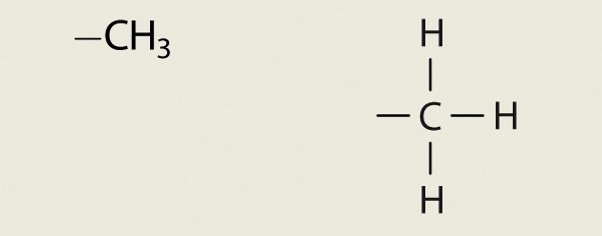Biology 101- Chapter 2
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Freshman year Biology 101
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Atoms
Smallest Unit of Matter
What do Atoms Consist of?
Protons (+), Neutrons (No Charge), Electrons (-)
Shells
Electrons distributed around the nucleus at different energy levels
Valence Shell
The Outermost electron shell of an atom
How much can Each Shell Hold?
1st Shell has a Max of 2 electrons
All other shells have a max of 8 electrons
How does a Valance Electron Fill up it’s shell?
Chemical bonding between atoms
Molecule
2 or more atoms linked by chemical bonding
What are the 4 types of Chemical Bonds?
Nonpolor covalent
Polar covalent
Ionic
Hydrogen
Nonpolor covalent
Equal sharing of e: Their electronegative are equal or almost the same
Polar Covalent
Unequal sharing of e: Due to a difference of electronegative
Ionic Bonding
Donating/ Stealing: Due to a LARGE difference of electronegative
Hydrogen Bonding
No sharing or Donating: When there’s a partial positive Hydrogen interacts with a partial negative atom of a different Molecule
Electronegativity
Tendency to attract electrons. (More = Higher)
What Does Electronegativity influence?
Chemical Bonding
What kind of Molecule is Water?
Polar Molecule
Hydrophillic
Loves Interacting with water
Hydrophobic
Hates interacting with water
What is the result of the H and O bond in water?
Water always has a partial positive Hydrogen and a partial negative Oxygen
Water
required for living organisms and is a universal solvent
PH
Influences the rate of chemical reactions and homeostasis
What is the PH of Water?
7
[H+] = [OH-]
Acidic Solution
[H+] > [OH-]
Basic Solution
[H+] < [OH-]
Cohesion
The attraction of water molecules to one another. A result of Hydrogen bonding.
An Example of Cohesion
When water is Frozen. The water is more stable (bonds) but less dense (why it floats)
What Chemical make up Living Organisms?
Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen
What Molecules do you need to be consider an Organic Molecules?
Carbon and Hydrogen
What Special about Carbon?
Can from 4 covalent bonds and allows for structurally diverse molecules to be made
Structurally diverse molecules allows for?
Functionally diverse organic molecules.
Structure and function?
Go hand in hand!!
4 Types of Organic Molecules
Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids
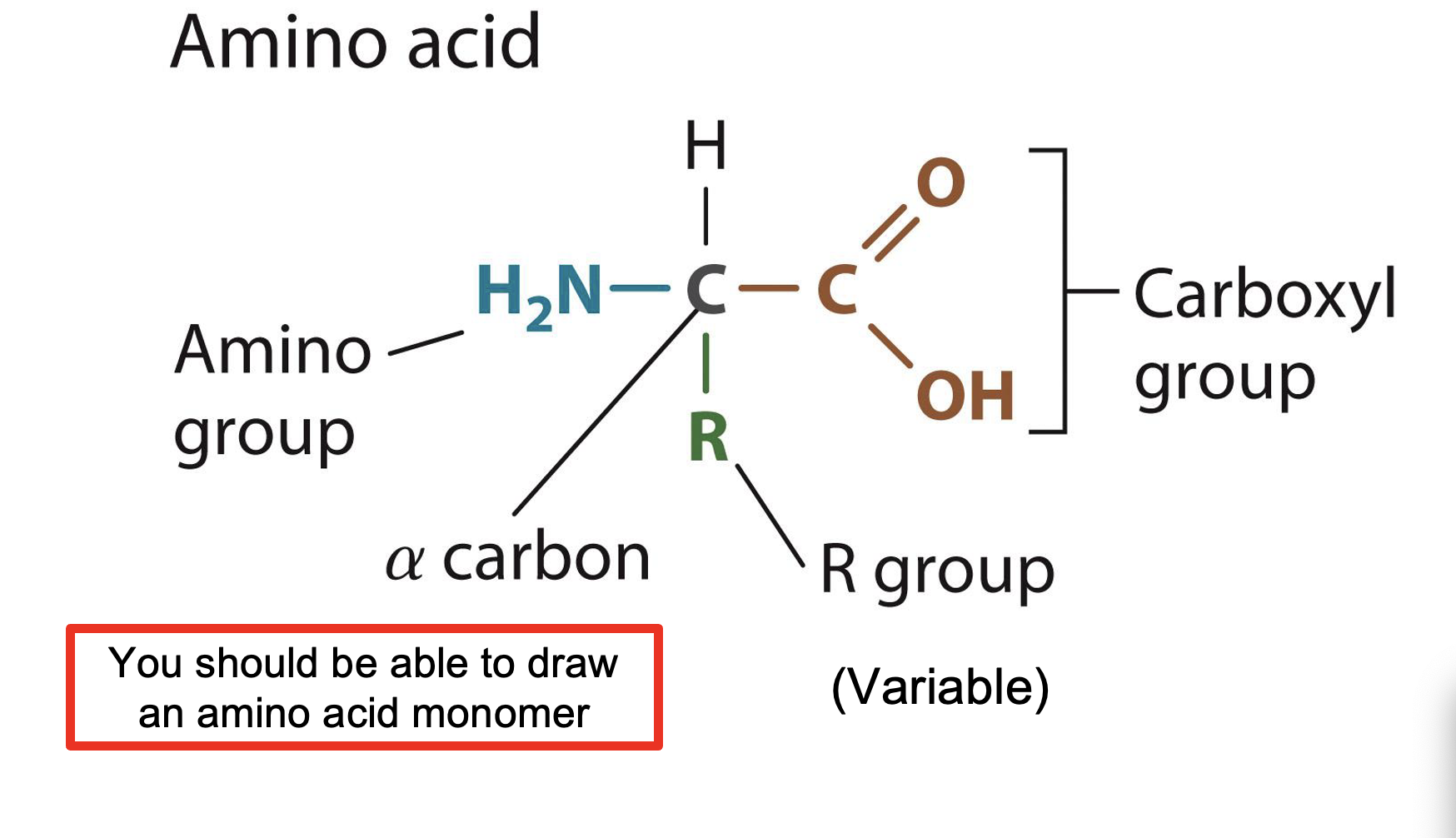
Proteins
-Provides structural support of cells and helps chemical reactions occur (enzymes)
-They are also known as Polypeptides
What are the Polymers and Monomers of Proteins?
They are Polymers that are created by joining amino acids (monomers) by using a covalent bonds called peptide bonds.
They are also linked by peptides bonds
How do Proteins look like?
Nucleic Acids
Encode and transmit genetic information
DNA and RNA
What Polymers and Monomers do Nucleic Acids have?
They are polymers created by linking nucleotide monomers together via a covalent bond called a phosphodiester bond.
What are the Nucleotides Bases?
Cytosine, Thymine(DNA), Uracil (RNA), Guannie, Adenine
What are Pyrimidine bases?
Cytosine, Thymine(DNA), Uracil (RNA)
What are Purine bases?
Guannie, Adenine
What are the inches ends of the Polynucleotide strand?
5’ end (1st) and 3’ end (last)
What can DNA structural look like?
Double helix: 2 twisted polynucleotide strands
Base Pair: 2 nitrogenous based on opposing polynucleotides strands held together by hydrogen bonds
Base Pairs are found in Double helix.
Carbohydrates
Provide structural support for many organisms and a source of energy.
Vary in their structures and functions
What are Carbohydrates polymers and monomers?
They polymers created by linking monsaccharide monomers who are linked via covalent bonds called glycosidic bonds.
Monosaccharides
CnH2nOn
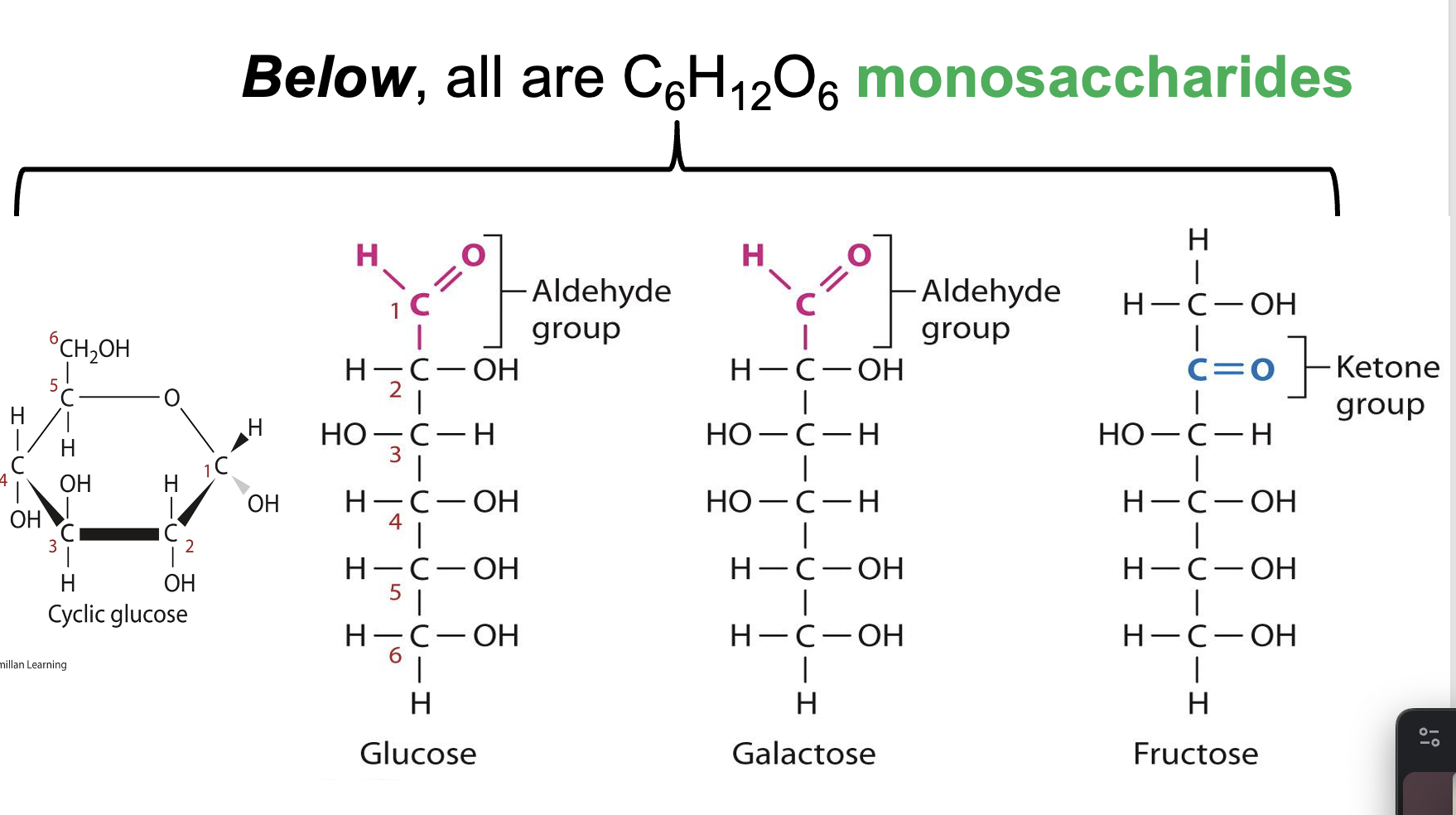
Types of Sugar Molecules
Monosaccharides and Polysaccharides (Glycosidic bonds)
Lipids
Make up cell membranes, store energy, and are important in cell communication.
They are all hydrophobic.
What are Lipids polymers and monomers?
They are not polymers therefore no monomers are able to link up with them.
What are the Lipids groups?
Triglycerides (fats), Steroids, Phospholipids
Triglycerides
Are composed of 3 fatty acids and Glycerol
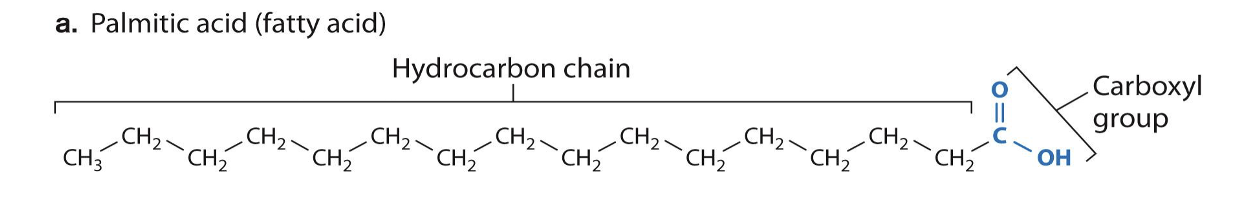
Fatty acids
Long chains of carbons with a carboxyl group at the end
Saturated Fatty acids
Single-bonded carbons
Max # hydrogens
Straight structure
Solid at room temperature
Unsaturated Fatty acids
Double-bonded carbons
Less than Max # of hydrogens
Bent structure
Liquid at room temperature
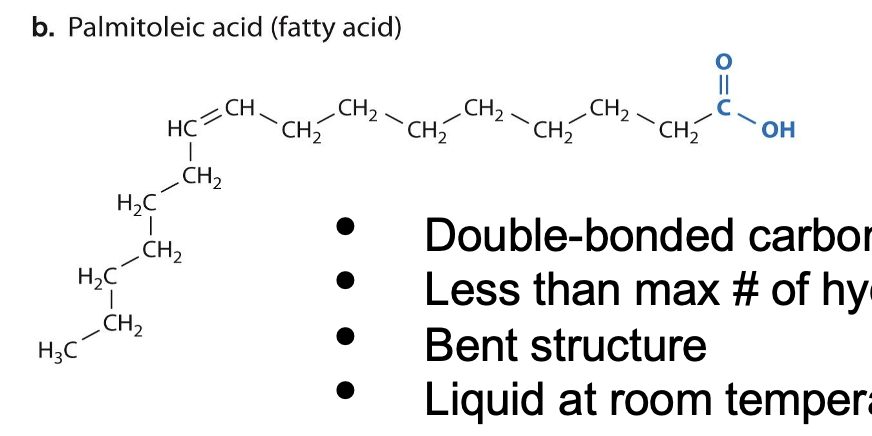
Amino

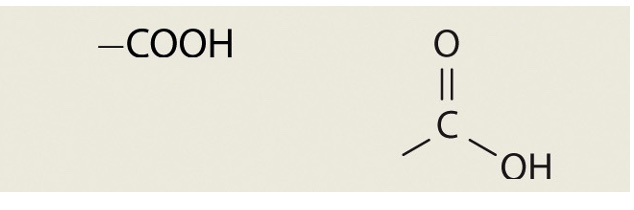
Carboxyl
Phosphate
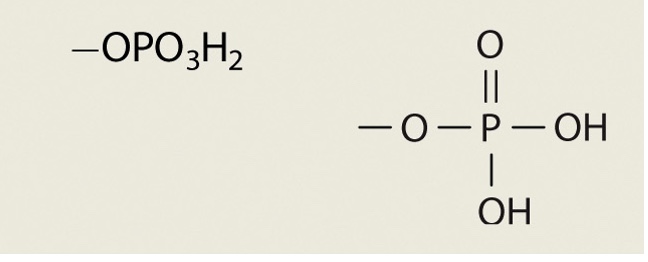
Hydroxyl

Methyl