MGCR 293 Chapter 8: Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary related to Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition, enhancing understanding of important economic concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Monopoly
A market structure characterized by a single seller of a product with market power to set the price unlike perfect competition.
Characteristics of a monopoly
One seller and many buyers in the market. There is only one seller, who supplies the entire market
The firm’s product is unique and has no close substitutes
High barriers of entry that prevent other firms from entering the market
What are the most common barriers of entry to monopoly markets?
Legal restrictions such as patents or copyrights that prevent other firms from producing the same product, licensing requirement
Economies of scale. One firm can supply the entire market at the lowest possible cost
The monopolist’s control of input supplies
Technology controlled by the monopolist such as pharmaceuticals
Monopolistic Competition
A market structure that blends characteristics of perfect competition and monopoly, where firms sell differentiated products.
Lerner Index
A measure of a firm's market power, calculated as (P - MC) / P, indicating the ability to price above marginal cost.
Monopoly Profit Maximization Condition
The condition for maximizing profit, determining its profit-maximizing output by setting MR = MC (Marginal Revenue equals Marginal Cost). The firm sets the profit-maximizing price from the inverse demand function at the profit-maximizing output level.
A monopoly will shut down or continue producing if…
In the short run: if price at profit-maximizing output < AVC
In the long-run: if price < LAC
Monopoly demand curve
Since the monopolist supplies the entire market, the monopolist’s demand curve is the downward-sloping demand curve.This indicates that the monopolist has market power to set its price above marginal cost and let the consumers choose how much they wish to buy at that price.
MR expressed in terms of price elasticity of demand
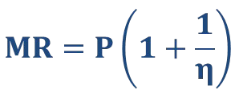
What is the profit-maximizing condition of a monopoly?
As long as MC>0 and P>MC, then to maximize profit the monopolist must operate on the elastic portion of its demand curve (n < -1)
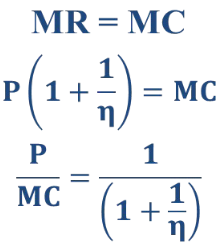
What is the learner index and its function?
It measures a firm’s level of market power. A larger learner index indicates more market power and vice versa. It is a positive number ranging from 0 to 1. The more elastic “n” is, the smaller learner index and price will be.
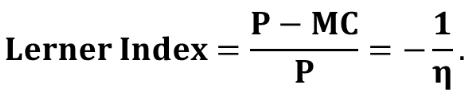
What is monopolistic competition and its main characteristics?
Monopolistic competition is a mixture of perfect competition and monopoly.
There are many small firms in a market in which barriers to entry are very low.
Each firm offers differentiated products
downward sloping demand curve
profit maximizing contition MR = MC
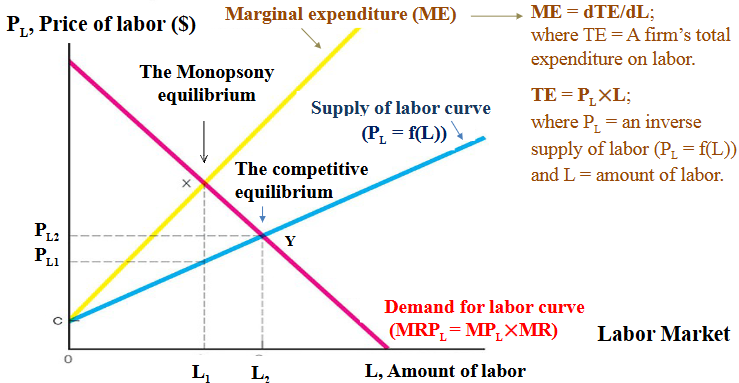
Monopsony
A market structure in which there is a single buyer with market power that can influence the price of goods. The monopsony power enables the buyer to purchase a good for less than the price that would prevail in a competitive market.
Profit-maximizing condition for monopsony market
To maximize profit, the monopsony firm hires quantity L1, where marginal expenditure and MRPL intersect (point X). Marginal benefit = marginal expenditure
Barriers to Entry
Obstacles that prevent new competitors from easily entering an industry or area of business.
Marginal Revenue (MR)
The additional revenue gained from selling one more unit of a product.
Downward-Sloping Demand Curve
A demand curve that shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded, indicating that as price decreases, quantity demanded increases.
Economic Profit
The difference between total revenue and total costs, including both explicit and implicit costs.
Long-Run Equilibrium
A situation in which all firms in a market earn zero economic profit, and the demand curve is tangent to the average total cost (ATC) curve.
Short-Run Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition
Occurs where MR = MC, and the firm sets the price from the demand curve.
Joint Products-Fixed Proportions
A production process where two or more products are produced together, in fixed proportions.