EENT - Health Assessment
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Diplopia
Double vision
Scotomas
Area of vision loss
Strabismus
Misalignment
Photophobia
Light sensitivity
Glaucoma
Optic nerve damage often from high eye pressure
Cataracts
Cloudy lens opacity
Macular degeneration
Age related effects to retina and central vision
Conjunctivitis
Pink eye
Inflammation of infection of the eye
Tinnitus
Ringing
Vertigo
Room spinning
Rhinorrhea
Discharge of mucus from the nasal passage (runny nose)
Epistaxis
Bleeding of the nose tissue (nosebleed)
Dysphagia
Difficulty swallowing
Odynophagia
Painful swallowing
Ears
CN VIII
Eyes
CN II, III, IV, VI
Nose
CN I
Throat
CN IX, X, XII
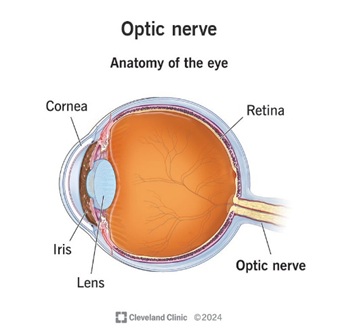
Sclera
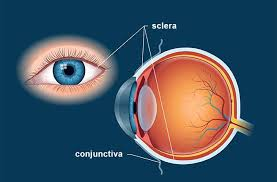
Pupil

Lens
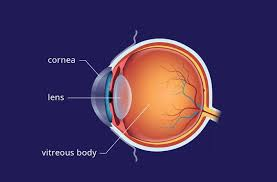
Cornea
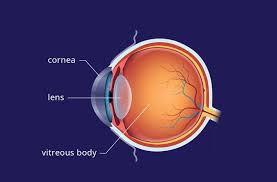
Retina
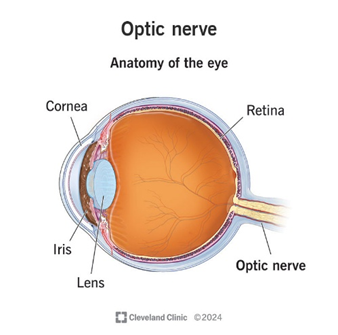
Optic nerve (CN II)
Superior oblique
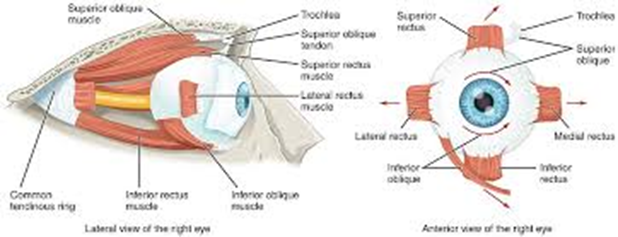
Inferior oblique
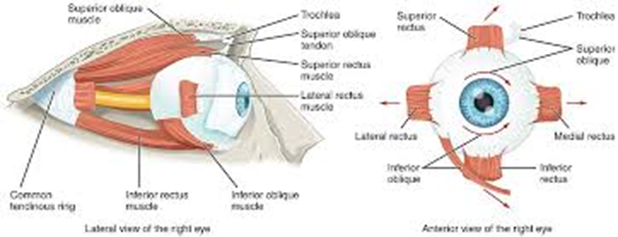
Superior rectus
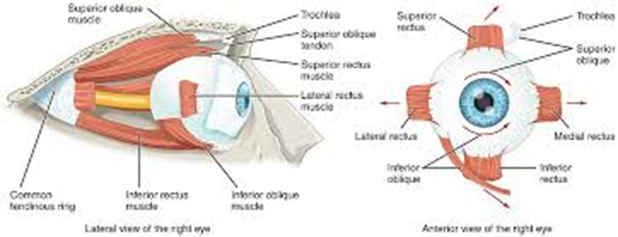
Inferior rectus
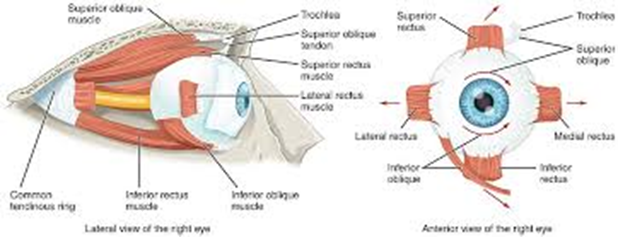
Lateral rectus
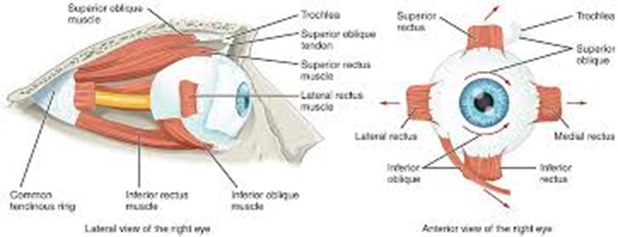
Medial rectus

Conductive Hearing Loss
Impairment of either the outer, middle, or even both parts of the ear, obstructing the transmission of sound to reach the ossicles
More amplitude of sound and usually allow sound to reach the inner ear
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Impairment of the inner ear, leading to not being able to understand speech. This impairment can either be resulted from the vestibulocochlear nerve or the entire inner ear in general.
Weber test
Test equal lateralization of hearing by using a tuning fork and placing it on the top of the head or mid-forehead.
Rinne test
Tests sound through air conduction and bone conduction. Normally, air conduction should last longer than bone conductive.
Cerumen
Waxy substance secreted in the ear canal
Outer Ear
Helix, anti-helix, pinaa/auricle, lobule, tragus
Middle Ear
Ear canal, tympanic membrane (eardrum), ossicle (malleus, incus, stapes)
Inner Ear
Semicircular canal, cochlea, vestibular nerve, eustachian tube
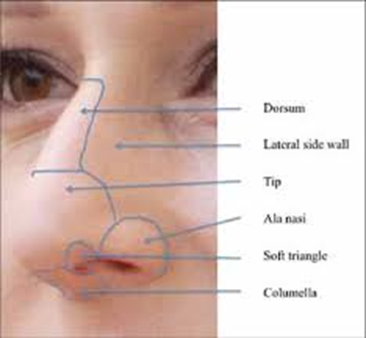
External Nose
Bridge, ala nasi, vestibule
Internal Nose
Superior turbinate, middle turbinate, inferior turbinate, vestibule, nasopharynx, opening to the eustachian tube
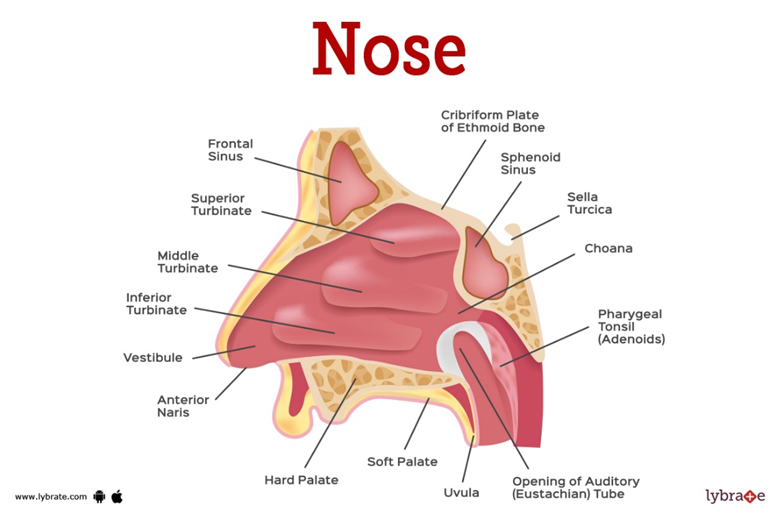
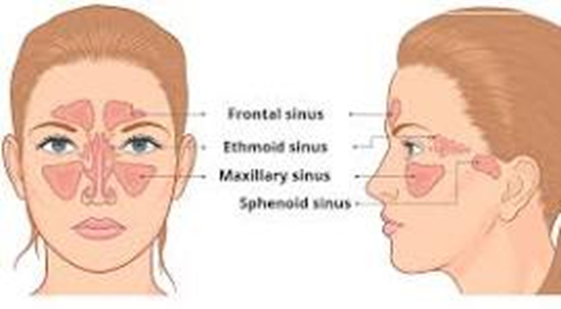
Sinuses
Frontal and maxillary sinus
Otitis media
Inflammation of the middle ear, the space behind the eardrum
Mouth
Comprised of the hard/soft palate, uvula, tonsils
Candidiasis
Fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast
Visible tonsils
+1
Between tonsillar pillars/uvula
+2
Touching uvula
+3
Tonsils touching each other
+4
Esotropia

Exotropia

Hypertropia

Hypotropia

Chalazion
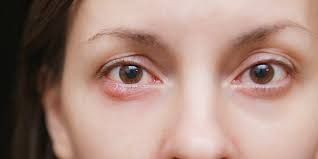
Stye
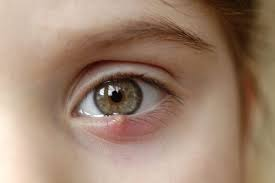
Anisocoria
Difference in pupil shape by <1 mm in diameter

Hemianopsia
Unable to see half of visual field
Nystagmus
Involuntary, rhythmic eye movement
Jaundice
Can cause the sclera to appear yellow
Visual Fields
Superior Temporal/Nasal
Inferior Temporal/Nasal
Presbyopia
Age-related condition that affects the eyes’ ability to focus on near objects
Cranial Nerves responsible for Cardinal field of gaze
CN III, IV, VI
Distal Visual Acuity Test
Use of Snellen eye chart
Near Visual Acuity Tests
Rosenbaum or Jaeger chart
Peripheral Visual Acuity Test
Confrontation test (the wiggle dinger test that tests the patients blind spots/peripheral vision)
Consensual
When light is flashed in one eye and the other pupil constricts
Whisper test
Stand behind the patient and whisper a sequence with 3 numbers/letters and then ask the patient to repeat what they heard