Week 11: Digestive System
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
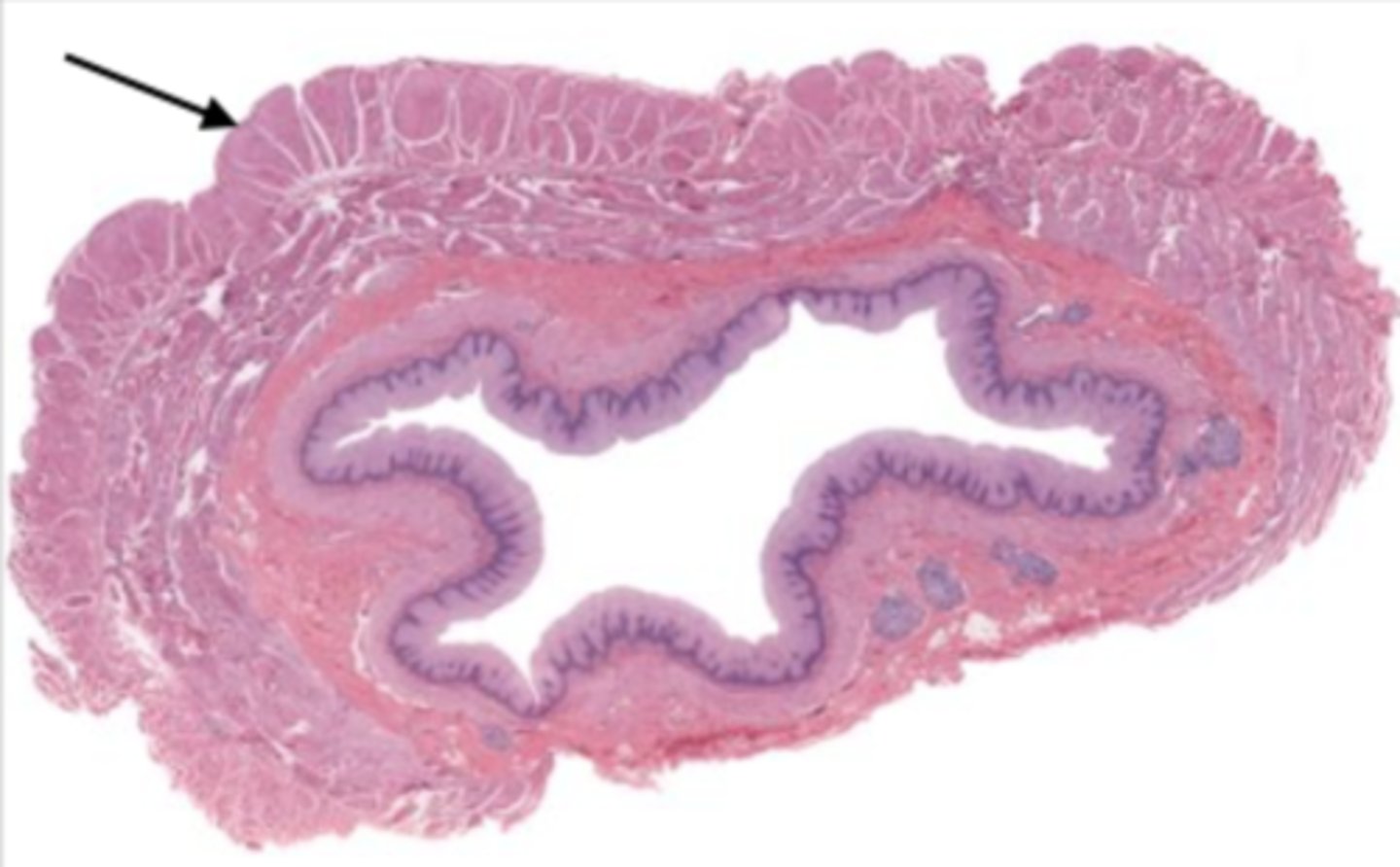
esophagus (histology)
lumen (esophagus)
mucosa (esophagus)
mucosal epithelium (esophagus)
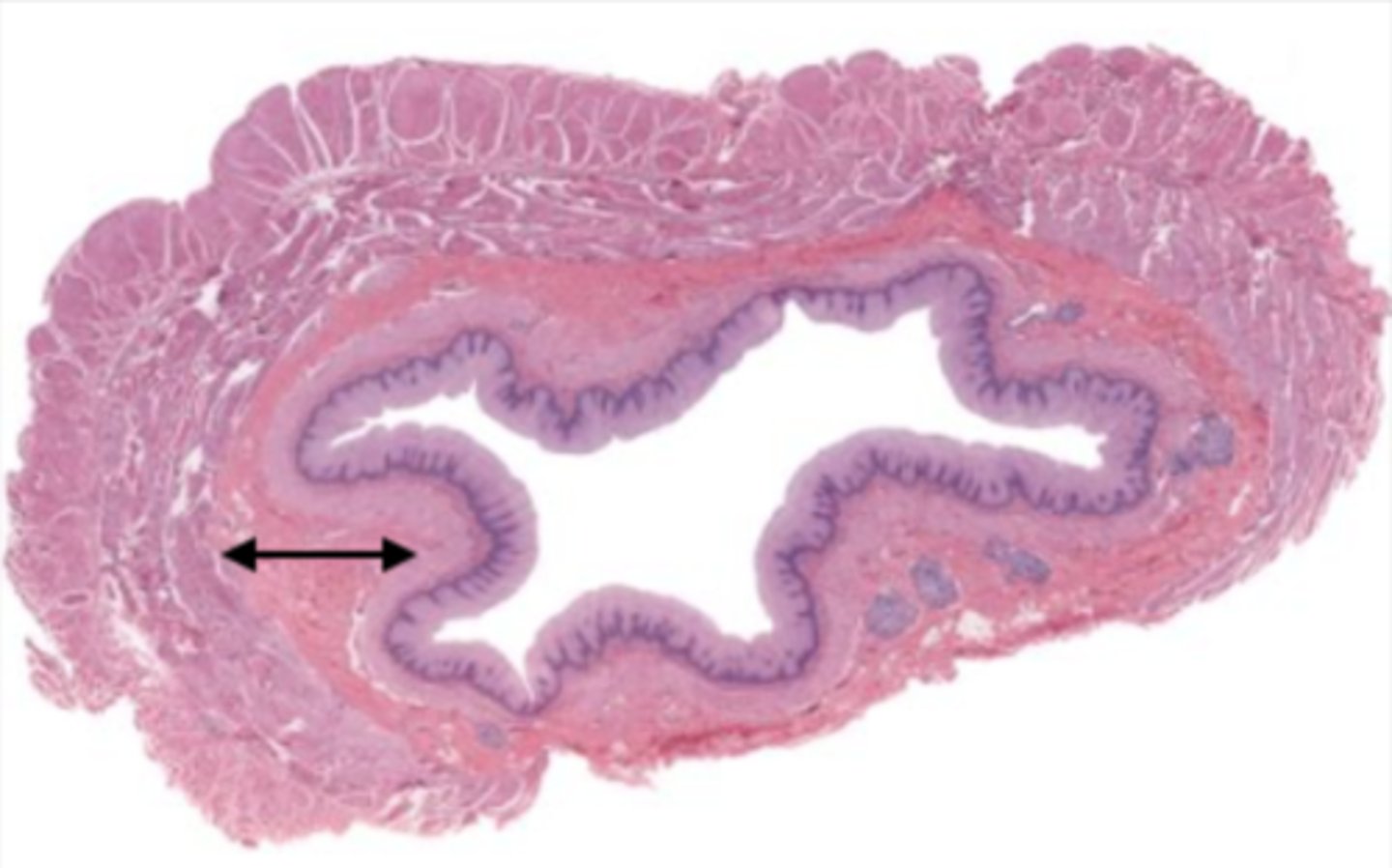
stratified squamous epithelium
what kind of epithelium lines the mucosa of the esophagus?
lamina propria (esophagus)
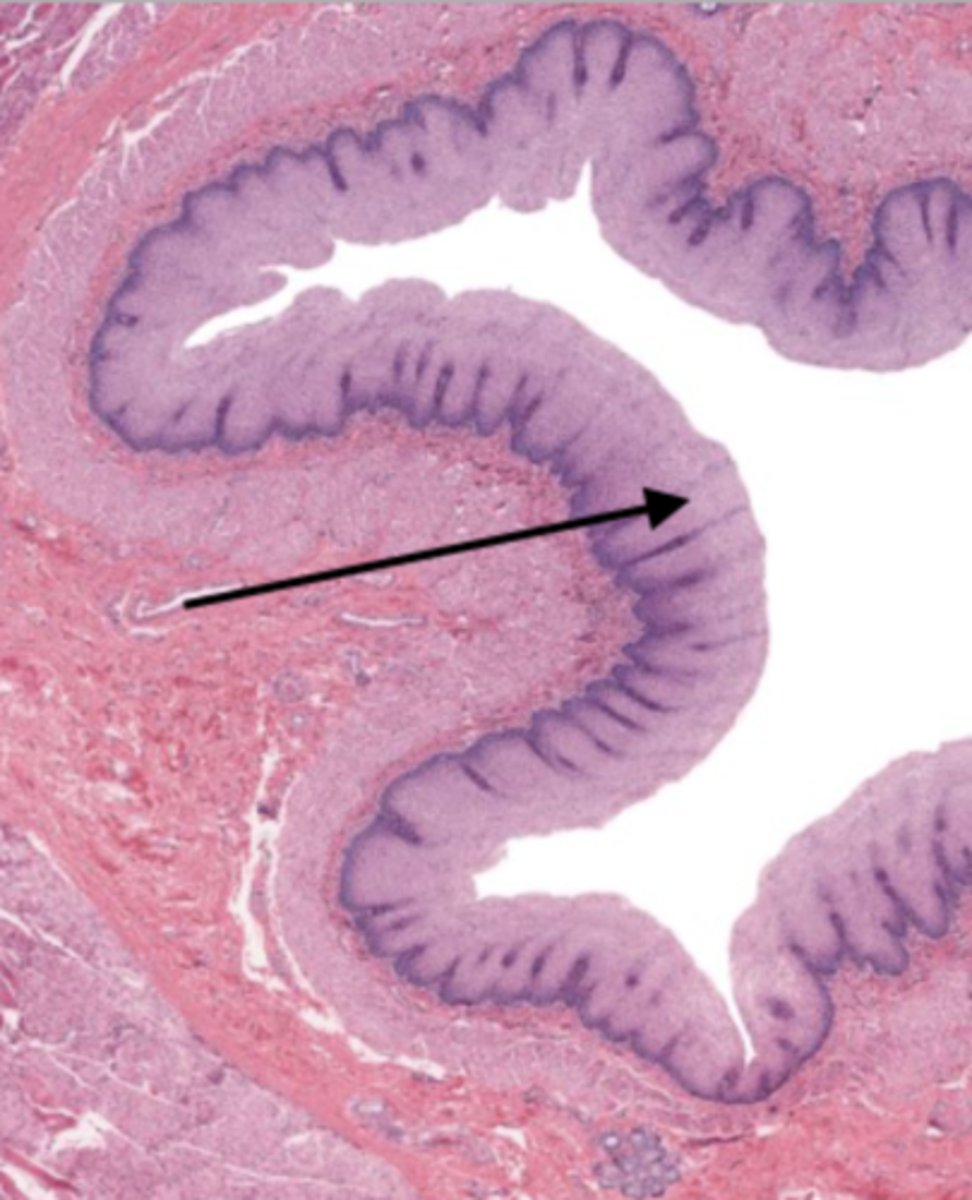
muscularis mucosa (esophagus)
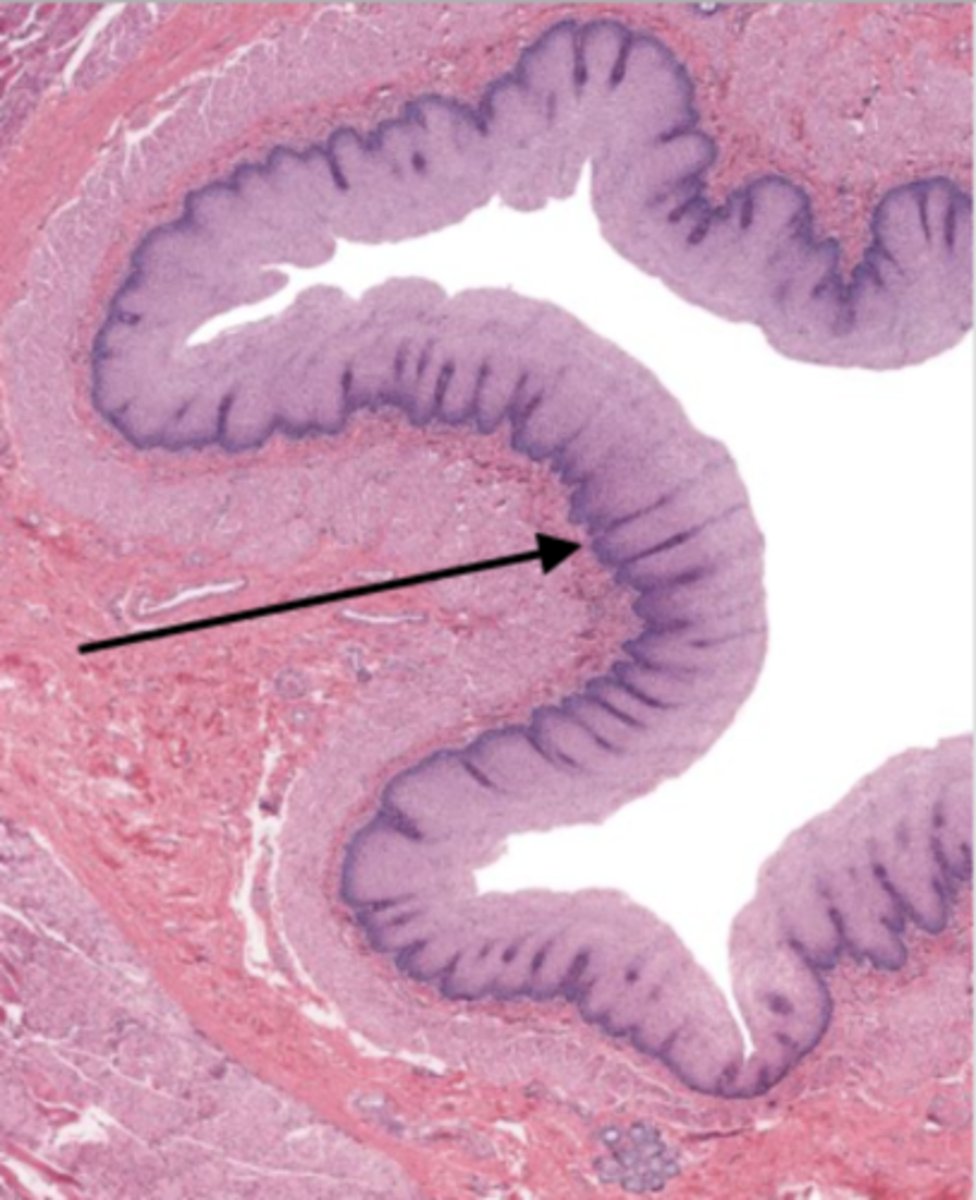
submucosa (esophagus)
contains glands and blood supply
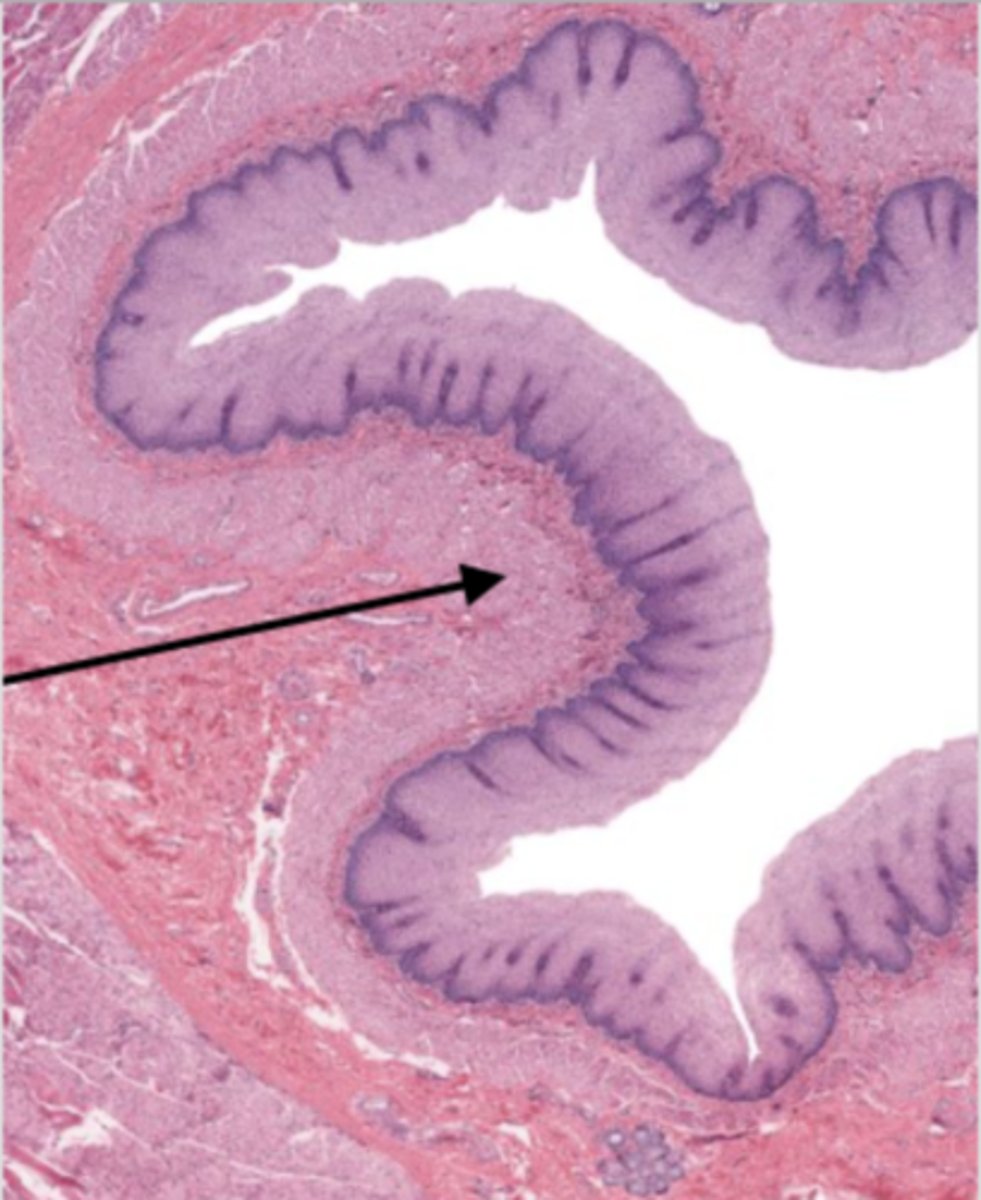
muscularis externa (esophagus)
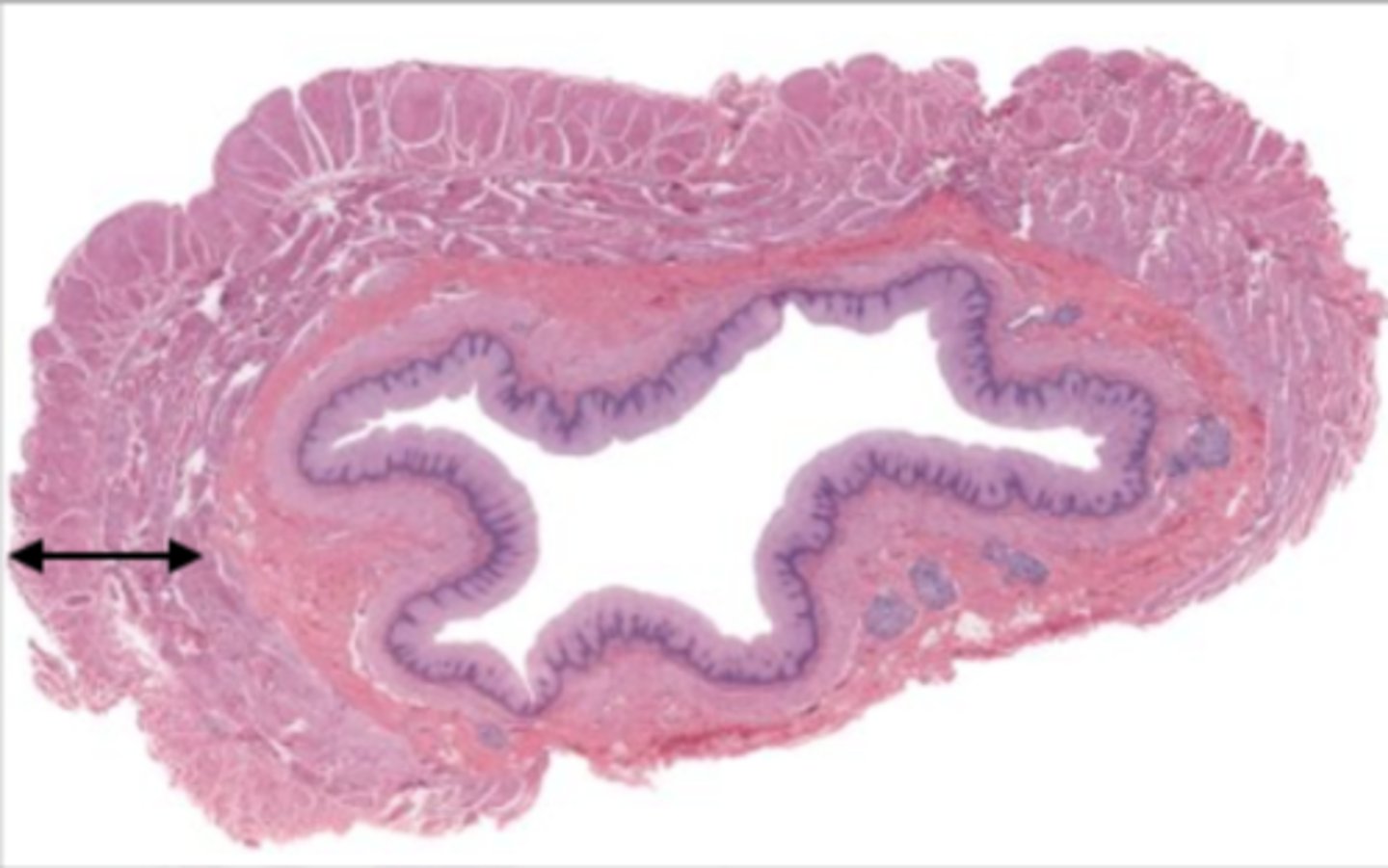
serosa/adventitia (esophagus)
cardiac stomach (histology)
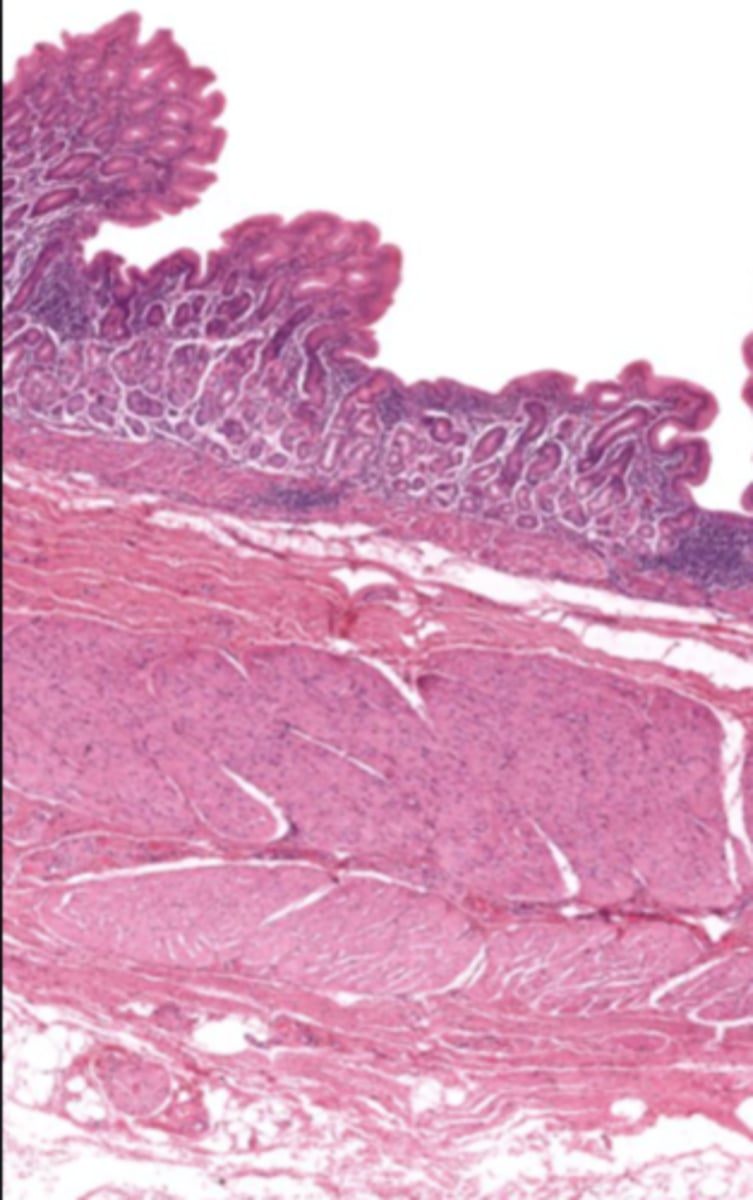
simple columnar epithelium
what kind of epithelium lines the mucosa of the cardiac stomach?
gastric pit (cardiac stomach)
lumen (cardiac stomach)
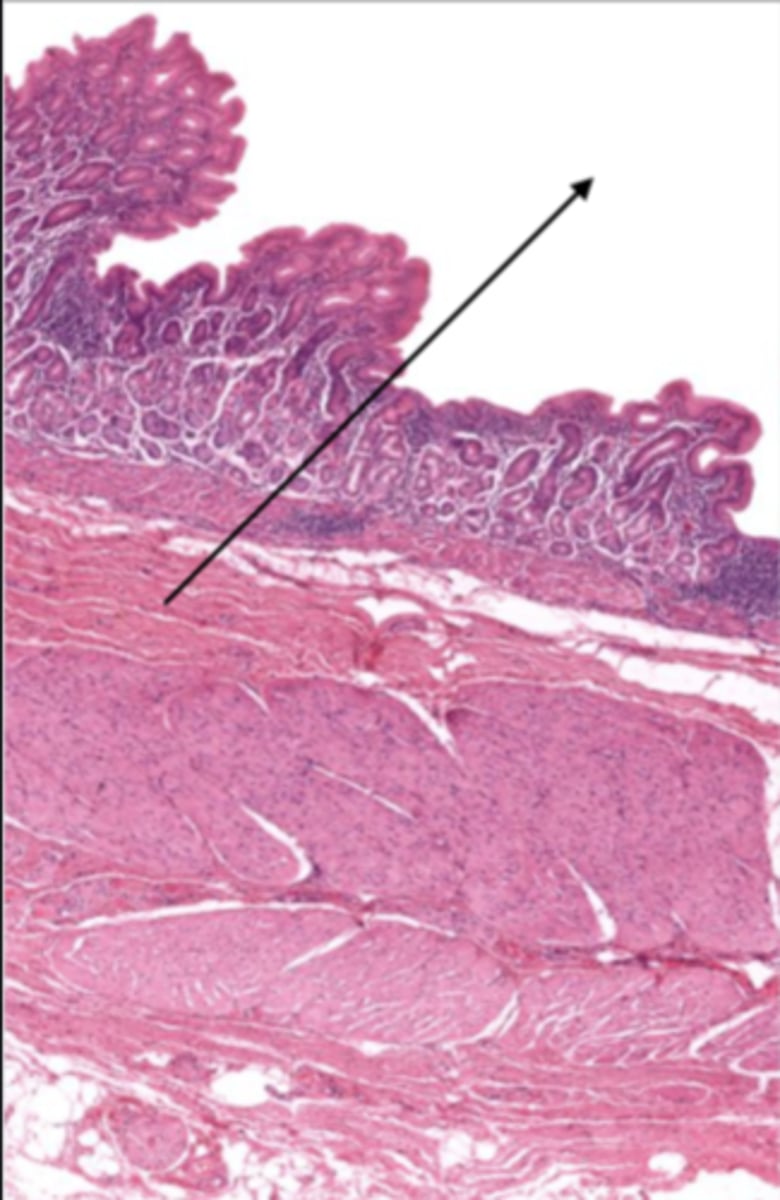
mucosa (cardiac stomach)
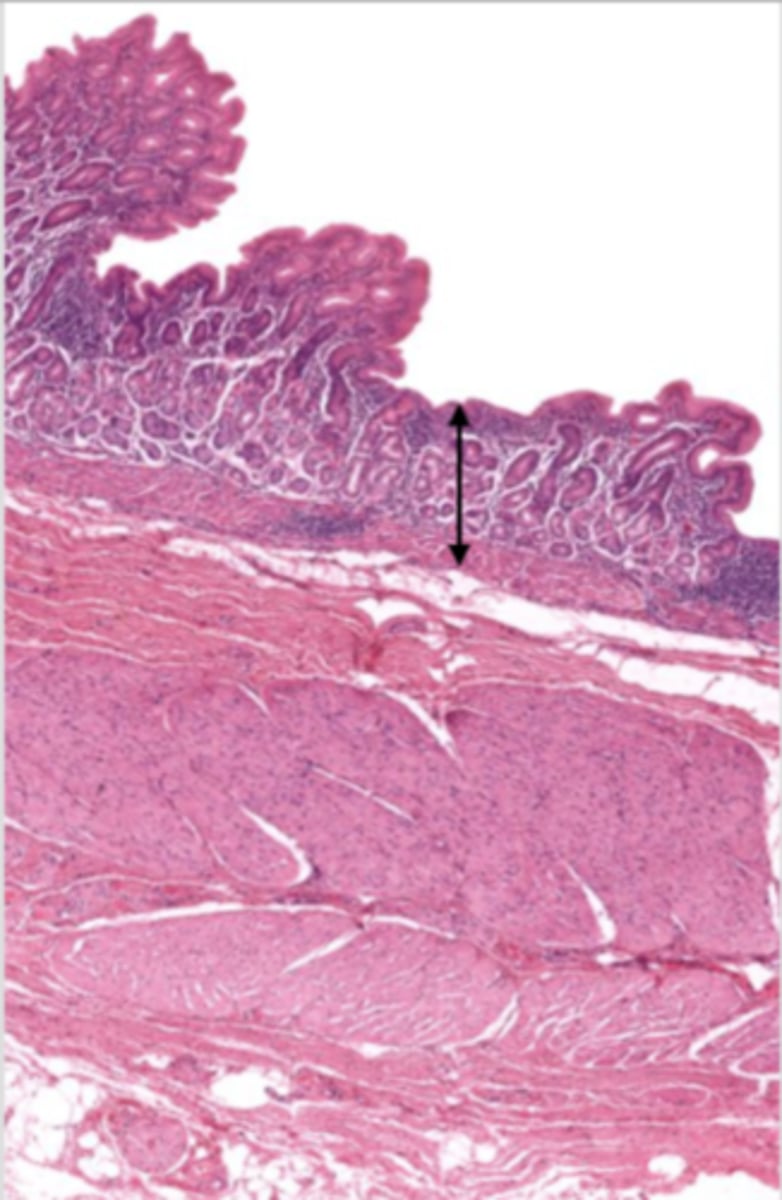
mucosal epithelium (cardiac stomach)
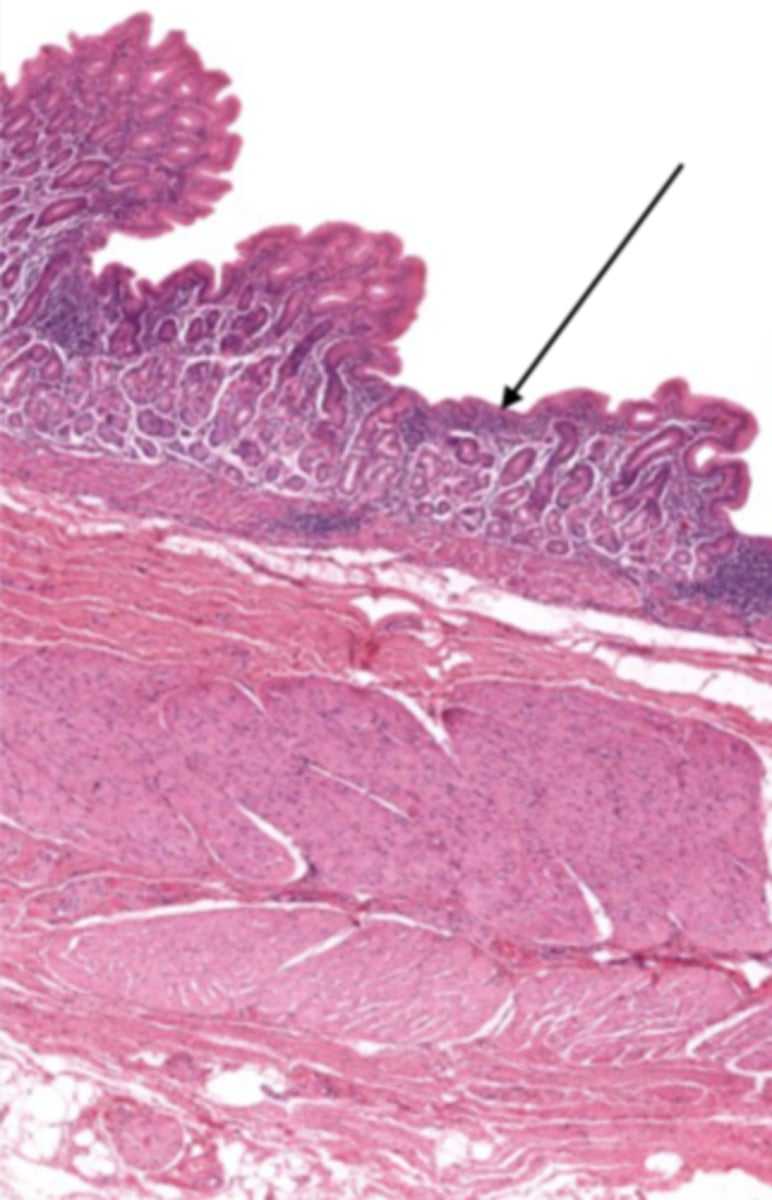
lamina propria (cardiac stomach)
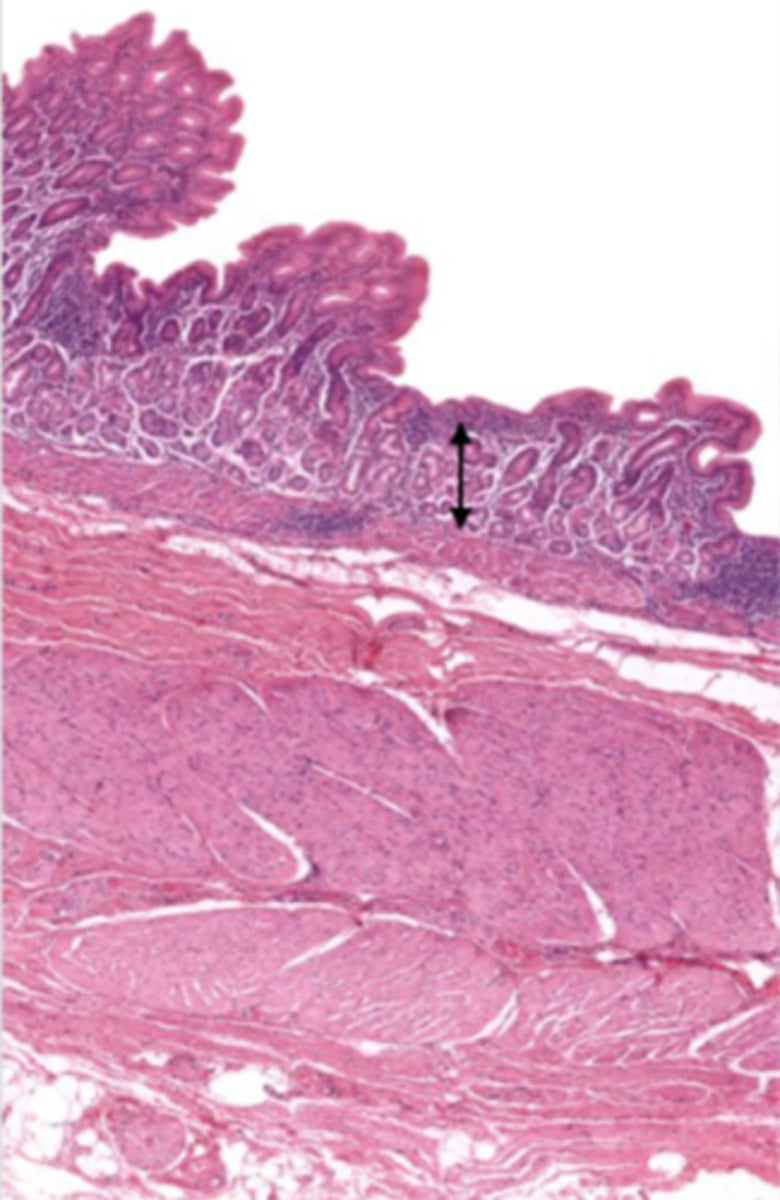
muscularis mucosa (cardiac stomach)
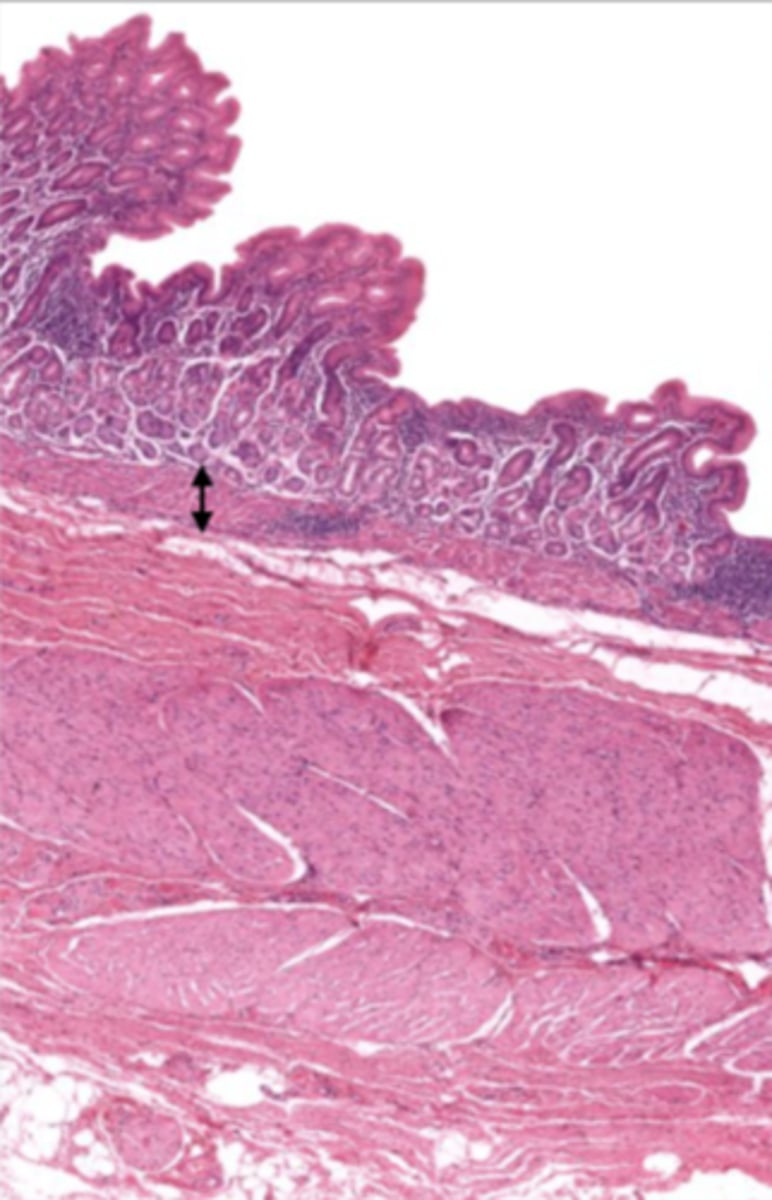
submucosa (cardiac stomach)
contains glands and blood supply
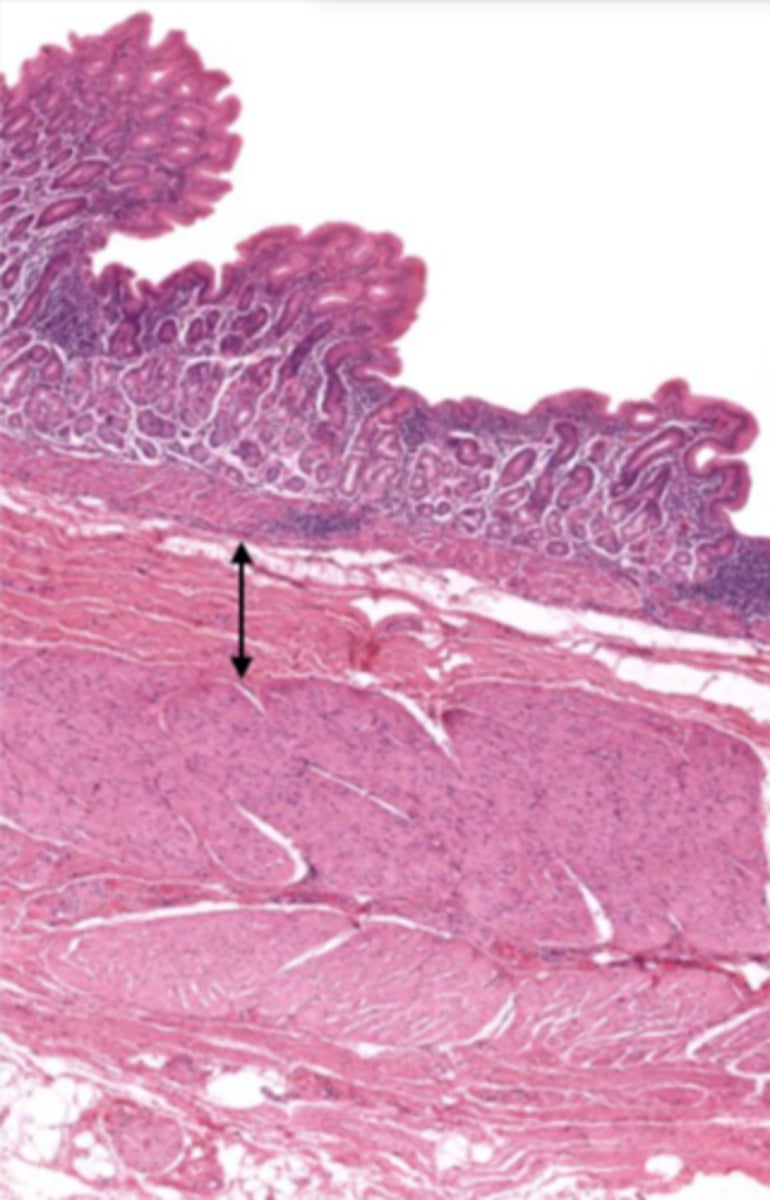
muscularis externa (cardiac stomach)
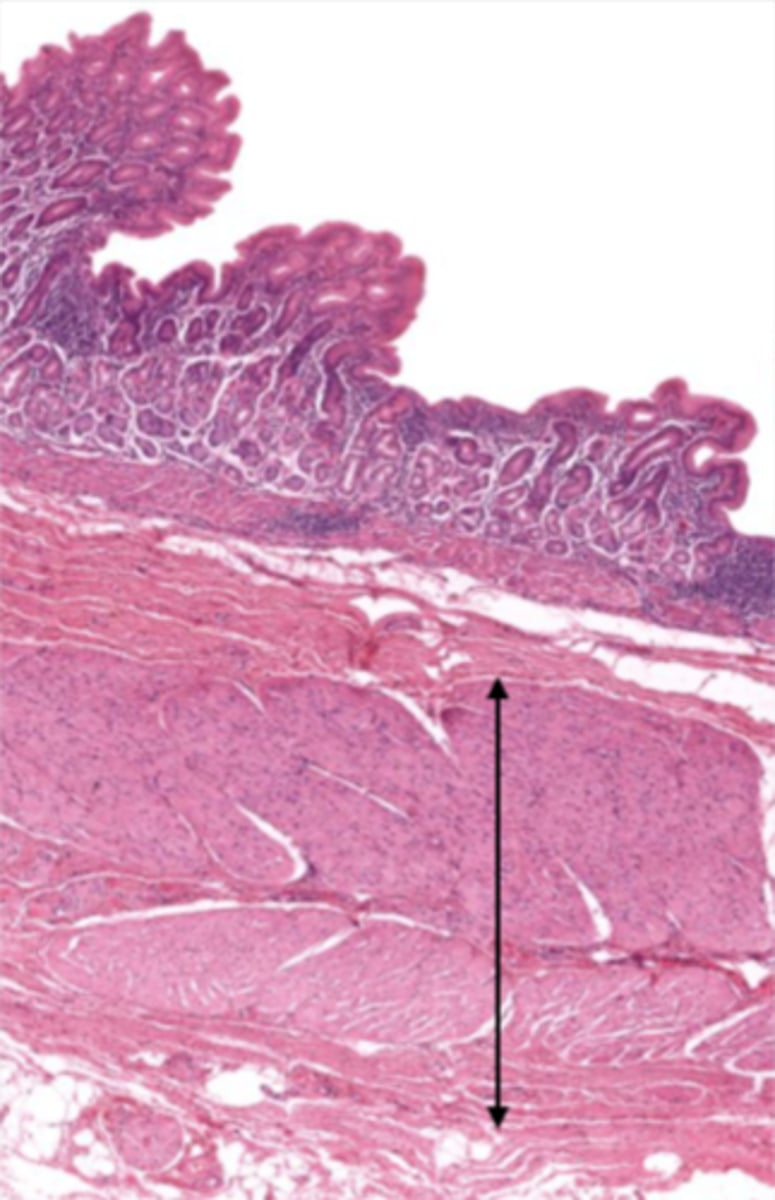
serosa/adventitia (cardiac stomach)
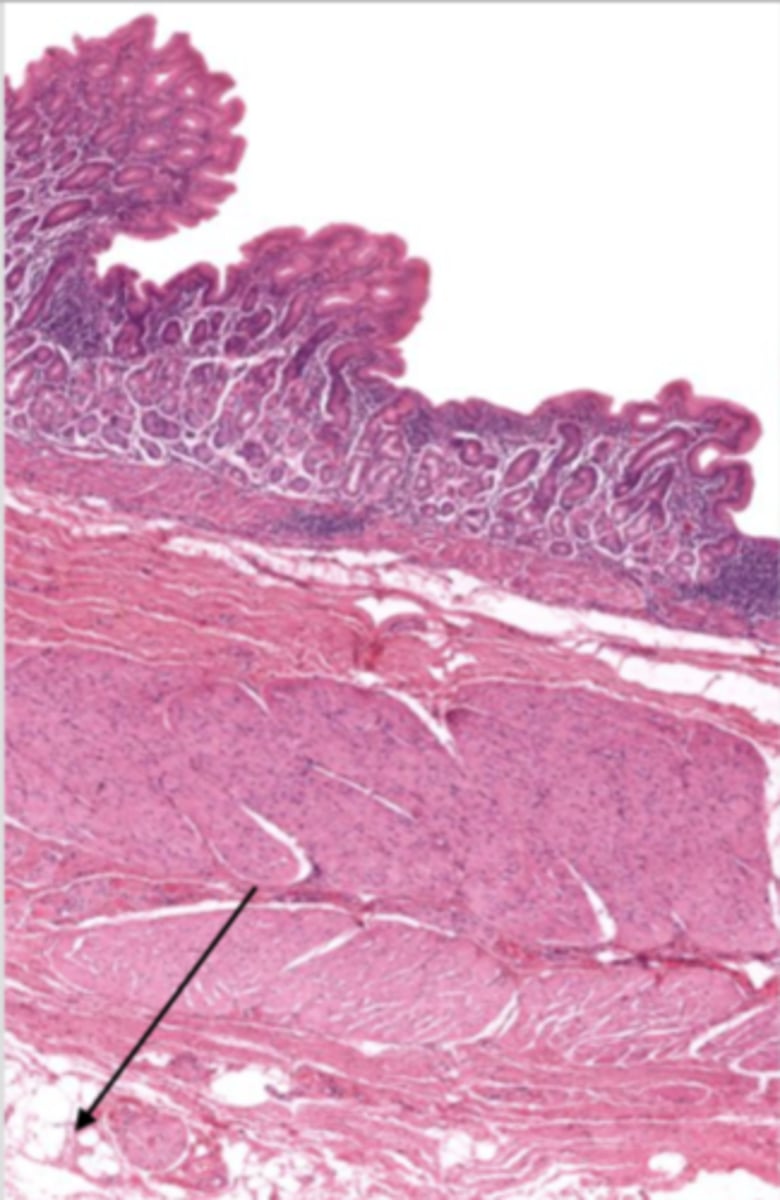
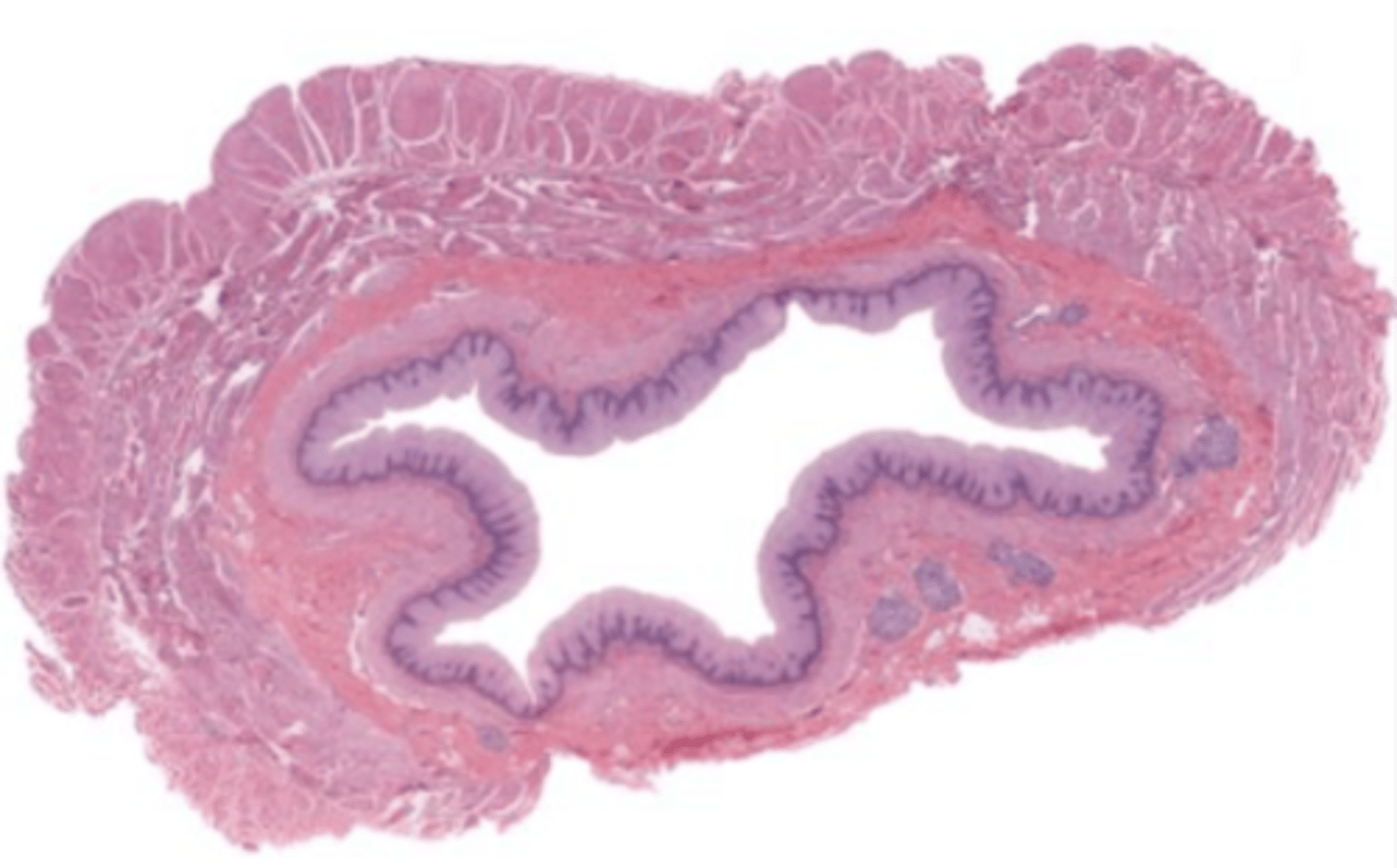
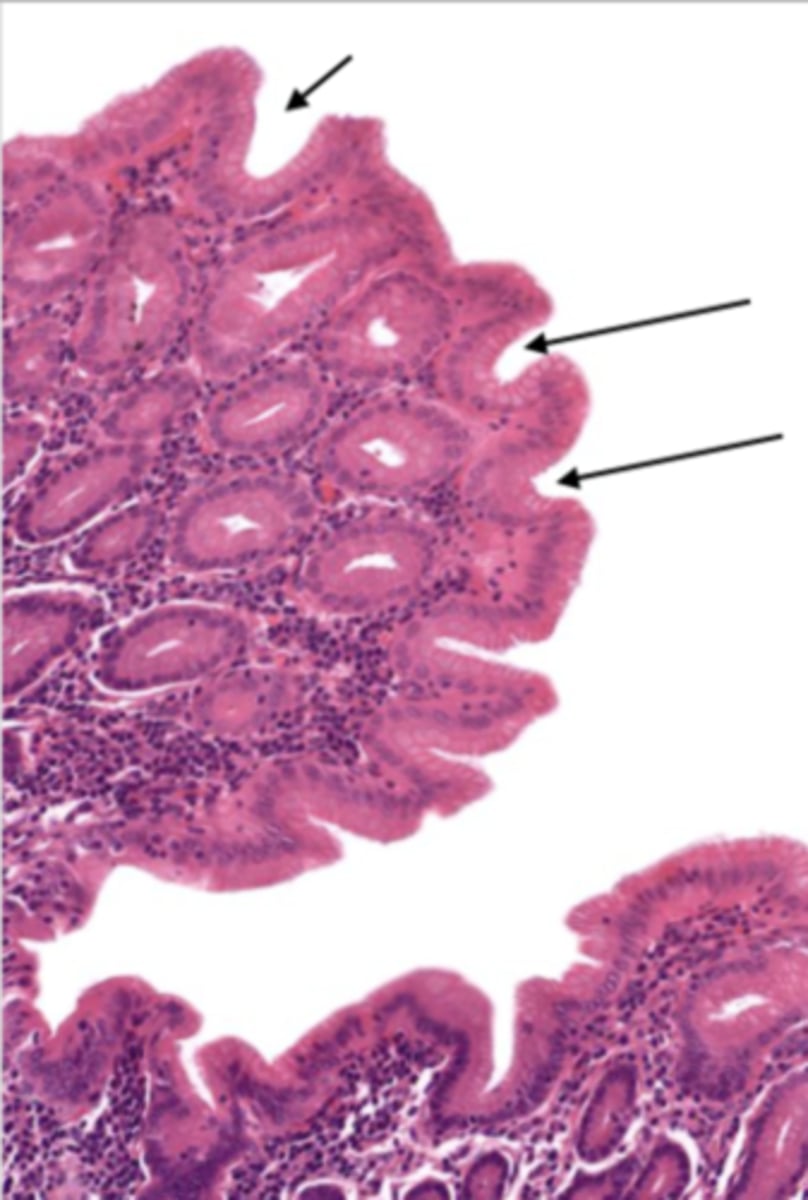
jejunum (histology)
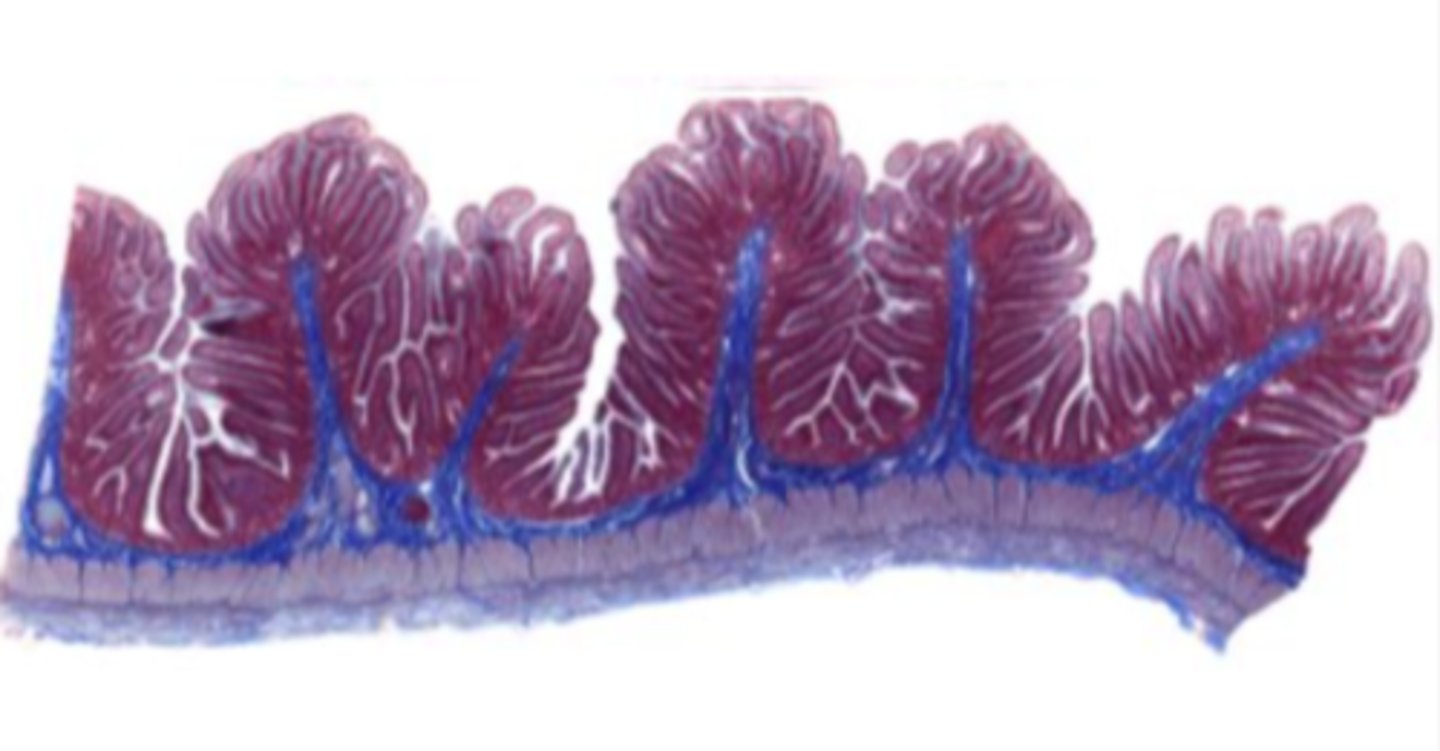
simple columnar epithelium
what kind of epithelium lines the mucosa of the jejunum?
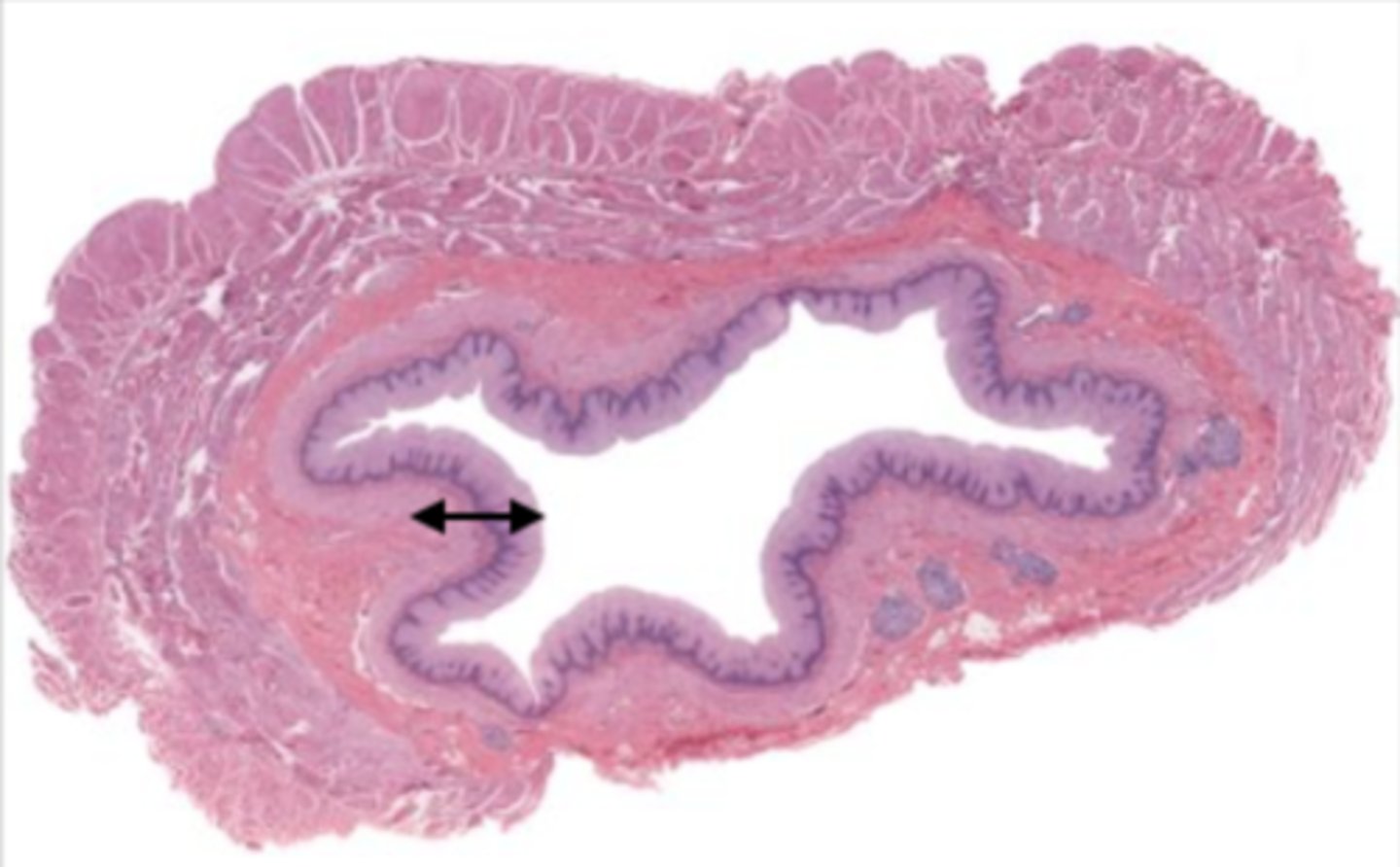
villi (jejunum)
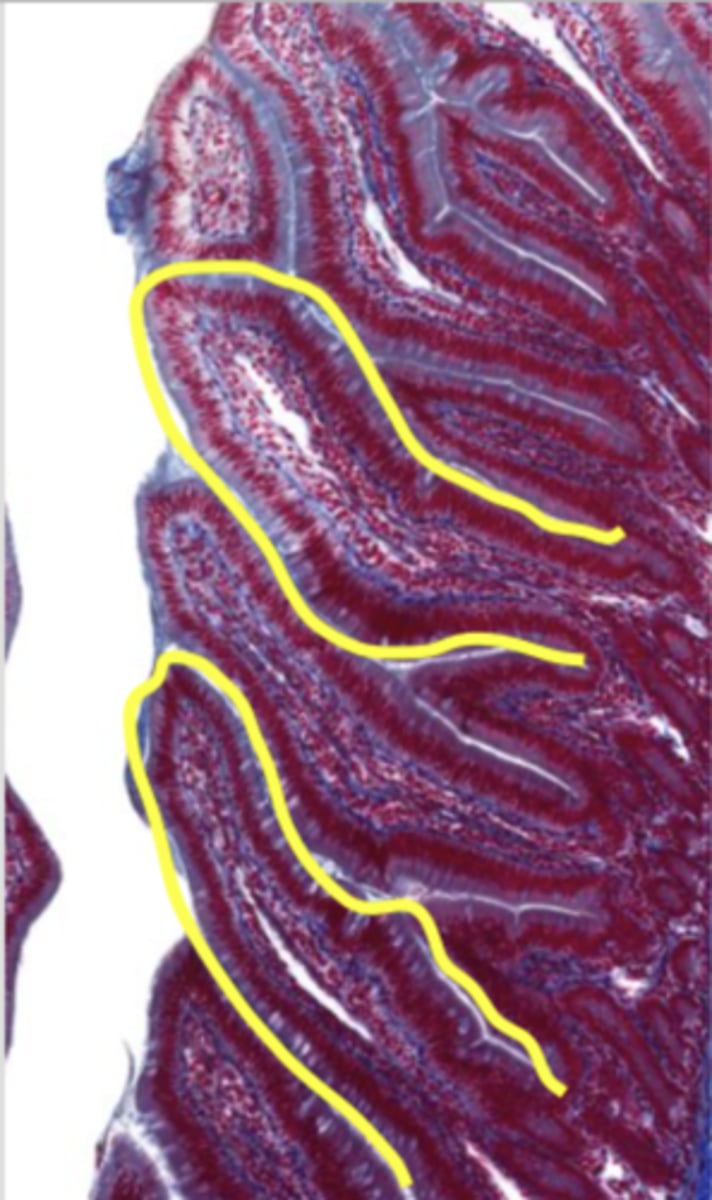
intestinal crypts (jejunum)
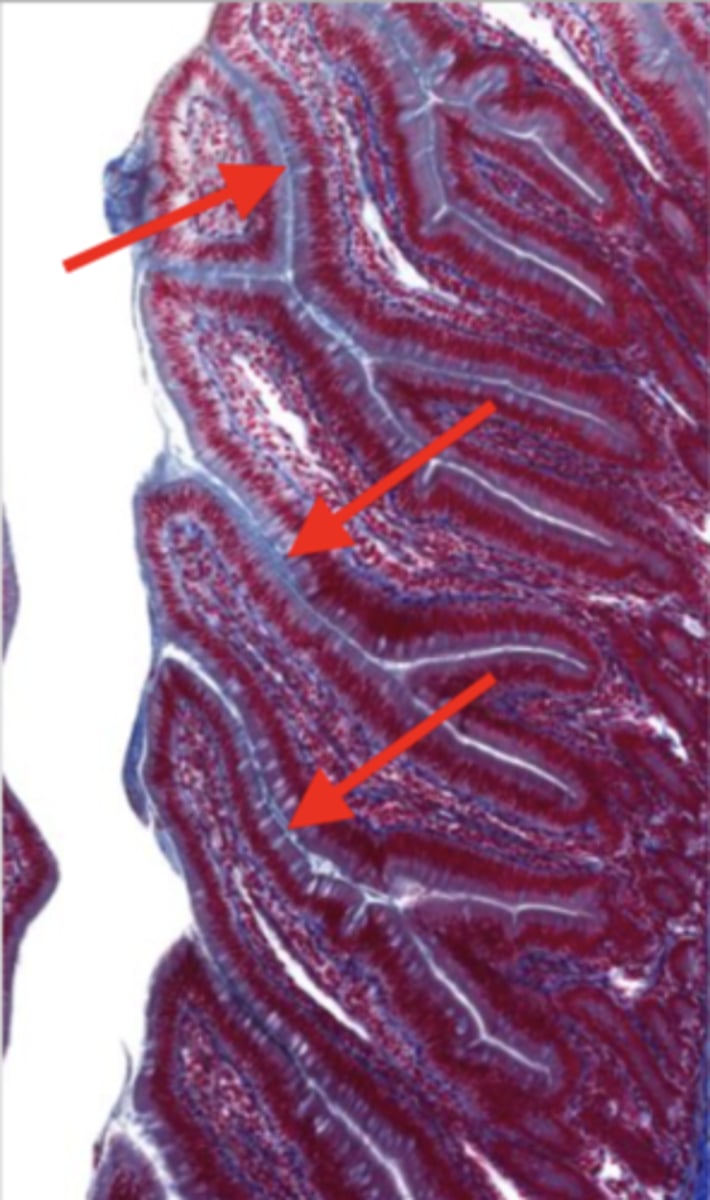
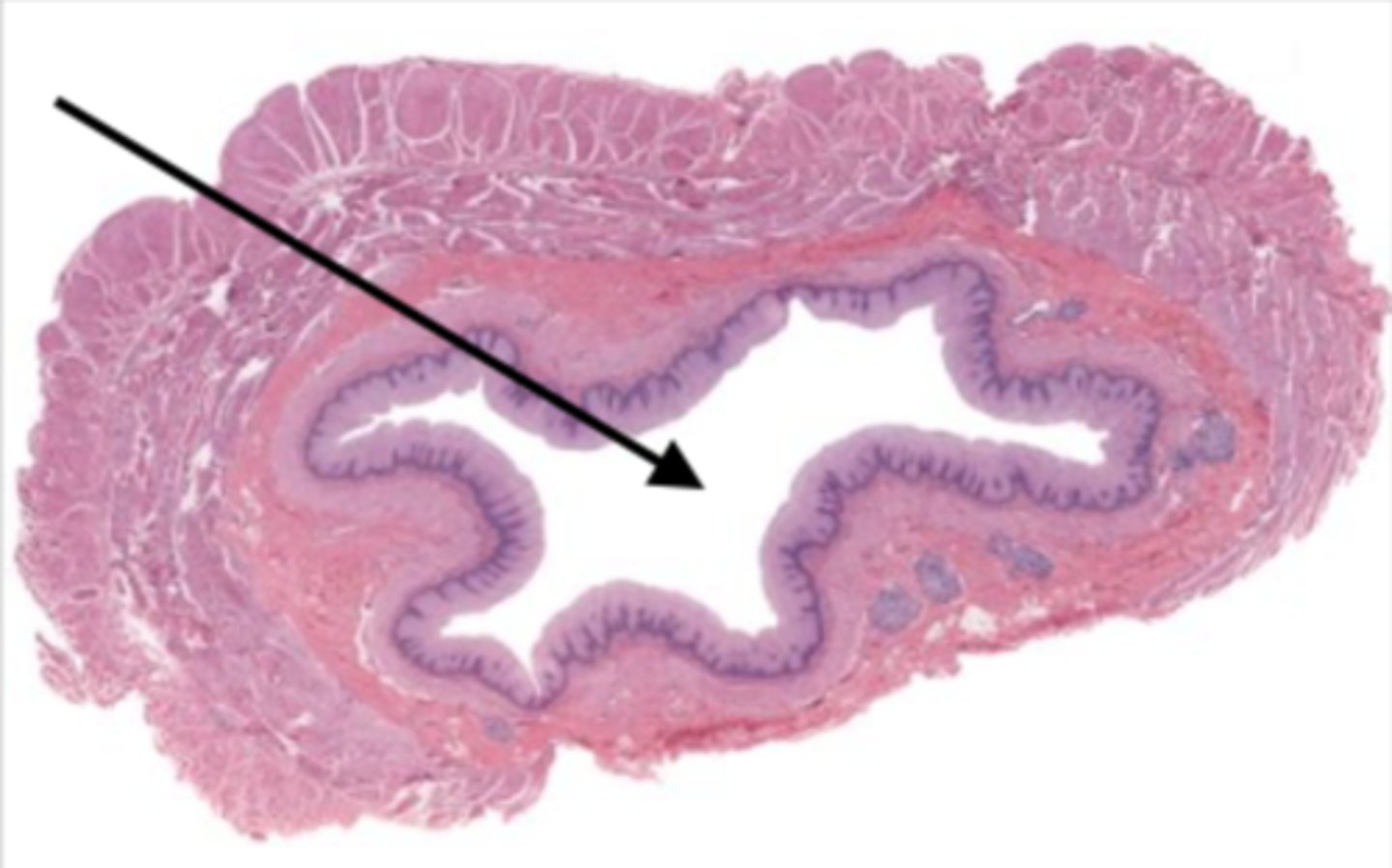
lumen (jejunum)
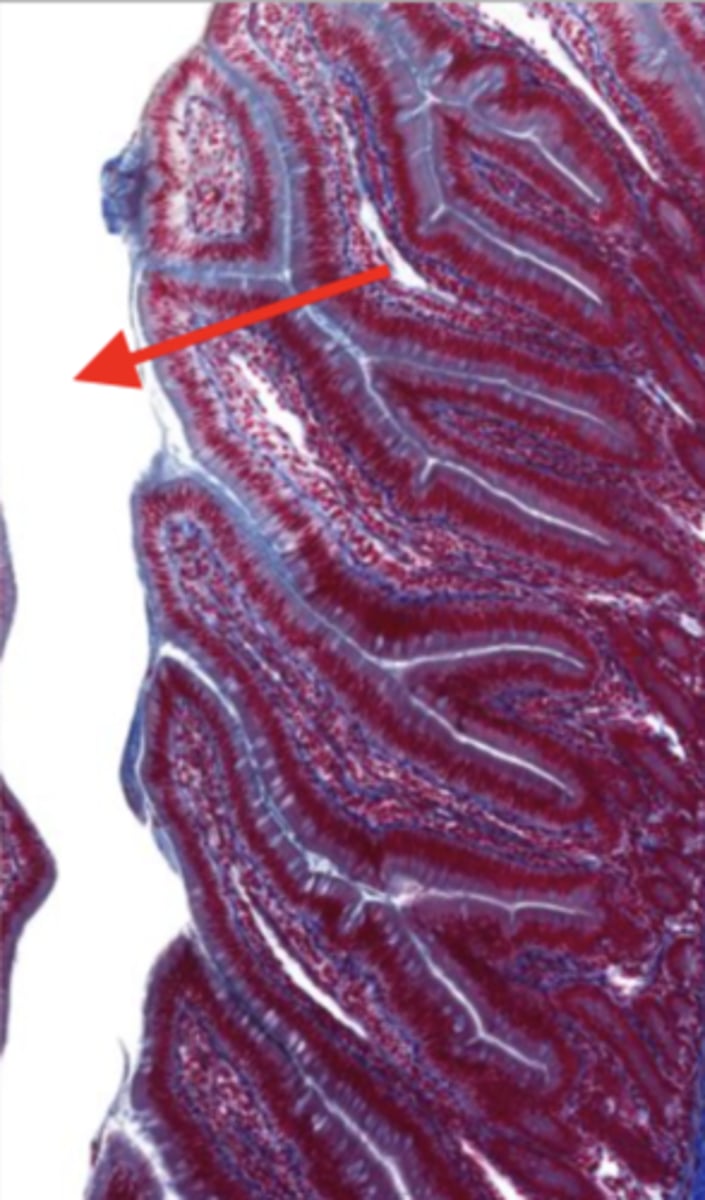
mucosa (jejunum)
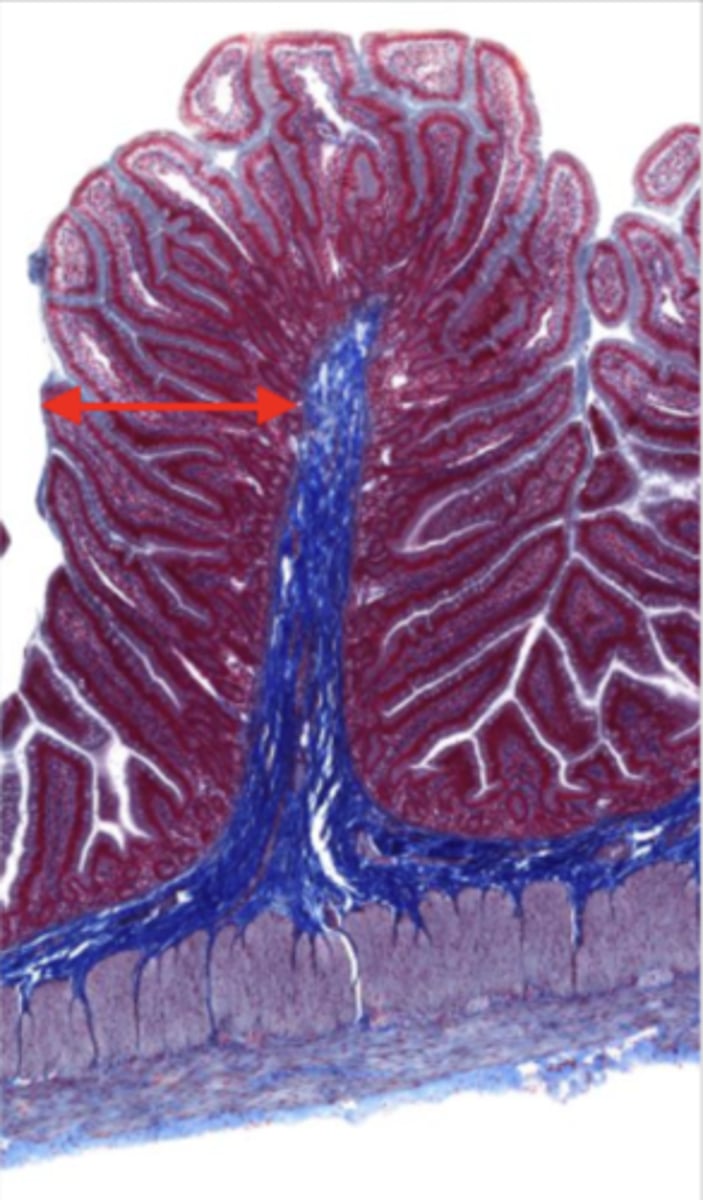
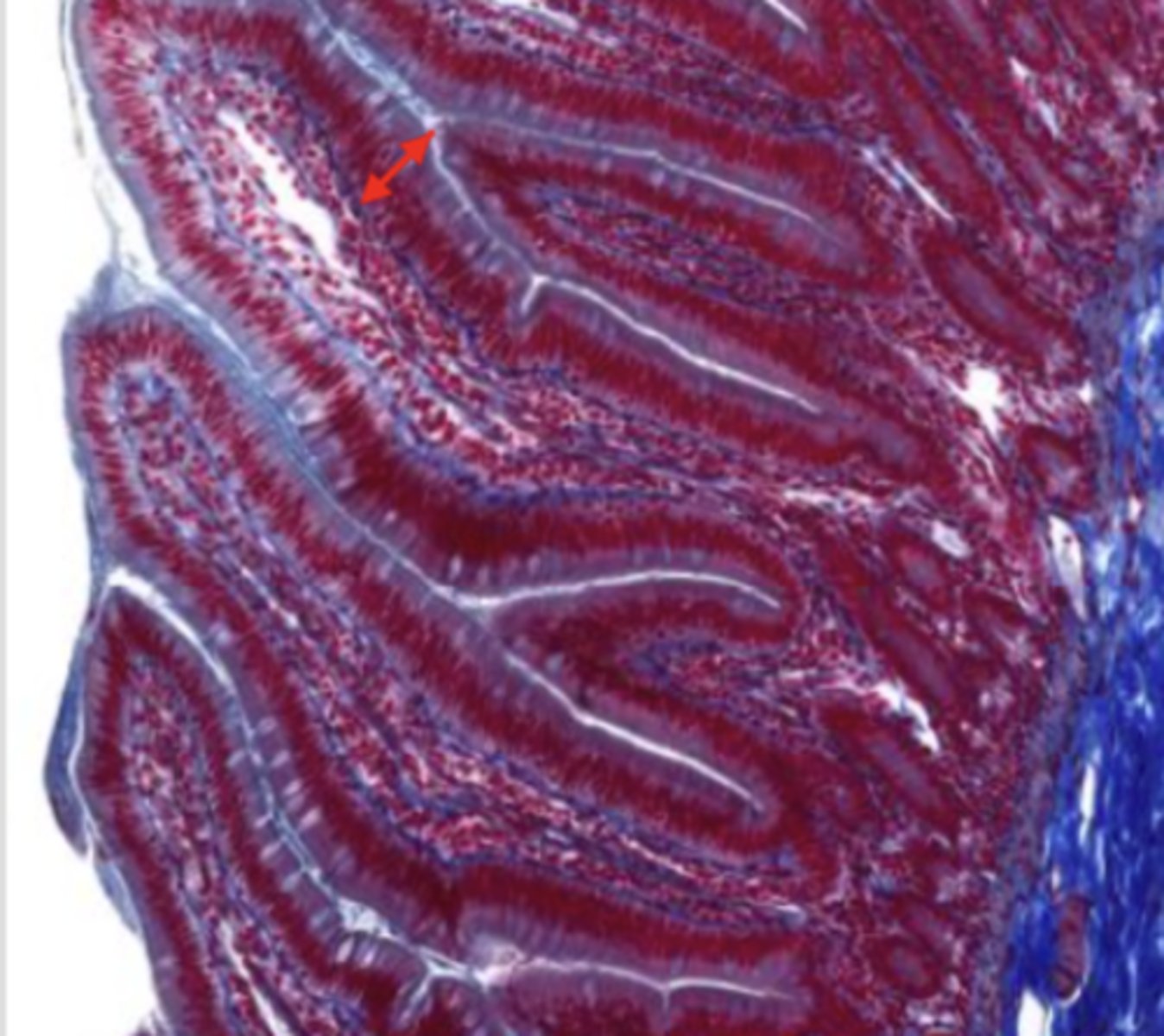
mucosal epithelium (jejunum)
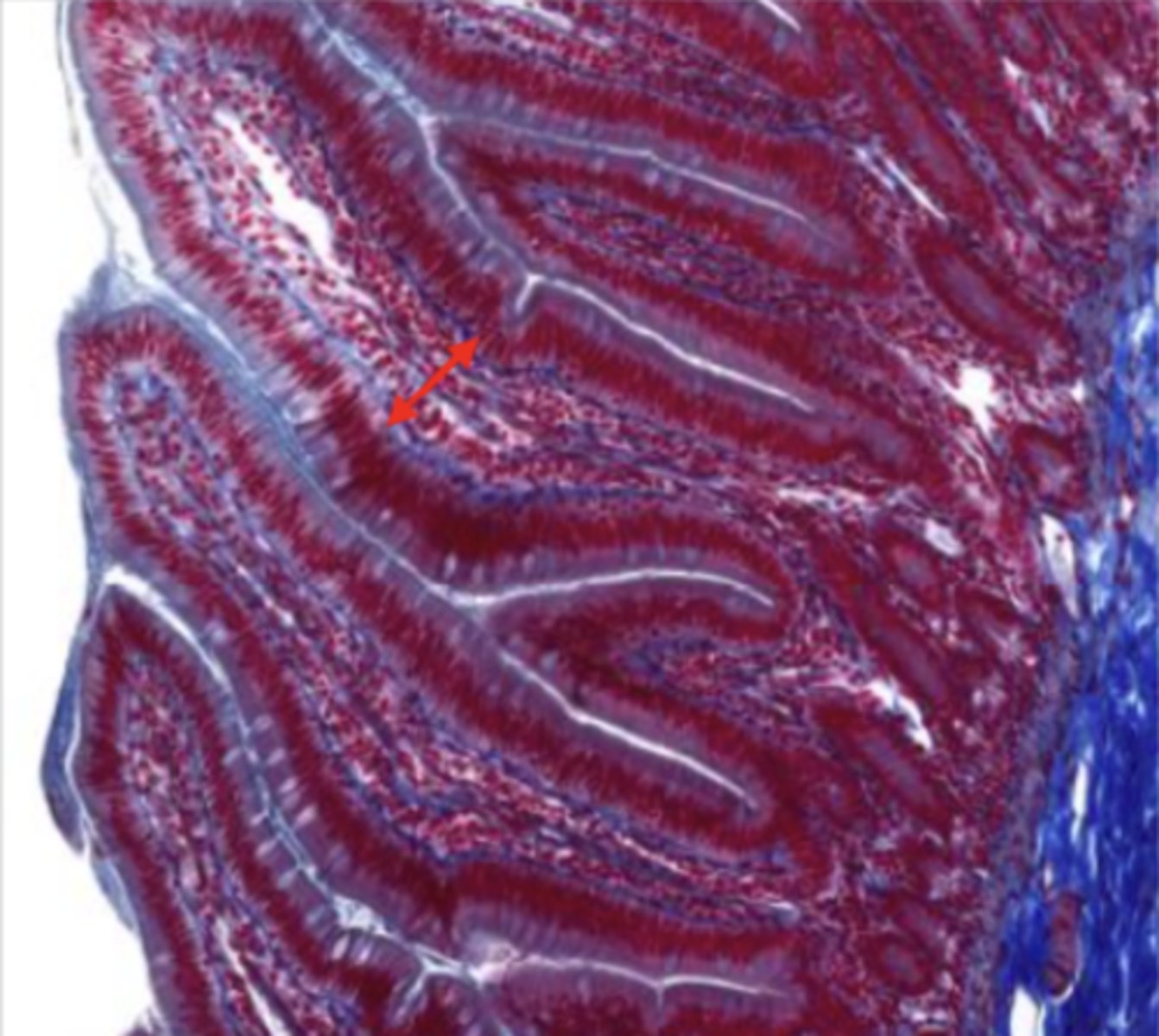
lamina propria (jejunum)
muscularis mucosa (jejunum)
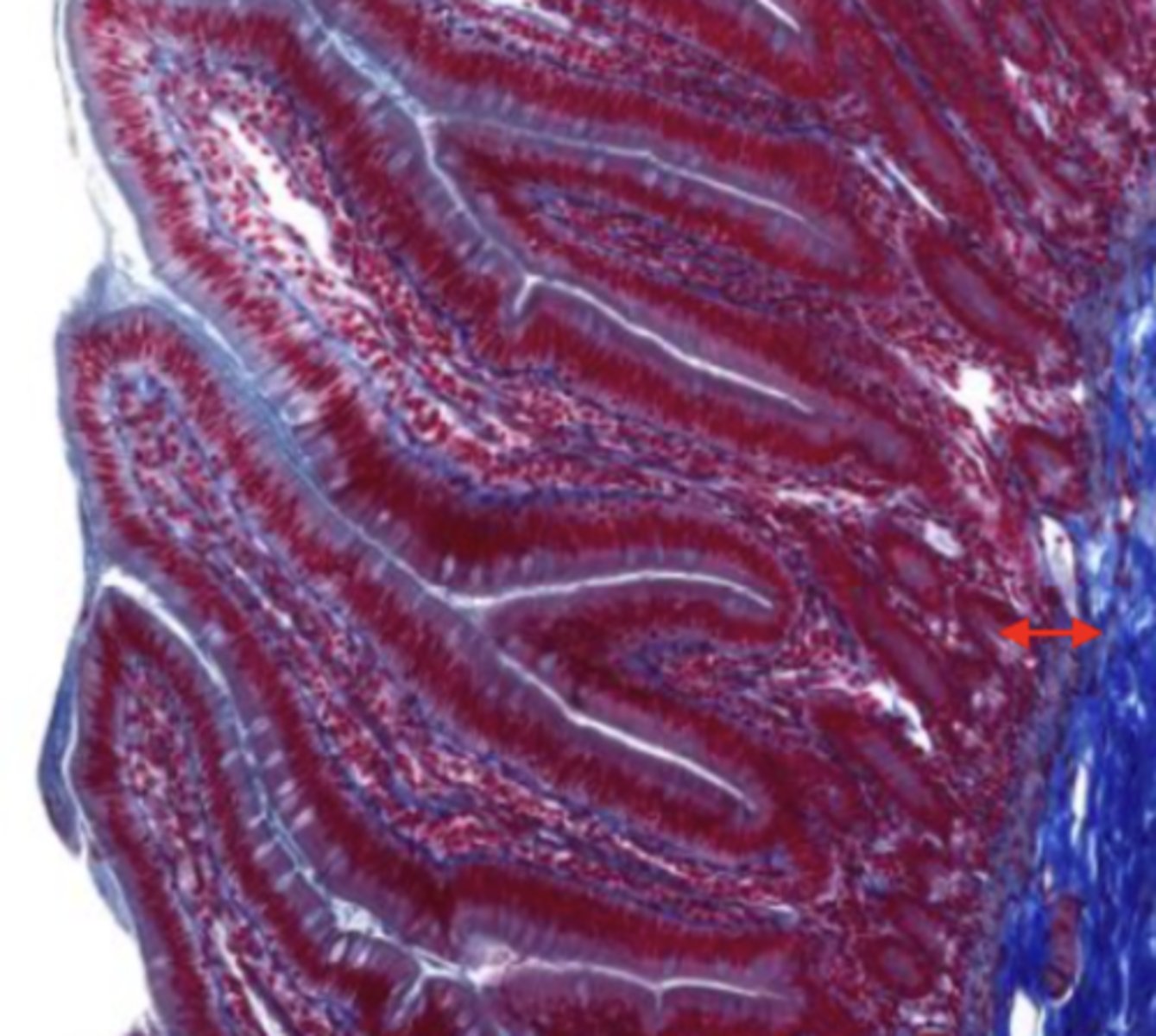
submucosa (jejunum)
contains glands and blood supply
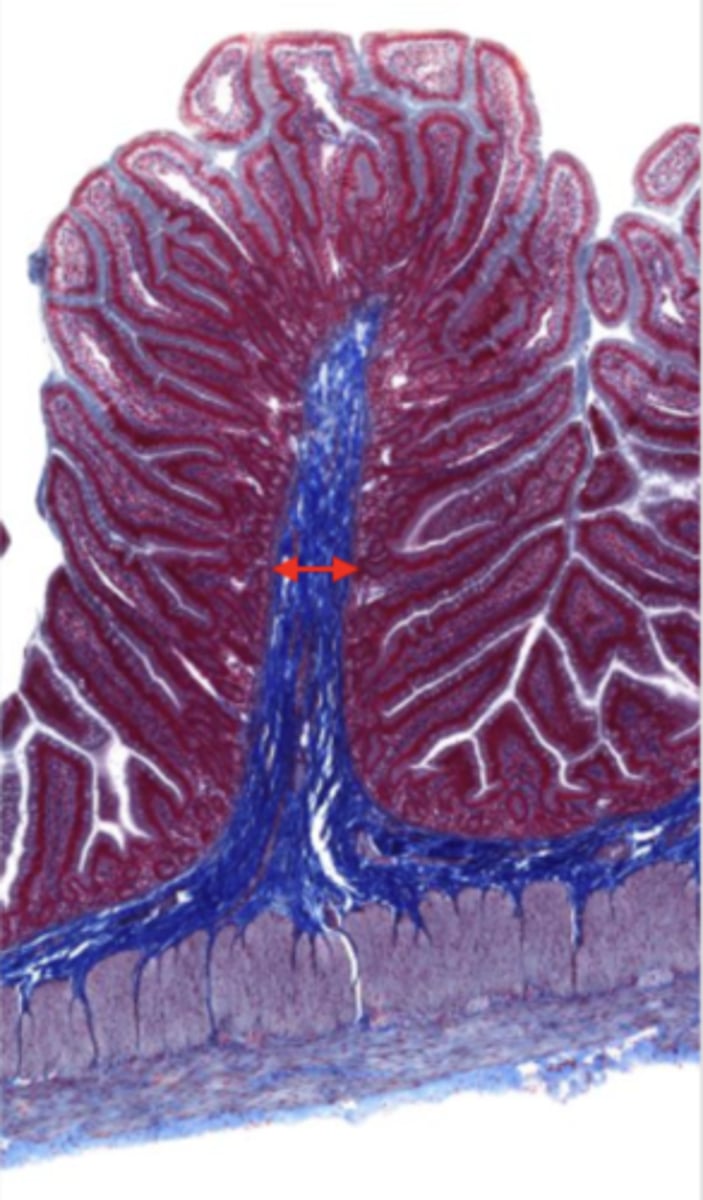
muscularis externa (jejunum)
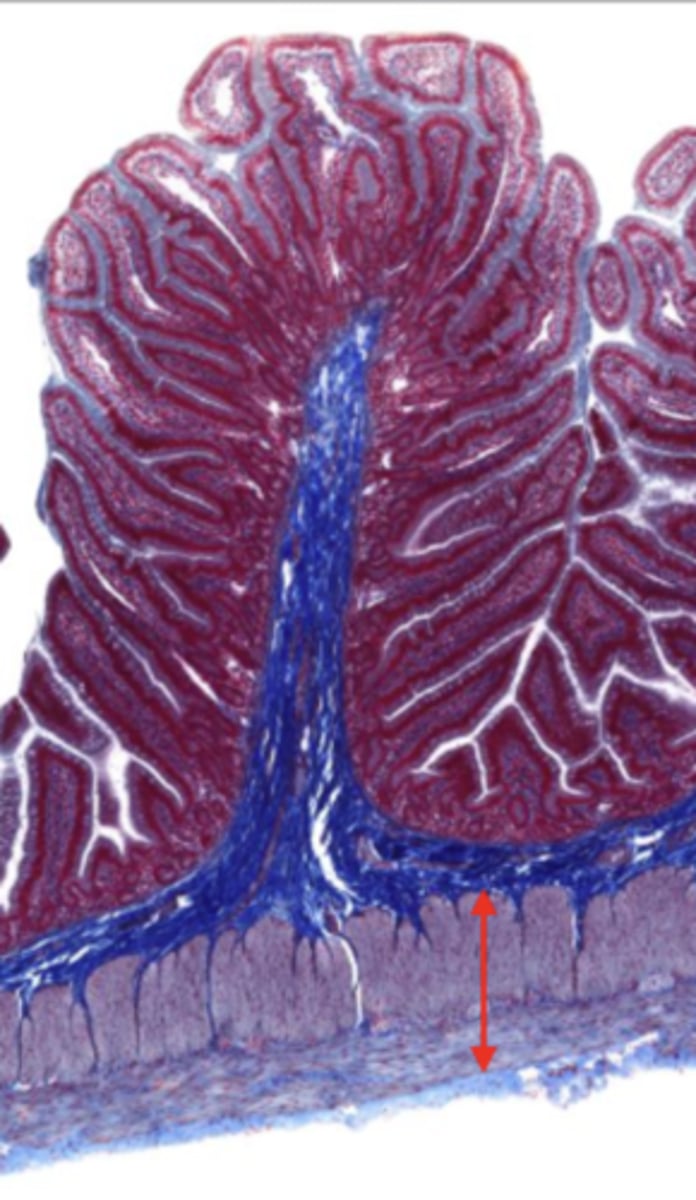
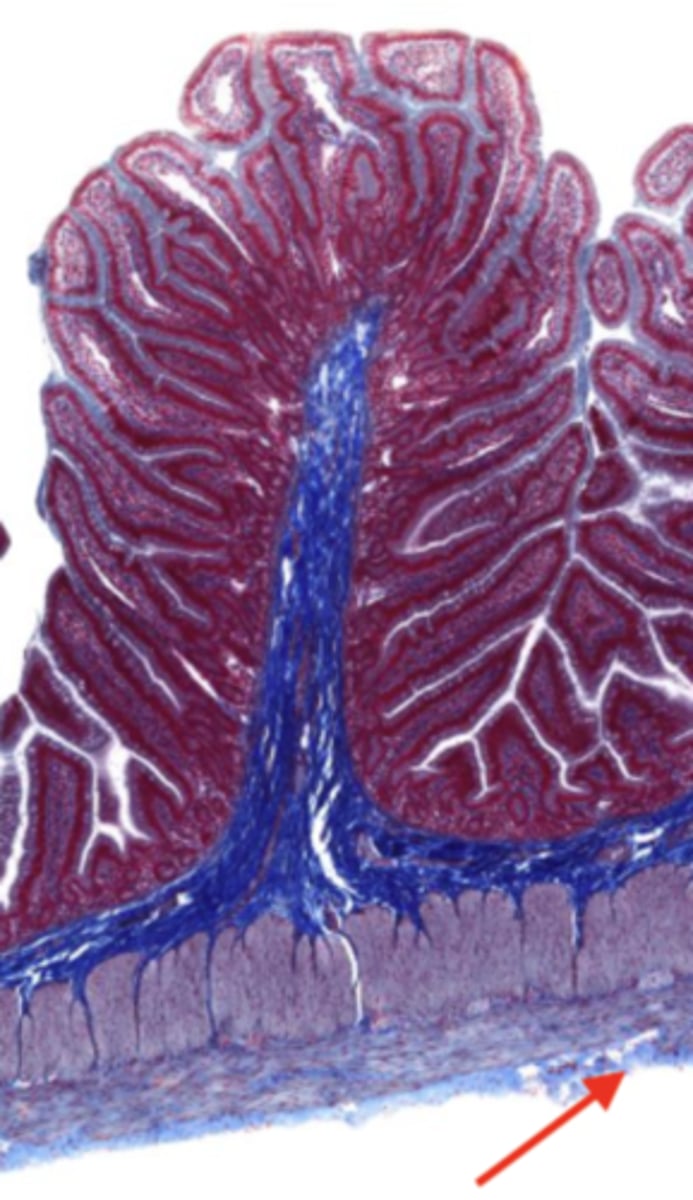
serosa/adventitia (jejunum)
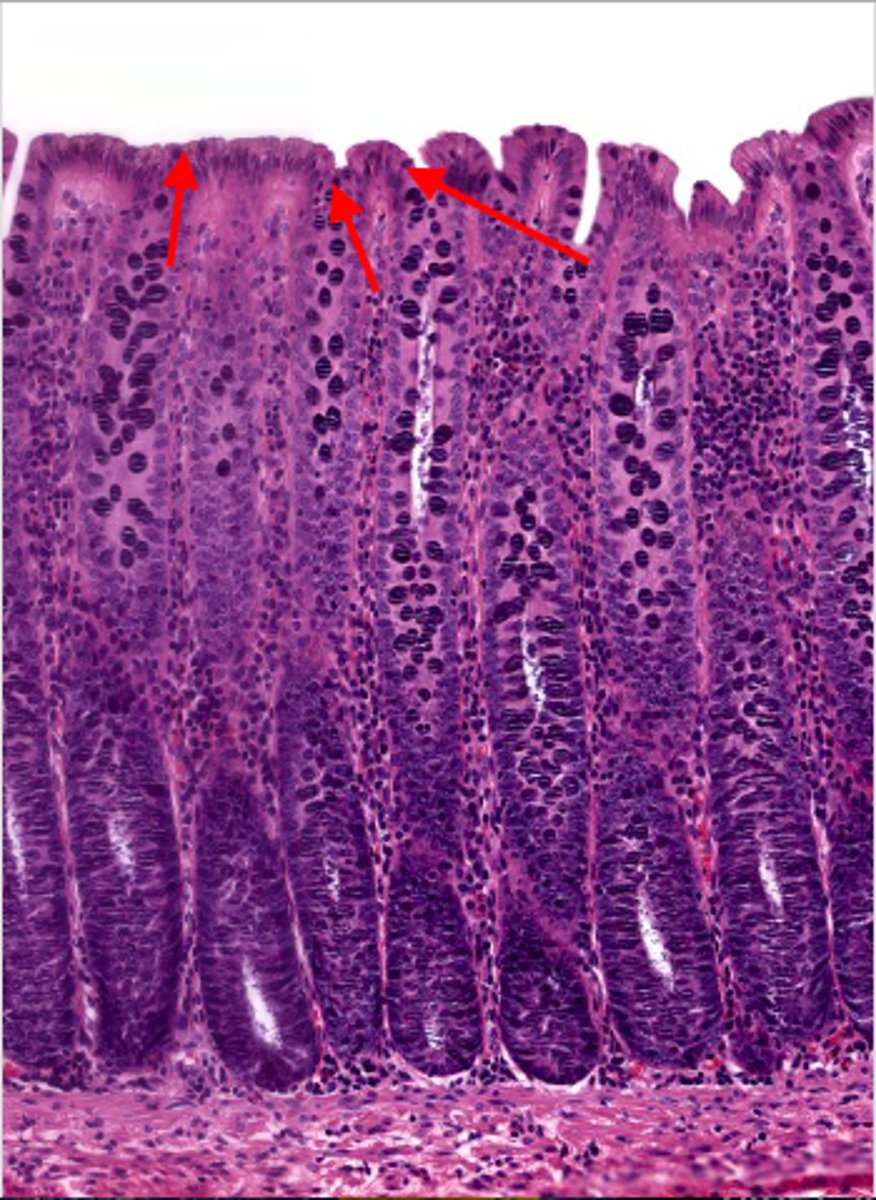
colon (histology)
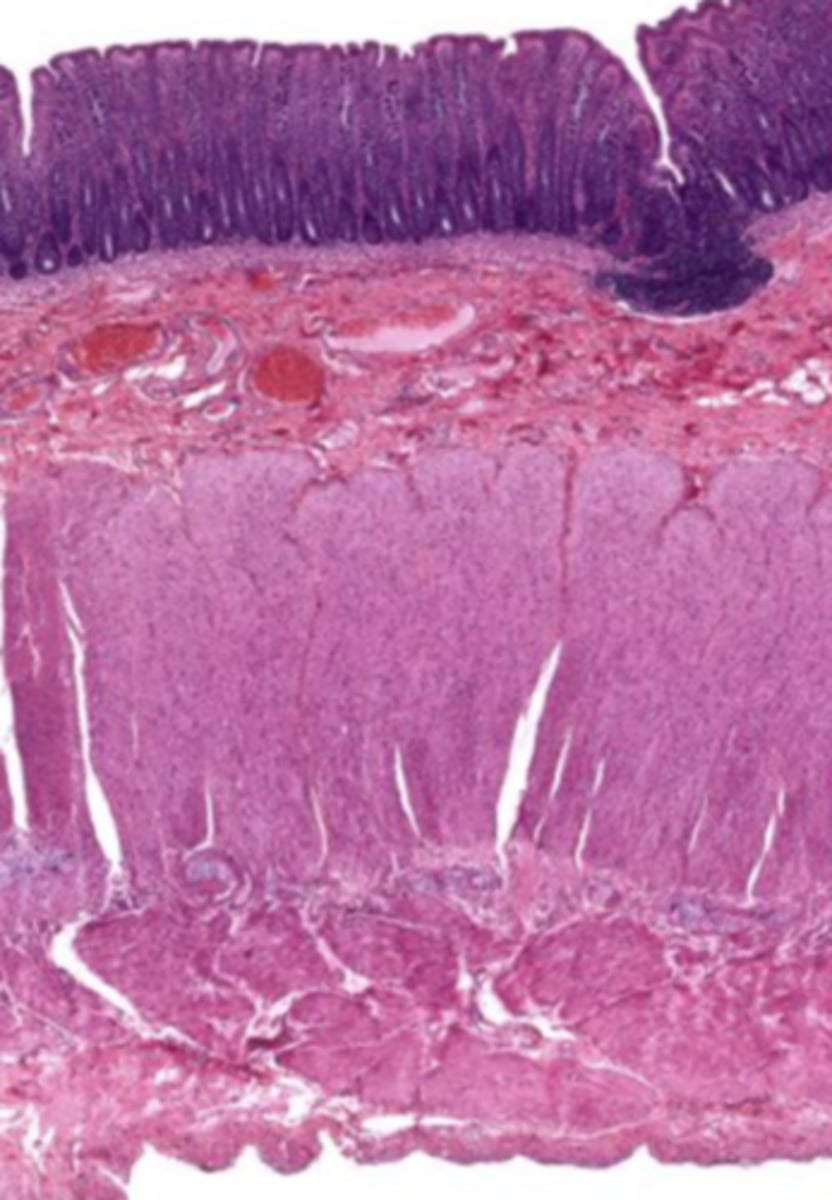
simple columnar epithelium
what kind of epithelium lines the mucosa of the colon?
intestinal glands/crypts (colon)
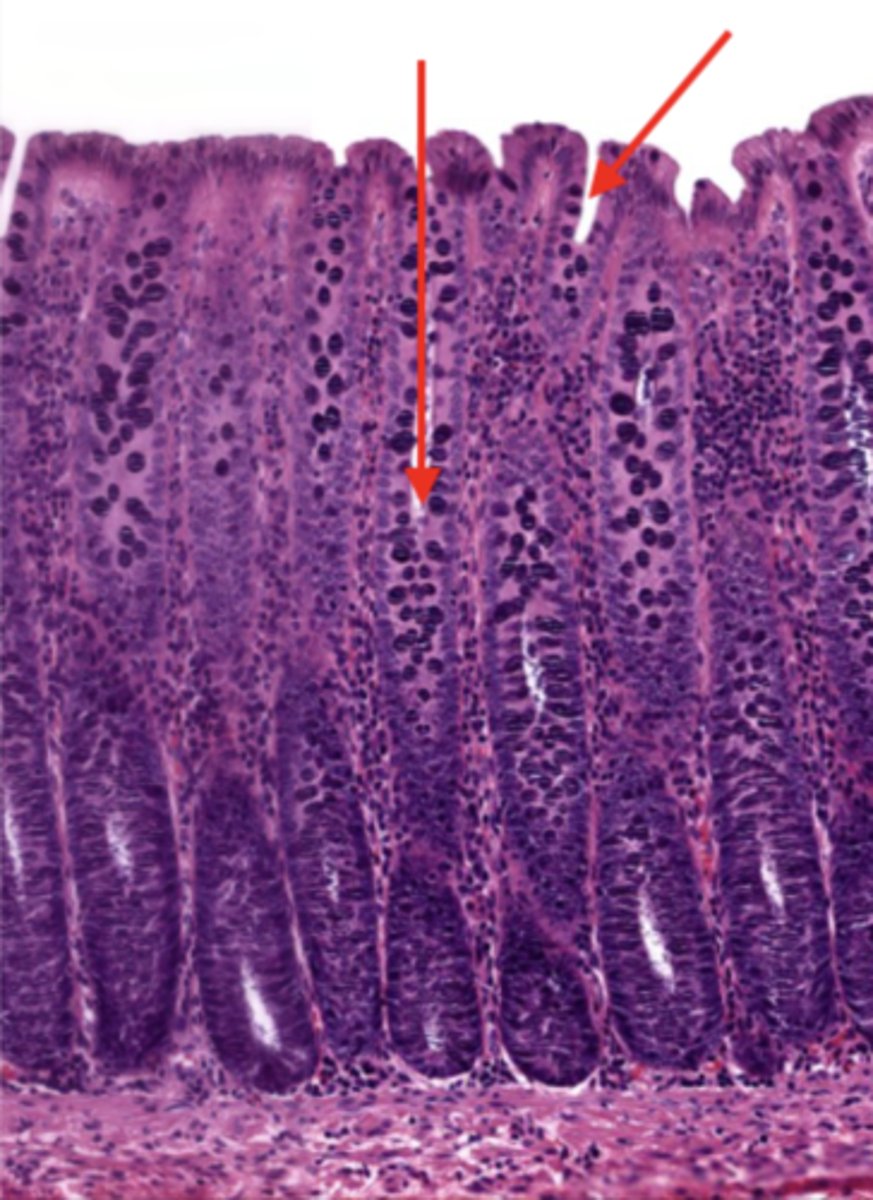
lumen (colon)
mucosa (colon)
mucosal epithelium (colon)
lamina propria (colon)
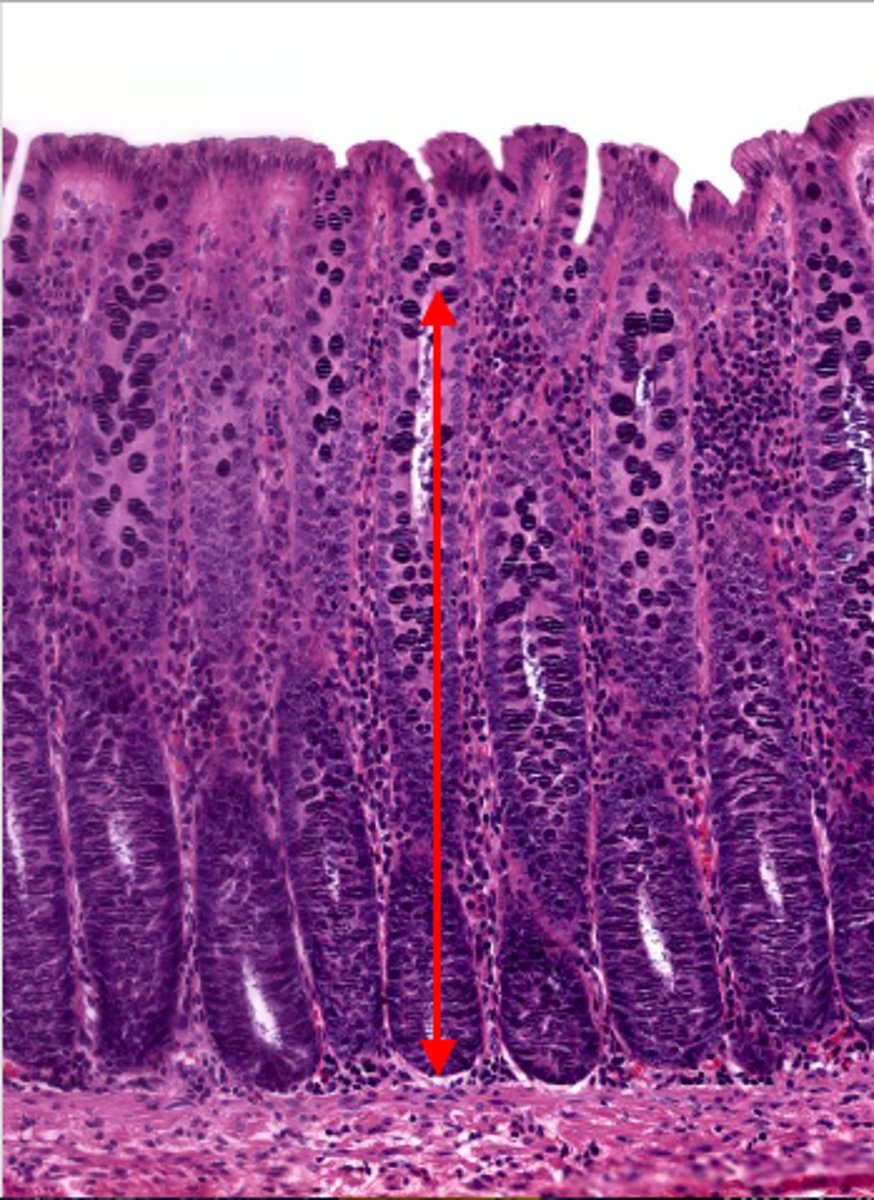
muscularis mucosa (colon)
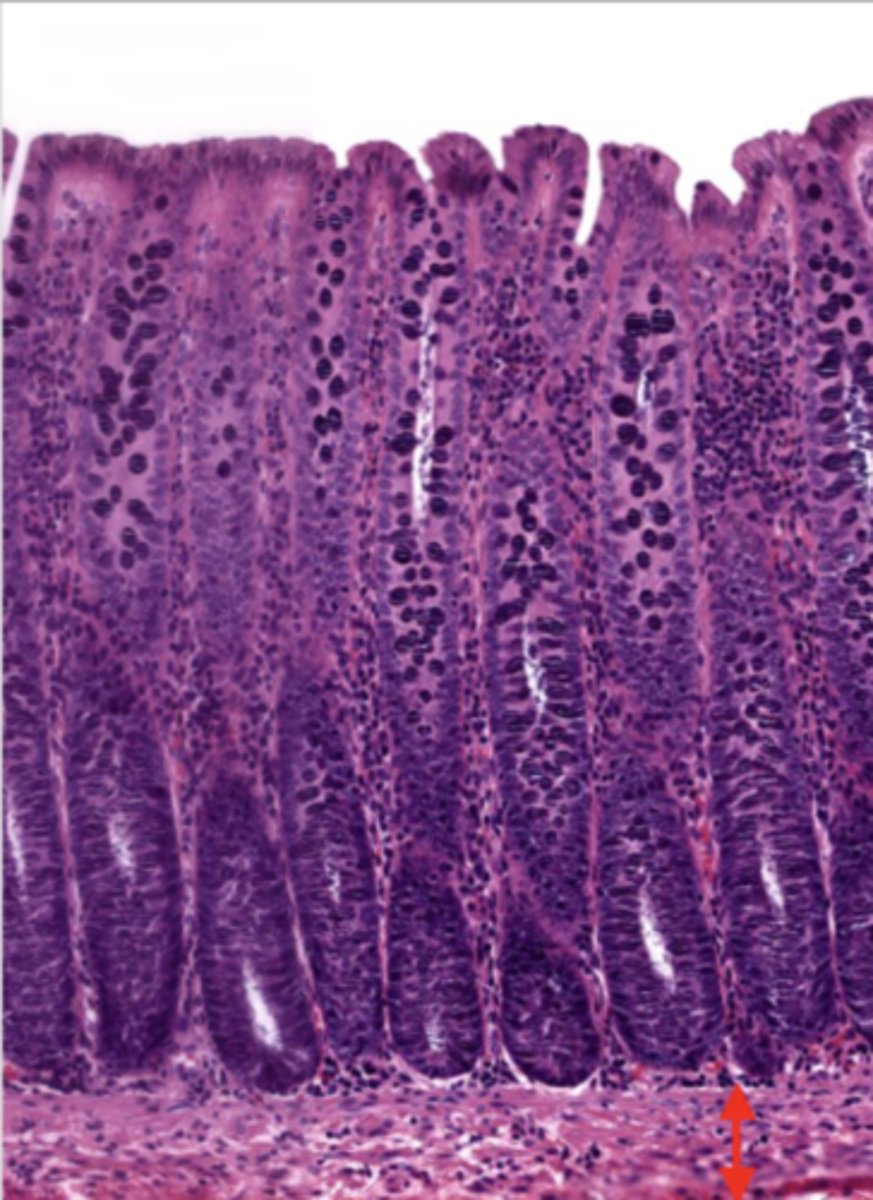
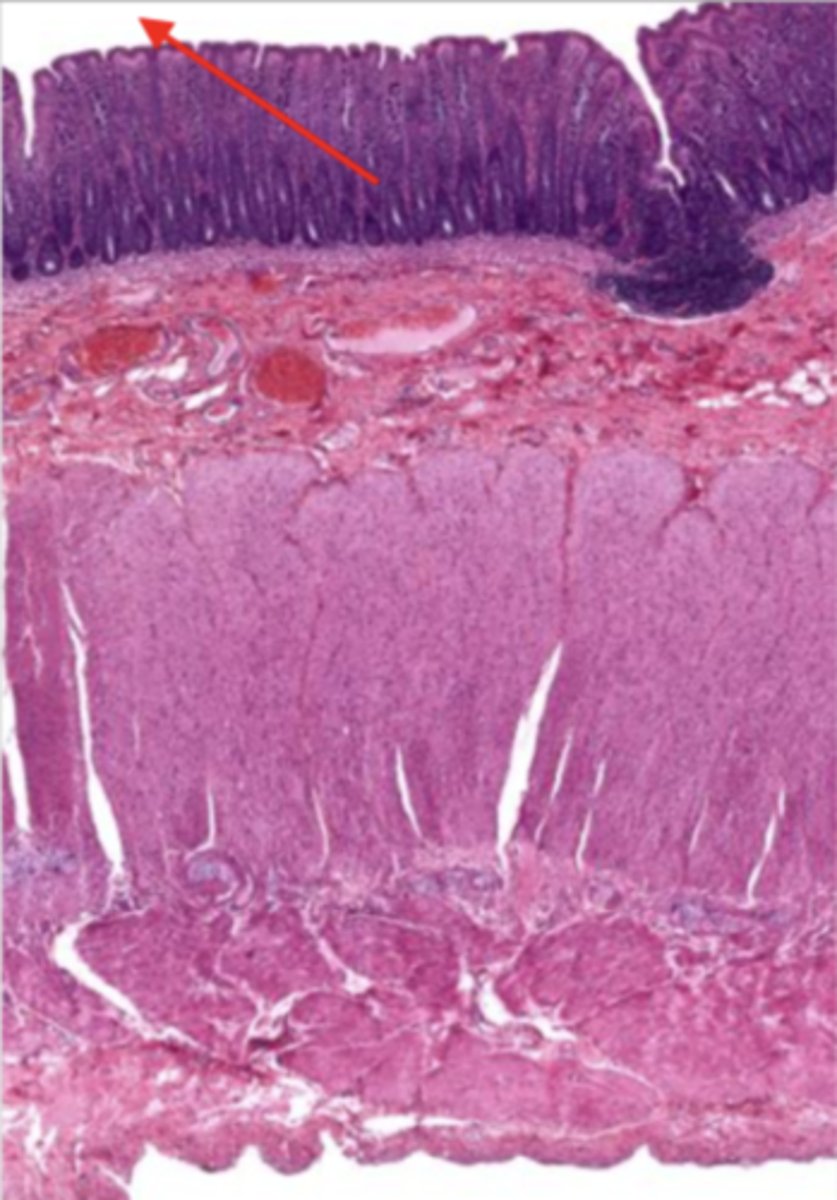
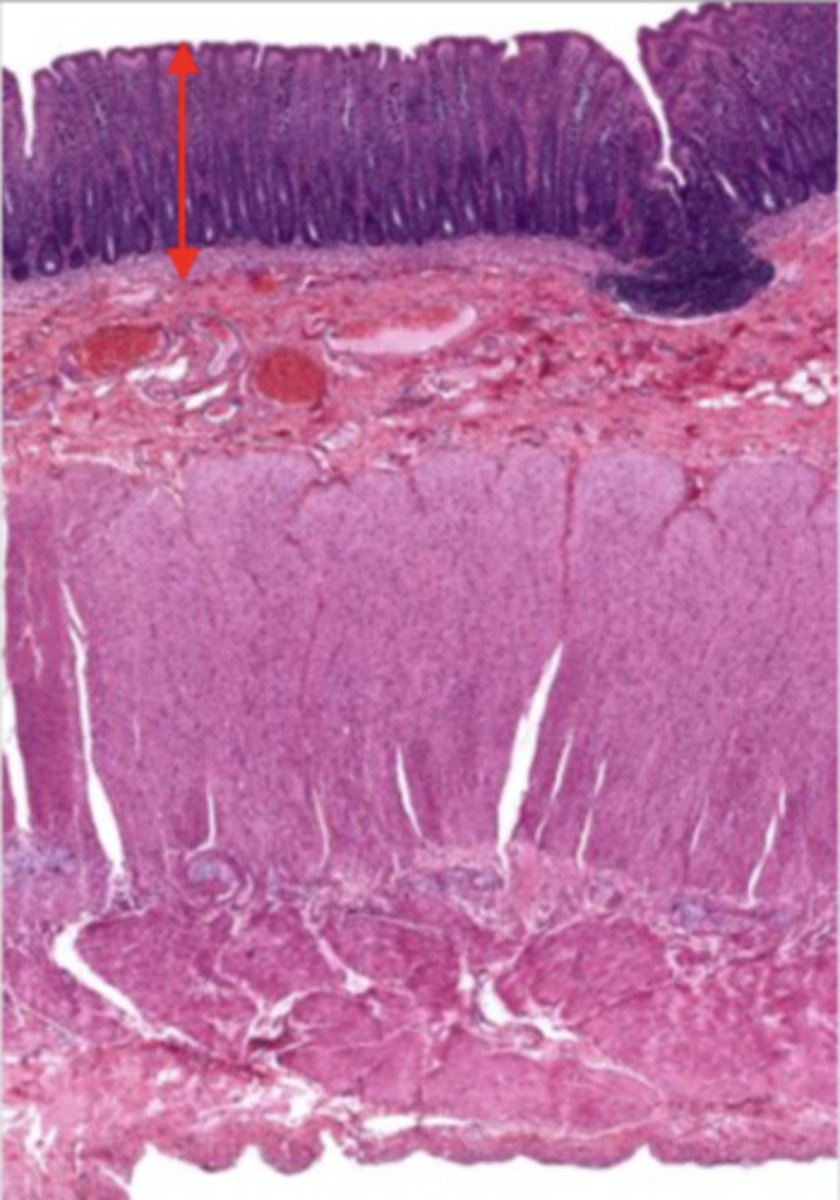
submucosa (colon)
contains glands and blood supply
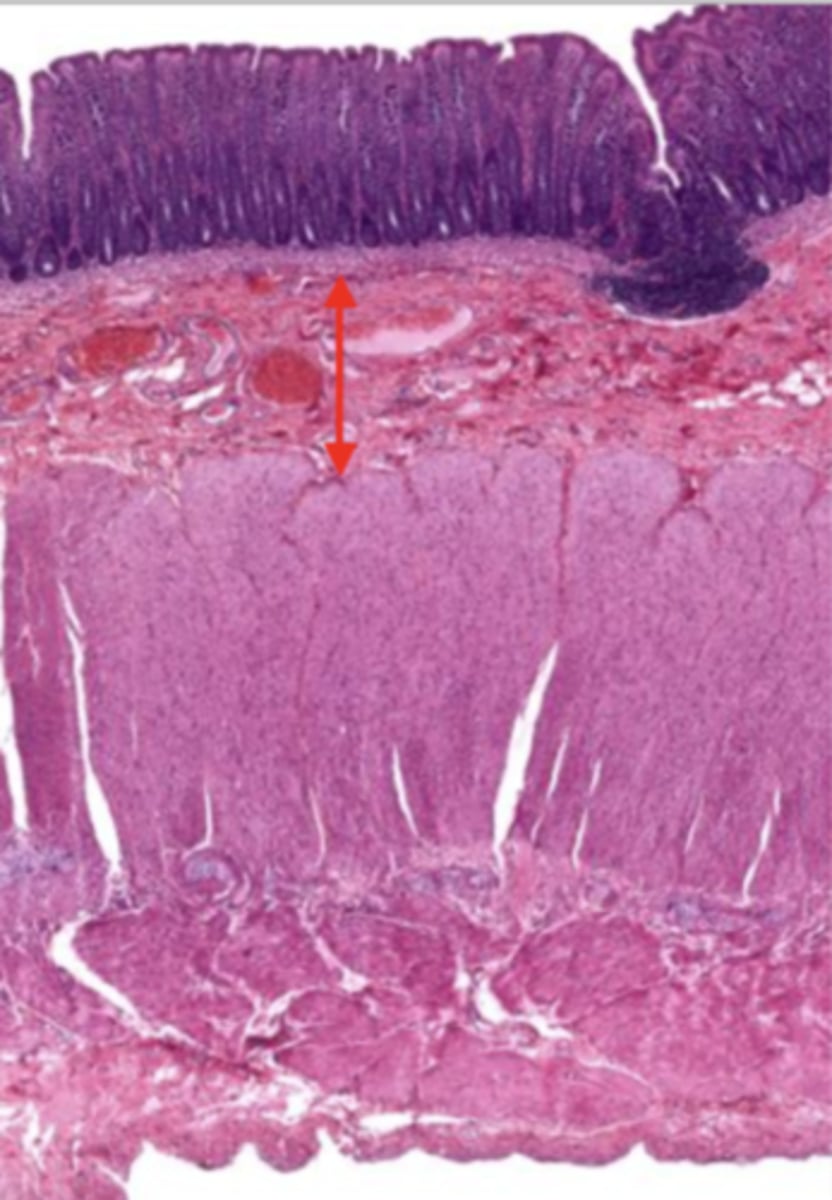
muscularis externa (colon)
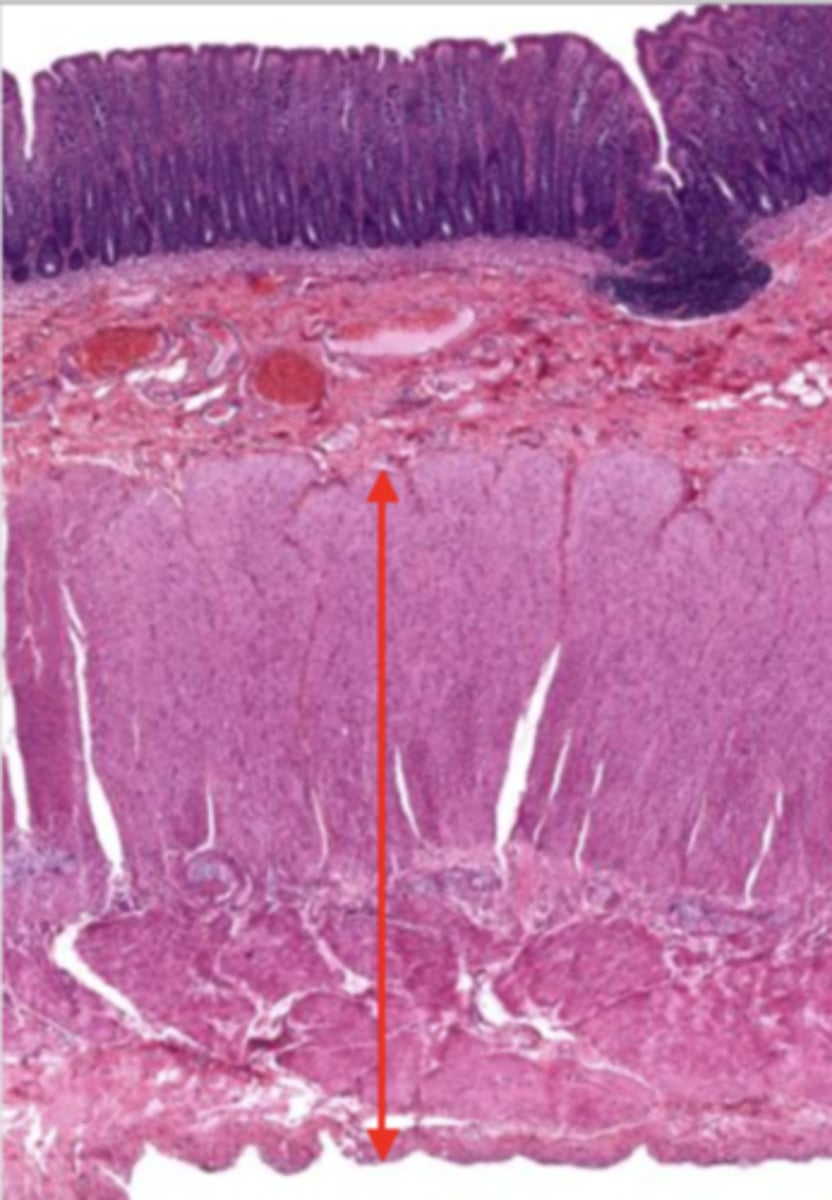
serosa/adventitia (colon)
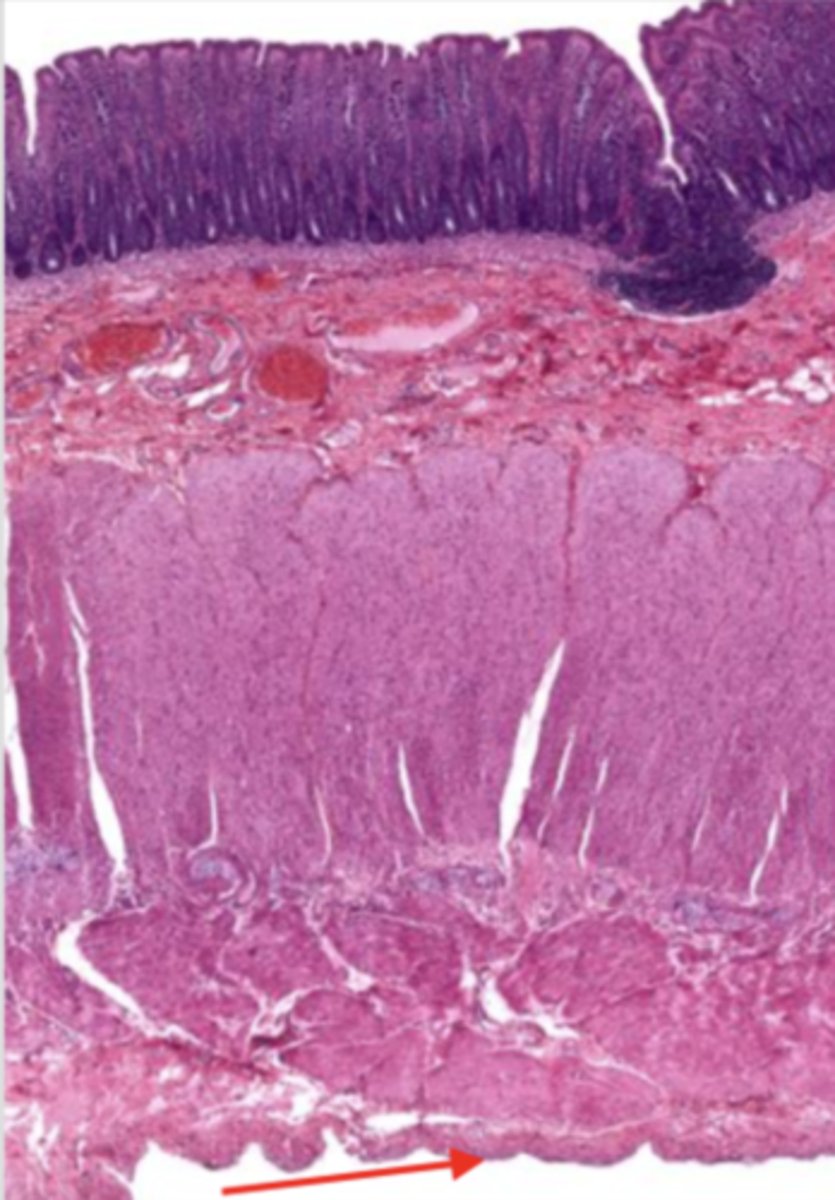
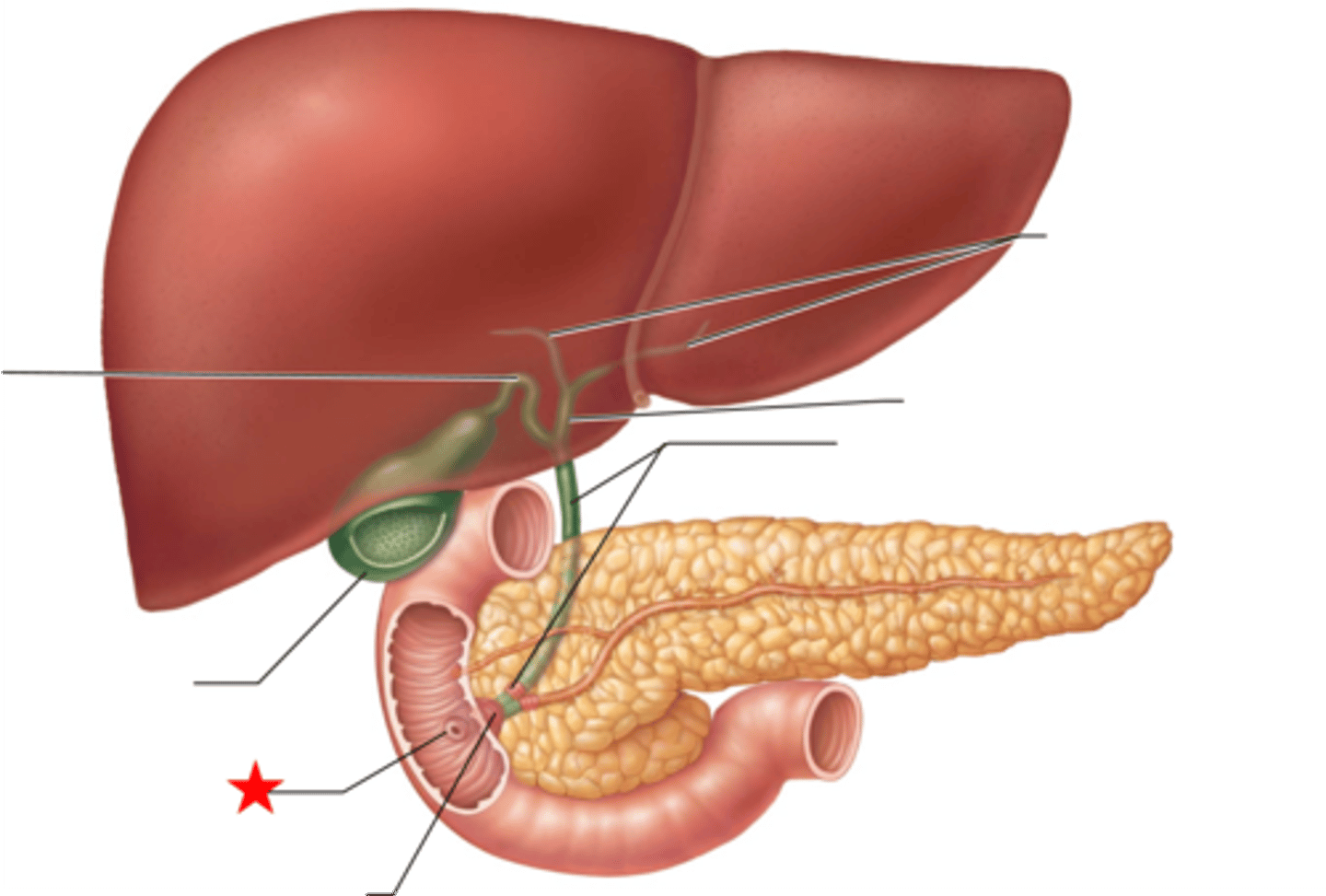
liver (histology)
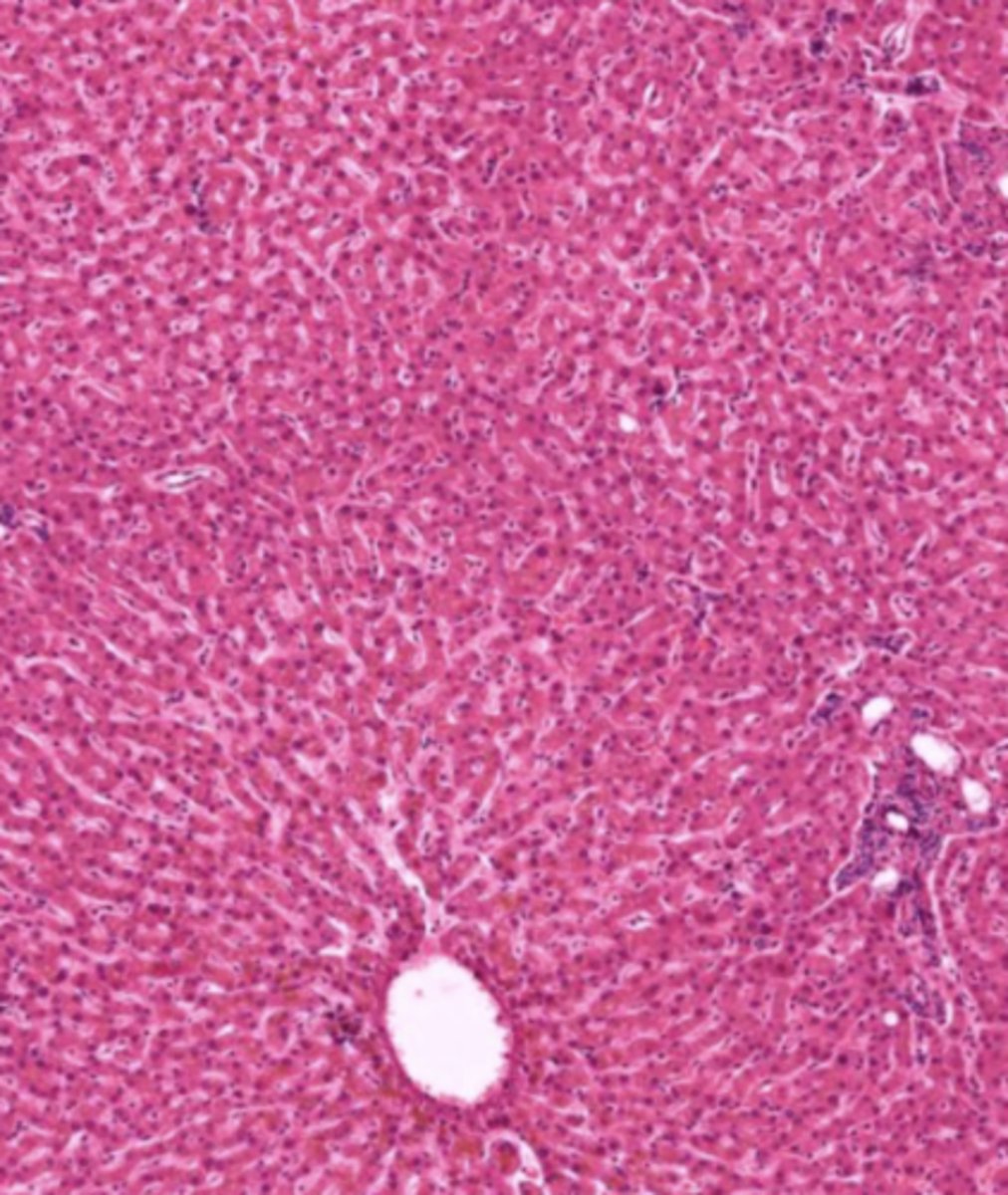
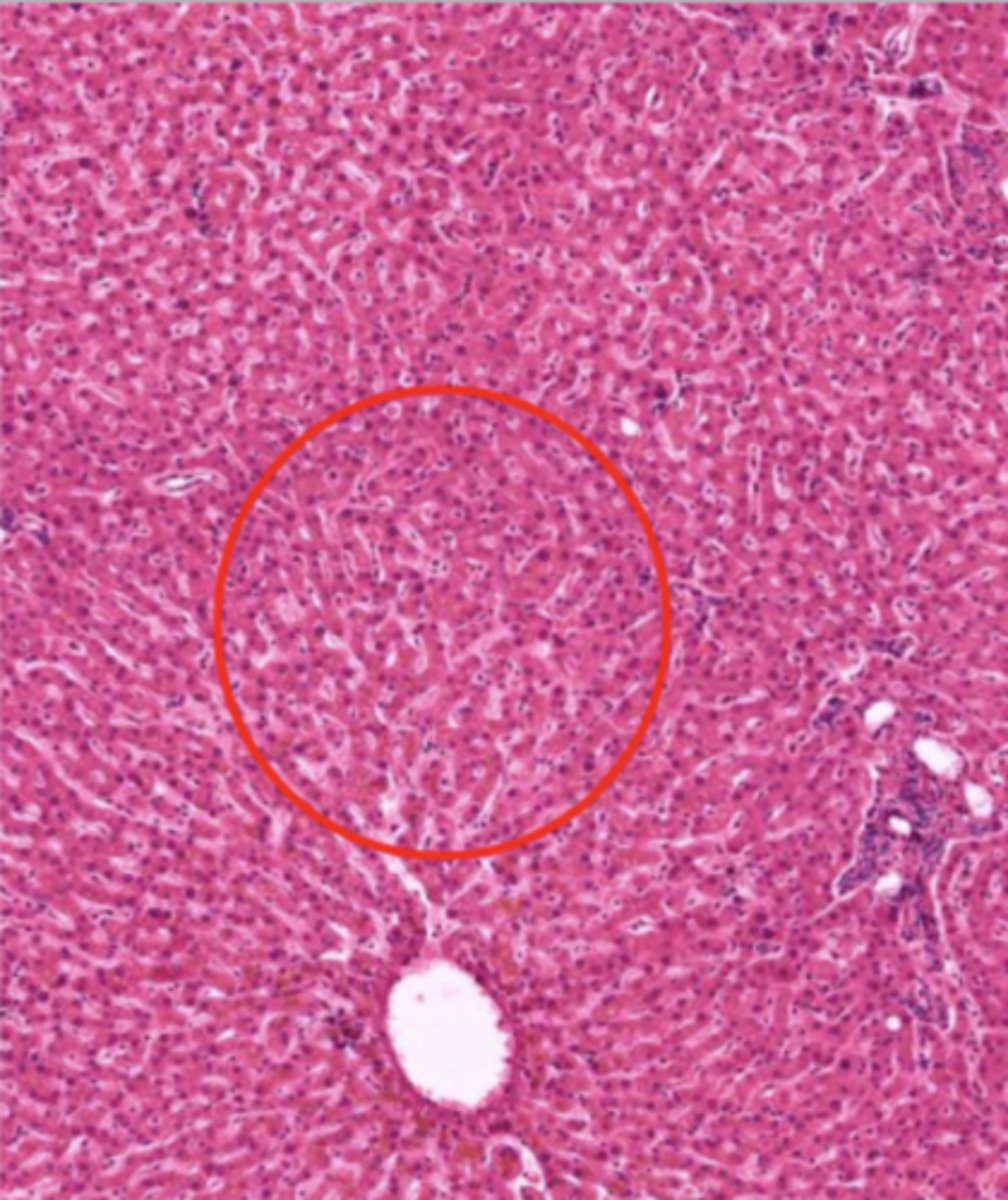
hepatocyte (liver)
gallbladder (histology)
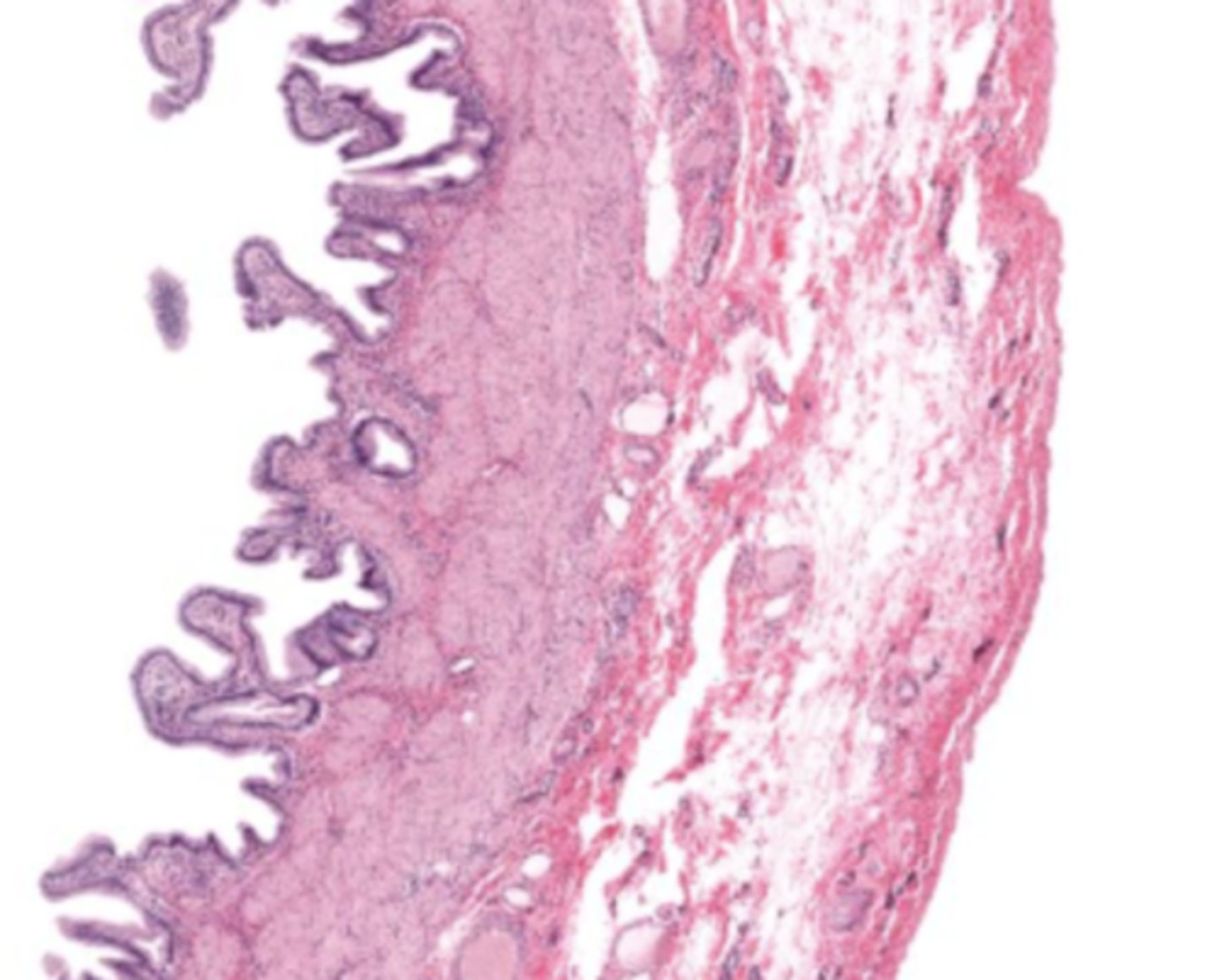
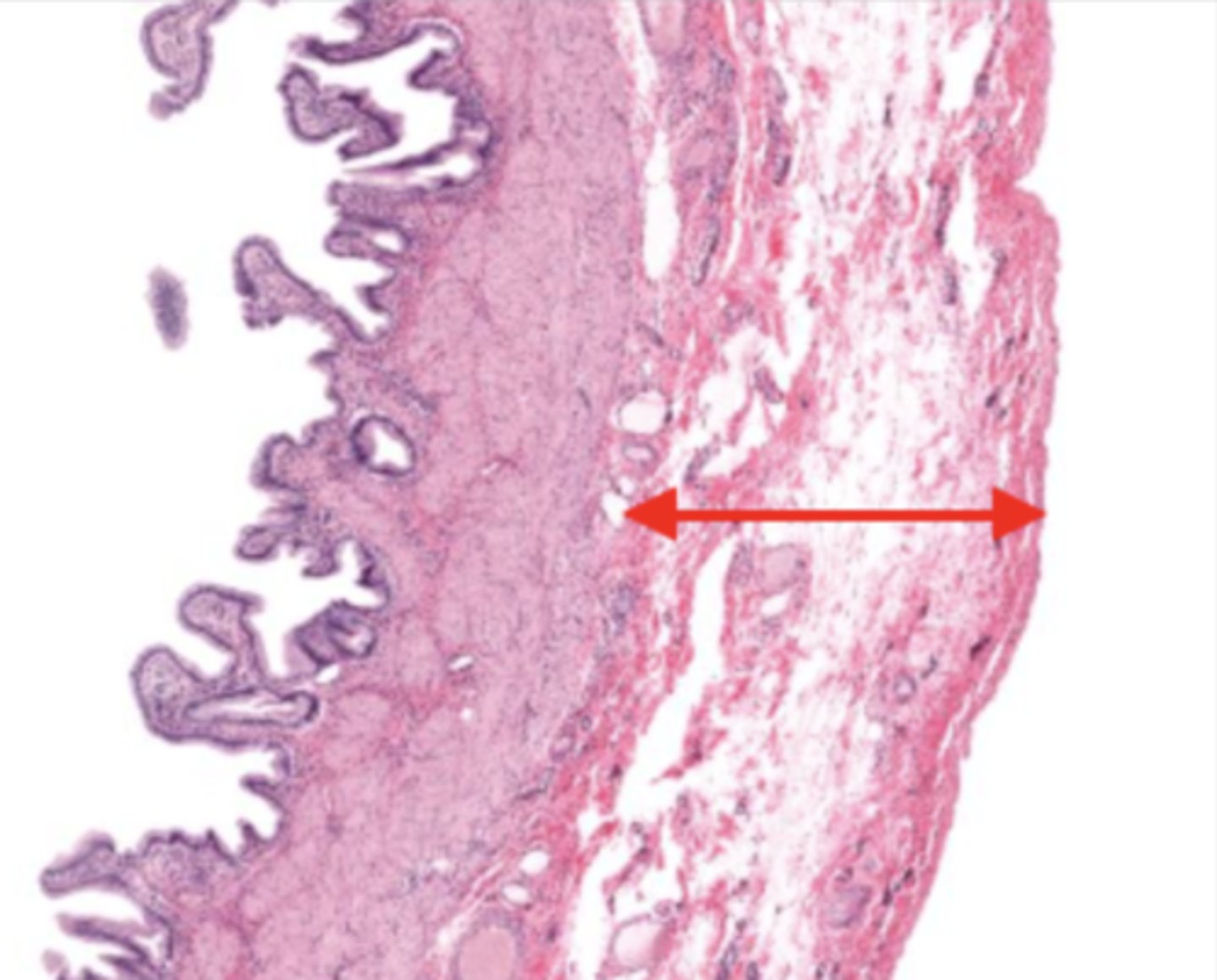
gallbladder
this tissue's wall structures/layers are different than the rest of the organs
simple columnar epithelium
what kind of epithelium lines the mucosa of the gallbladder
lumen (gallbladder)
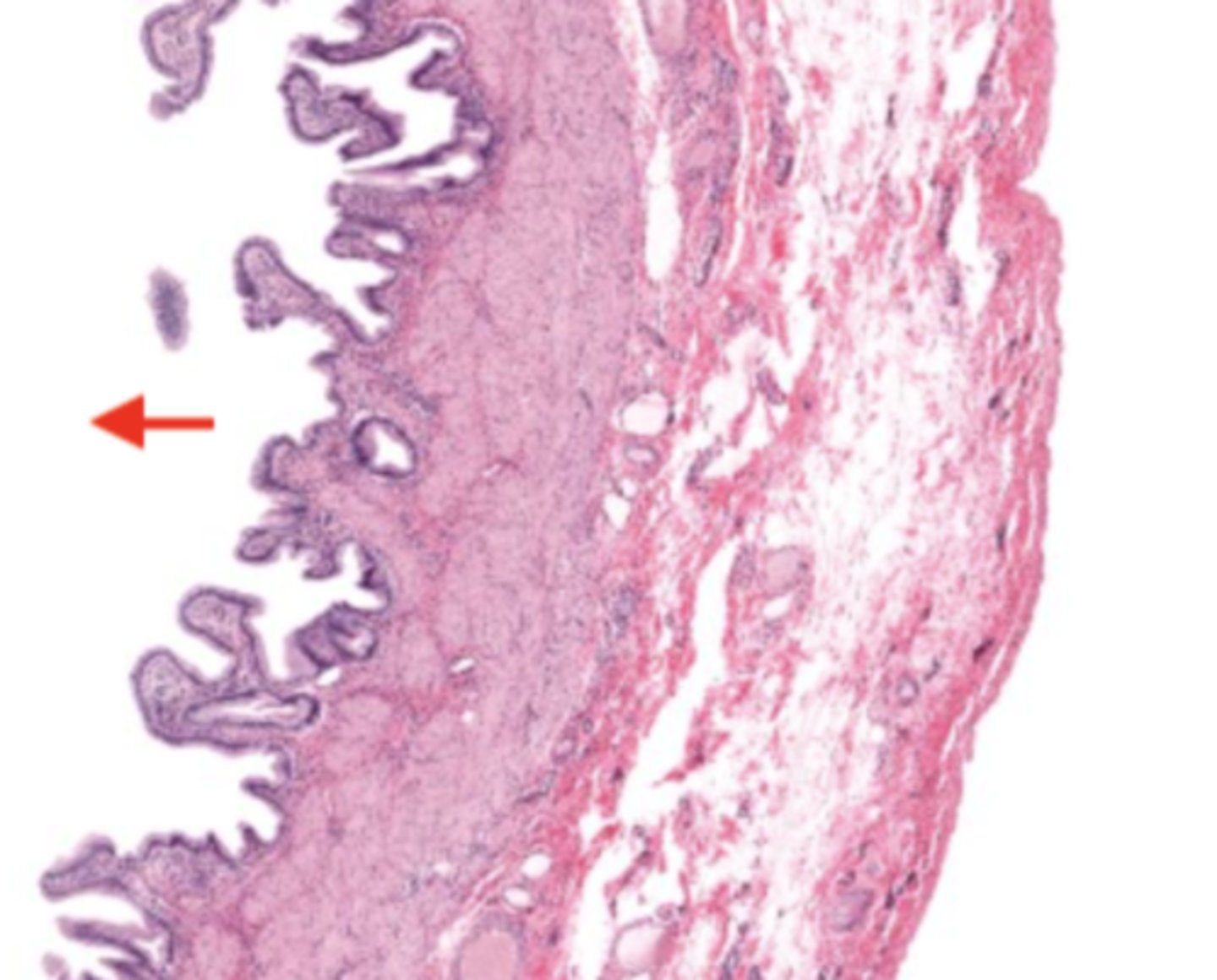
mucosa (gallbladder)
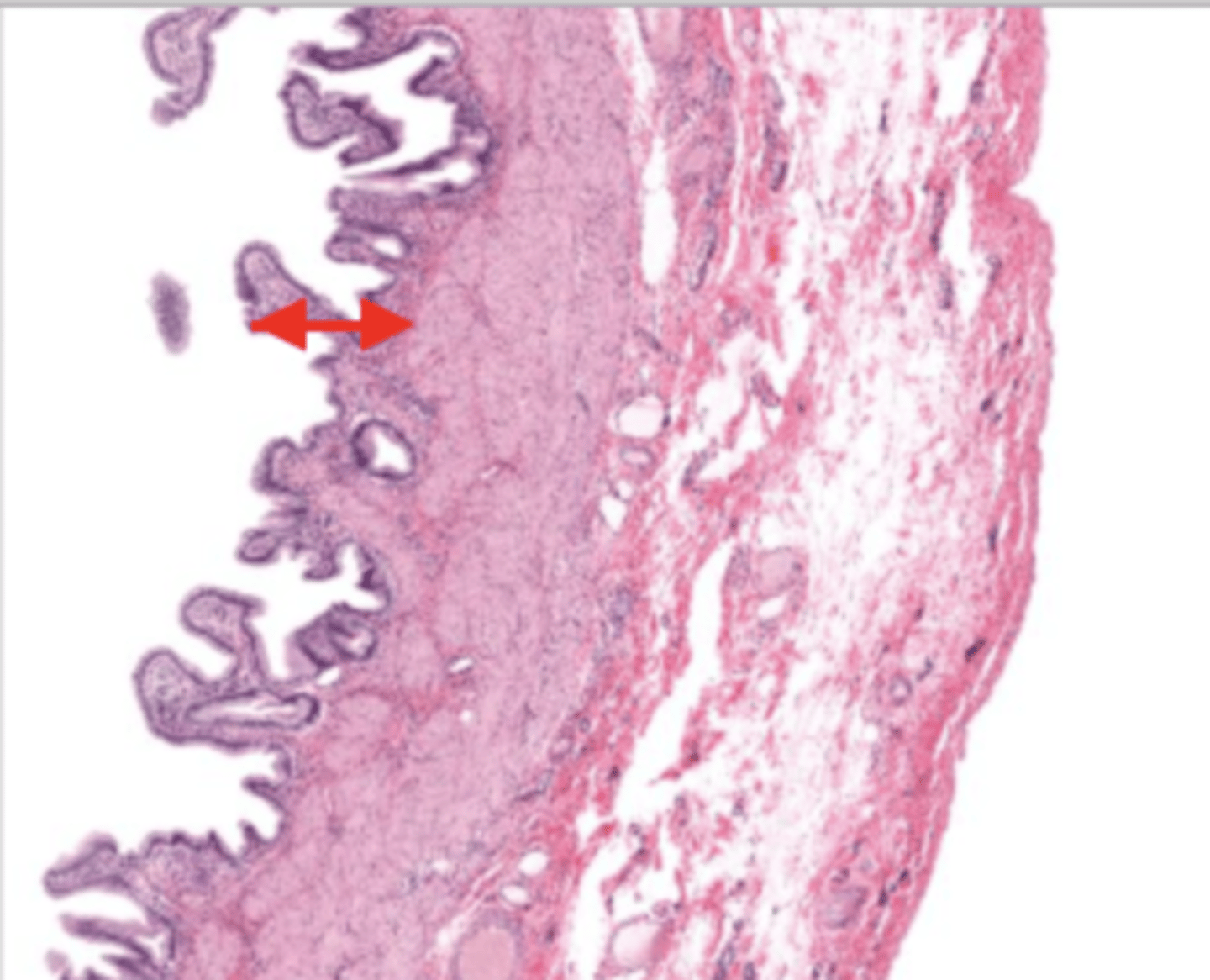
mucosal epithelium (gallbladder)
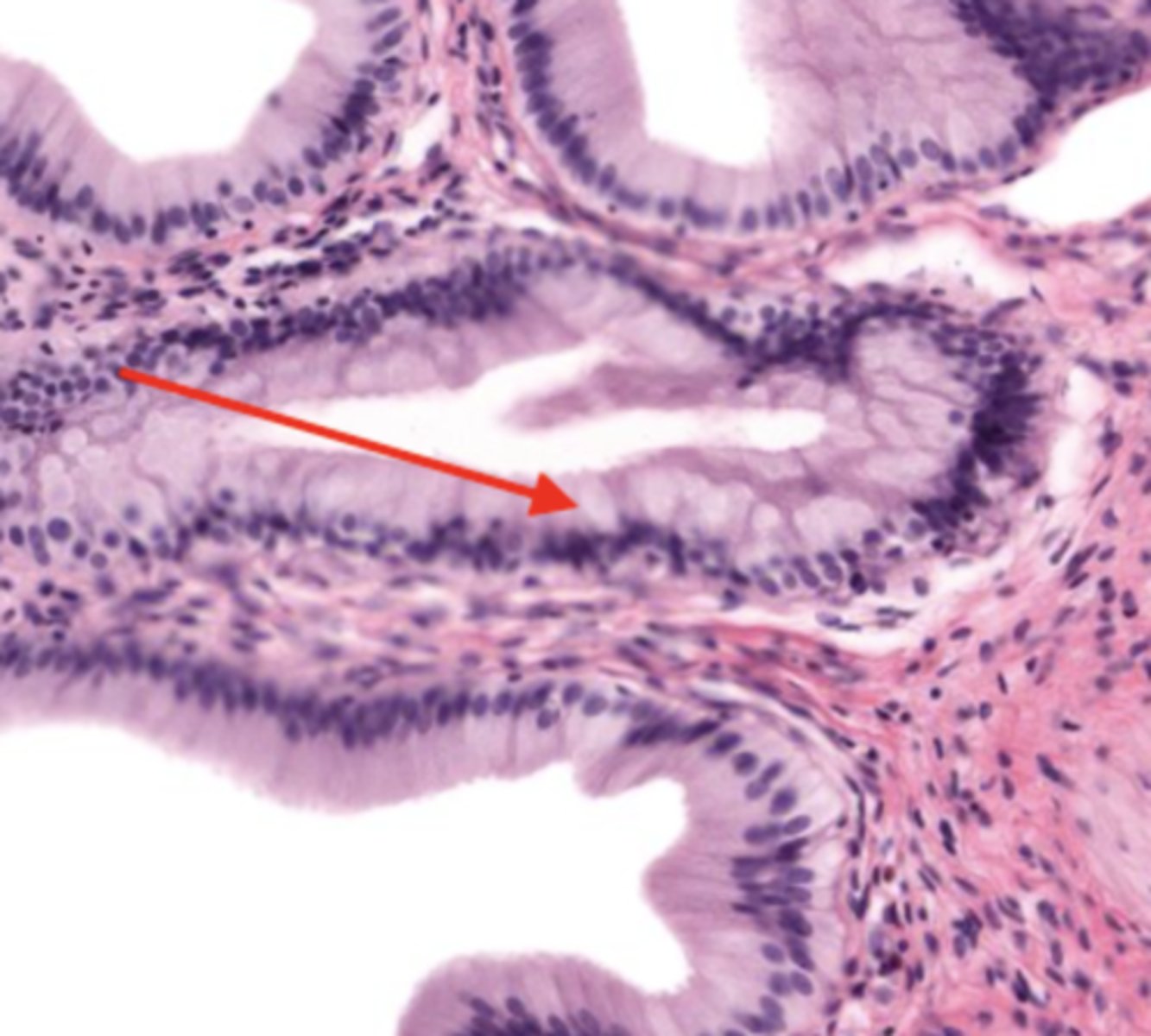
lamina propria (gallbladder)
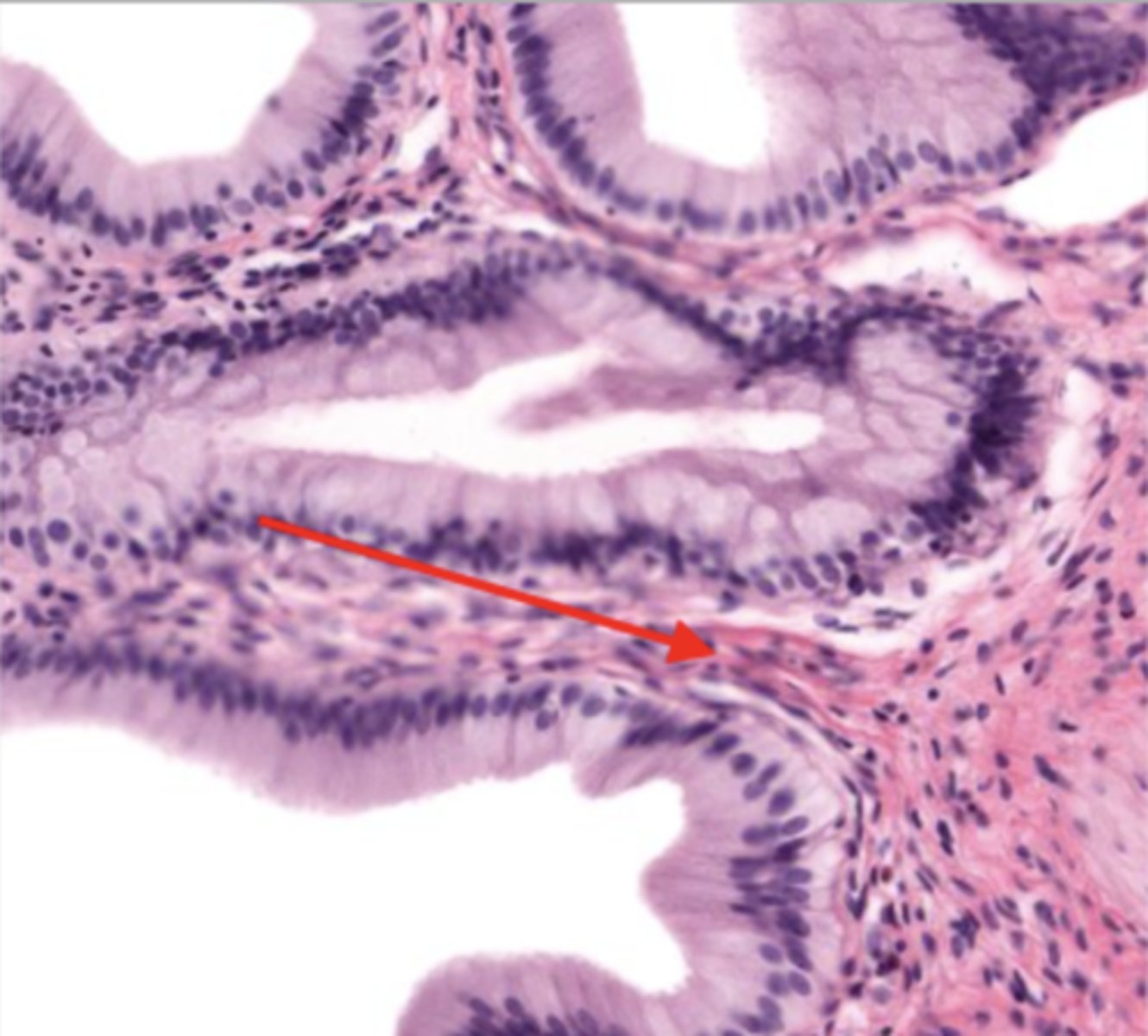
muscularis mucosa and submucosa
gallbladder tissue does not have _______ and ______
muscularis externa (gallbladder)
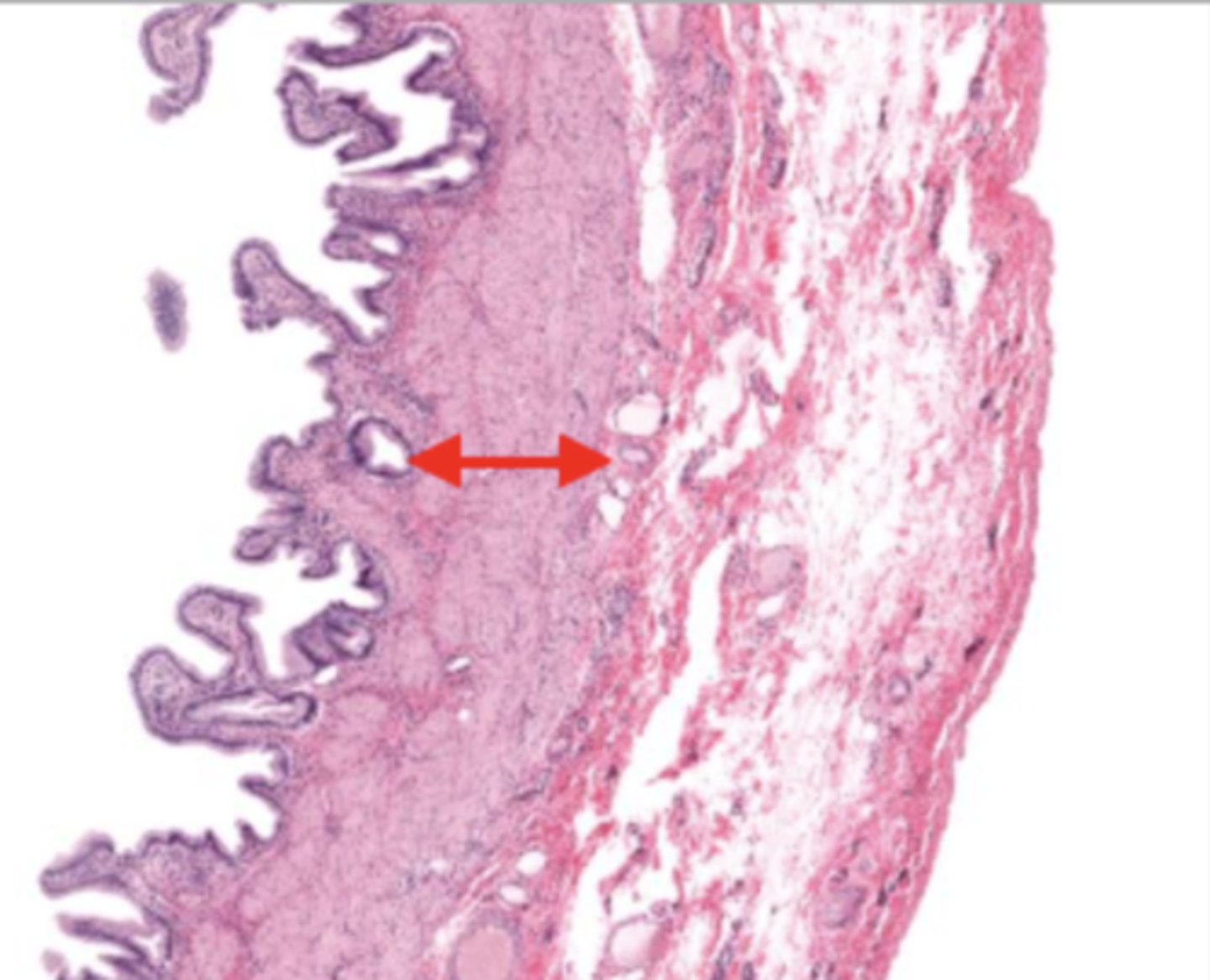
serosa/adventitia (gallbladder)
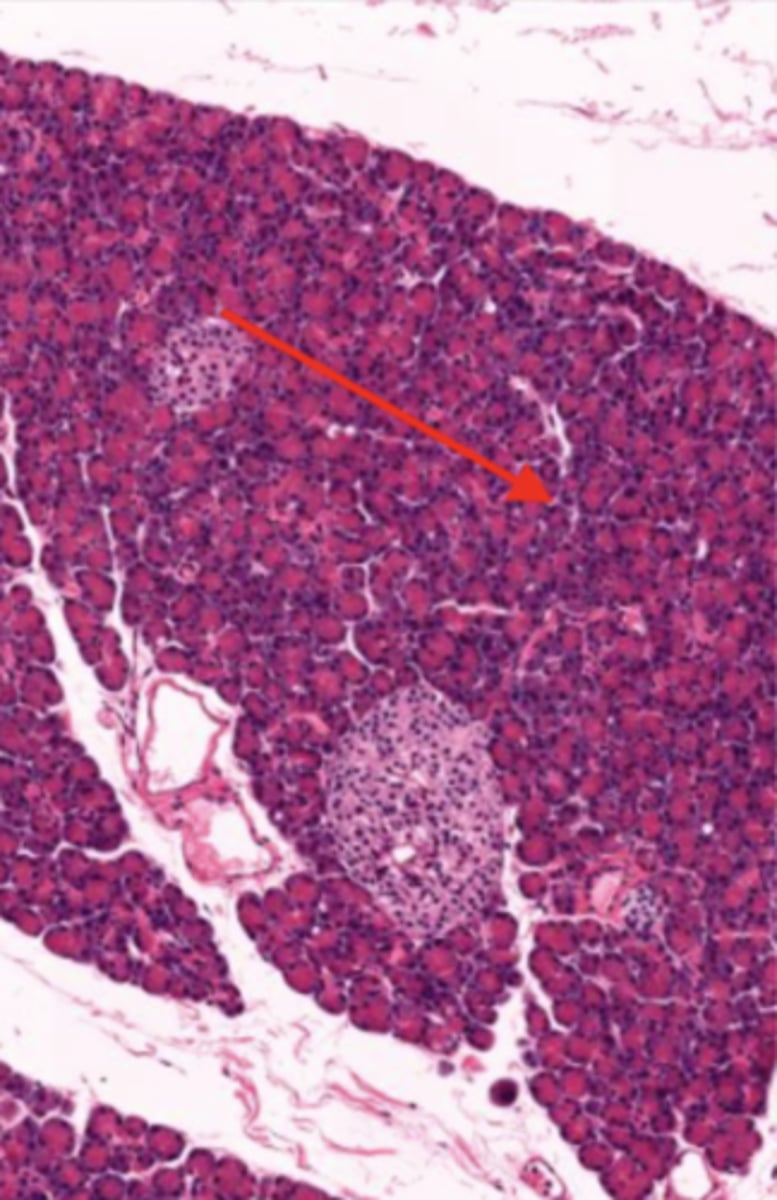
pancreas (histology)
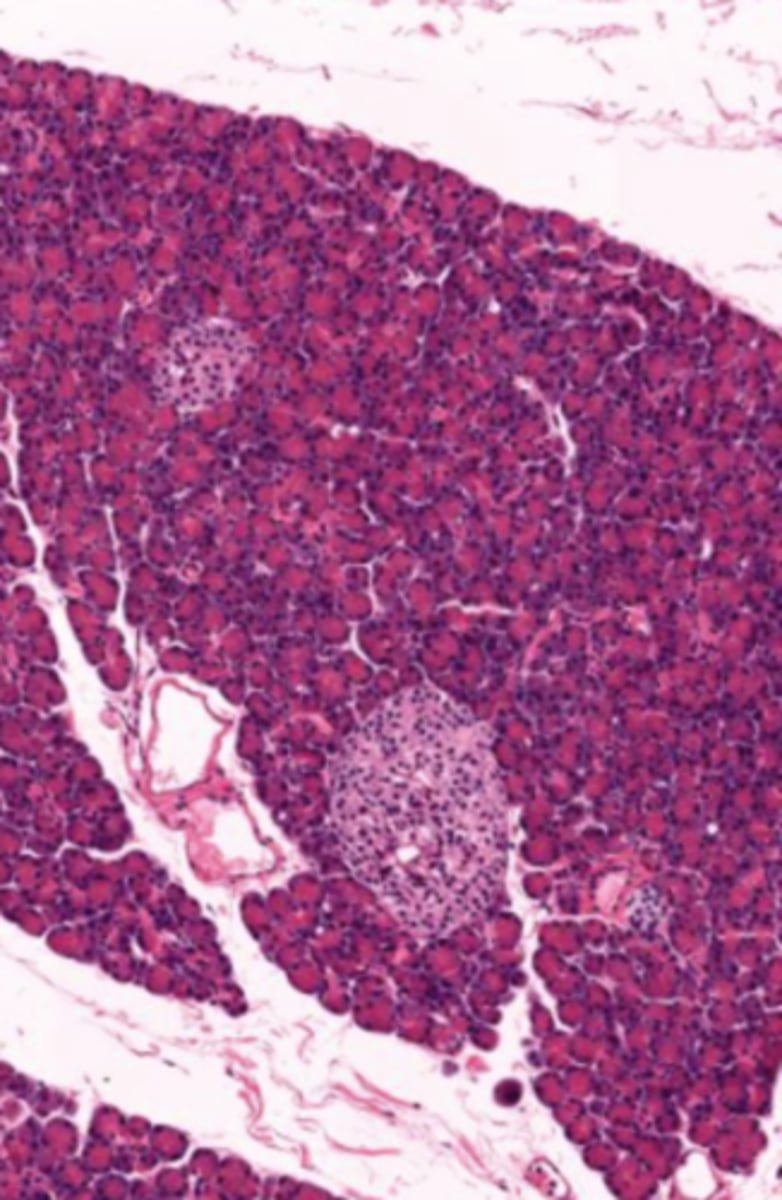
islet of Langerhans (pancreas)
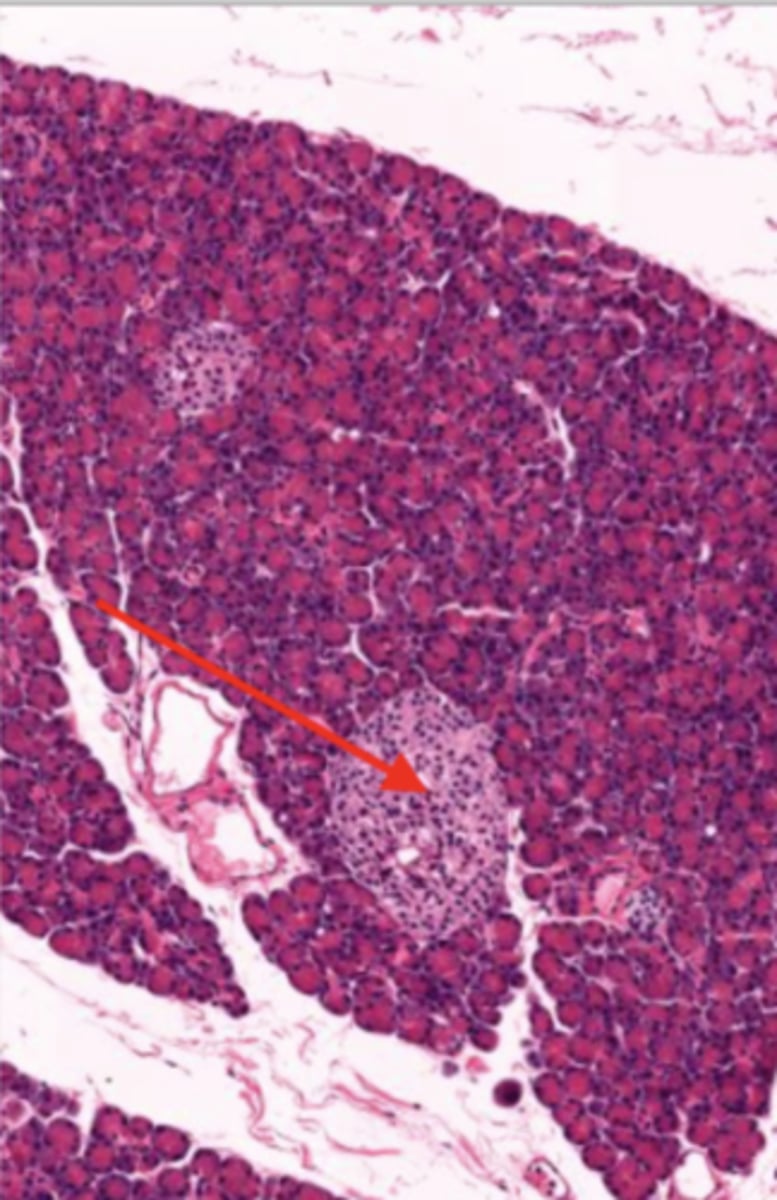
Acinar cells (pancreas)
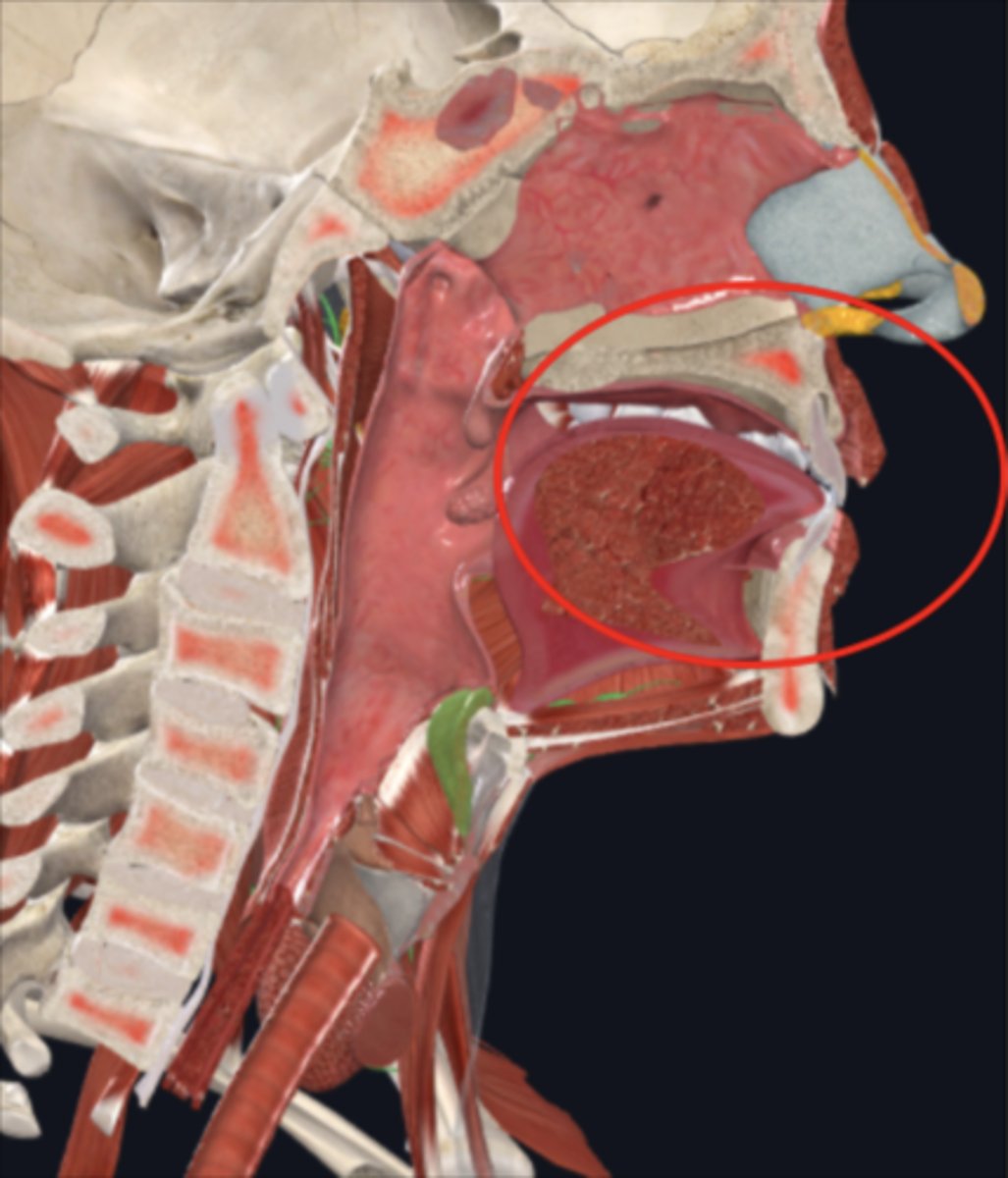
mouth
where digestion begins
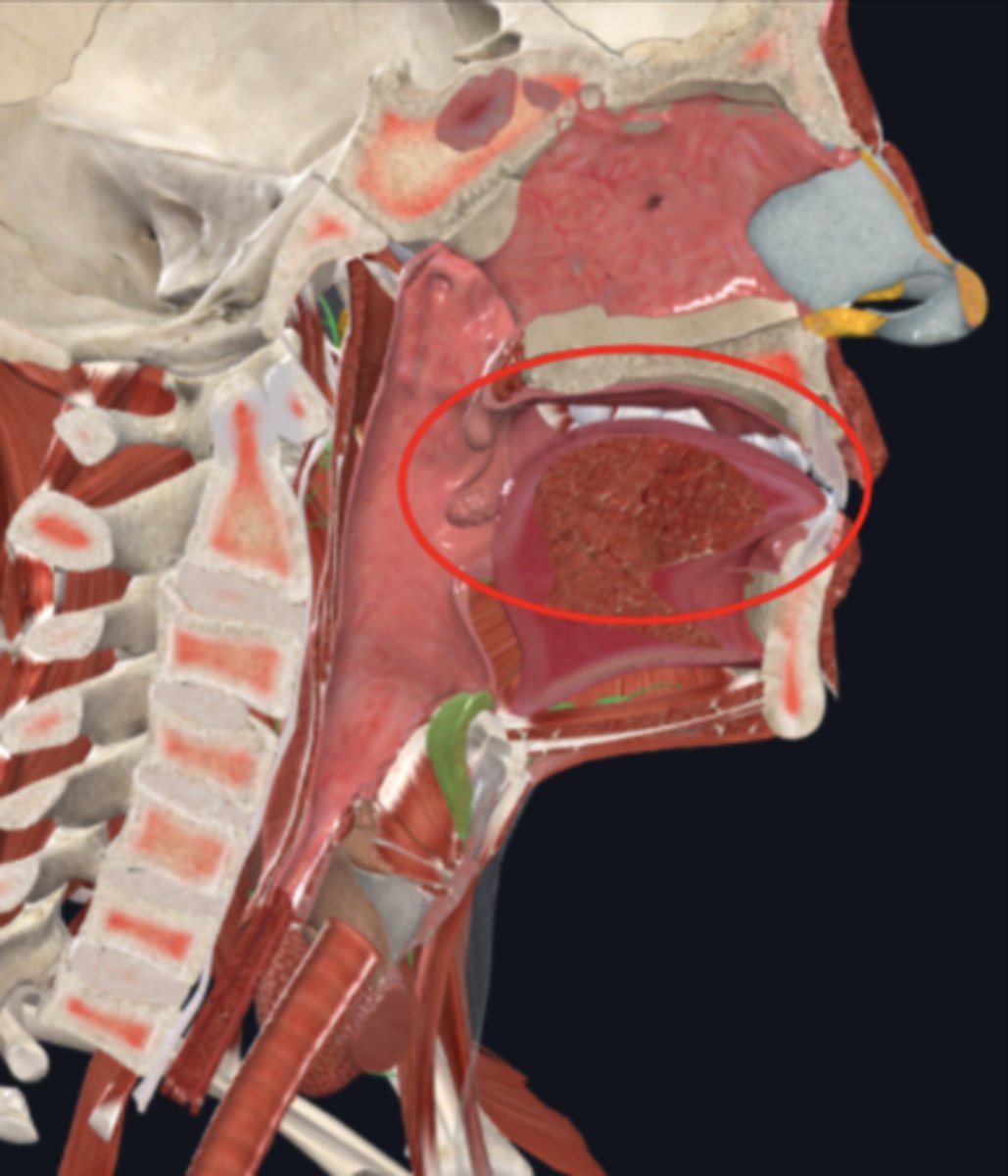
tongue
manipulates food for chewing and swallowing; a taste organ
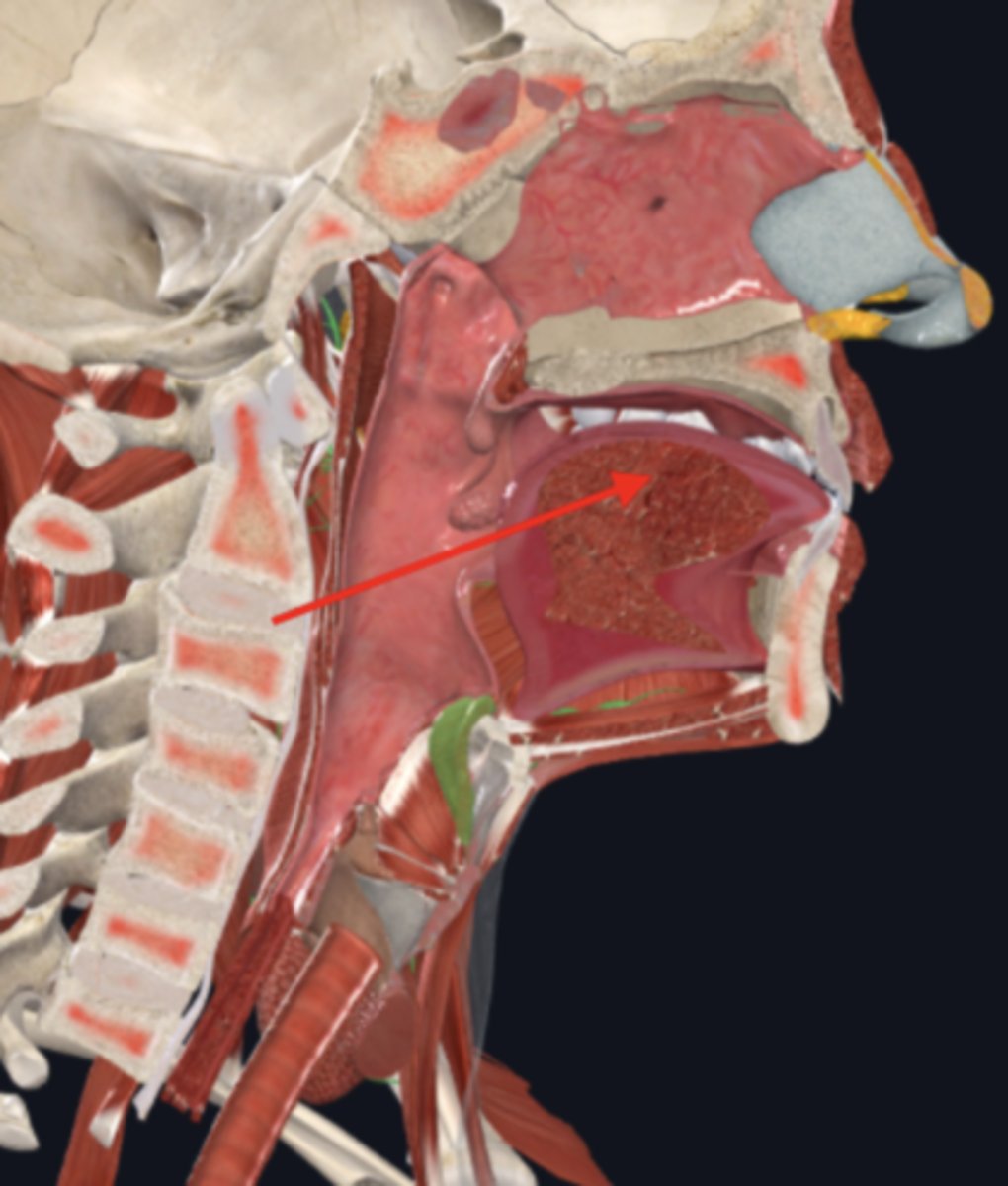
body of tongue
anterior two thirds of the tongue
root of tongue
posterior portion of the tongue
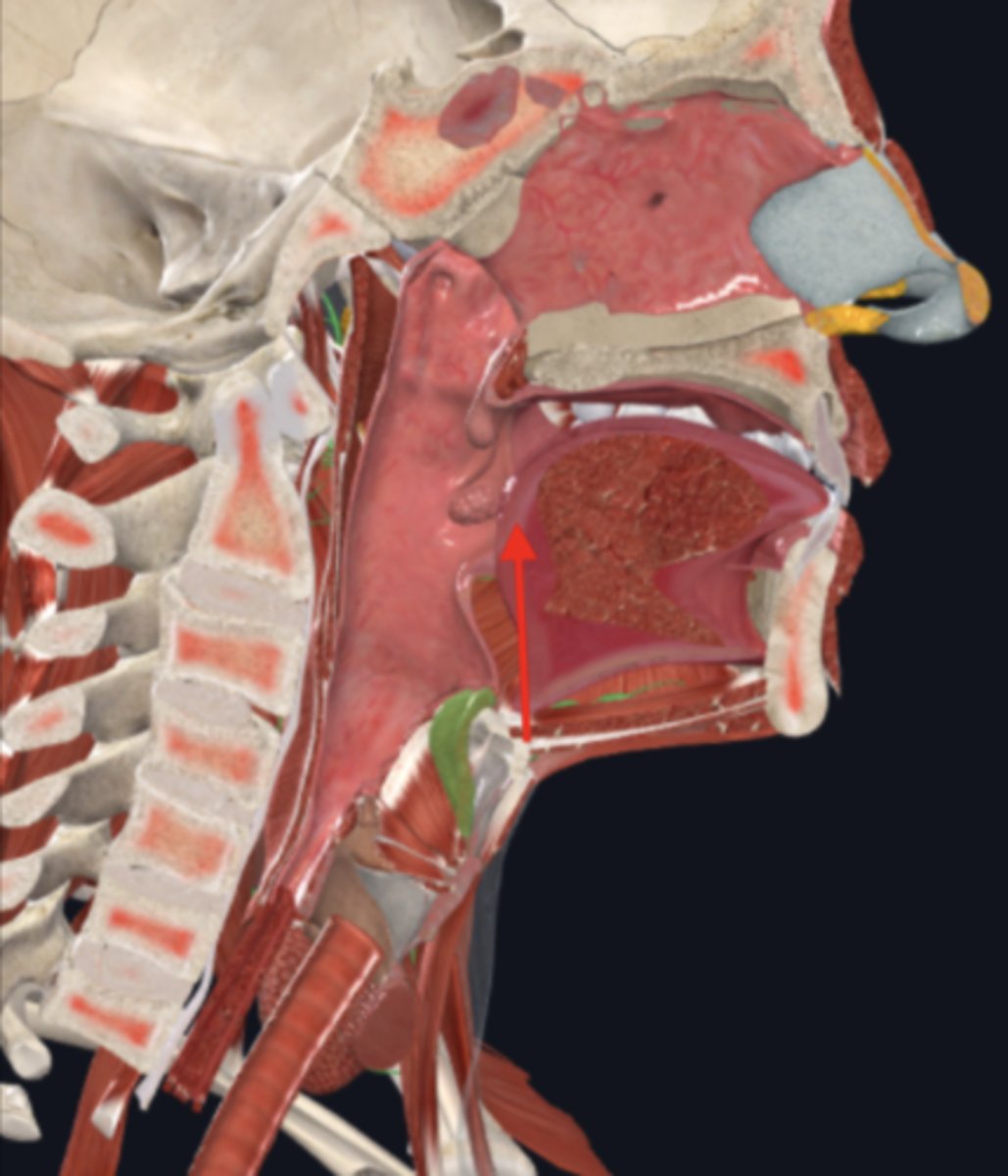
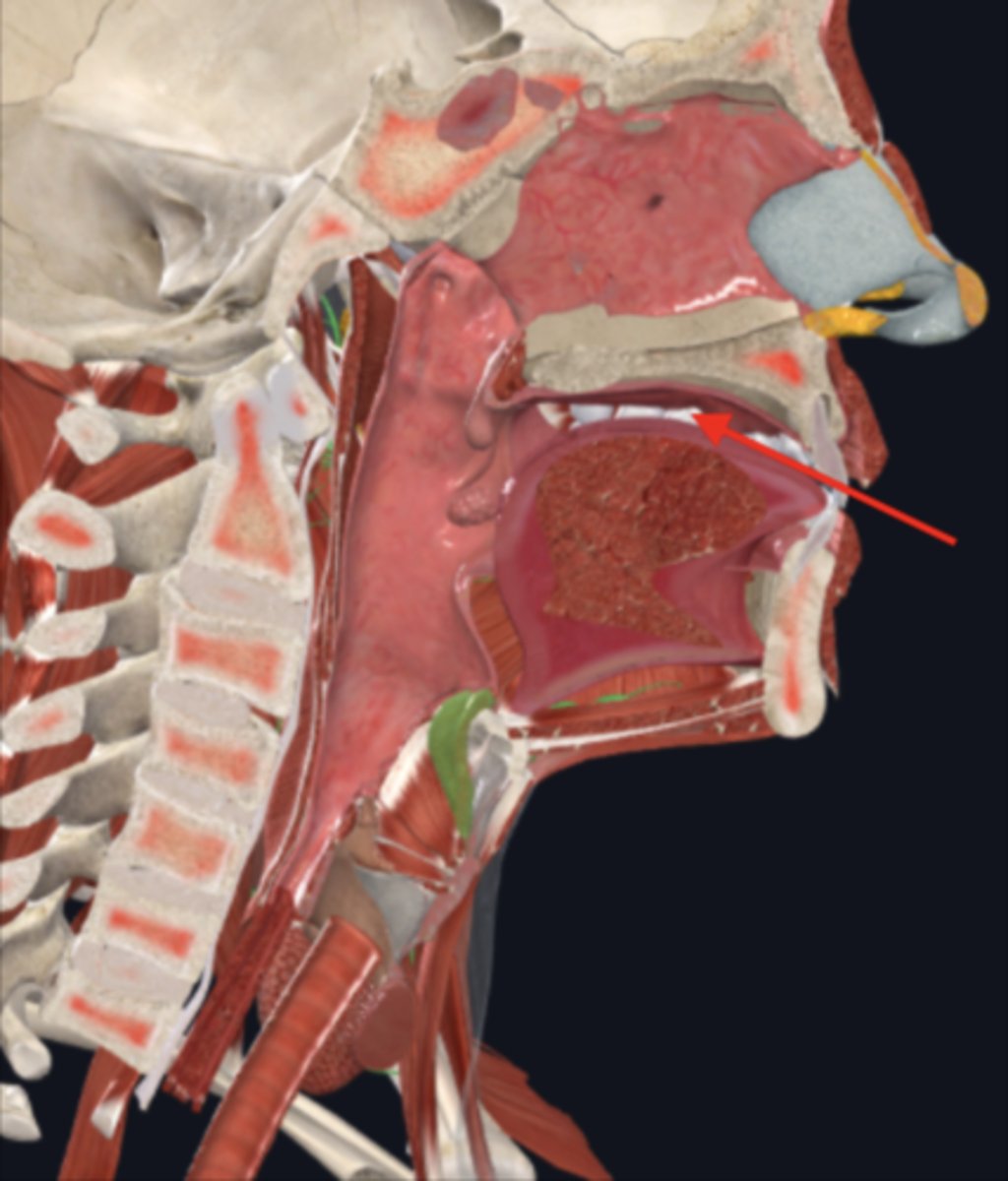
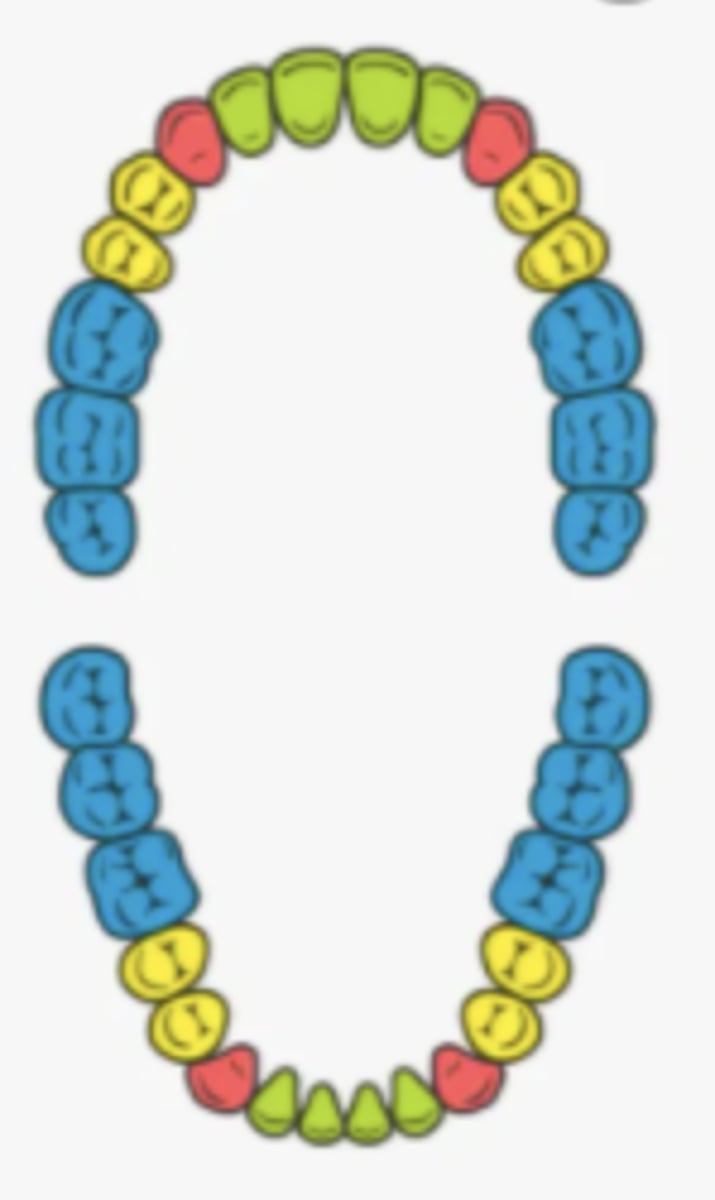
teeth
used for masticating (chewing) food
incisors
- name the teeth marked green
- 8 of these teeth
- teeth between the canines that are used for cutting
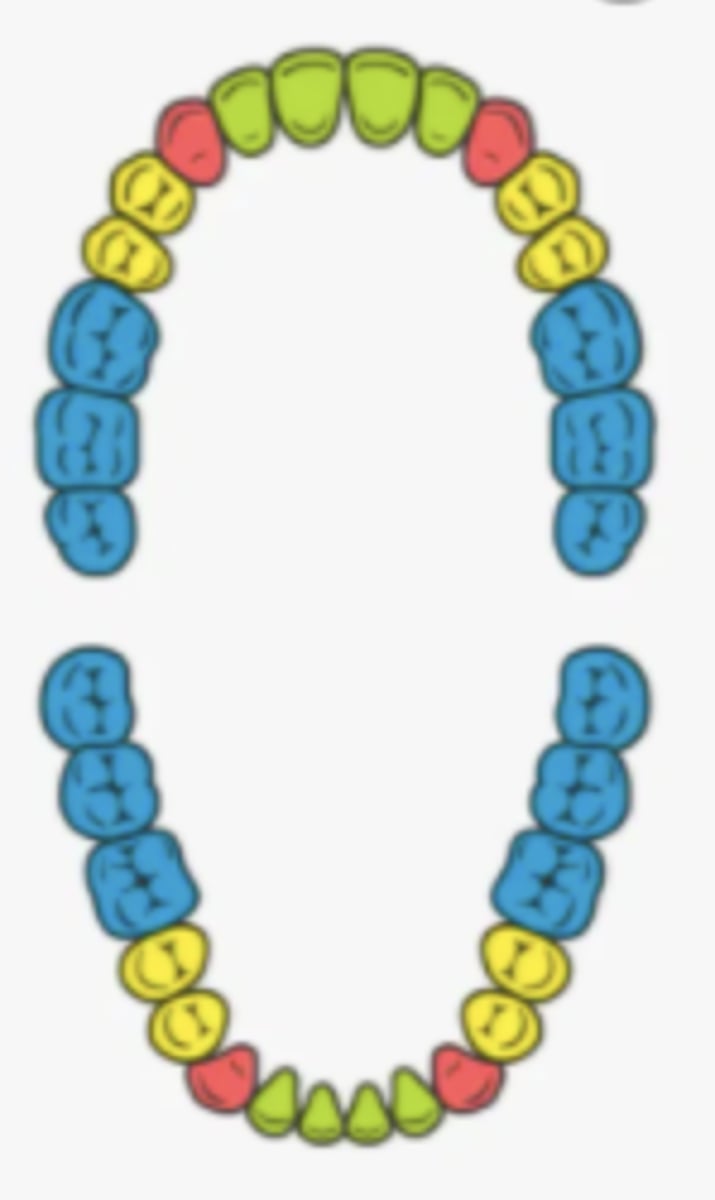
canine (cuspids)
- name the teeth marked red
- 4 of these teeth
- used for ripping and tearing
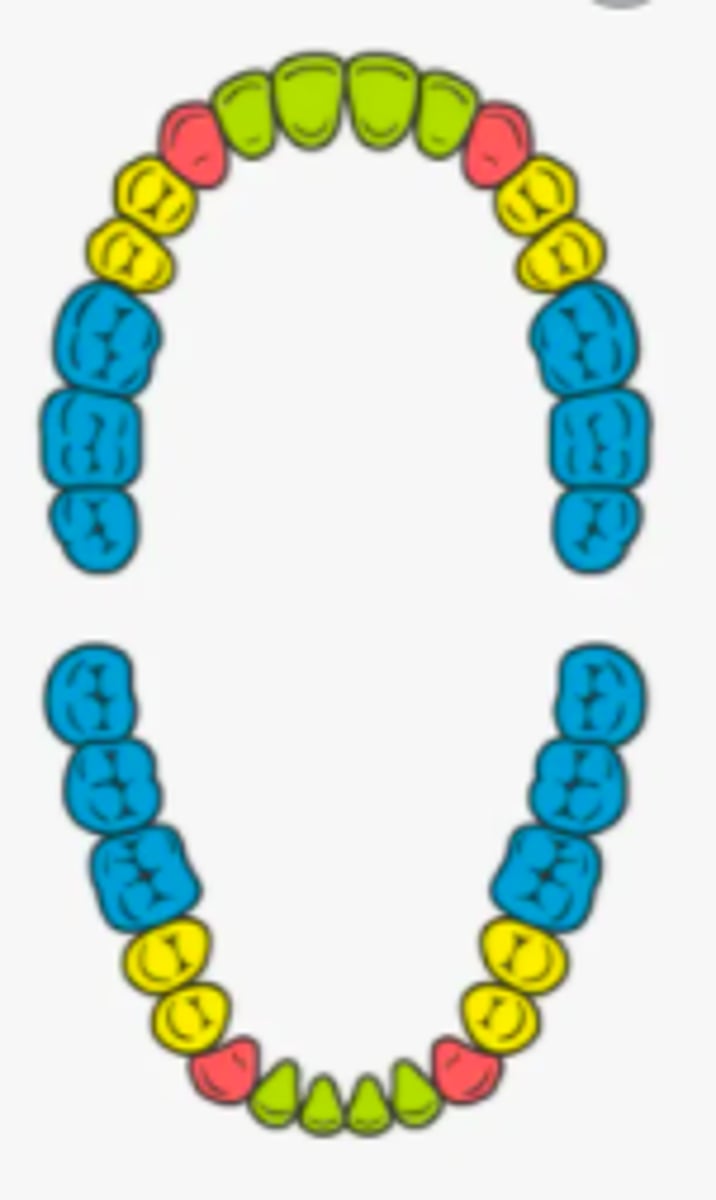
premolars (bicuspids)
- name the teeth marked yellow
- 8 of these teeth
- used for grinding and crushing
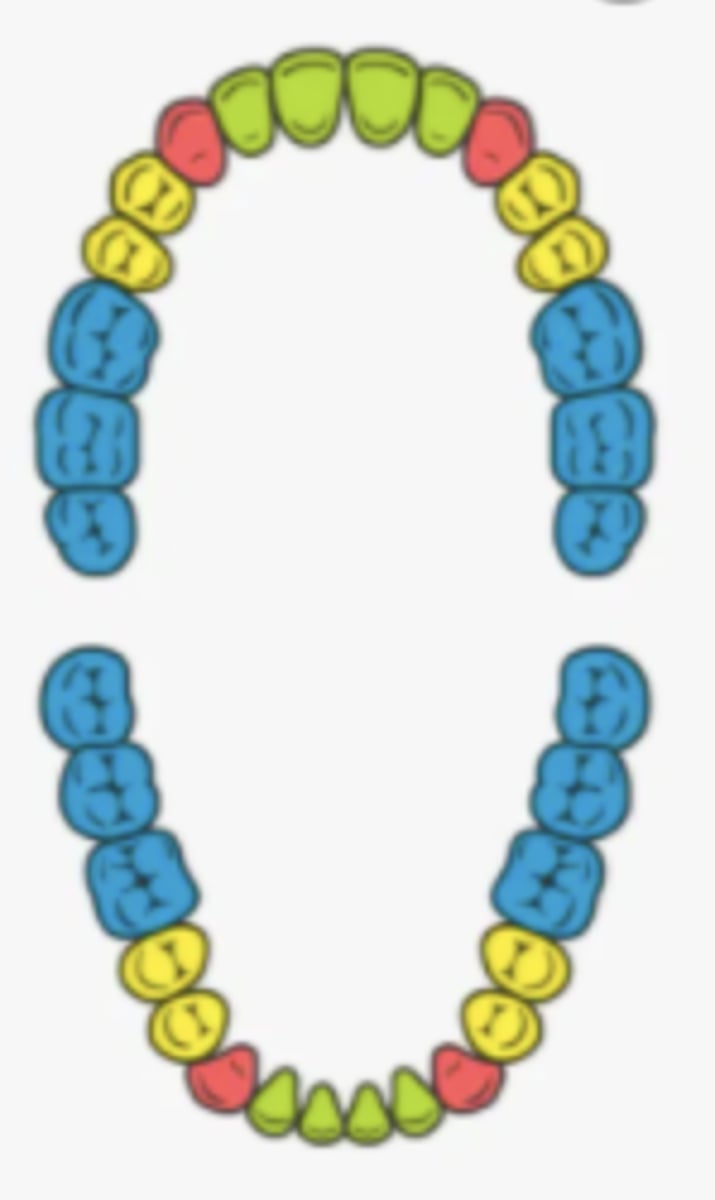
molars
- name the teeth marked blue
- 12 of these teeth
- back teeth that grind food
hard palate
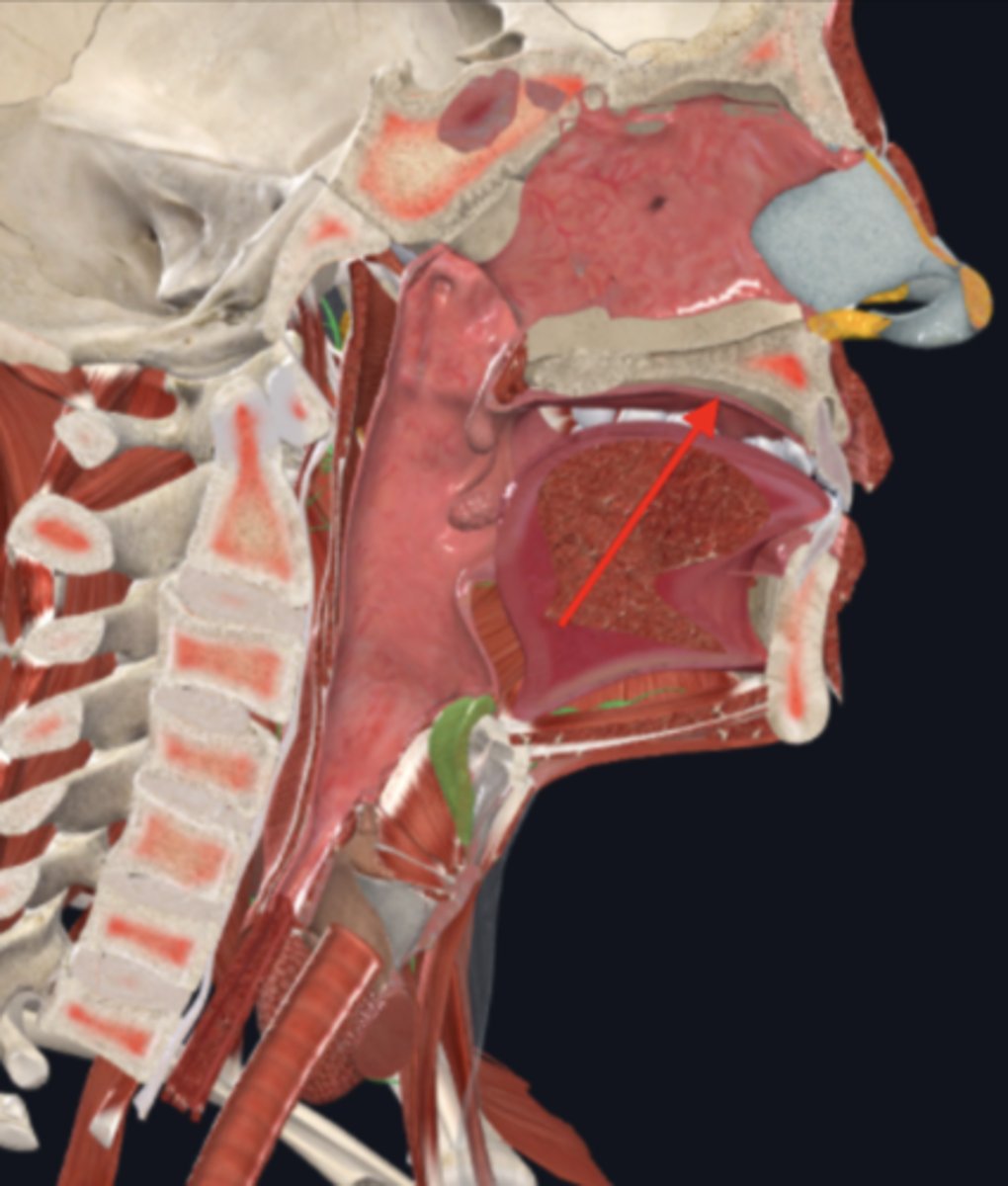
soft palate
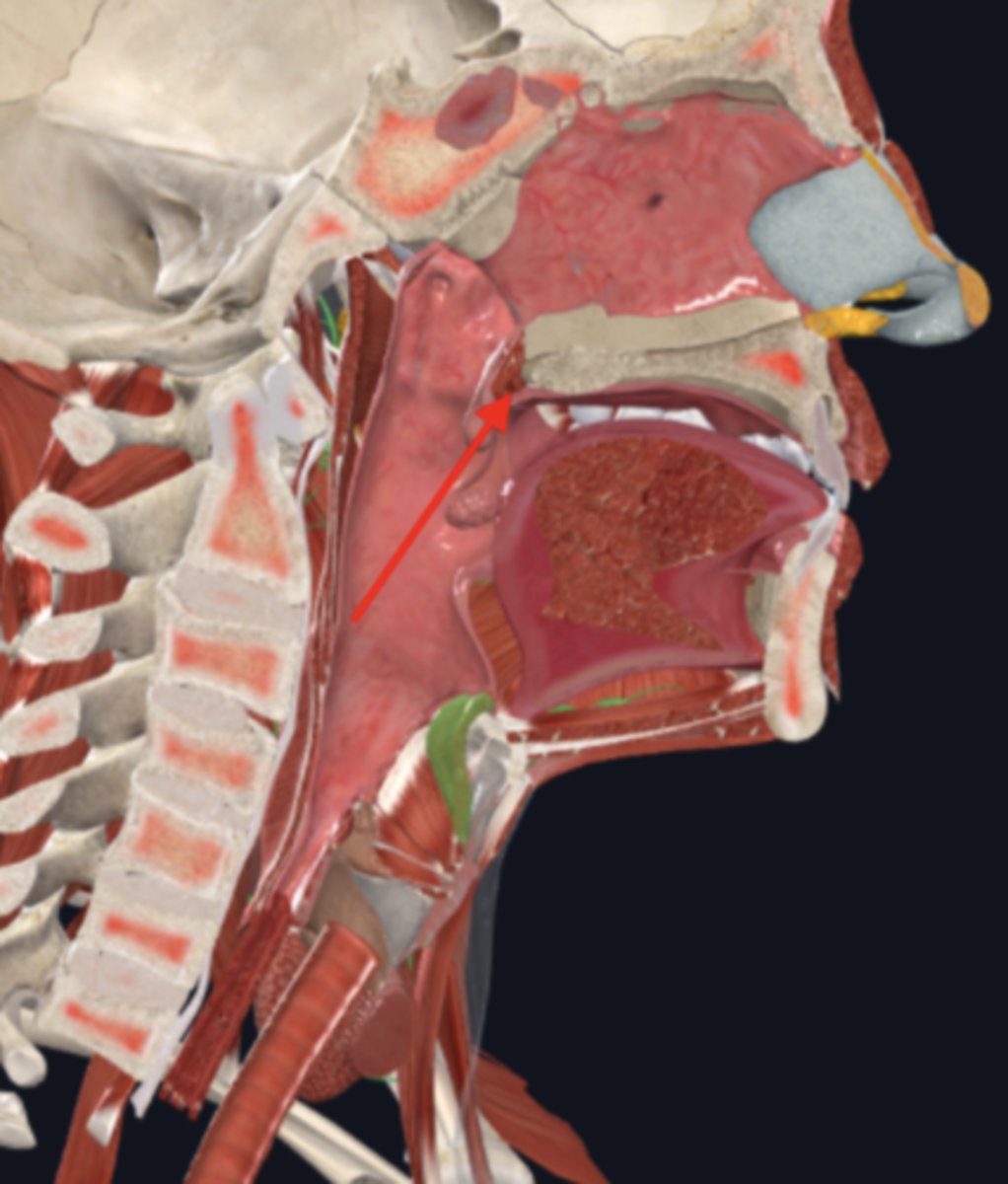
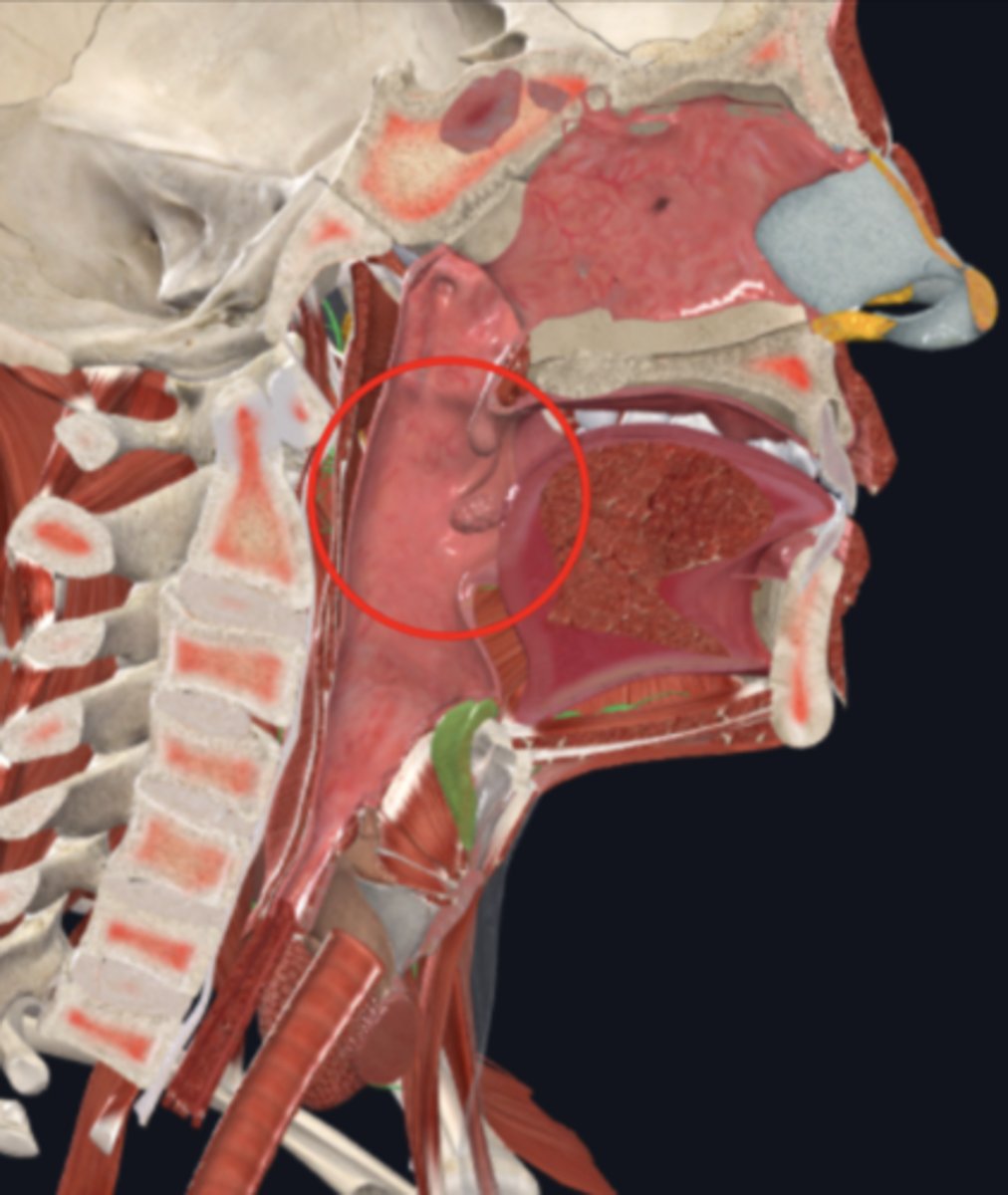
uvula
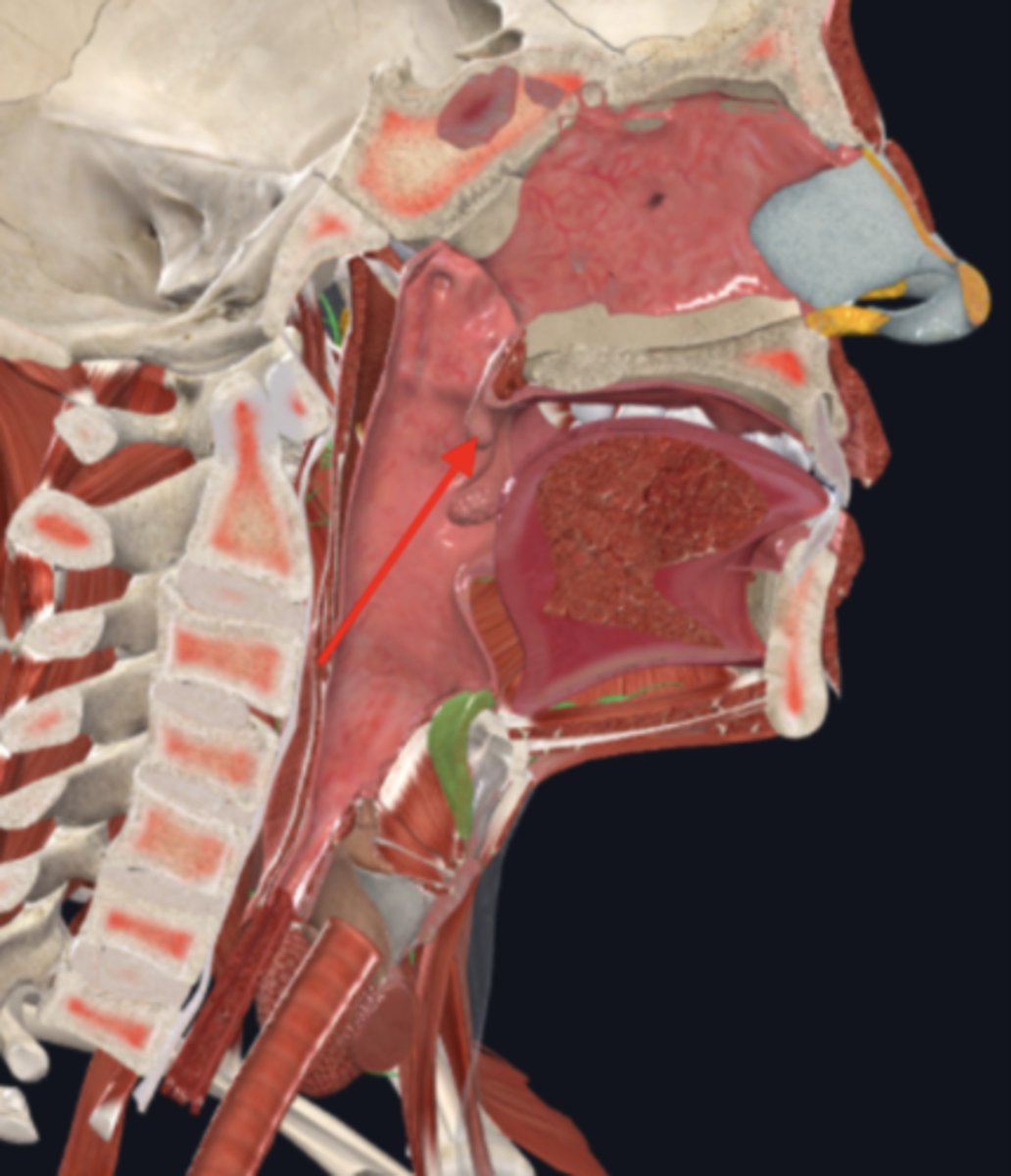
palatine tonsils
nasopharynx
name the circled region
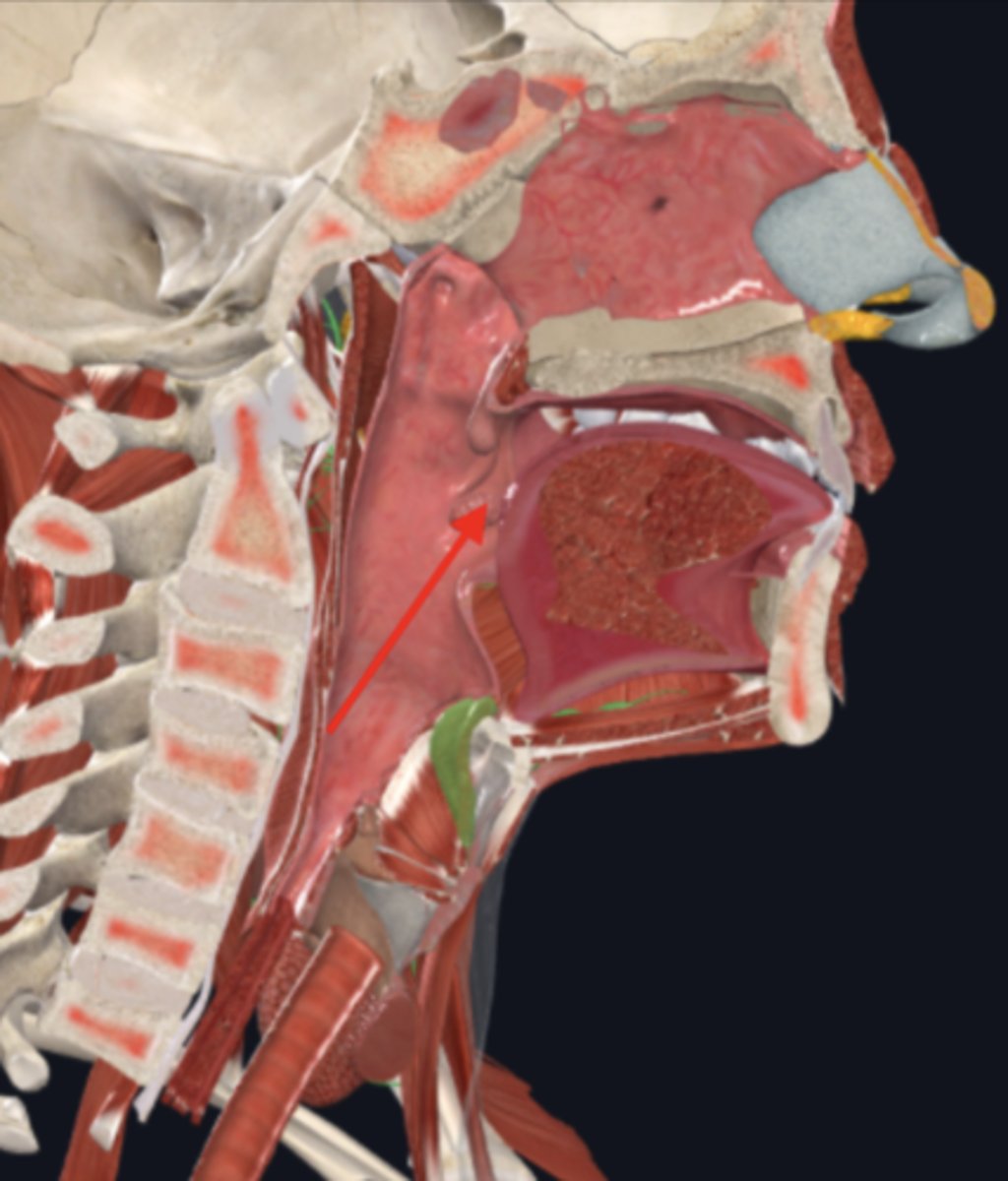
oropharynx
name the circled region
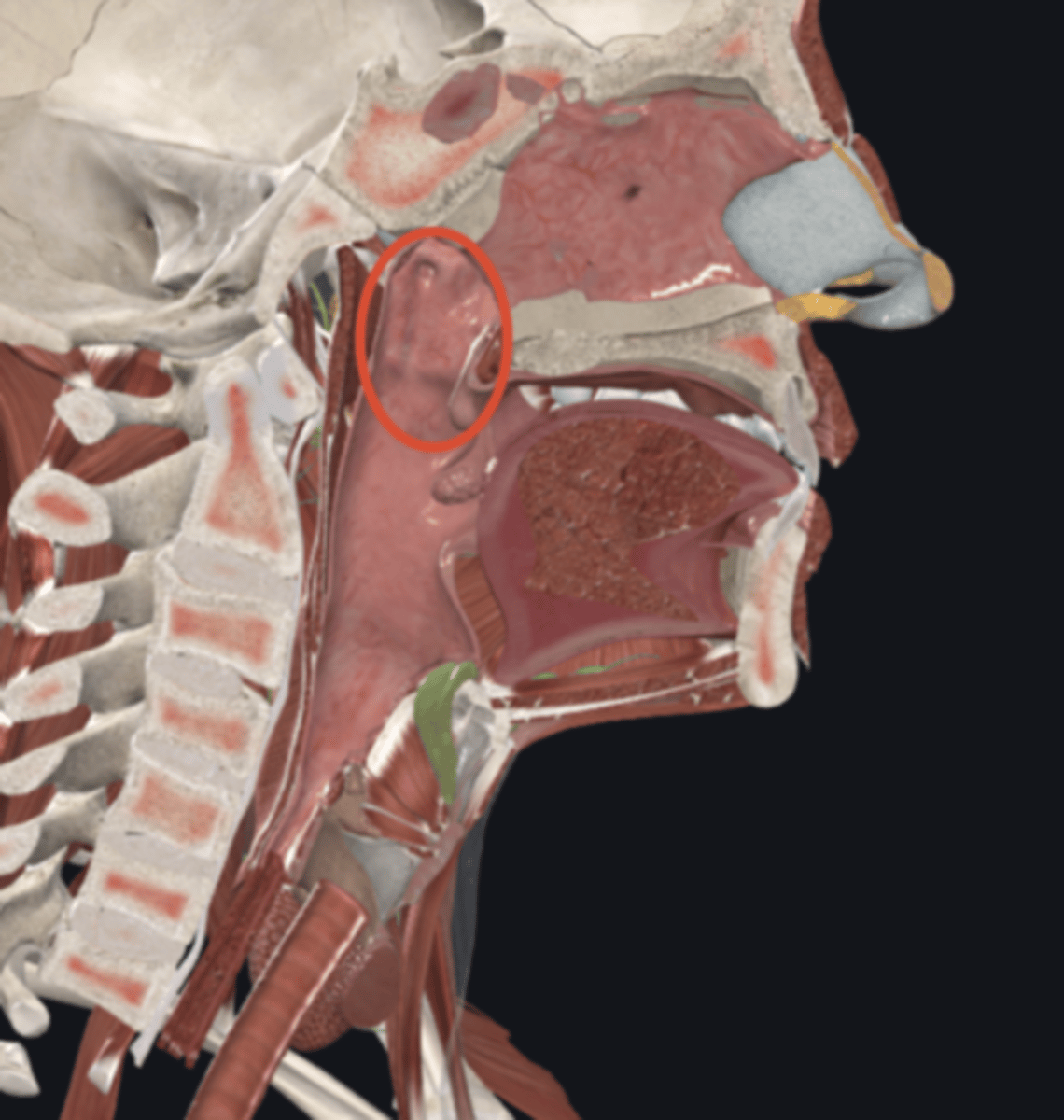
laryngopharynx
name the circled region
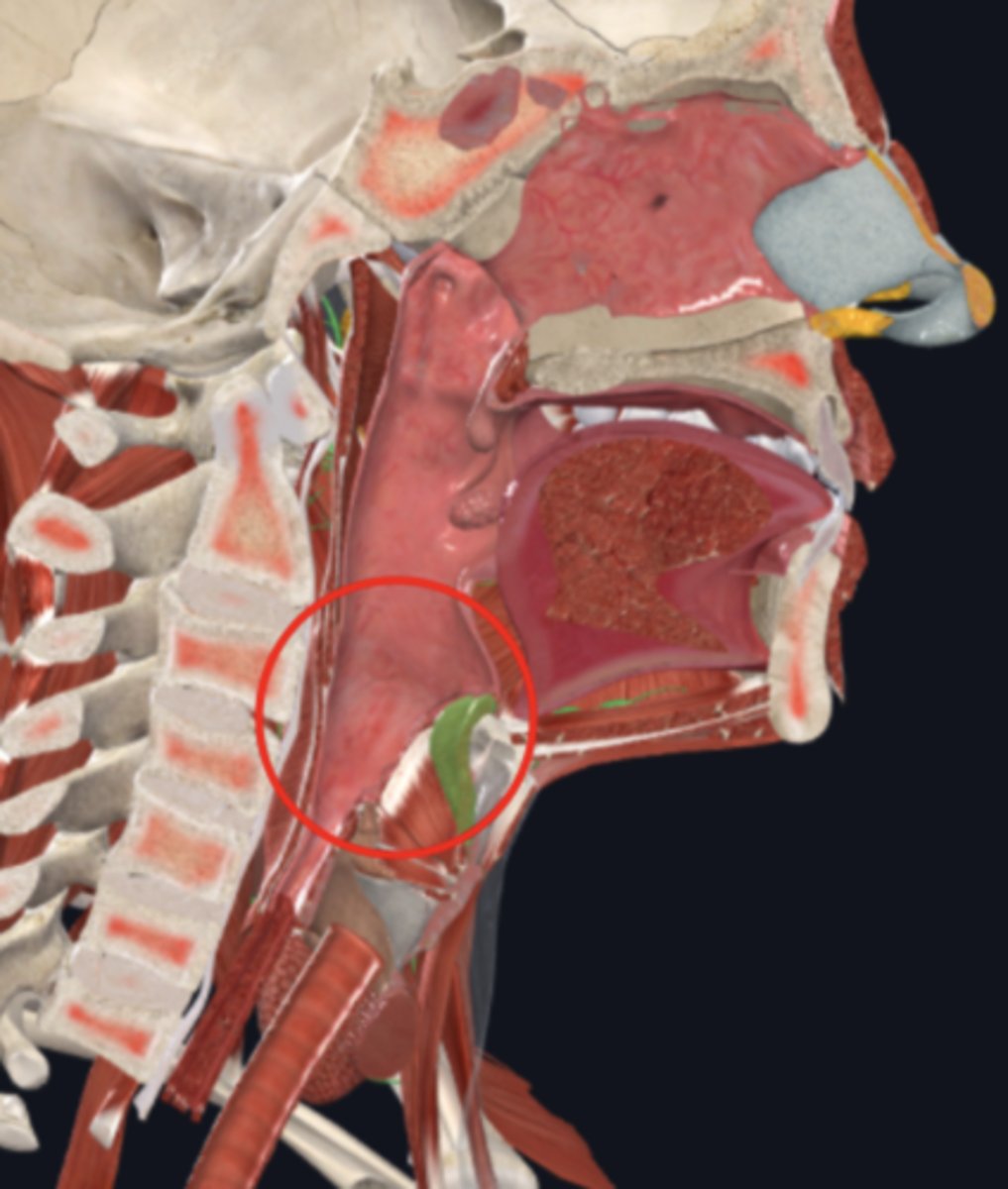
epiglottis
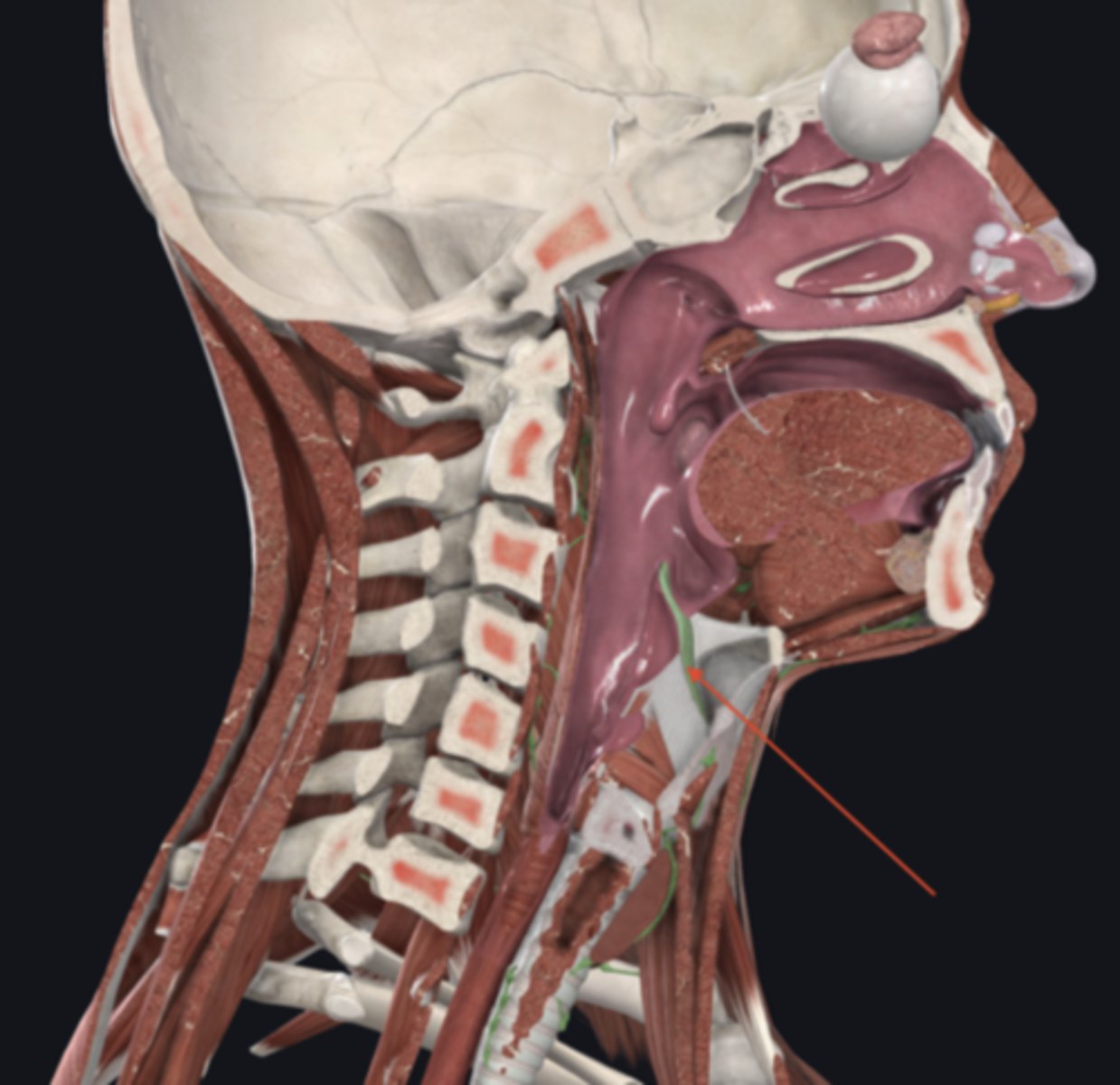
esophagus
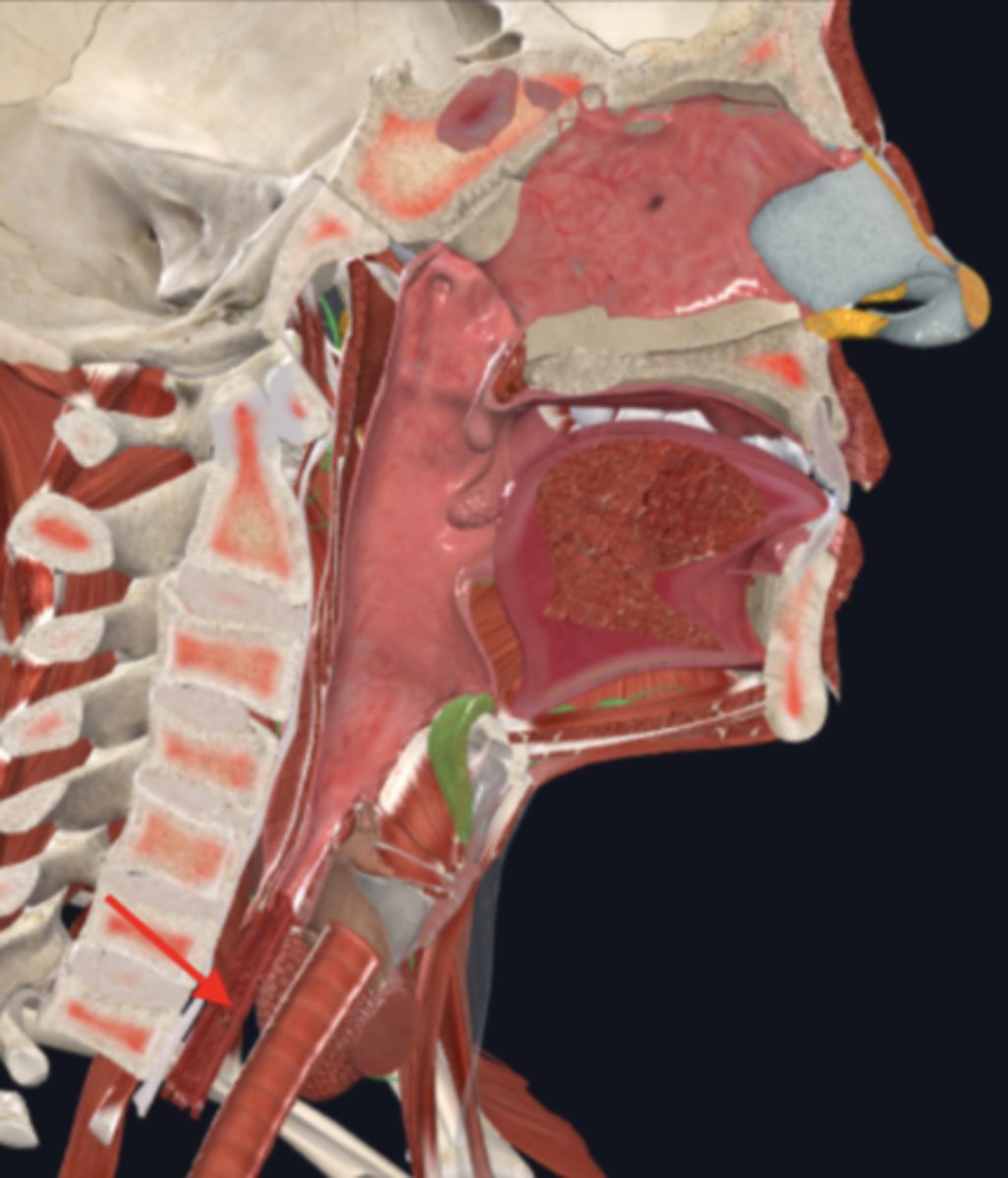
upper esophageal sphincter
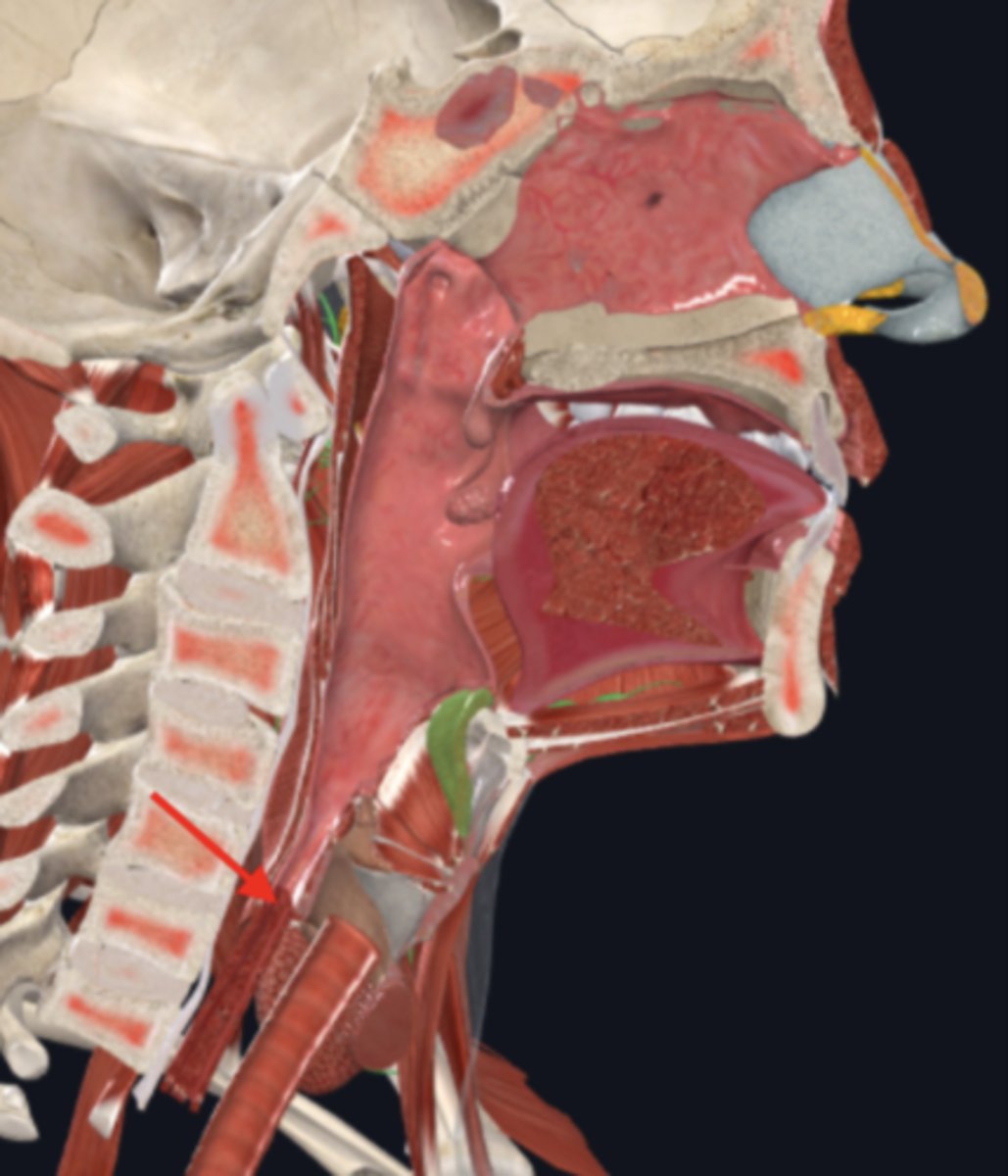
cardiac sphincter (lower esophageal sphincter)
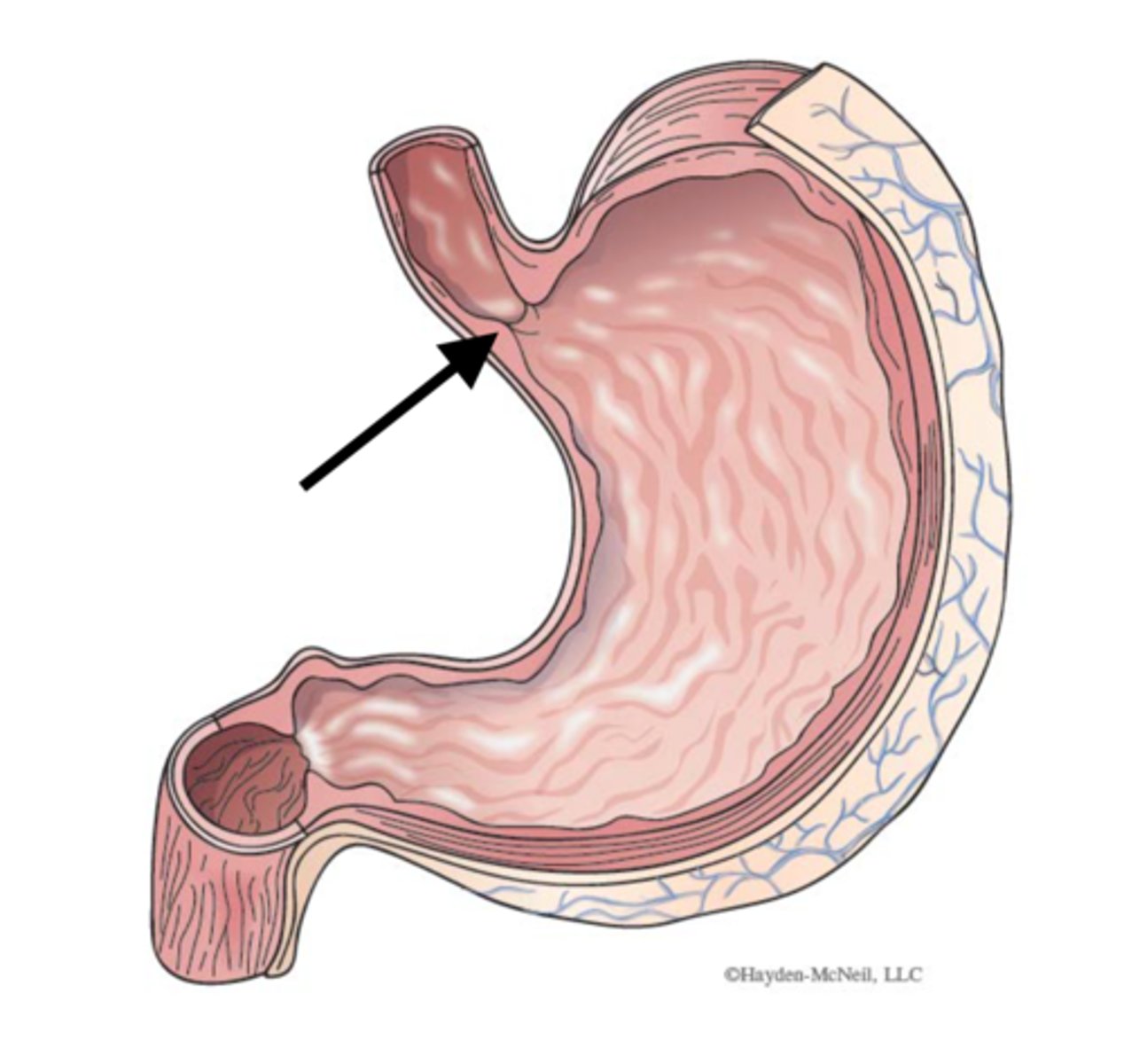
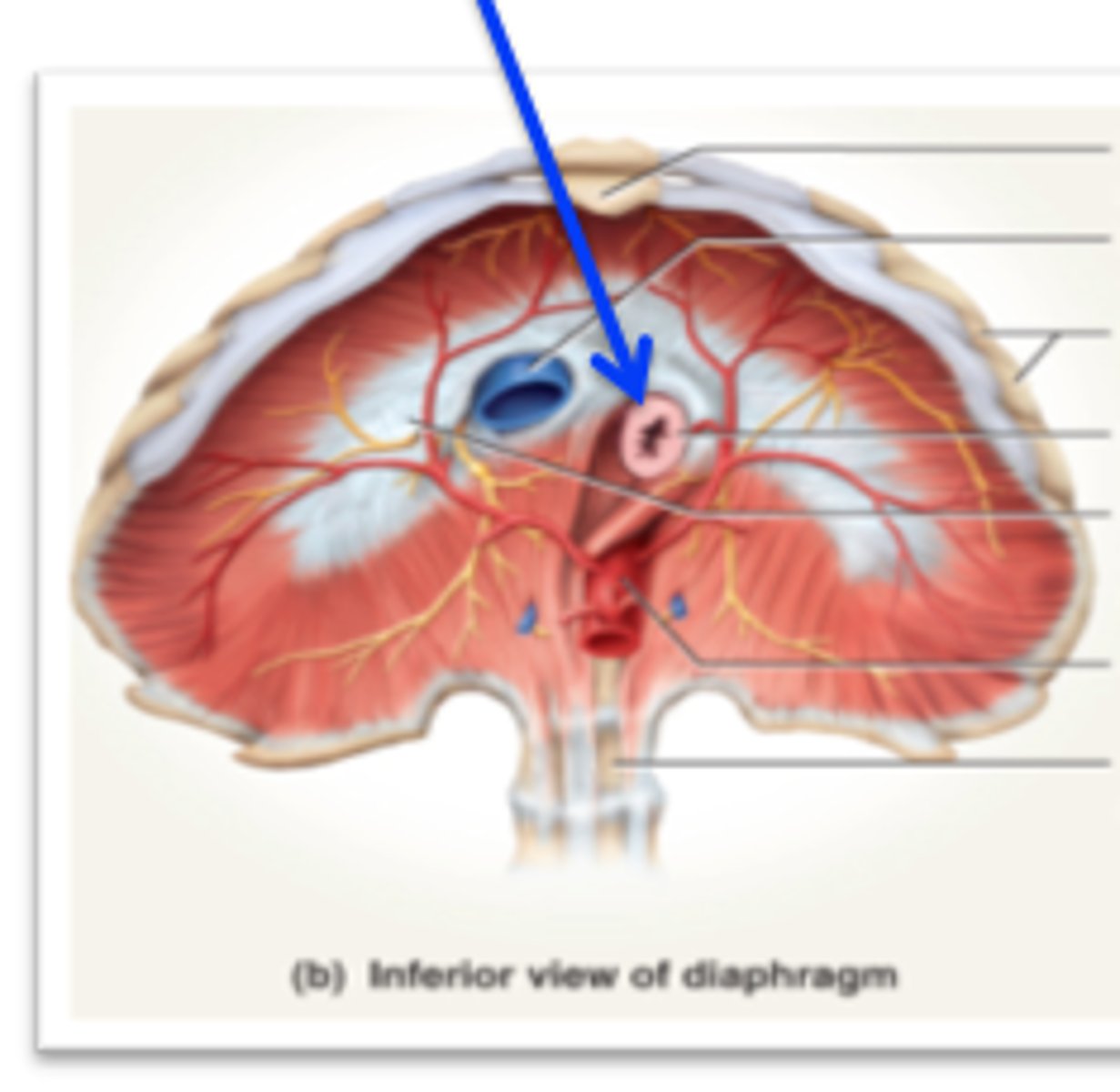
esophageal hiatus
hole in diaphragm for esophagus
stomach
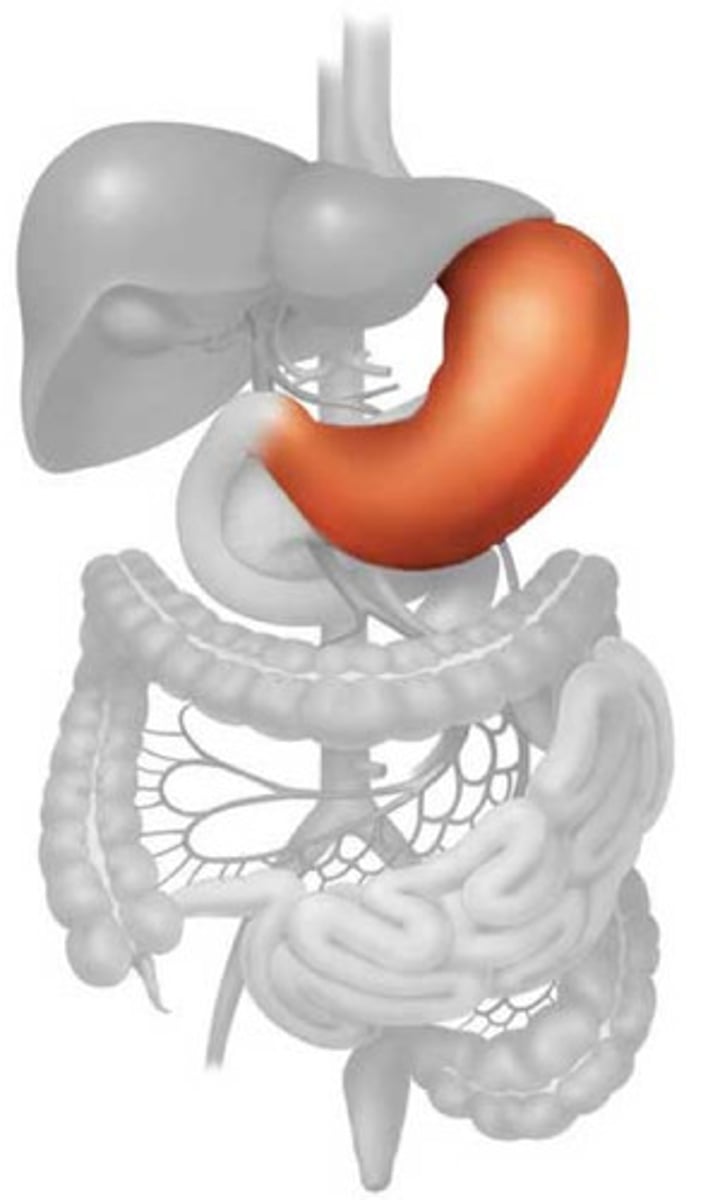
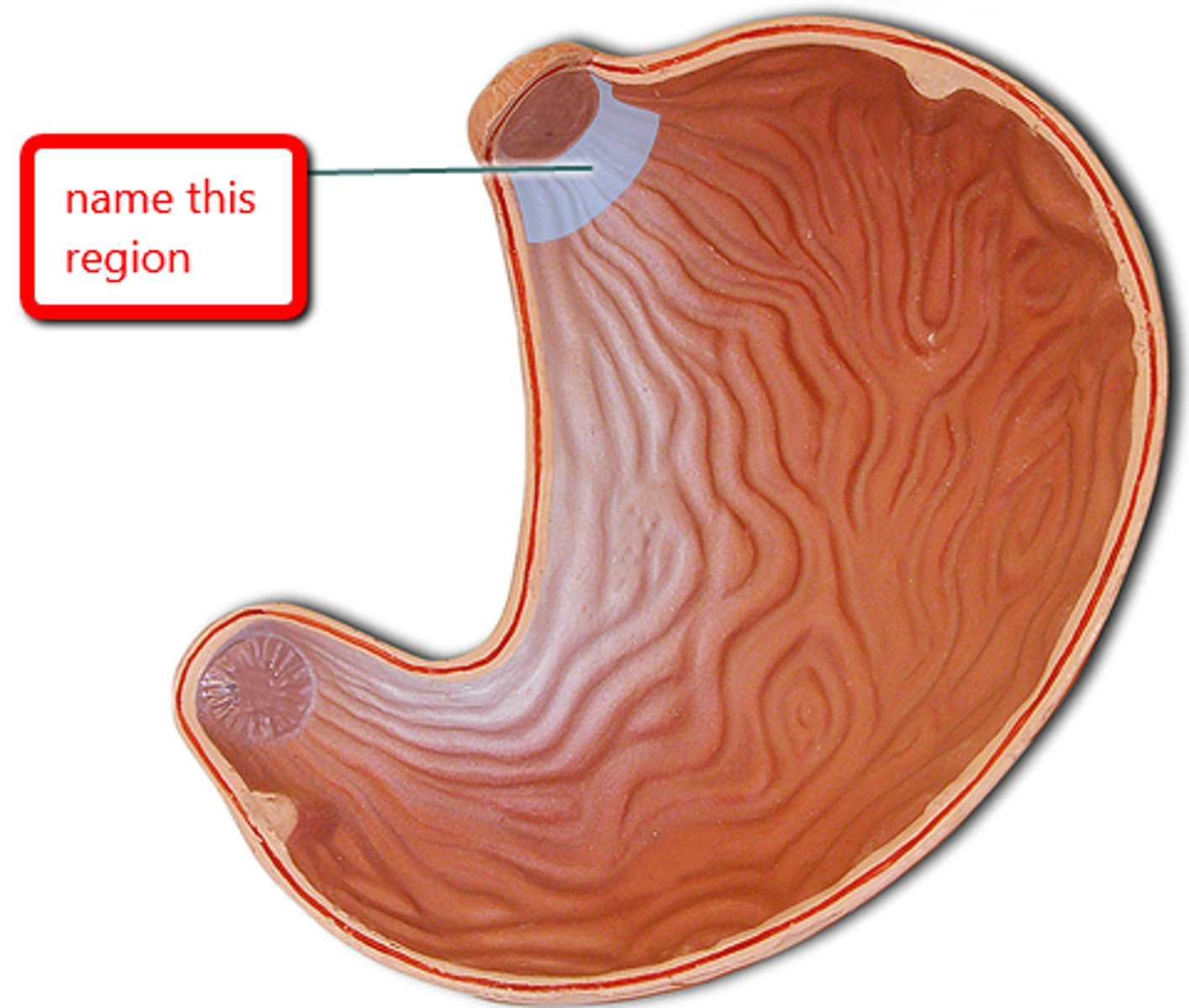
cardia
fundus (stomach)
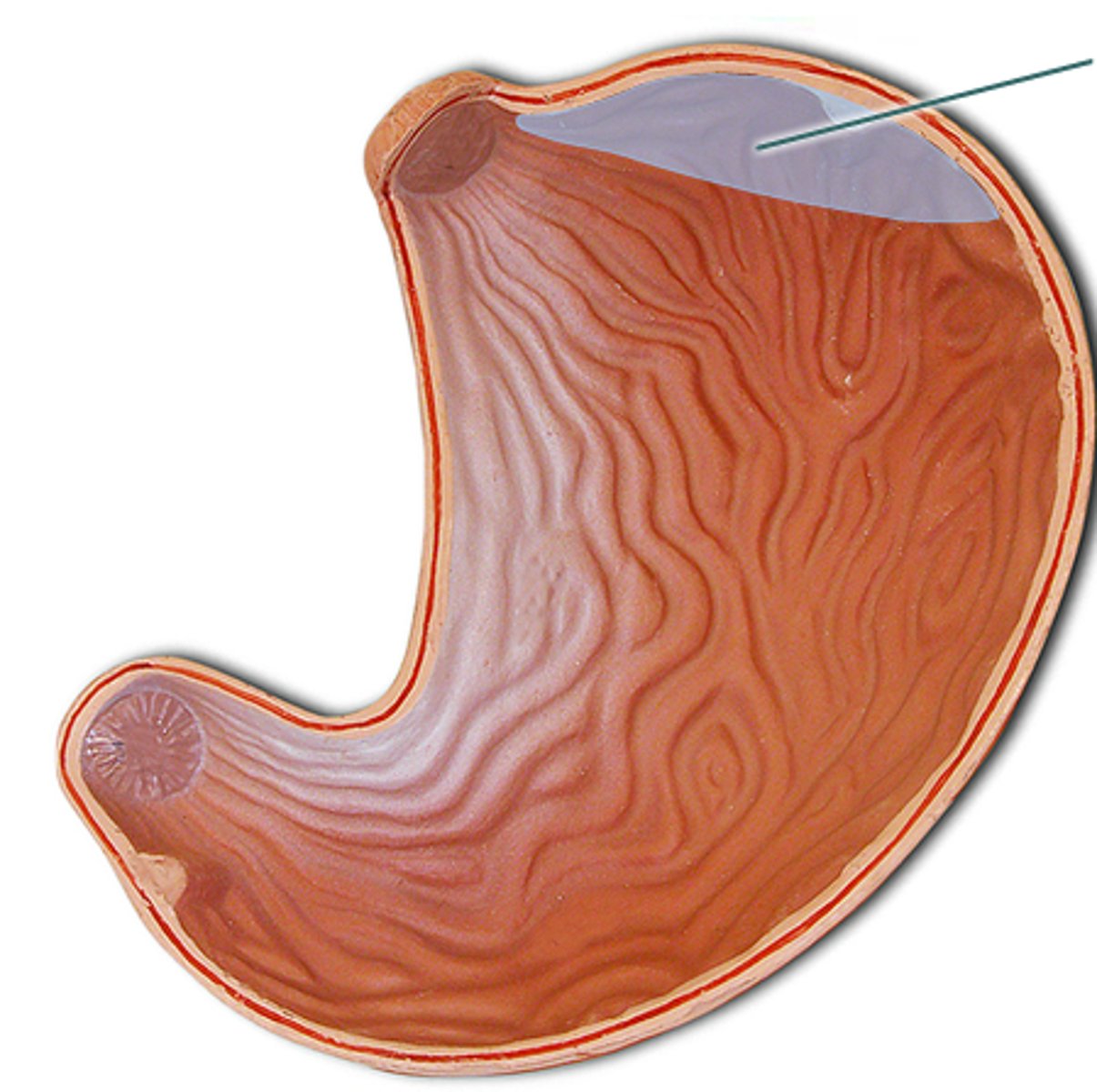
body (stomach)
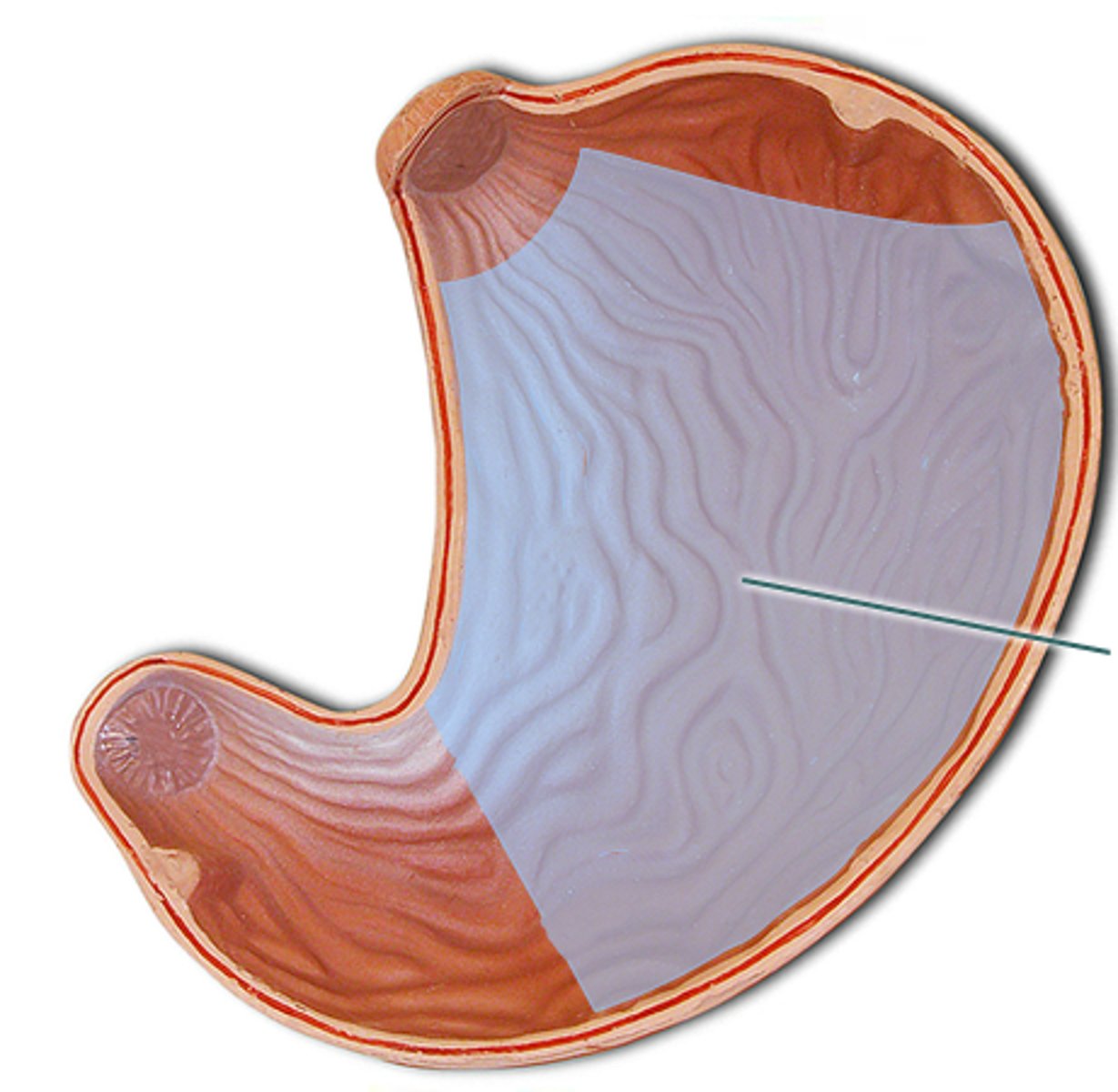
pylorus
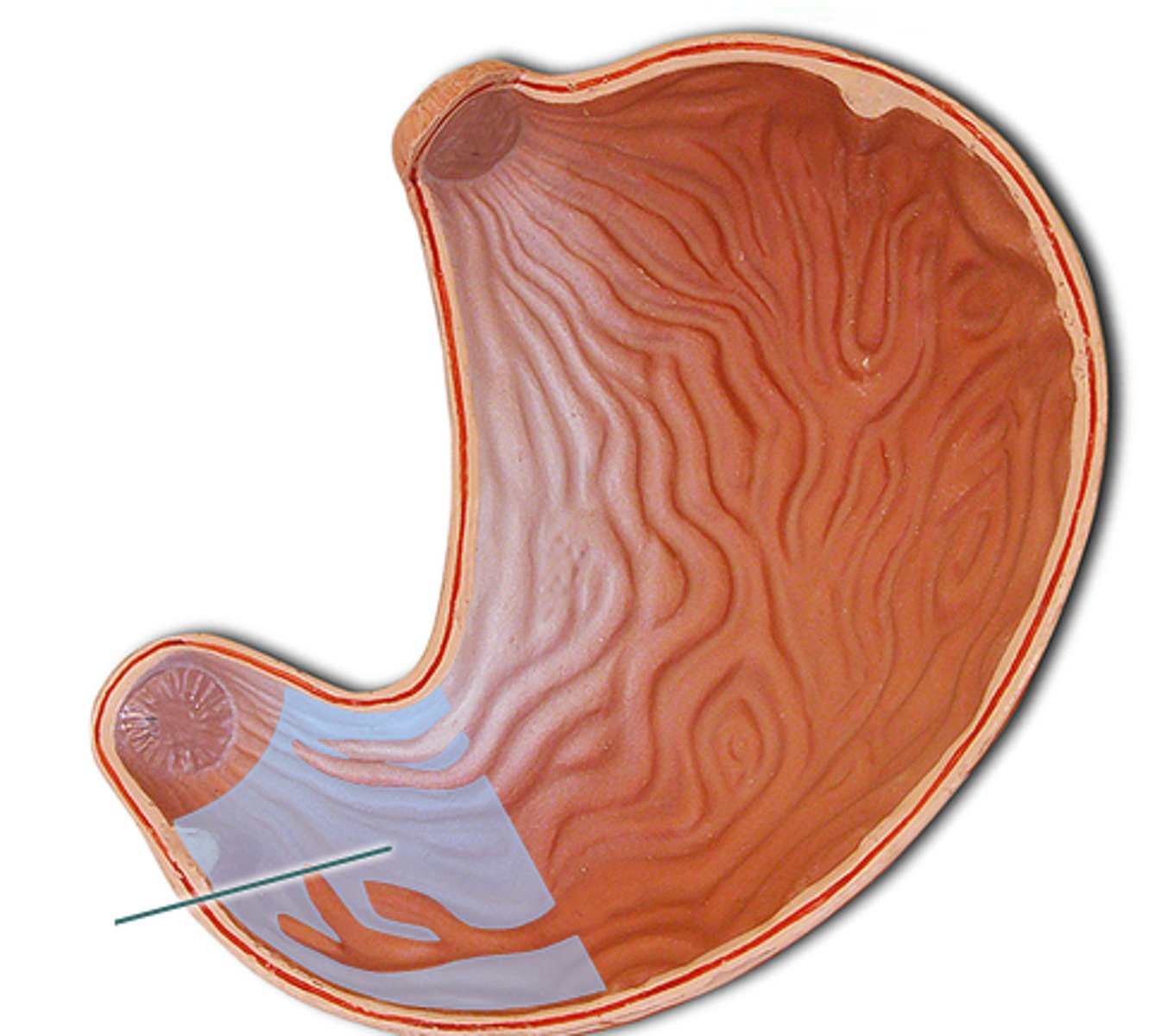
pyloric sphincter
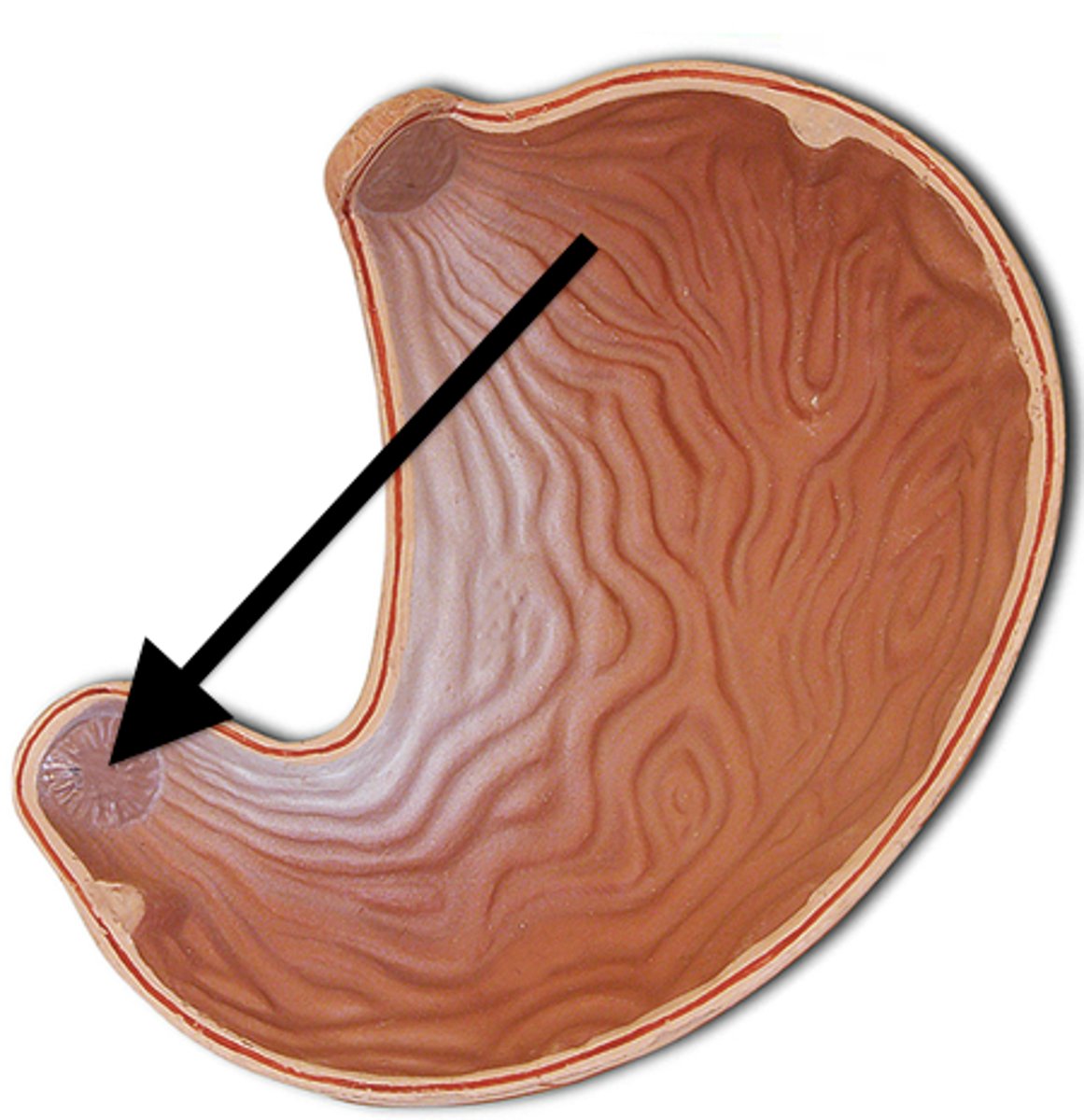
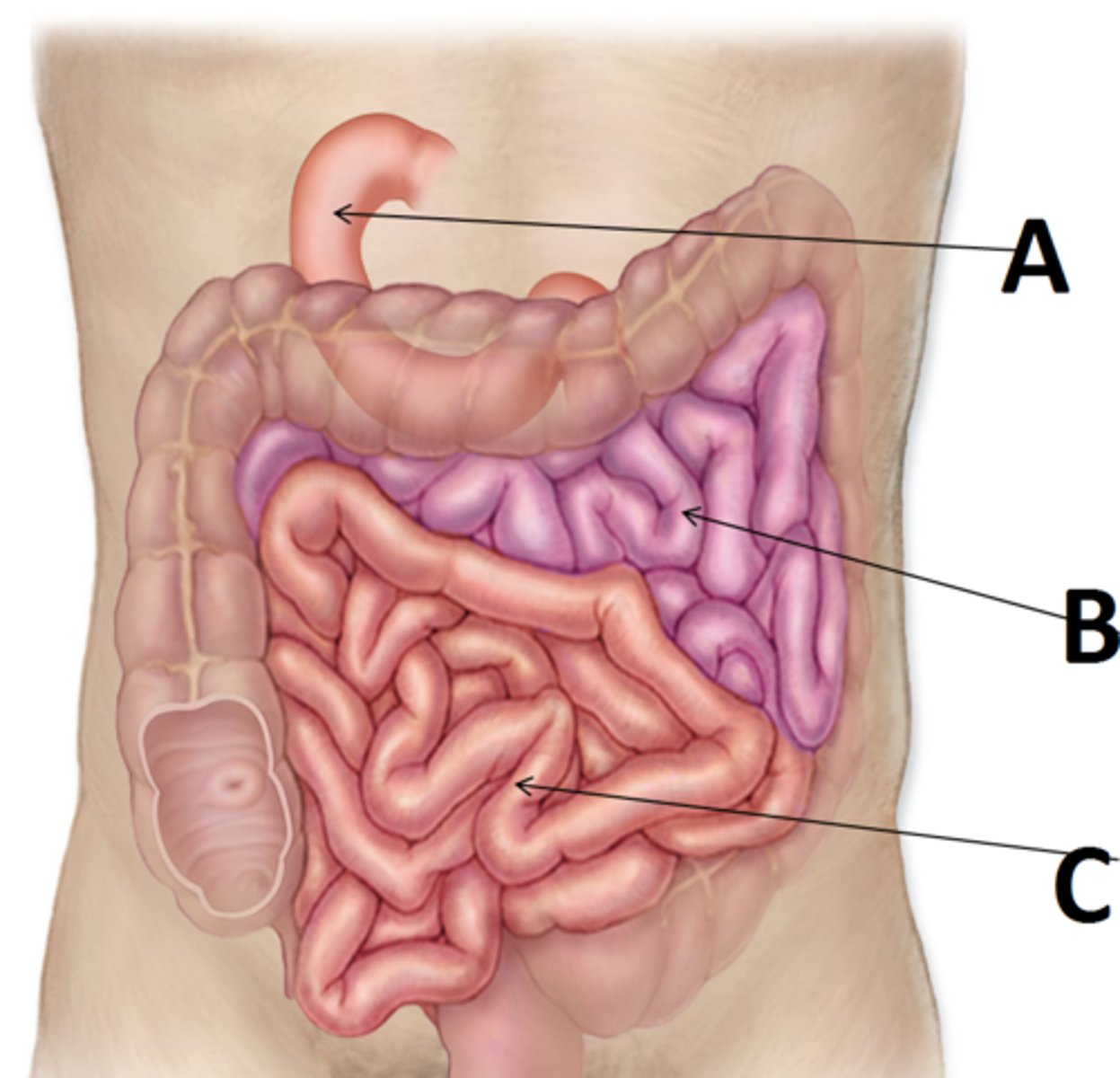
small intestine
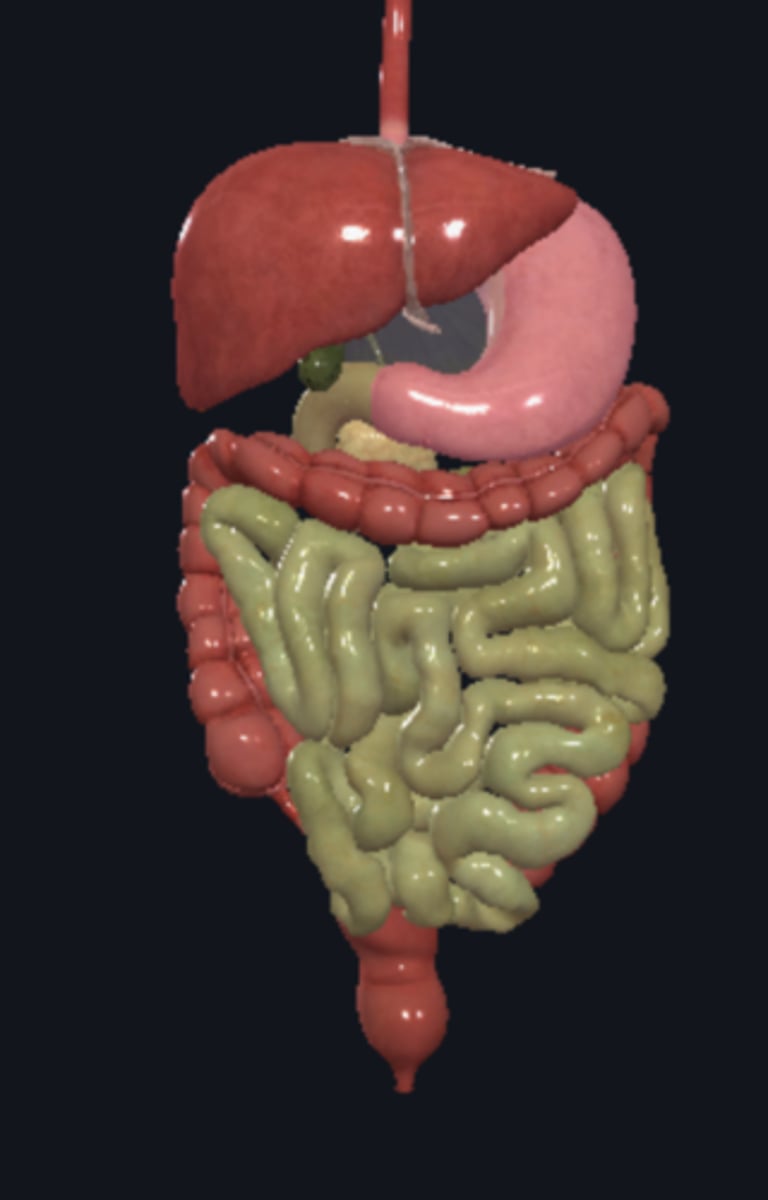
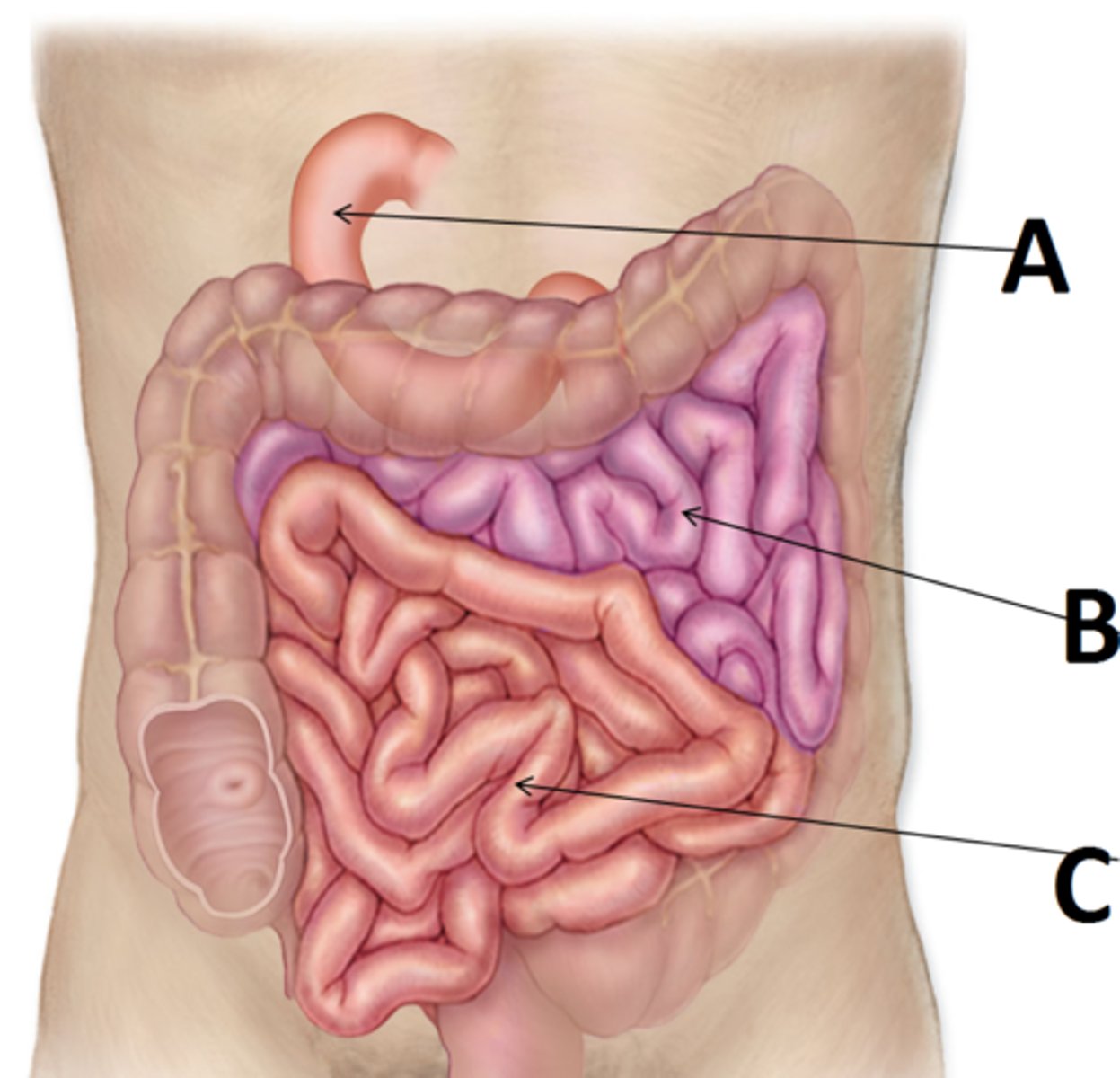
duodenum
A
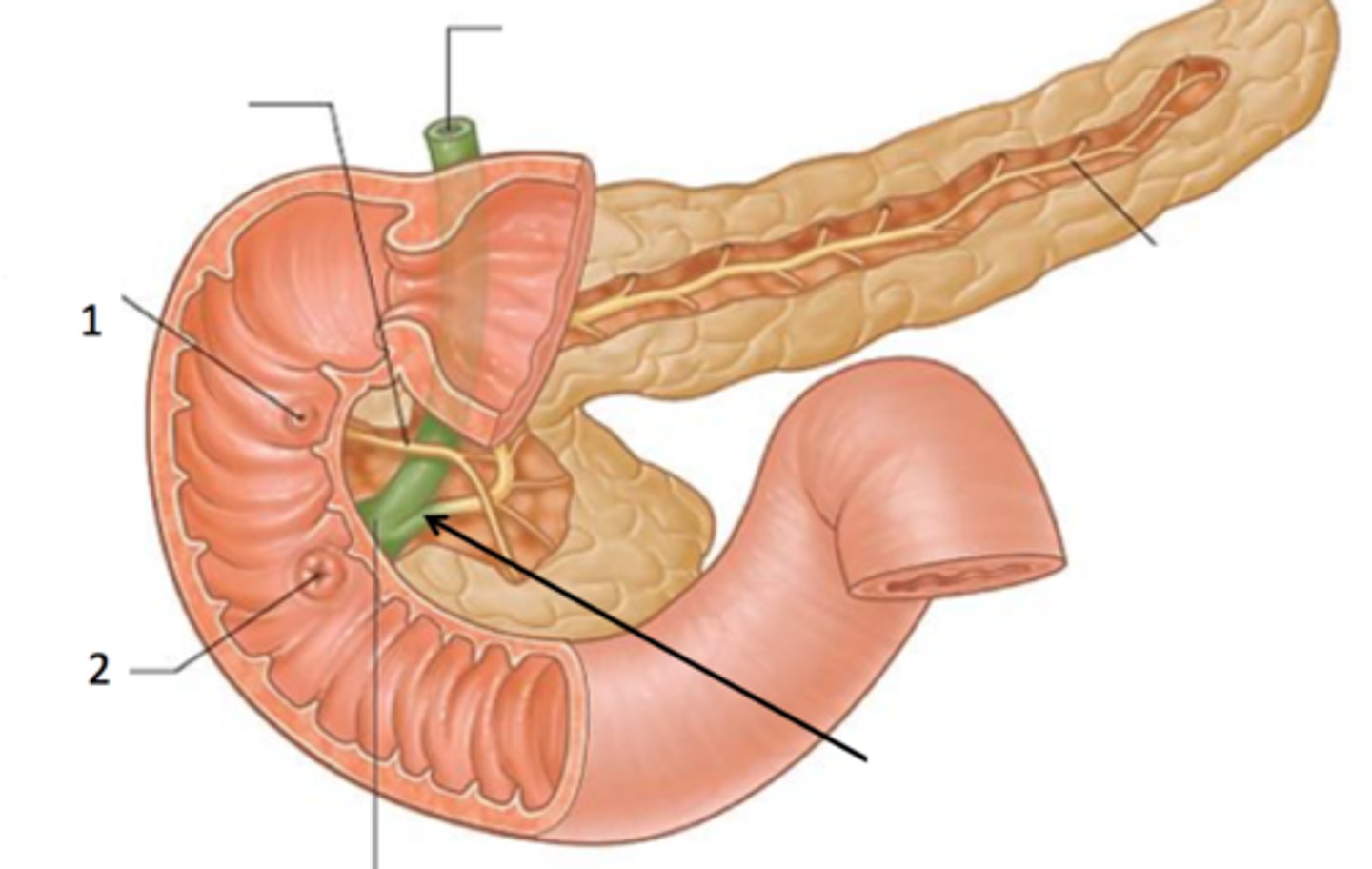
major duodenal papilla
exit of hepatopancreatic duct
minor duodenal papilla
- #1
- exit for accessory pancreatic duct
jejunum
B
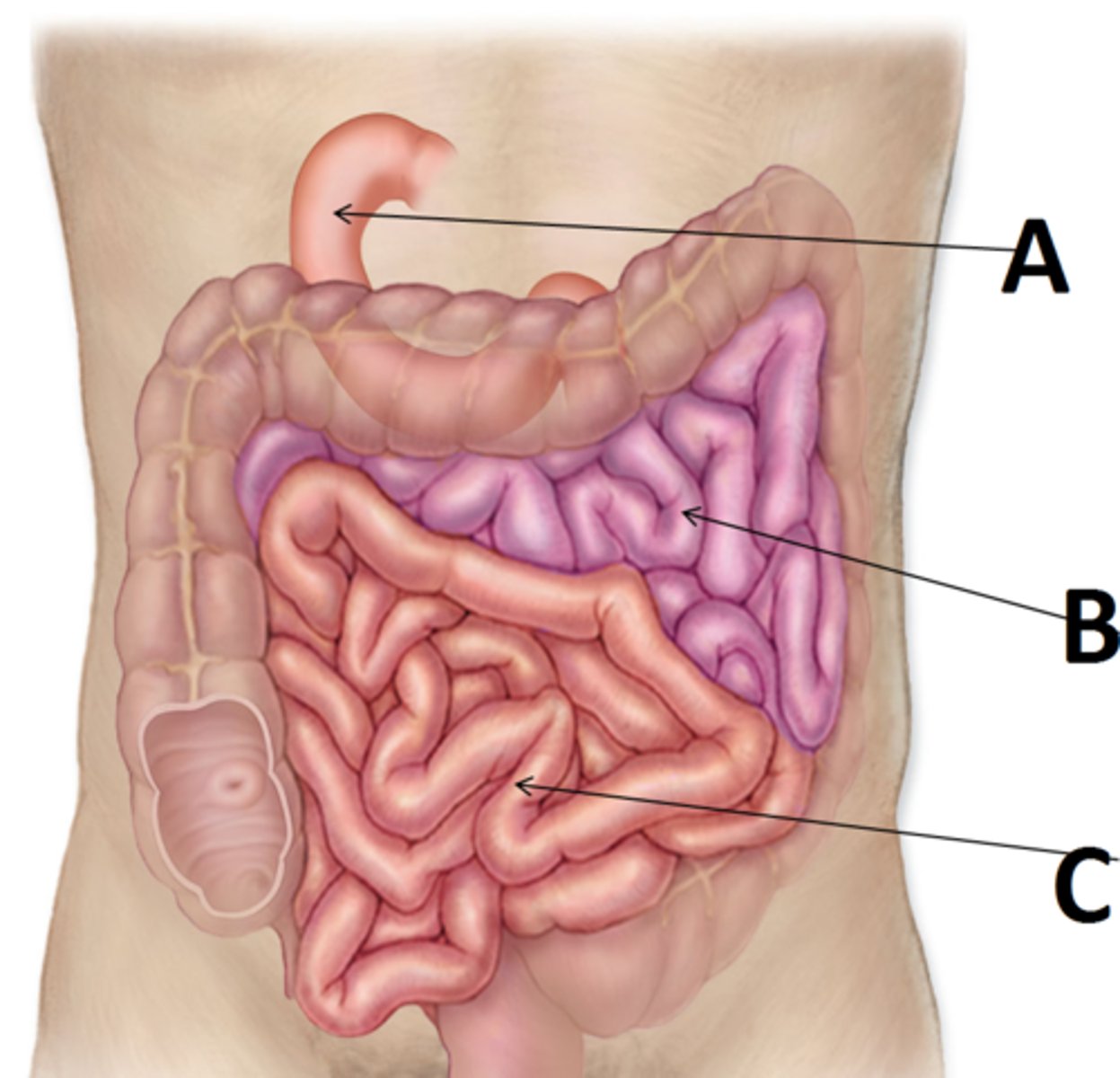
ileum
C
ileocecal orifice
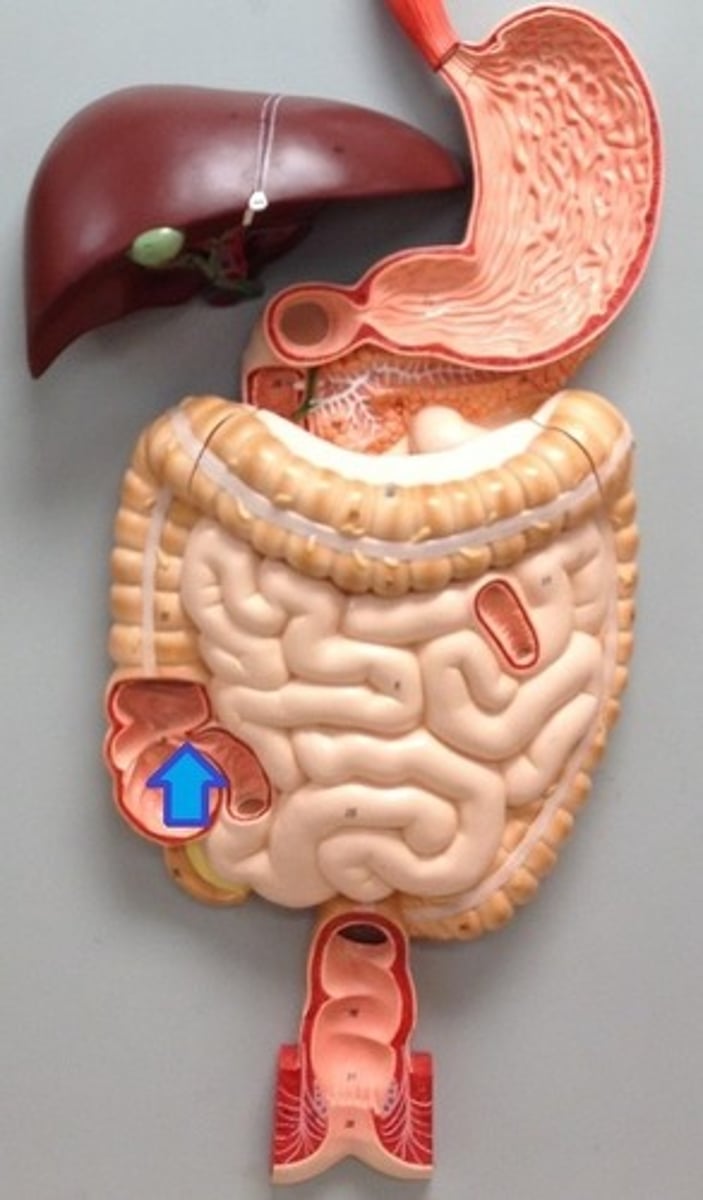
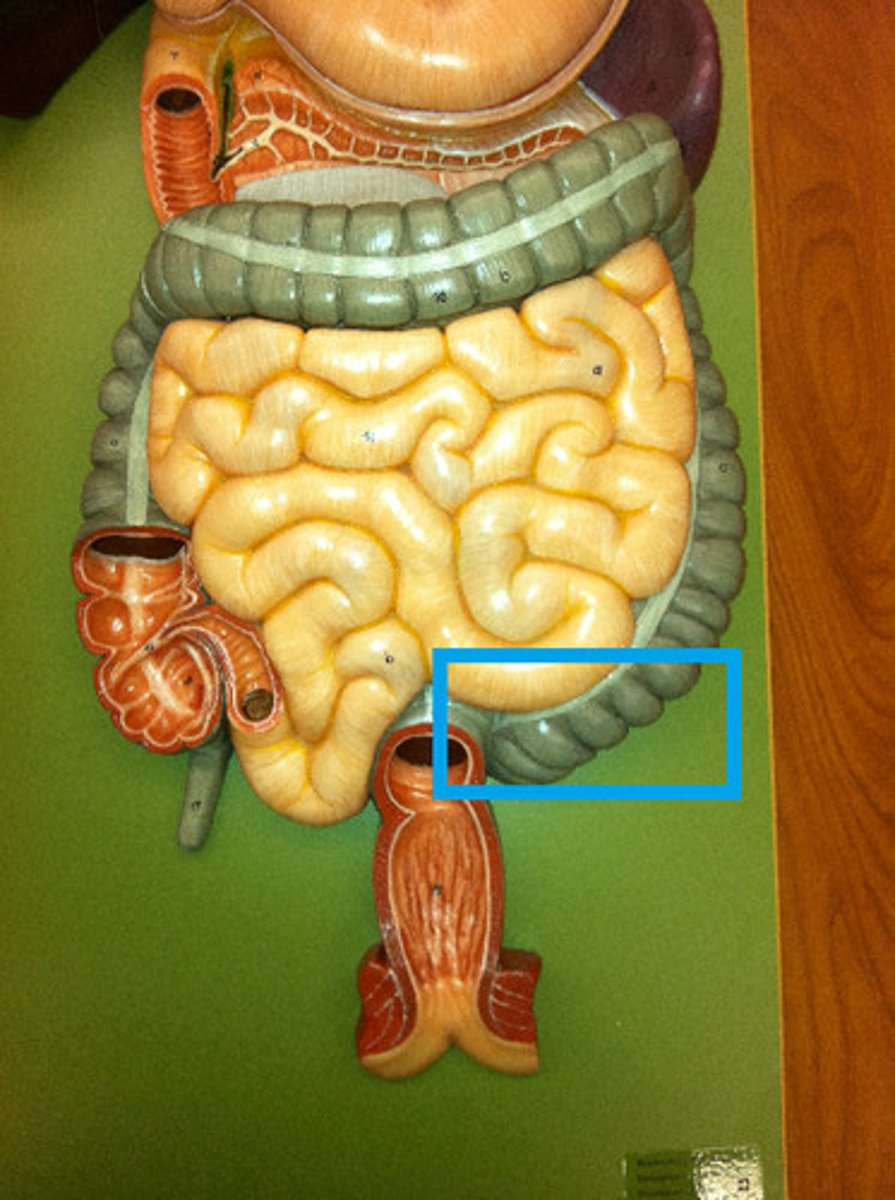
large intestine
vermiform appendix
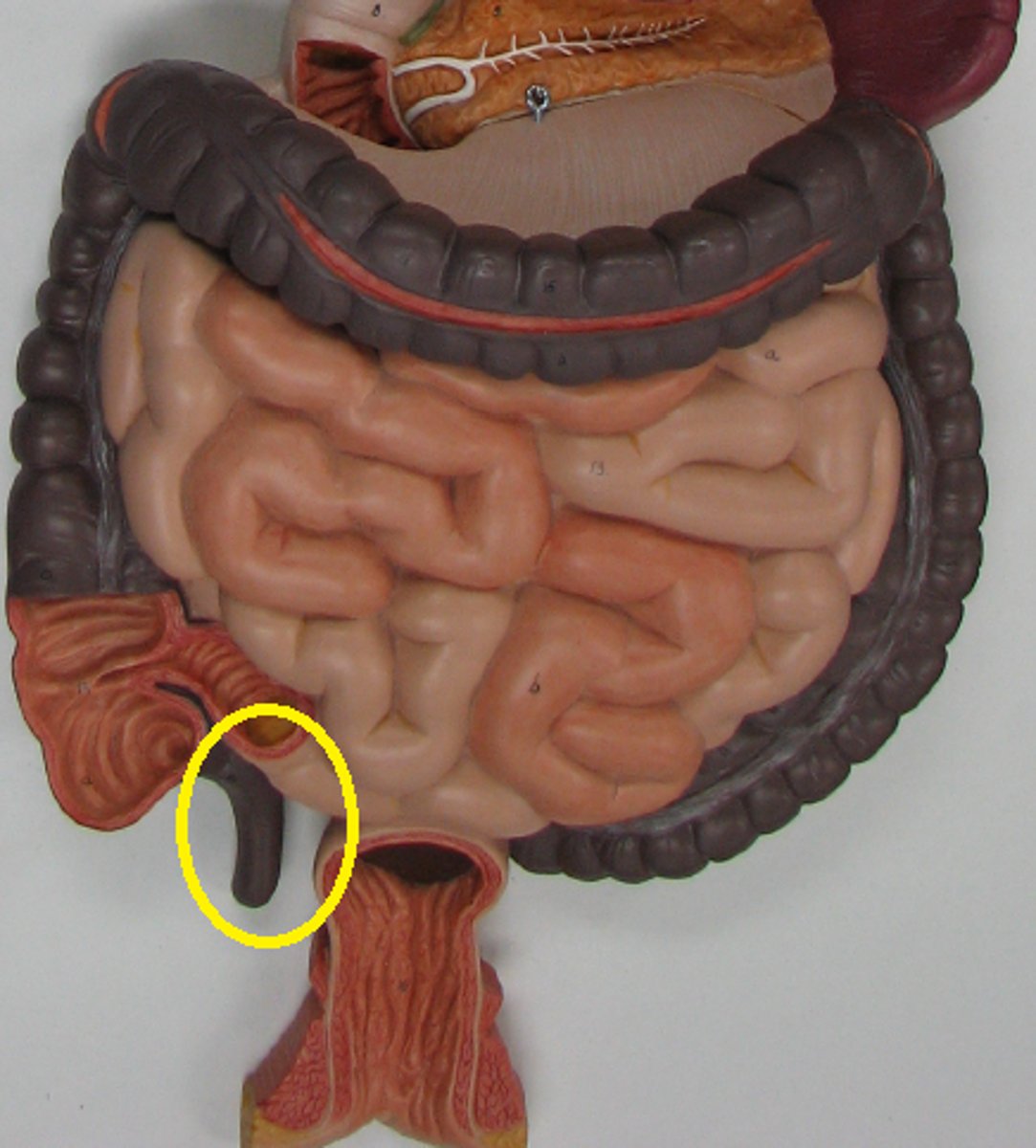
cecum
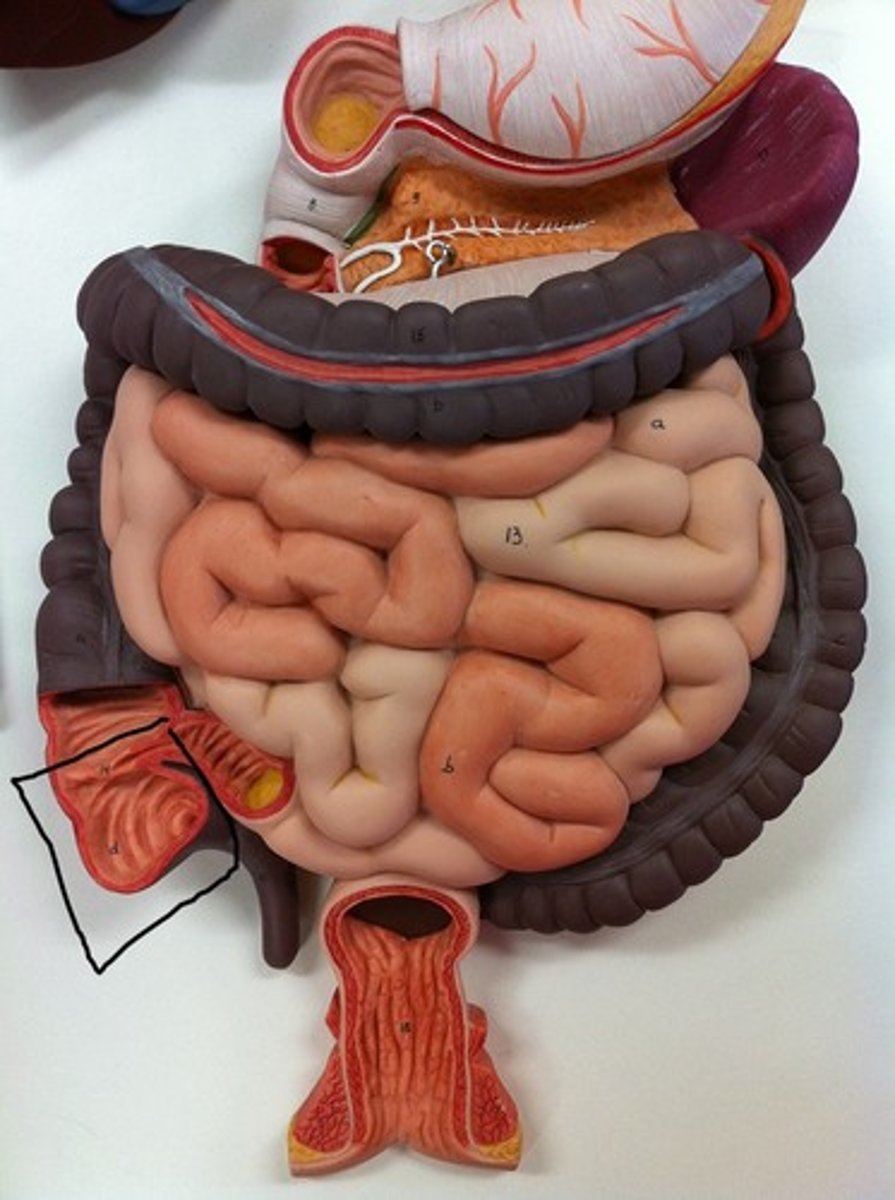
ascending colon
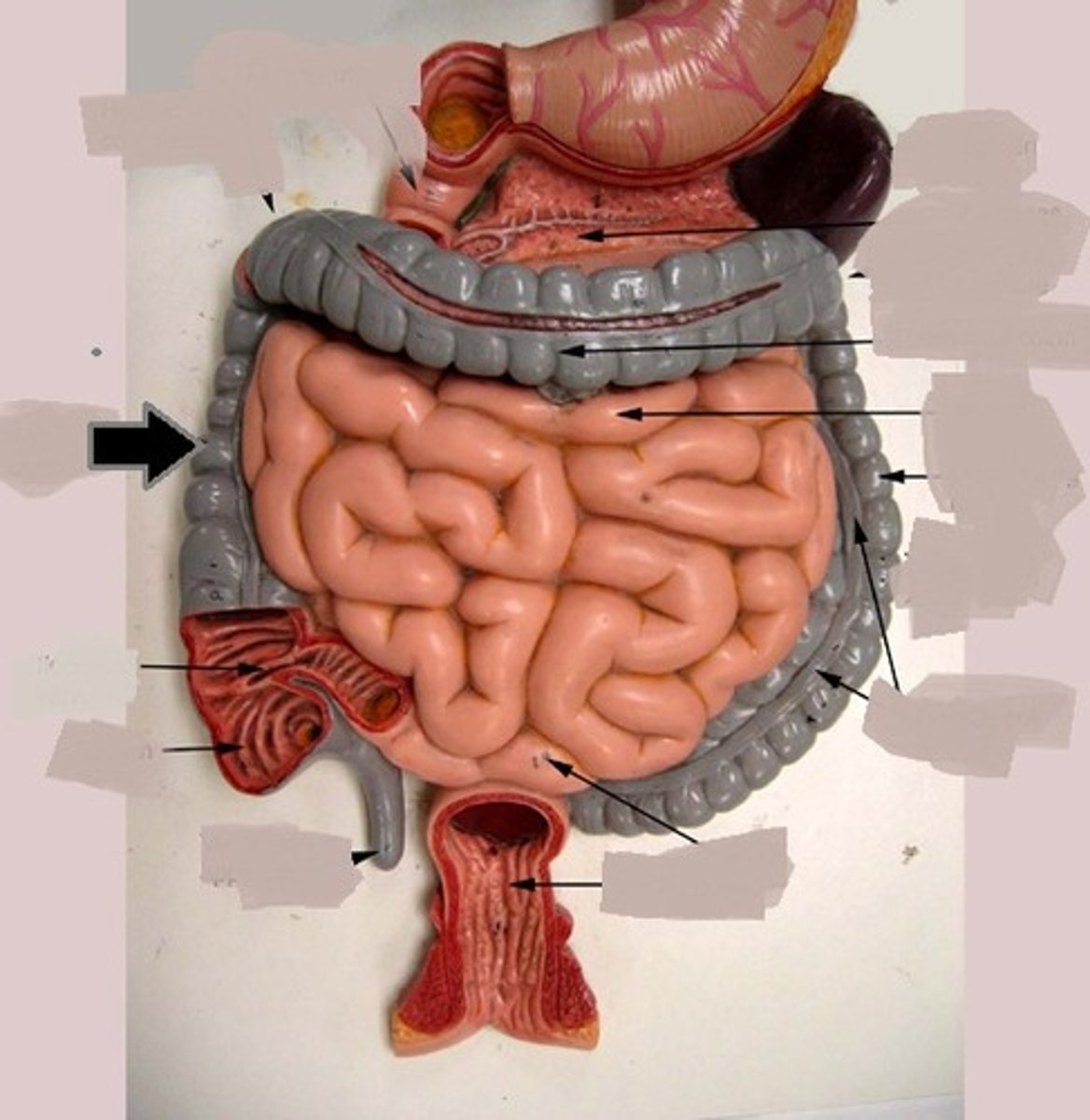
transverse colon
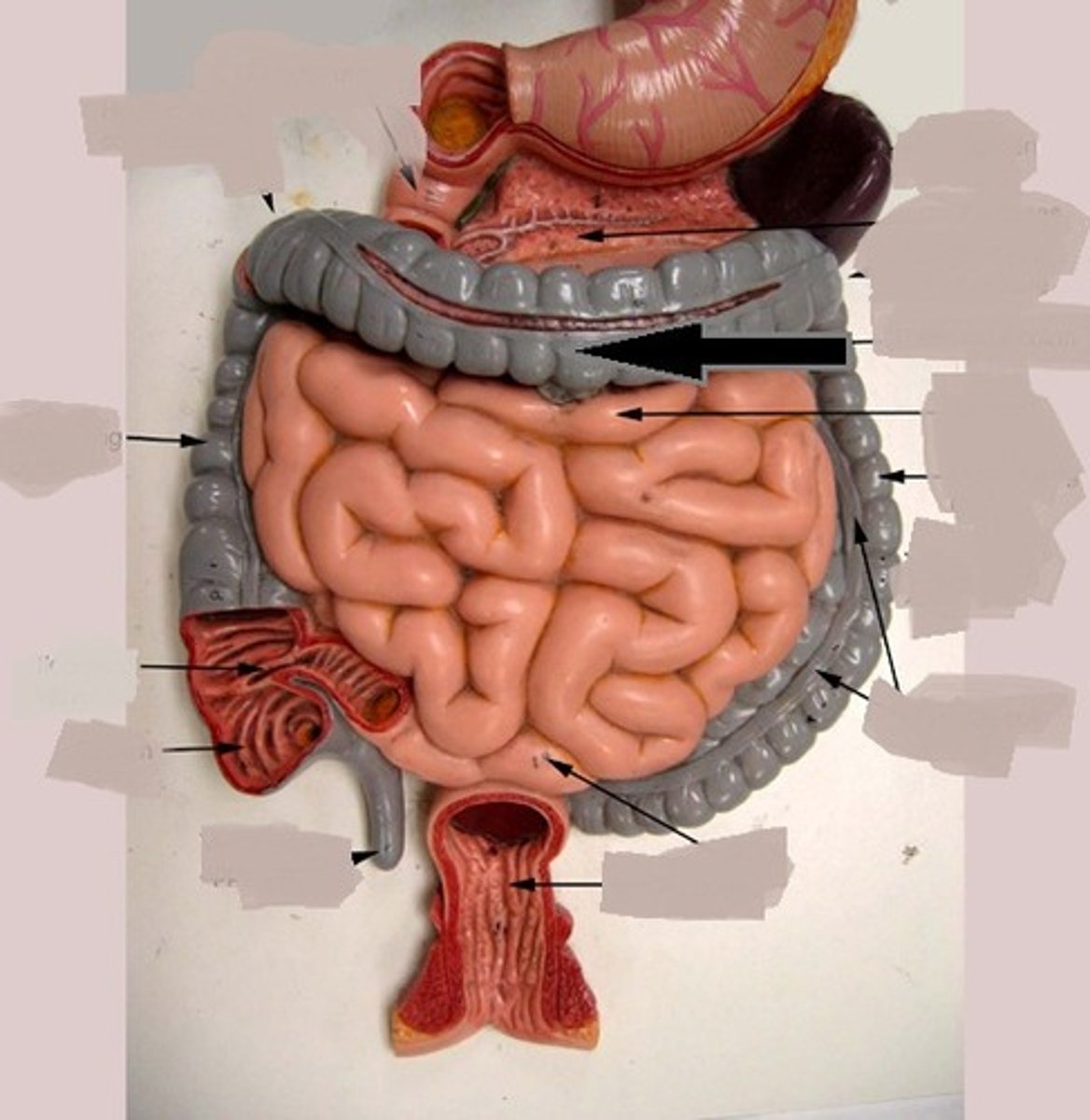
descending colon
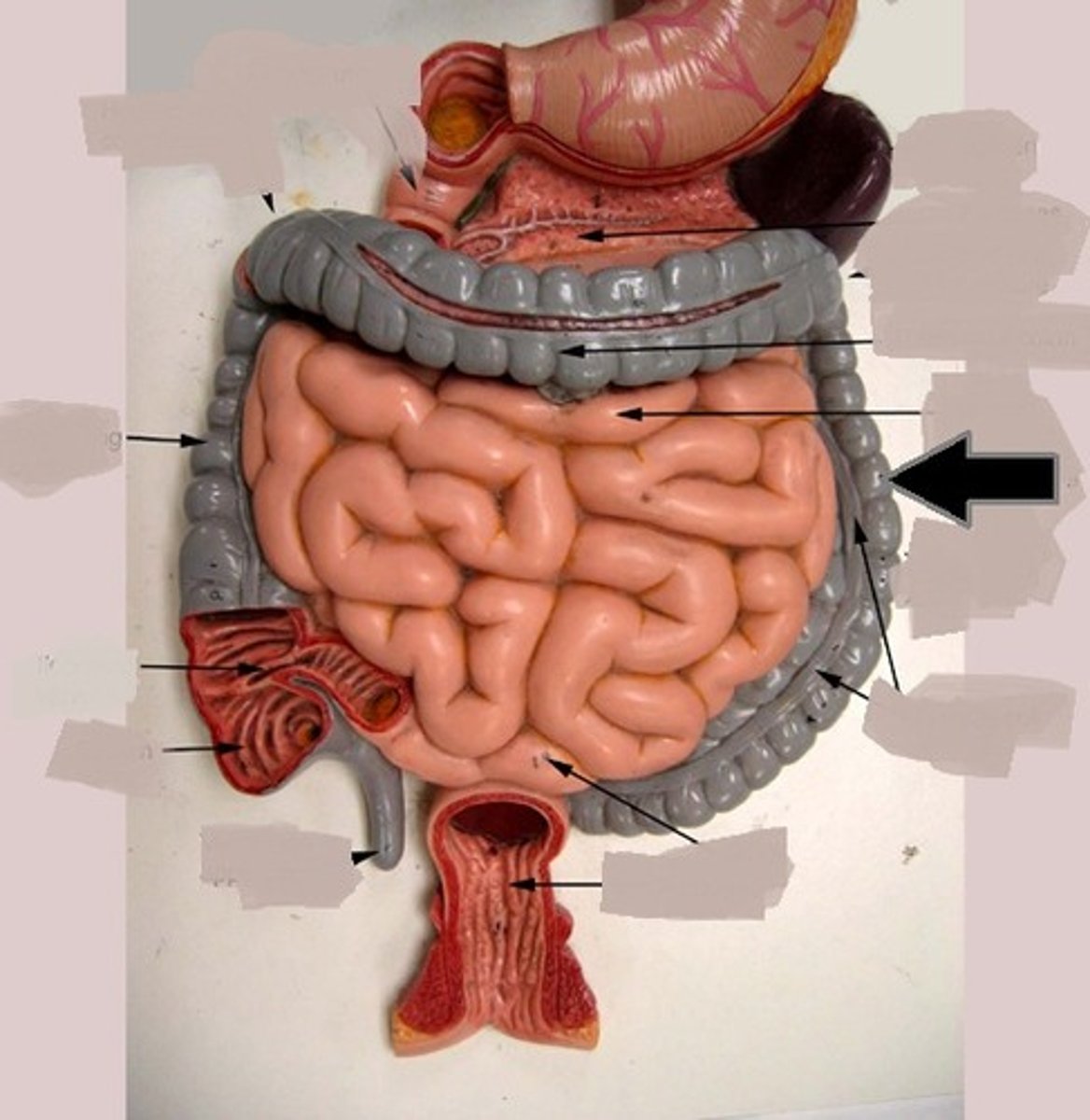
sigmoid colon