Human physiology chapter 1 part 1 test review
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Oncology
cancers
gerentology
the aging process
pathologist
diseases and the changes they cause
cardiologist
heart diseases
OBGYN
Pregnancy and child birth
epidemiology
factors determining the frequency of health related conditions
pediatrician
children and their diseases
Immuneology
bodys resistance to infectious dieases
Dermatology
skin and its diseases
Neurology
nervous system and its disorders
pharmacist
drugs and their uses in treatment of disease
orthopedics
muscular and skeletal system problems
toxicology
poisonous substances
radiology
x-ray and radioactive substances
hematology
blood and blood diseases
cytology
cells
endocronology
hormones and hormone secreting glands
gynocology
female reproductive system
optomitrist
eye and eye diseases
podiatrist
care and treatment of the feet
otolaryngdologist
ears nose and throat specialist
nephrology
diseases and disorders relating to the kidney
Gastroentologist
stomach and intestines and their diseases
urologist
urinary tract and organs of the urogenital system
phlebotemist
specifically deals in drawing of the blood
psychiatrist
mental health
PT
physical therapist
RN
registered nurse
MD
medical doctor
EMT
emergency medical technician
DMD
doctor of medical dentistry
PA
physicians assistant
OT
occupational therapy
LPN
licensed practical nurse
DVM
doctor of veterinary medicine
NP
nurse practitioner
DO
doctor of osteopathic medicine
Ancient medicine
magical and superstitious, herbs and natural resources
Homeostasis
keeping things in the body stable/self regulation.
3 components to self regulation
1) receptors receive info from environment, 2) set point/ value for stability , 3) effector/ part that carry out an action
positive feedback
change causes additional changes, produces increasingly unstable conditions. Body moves further away from normal state.
Examples of positive feedback
labor contractions, blood clotting
Anatomy
structure of body parts
physiology
what and how the body parts do
metabolism
sum total of all of the chemical reactions in the body
receptor
provides information about specific condition
effectors
cause responses that alter conditions in internal enviornment
set point
what values should be
vertebral canal
spinal cord
thoracic and abdominal pelvic
in backbone
diaphram
seperates thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity
abdominal cavity
stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys and most of the small and large intestine
pelvic cavity
most of the large intestine, urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs
oral cavity
teeth and tongue
nasal cavity
nose
orbital cavities
eyes, skeletal, muscles and nerves
middle ear cavities
middle ear bones
integumentary system
skin, hair, nails
skeletal system
bones, ligaments and cartilage
muscular system
muscles stretching and contracting
nervous system
brain, spinal cord, nerves and sense organs
endocrine system
hormones and glands
cardiovascular system
heart, arteries, veins, capillaries and blood
lymphatic system
lymph nodes and thymus
digestive system
breaks down food and molecules into simpler forms to be absorbed
respiratory system
moves air in and out and exchanges gases between blood and air
reproductive system
penis, uterus, ovaries, testies, vagina
levels or organization
atom, molecule, macromolecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
anatomical position
standing face forward
Superior
above another
inferior
below another
anterior
towards the front
posterior
towards the back
medial
divides the body into left and right
lateral
towards the side
bilateral
paired structures, symmetrical
Distal
further away
Proximal
close to
Superficial
toward the surface of the body
Deep
further away from the surface
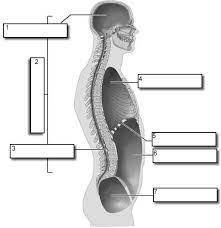
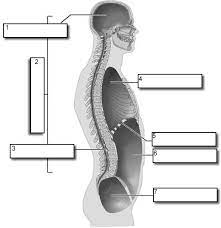
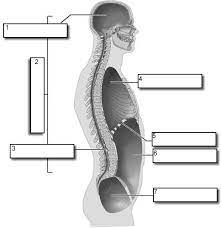
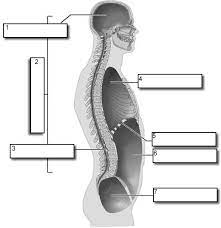
1
Cranial
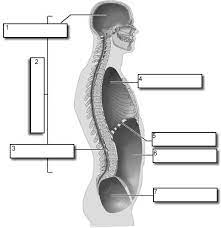
2
Dorsal
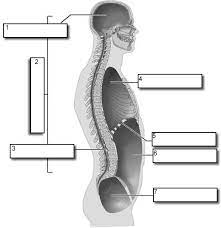
3
Vertebral
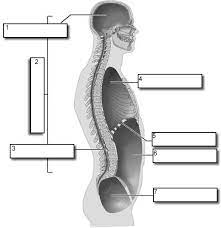
4
Thoracic
5
Diaphram
6
Abdominopelvic
7
Pelvic
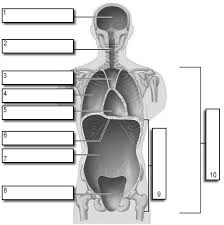
1
Cranial
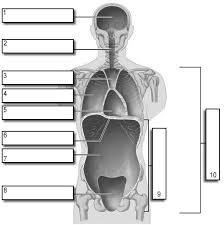
2
Vertebral
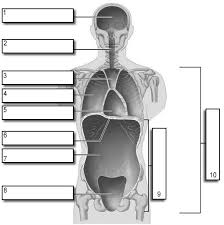
3
Superior Mediastinum
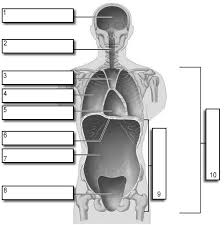
4
Pleural
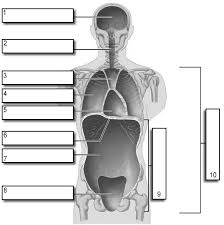
5
pericardial
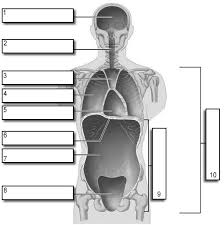
6
Diaphram
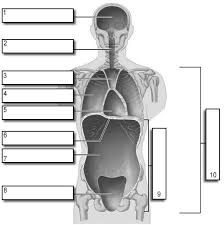
7
Abdominal
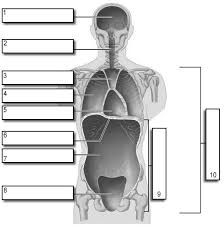
8
Pelvic
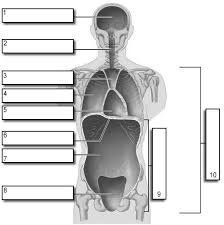
9
Abdominopelvic
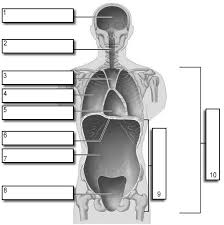
10
Ventral
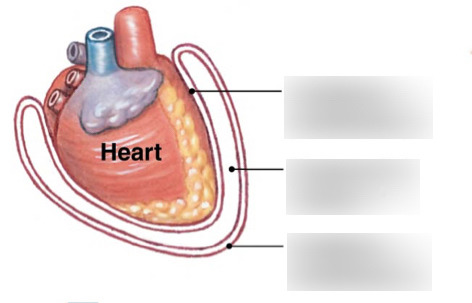
top
visceral pericardial
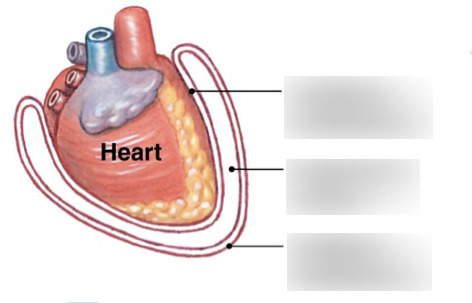
middle
pericardial cavity