Week 4 Prep Vid
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What information do pulmonary function tests give us & what is it used for
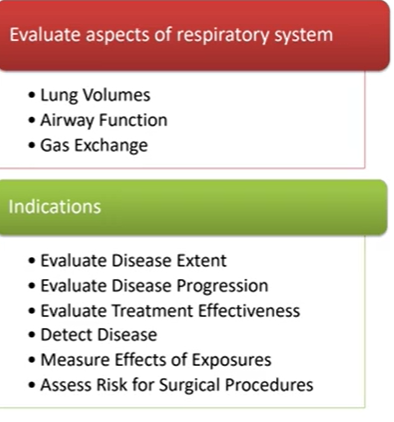
When are these tests used
Not in emergency patient care - patient already under stress
These are used for ongoing patient care
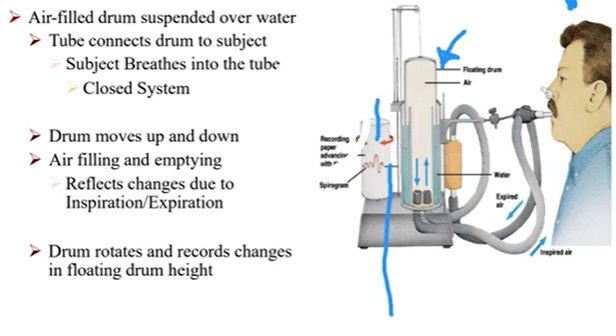
Spirometer
A devise that measures the volume of air that moves in or out of the lungs
How does a spirometer work
It’s an air filled drum suspended over
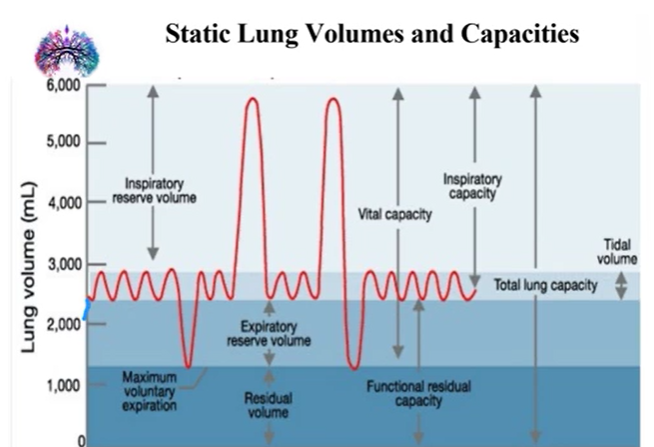
Tidal volume
what is it
what are normal values
what varies it
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
what is it
what are normal values
what is its use
what varies it

Expiratory Reserve Volume
what is it
what are normal values

Residual volume (in L and % of total lung capacity (TLC))
1.2L
25% of TLC
Who would have an increased residual volume
Emphysema - due to loss of elastic recoil of the lungs thoracic cavity can’t move down and in like it should during expiration. Air gets trapped and can’t get out - RV goes up
What would cause you to have a decreased residual volume
An increase in the contractility / elastic recoil of the lungs
Lung volume vs capacity
Lung capacity is 2 or more lung volumes added together
Inspiratory capacity
what is it
normal value
formula
The largest volume that can e inspired from resting end expiration
3.5 L
IC = TV (tidal volume) + IRV (inspiratory reserve volume)
Expiratory capacity
what is it
normal value
formula
Forceful expiration after a normal inhalation
1.6L
EP = TV (tidal volume) + ERV (expiratory reserve volume)
Pulmonary vascular resistance is lowest at what point
Functional residual capacity
Functional residual capacity
what is it
normal value
formula
what percentage of TLC
The volume of gas remaining in the lungs after a normal expiration
2.3 L
FRC = RV + ERV
40% of TLC
How do you measure FRC
Helium dilution method
hook up patient to spirometer filled with air & known conc. of helium
patient expires to end of normal expiration
the volume in the lungs is FRC (V2)
Let patient breathe in & out until it reaches equilibrium
A formula is used to estimate V2
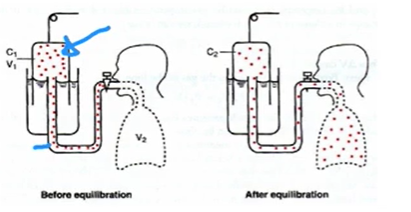
Formula to estimate FRC (V2) from helium dilution method for measuring FRC

Vital capacity
what is it
normal value
formula
Volume change between maximal inspiration and maximal expiration
4.8L
VC = IRV (inspiratory reserve volume) + TV (tidal volume) + ERV (expiratory reserve volume)
TLC
what is it
normal value
formula
Total volume of air in lungs after maximal inspiration
5.8L
TLC = VC (vital capacity) + RV (residual volume)
Why can’t you measure TLC with a spirometer
The residual volume can’t be expired
How do you measure TLC
helium dilution technique
What is a vitalograph used to measure
Dynamic changes
Flow rate
Forced vital capacity (FVC) (forceful expiration for 6 seconds after maximal inhalation)
FEV1
Forced expiratory value in 1 second
(the first second on a FVC graph)
What percentage of someone’s FVC is normally expired in the first second (normal range)
75-80%
What is FEV1 used for
Used to characterise lung disease as restrictive / obstructive
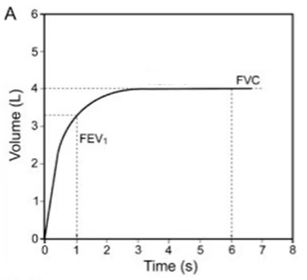
Is this a normal curve
Yes
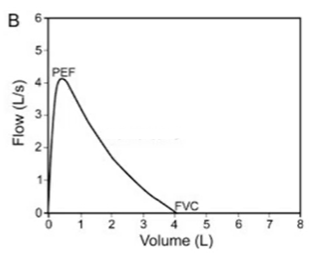
Is this a normal curve
Yes - most air flow at the start of the 6 seconds