of all animals except sponges are organized into tissues
* the cells of all animals except sponges are organized into tissues
12
New cards
what are tissues?
a group of cells that are specialized to perform a specific function
13
New cards
what evolved which enabled animals to move in more complex ways than other kingdom’s organisms?
the evolution of nerve and muscle tissues
14
New cards
how do animals reproduce?
most reproduce sexually, some organisms reproduce asexually
15
New cards
what are hermaphrodites?
animals that can produce both sperm and eggs in the same body
16
New cards
what is fertilization?
type of sexual reproduction that occurs when the sperm penetrates the egg to form a fertilized egg called the zygote
17
New cards
when does internal fertilization occur?
when sperm and egg meet inside the animal’s body
18
New cards
when does external fertilization occur?
when sperm and egg meet outside the animal’s body
19
New cards
what are the common methods of asexual reproduction in animals?
budding, fragmentation, and regeneration
20
New cards
budding:
offspring develops as a growth on the parent body
21
New cards
fragmentation:
parent breaks into pieces and each piece can develop into adults
22
New cards
regeneration:
a new organism can regrow from a lost body part if the part contains enough genetic information
23
New cards
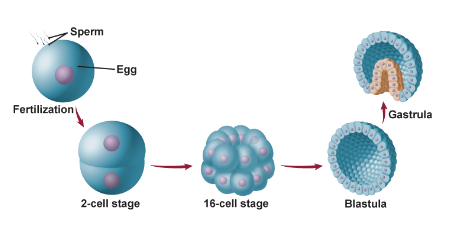
state the three stages of early development:
1. zygote undergoes mitosis and a series of cell divisions to form new cells
2. blastula forms as the cells continue to divide
3. gastrula forms
24
New cards
blastula:
fluid-filled ball of cells
25
New cards
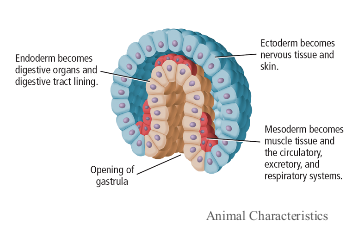
gastrula:
a few cells that form a two-layer sac with an opening at one end from the blastula
26
New cards
what is gastrulation?
the forming of the three germ layers (endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm)
27
New cards
endoderm:
the inner layer of the gastrula that develops into the digestive organs
28
New cards
ectoderm:
the outer layer of the gastrula that develops into the nervous tissue and the skin
29
New cards
mesoderm:
the third cell layer between the endoderm and ectoderm that forms the muscle, circulatory, excretory, and respiratory system in some animals