Exam semester 2 (multiple choice)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/176
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
1
New cards
first person to study how traits are passed down from one generation to the next
gregor mendel
2
New cards
who’s studies on pneumonia discovered the process of transformation
Frederick griffith
3
New cards
whose X-ray diffraction pictures helped determine the structure of DNA
rosalind franklin
4
New cards
whose experiment, using digestive enzymes, showed DNA was responsible for transformation
oswald Avery
5
New cards
who (w help from others) correctly built the structure of DNA
James Watson and Francis crick
6
New cards
In the experiment with pneumonia bacteria and transformation, what was being passed from one strain of Bactria to the other
plasmids
7
New cards
what two parts of the nucleotide make up the “backbone” of the nucleic acid strand
the phosphate group and the 5 carbon sugar
8
New cards
which DNA nucleotides are **pyrimid**ines, having just **one** ring in the nitrogenous base?
cytosine and thymine
9
New cards
how many hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine as they “base pair”
2
10
New cards
which carbon determines whether the nucleotide is ribose or deoxyribose
C2
11
New cards
which carbon is the one that the nucleotide can be added to in the growing strand of nucleotides
C3
12
New cards
which protein does DNA wrap around to form the “bead on a string” structure of chromatin
Histone
13
New cards
DNA is replicated in which form?
chromatin
14
New cards
DNA polymerase I preforms which of the following functions?
cuts out the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA nucleotides
15
New cards
DNA gyrase does which of the following during replication
unleashes the tension that builds as DNA is unwound
16
New cards
RNA polymerase does which of the following
lays down RNA nucleotides across from the gene during transcription
17
New cards
what is the function of DNA polymerase II
“spell checks” the growing strand of DNA as it is made during replication
18
New cards
a repressor protein would do which of the following
bind to an inhibitory site and slow down/decrease transcription
19
New cards
RNA polymerase lands on an area of DNA known as which of the following?
the promoter
20
New cards
which RNA type helps shut down translation
miRNA
21
New cards
of the editing steps of pre-mRNA, which of the following brings the ribosomes to the mRNA strand
the 7-methyl guanosine cap
22
New cards
what is the function of telomerase
prevent any of the important DNA from not being copied
23
New cards
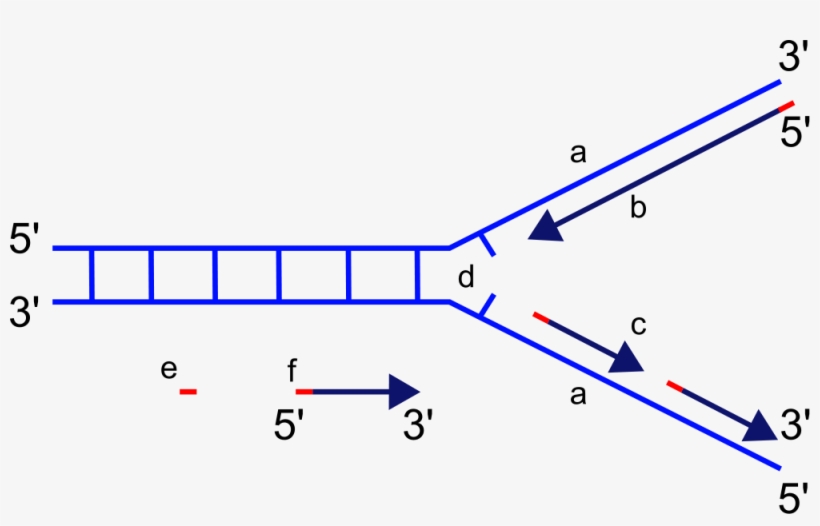
which letter on the diagram is the leading strand
b
24
New cards
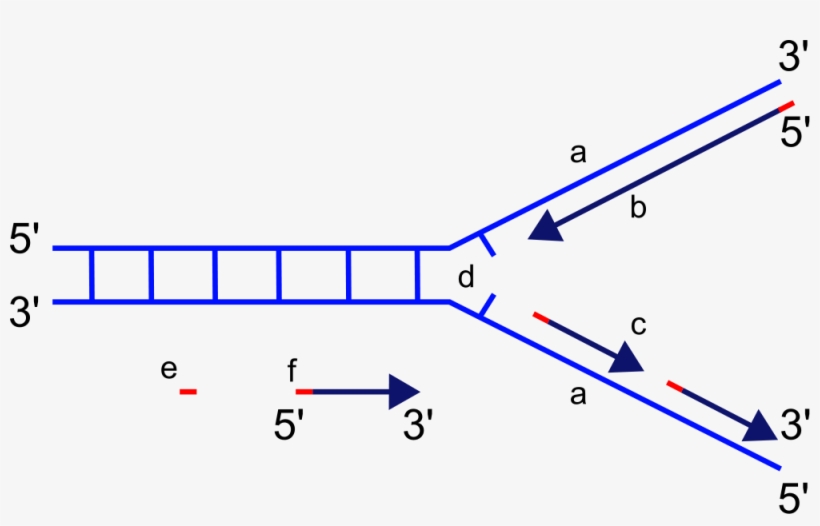
what is the lagging strand on the diagram?
c
25
New cards
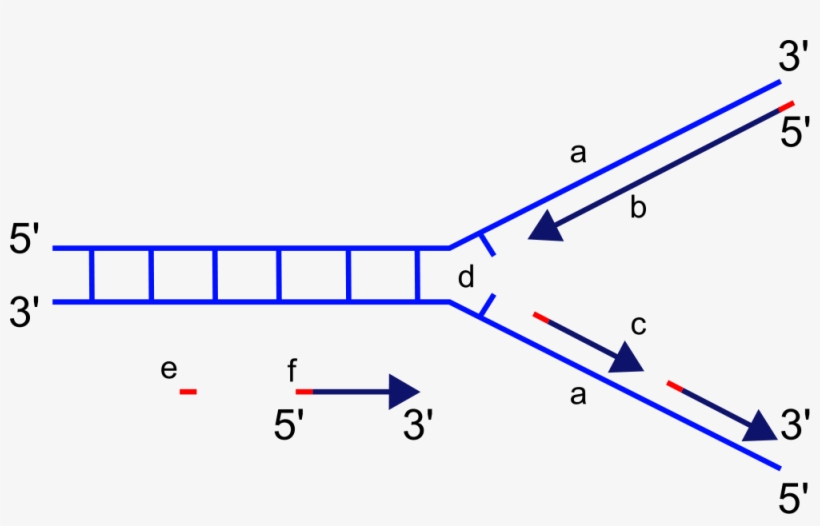
what are the Okazaki fragments on the diagram?
c
26
New cards
which type of mutation changes a nucleotide for another, causeing a change in the amino acid laid down for the protein
point mutation
27
New cards
a deletion of two nucleotides in a gene would result in which of the following?
Frame shift mutation
28
New cards
when people go to the beach they apply sunscreen to prevent uv rays from giving us skin cancer. in this instance uv rays are acting as ___?
a physical carcinogen
29
New cards
which of the following describes eukaryotes transcription control
one gene is under the control of one promoter and accessory regulatory sites
30
New cards
the Gardasil vaccine prevents around 75% of cervical cancers, by preventing the infection with the human papillomavirus, HPV. how does HPV cause these cancers
by entering the lysogenic cycle and mutating a cell control gene
31
New cards
which “part” of the ribosome connects the amino acids together with peptide bonds?
the P-site
32
New cards
what correctly describes what happened to babies in England who, after their mothers took morning sickness pills, became “flipper babies”
a chemical mutagen causing a mutation in a HOX gene
33
New cards
what name refers to the original strand of DNA that the DNA polymerases “read” during replication
template
34
New cards
what term refers to the stretch of DNA that is turned into RNA during transcription
gene
35
New cards
what is the structure of DNA
a double helix
36
New cards
DNA has what type of charge?
negative
37
New cards
what term refers to ALL of the DNA of a eukaryotic organism
genome
38
New cards
in the Lac operon, the genes are turned on when which of the following is present?
lactose
39
New cards
which of the following refers to transfer RNA?
I. carries an amino acid
II. has an anticodon to “pair” to the codon
III. lands at the A-site of the ribosome
I. carries an amino acid
II. has an anticodon to “pair” to the codon
III. lands at the A-site of the ribosome
I, II, and III
40
New cards
the Lac Operon is found in which of the following
prokaryotes
41
New cards
which of the following terms refers to a picture of a cells chromosome
karyotype
42
New cards
which of the following refers to the area where sister chromatids are connected together on a chromosome
centromere
43
New cards
bacterial cells divide by which. of the following processes
binary fission
44
New cards
which of the following is part of interphase
a. mitosis
b. S-phase
c. cytokinesis
d. prophase
e. anaphase
a. mitosis
b. S-phase
c. cytokinesis
d. prophase
e. anaphase
b. S-phase
45
New cards
during S-phase of the cell cycle, DNA can be found in which form
Chromatin
46
New cards
The majority of a cells growth takes place during which of the following?
G1
47
New cards
during which stage of mitosis do the sister chromatids separate
anaphase
48
New cards
which of the following occurs during telophase
DNA de-condenses
49
New cards
during which stage of the cell cycle do cells replicate their DNA
S phase
50
New cards
during which stage of mitosis do the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell?
Metaphase
51
New cards
During prophase which of the following would happen
I. chromosomes form
II. Centrioles split
III. Nuclear membrane dissolves
I. chromosomes form
II. Centrioles split
III. Nuclear membrane dissolves
III only
52
New cards
the length of time that it takes a cell to progress through the cell cycle is known as…
generation time
53
New cards
which of the following proteins is the primary protein in centrioles and spindle fibers
a. cyclins
b.collagen
c.actin
d.tublin
e.beta lactamase
a. cyclins
b.collagen
c.actin
d.tublin
e.beta lactamase
d. tubulin
54
New cards
which of the following is not a part of the mitotic spindle
a.centrioles
b.centrosome region
c.contractile ring
d.spindle fibers
e.polar fibers
a.centrioles
b.centrosome region
c.contractile ring
d.spindle fibers
e.polar fibers
c. contractile ring
55
New cards
the contractile ring is formed primarily from which protein
actin
56
New cards
which term refers to the indention that forms where a eukaryotic animal cell divides
cleavage furrow
57
New cards
the polar fibers of the mitotic spindle are involved in which of the following
a. connecting the spindle fiber to the chromosome
b.seperating the sister chromatid
c. elongating the cell before it divides
d. maneuvering the chromosomes to the middle of the cell
e. all of the above
a. connecting the spindle fiber to the chromosome
b.seperating the sister chromatid
c. elongating the cell before it divides
d. maneuvering the chromosomes to the middle of the cell
e. all of the above
elongating the cell before it divides
58
New cards
which family pf proteins is involved in controlling the cells progress through the cell cycle
cyclin family of proteins
59
New cards
in the cell cycle, external regulators typically direct cells to do which of the following
speed up or slow down the cell cycle
60
New cards
cyclin b, the first cyclin discovered, when it reaches the threshold amount level, would immediatly send a cell into which of the following stages
prophase
61
New cards
which of the follwing is involved in cell differentiation
a. through the expression of different genes
b. through the expression of the same genes but in different amounts
c. through the expression of the same genes but at different times of the cell’s cycle
d. by influences from neighboring cells
e. all of the above
a. through the expression of different genes
b. through the expression of the same genes but in different amounts
c. through the expression of the same genes but at different times of the cell’s cycle
d. by influences from neighboring cells
e. all of the above
all of the above
62
New cards
apoptosis is best described by which of the following examples
the cells in the webbing between the fingers going away as the hand develops
63
New cards
the frog regrowing limbs and the drugs used, and how that worked, would be best described as
external regulators directing the cells to grow but letting them (and the surrounding cells) to direct their path
64
New cards
which of the following describes using CAR-T cells, or chimeric antigen receptor cells, in cancer therapy
genetically manipulating one immune systems own t-cells to recognize the cancerous cells
65
New cards
cancers that occurs in the bone marrow, where blood cells are formed, is referred to as which of the following
leukemias
66
New cards
ultraviolet radiation from the sun is an example of which of the following
physical carcinogen
67
New cards
many cancers have been found to have mutation in which of the following genes
p53
68
New cards
cancers of epithelial tissue are known as which of the following
carcinoma
69
New cards
which term refers to a gene that, normally would control the cell cycle, but has mutated and is causing uncontrolled cell growth
an oncogene
70
New cards
which of the following statements is true?
I. tumor cells that are metastasizing must be activly going through the cell cycle
II. tumor cels that are metastasizing must be in cell cycle arrest
III. tumor cells that are benign must be in cell arrest
I. tumor cells that are metastasizing must be activly going through the cell cycle
II. tumor cels that are metastasizing must be in cell cycle arrest
III. tumor cells that are benign must be in cell arrest
II only
71
New cards
cells of the blastocysts inner cell mass are best described as ?
Pluripotent
72
New cards
what term is used to describe two of the same chromosomes?
homologous
73
New cards
what tern refers to the **different versions of a specific gene**?
alleles
74
New cards
Barbara McClintock made an unusual discovery during her research of corn, that genes do not always stay in one spot. what scientific term refers to these so called “jumping genes”
Transposons
75
New cards
to follow humanity lineage through the paternal line science would compare which of the following?
Y chromosomes
76
New cards

what is 1 in this diagram?
telomere
77
New cards

what is 2 in the diagram?
centromere
78
New cards

what is 3 in the diagram?
p arm
79
New cards

what is 4 in the diagram
q arm
80
New cards
what term refers to cells that have both chromosomes of each pair of chromosomes found in an organism
diploid
81
New cards
**somatic** refers to what?
all of the cells of the human body, with the exception of sperm and egg
82
New cards
in humans, spermatogenesis, in which one spermatocyte forms four sperm cells, creates which of the following
four viable sperm cells with 23 chromosomes
83
New cards
in humans, as one oocyte goes through the process of oogenesis, it creates which of the following
one viable egg w 23 chromosomes
84
New cards
which of the following occurs during meiosis II
I. the DNA gets replicated
II. the homologous chromosomes get separated
III. the sister chromatids get separated
I. the DNA gets replicated
II. the homologous chromosomes get separated
III. the sister chromatids get separated
III only
85
New cards
which of the following would occur during prophase II once the spindle apparatus was broken down during telophase I
I. the DNA condenses
II. the nuclear membrane dissolves
III. The spindle apparatus is formed
I. the DNA condenses
II. the nuclear membrane dissolves
III. The spindle apparatus is formed
III only
86
New cards
a **tetrad** forms during which stage of the gametic cycle?
prophase 1- metaphase 1
87
New cards
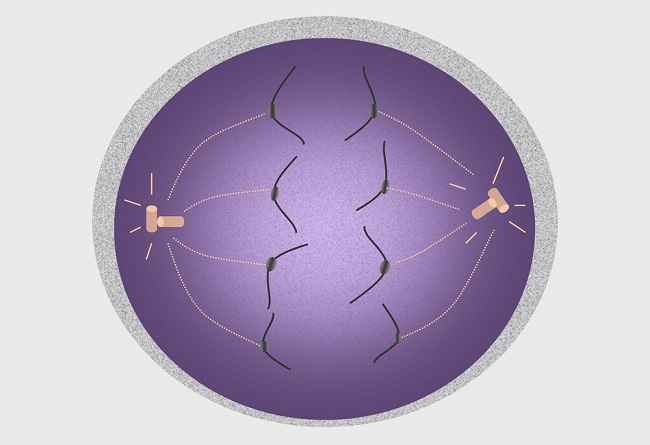
the following cell would be in which stage of meiosis?
anaphase
88
New cards
identify _____ (the “location” of the break)
chiasma
89
New cards
if a zygote has three homologous chromosomes, two genetically identical and one different which of the following must have happened
non-disjunction occurred during meiosis II
90
New cards
which of the following would occur during crossing over if the chiasma occurred at two different locations
one chromosome involved would undergo a chromosomal deletion, the other a chromosomal duplication
91
New cards
which of the following is NOT a characteristic that scientists would want in an organism used to study genetics: gives birth to one offspring at a time, becomes reproductive early in life / short life cycle, is inexpensive to care for, not dangerous, or all of the above are needed for a good genetic study organism a
gives birth to one offspring at a time
92
New cards
a punnet square is used to determine which of the following
the probable outcome of offspring from parents
93
New cards
what ratio would occur if model crossed two heterozygous pea plants for a characteristic that was a single gene trait with one dominant version and one recessive version
75% would have dominant phenotype and 25% would have the recessive phenotype
94
New cards
The **ab blood type** is a specific example of which principle of genetics?
==principle of codominance==
95
New cards
a trait that has a range of variation to its phenotype, like eye color, would be an example of which of the following?
a trait controlled by several genes
96
New cards
which of the following would be described as a “carrier” :homozygous individual that shows signs of the disorder, heterozygous individual that shows signs of the disorder, homozygous individual that does not show signs of the disorder, a heterozygous individual that does not show signs of the disorder, or males who have the sex linked, X-chromosome disorder
a heterozygous individual that **does not** show signs of the disorder
97
New cards
a autosomal disorder in humans would refer to which of the following?
any disorder that is caused by a mutation in the nucleotide sequence of a gene found on chromosome 1-22
98
New cards
which of the following would **not** be an example of epigenetics : laying out in the sun, different temp. in a turtle nest determining the gender of the offspring, males being more suseptible to sex-linked disorders, a mother being stressed during her pregnancy resulting with behavioral issues in her child, or all of the above are examples
males being more susceptible to sex-linked disorders
99
New cards
what terms refers to a gene, that when mutated, has multiple effects, in multiple areas, of the body?
pleiotropic
100
New cards
in the article concerning Down syndrome, what was the discovery that the scientists made cornering gene expression in the neural progenitor cells, or the cells that eventually form neural cells of the nervous system
genes from every chromosome were over expressed