Jean Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Jean Piaget
Swiss psychologist known for developmental theory.
Epistemology
Study of knowledge and its origins.
Standardized IQ tests
Tests developed to measure intelligence consistently.
Schema
Organized unit of knowledge for understanding situations.
Observation
Method of gathering data through watching behavior.
Interviews
Method of questioning to gauge children's understanding.
Intrinsic motivation
Internal drive to learn and explore.
Hypotheses
Proposed explanations tested by children.
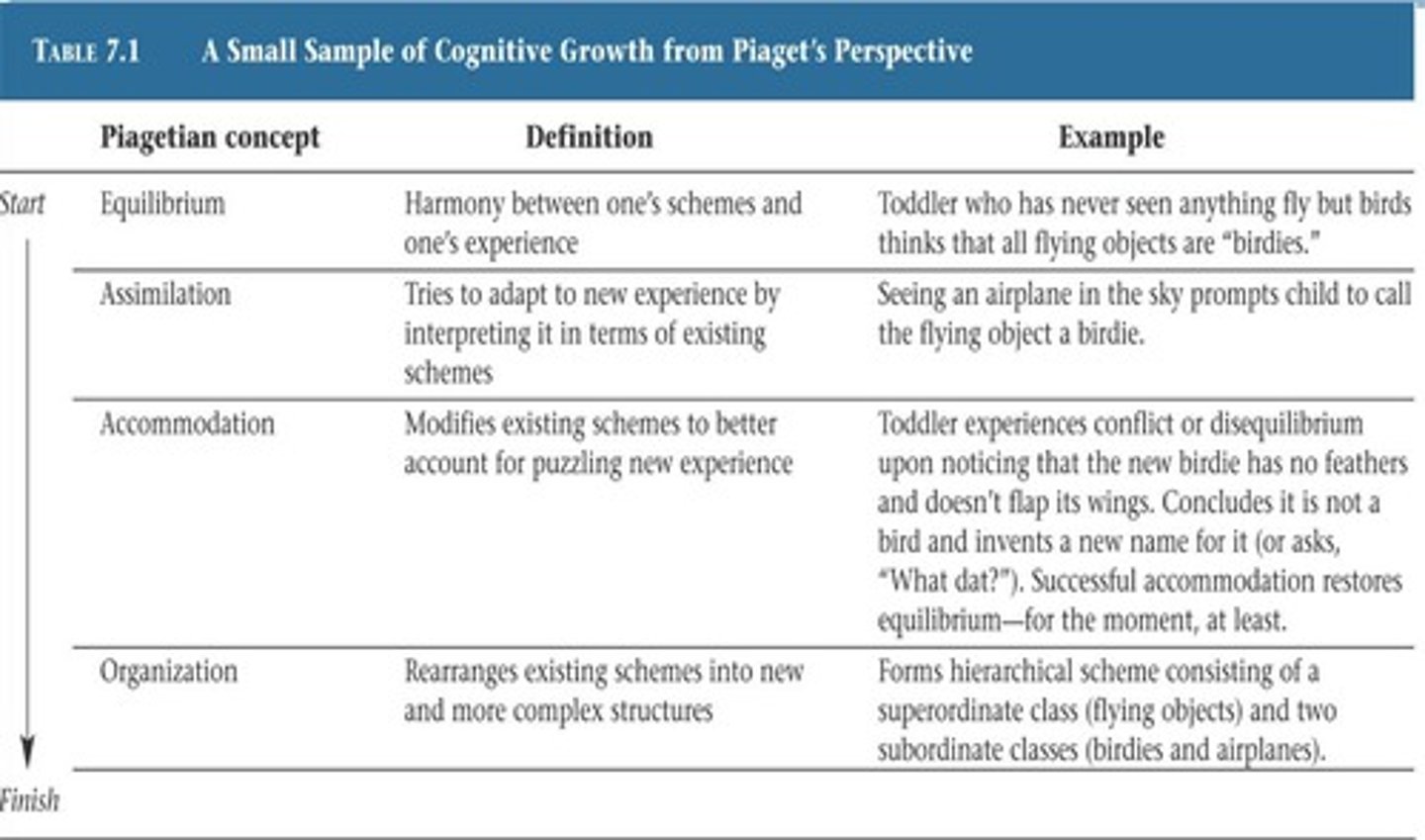
Assimilation
Incorporating new experiences into existing theories.
Accommodation
Modifying theories based on new experiences.
Equilibrium
Balance between assimilation and accommodation.
Disequilibrium
State when existing theories are inadequate.
Equilibration
Process of reorganizing theories for advancement.
Cognitive processes
Mental activities involved in learning and understanding.
Child as scientist
Children actively explore and test their environment.
Developmental observations
Key method for launching Piaget's career.
Assimilation
Integrating new experiences into existing schemas.
Accommodation
Modifying schemas to incorporate new experiences.
Equilibration
Balancing assimilation and accommodation processes.
Disequilibrium
State when existing schemas cannot handle new information.
Object Permanence
Understanding that objects exist when not visible.
A not B Error
Searching for an object where it was previously found.
Reflex Activity
Basic reflexes like sucking and grasping (0-1m).
Primary Circular Reactions
Repeating actions centered on the infant's body (1-4m).
Secondary Circular Reactions
Repeating actions involving objects (4-8m).
Coordination of Secondary Schemes
Coordinating actions to achieve goals (8-12m).
Tertiary Circular Reactions
Experimenting with object properties through trial and error (12-18m).
Symbolic Problem Solving
Using internal mental strategies for problem solving (18-24m).
Sensorimotor Knowledge
Knowledge gained through sensory and motor interactions.
Intentionality in Infants
Infants differentiate means and ends in actions.
Major Cognitive Changes
Significant cognitive development occurs at ages 2, 7, 11.
Substage One
Basic reflexes develop (0-1 month).
Substage Two
Beginning to operate on objects (1-4 months).
Substage Three
Repeats actions towards objects (4-8 months).
Substage Four
Achieves object permanence (8-12 months).
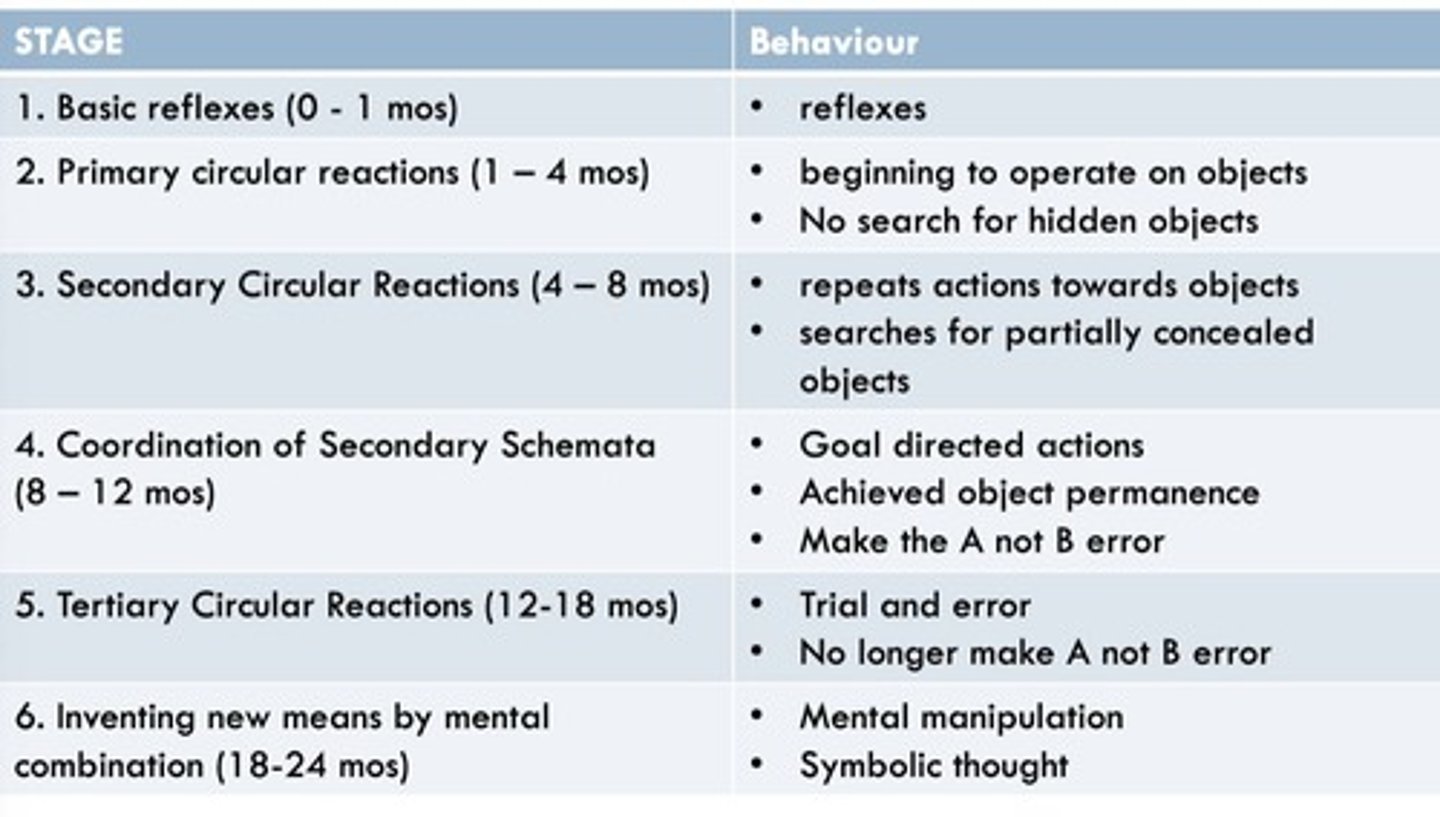
Substage Five
Trial and error learning about objects (12-18 months).
Substage Six
Beginning of symbolic thought and inference (18-24 months).
Poor hand-eye coordination
Difficulty coordinating visual input with motor actions.
Poor planning ability
Inability to organize tasks or foresee outcomes.
Preoperational Stage
Stage where symbolic function develops in children.
Symbolic function
Using symbols to represent objects and events.
Semi-logical thinking
Thinking that lacks full logical reasoning.
Preconceptual substage
Ages 2-4, characterized by egocentrism and animism.
Intuitive substage
Ages 4-7, develops dual representation capacities.
Centration
Narrowly focused thought limiting reasoning abilities.
Conservation of liquid task
Understanding that liquid volume remains unchanged.
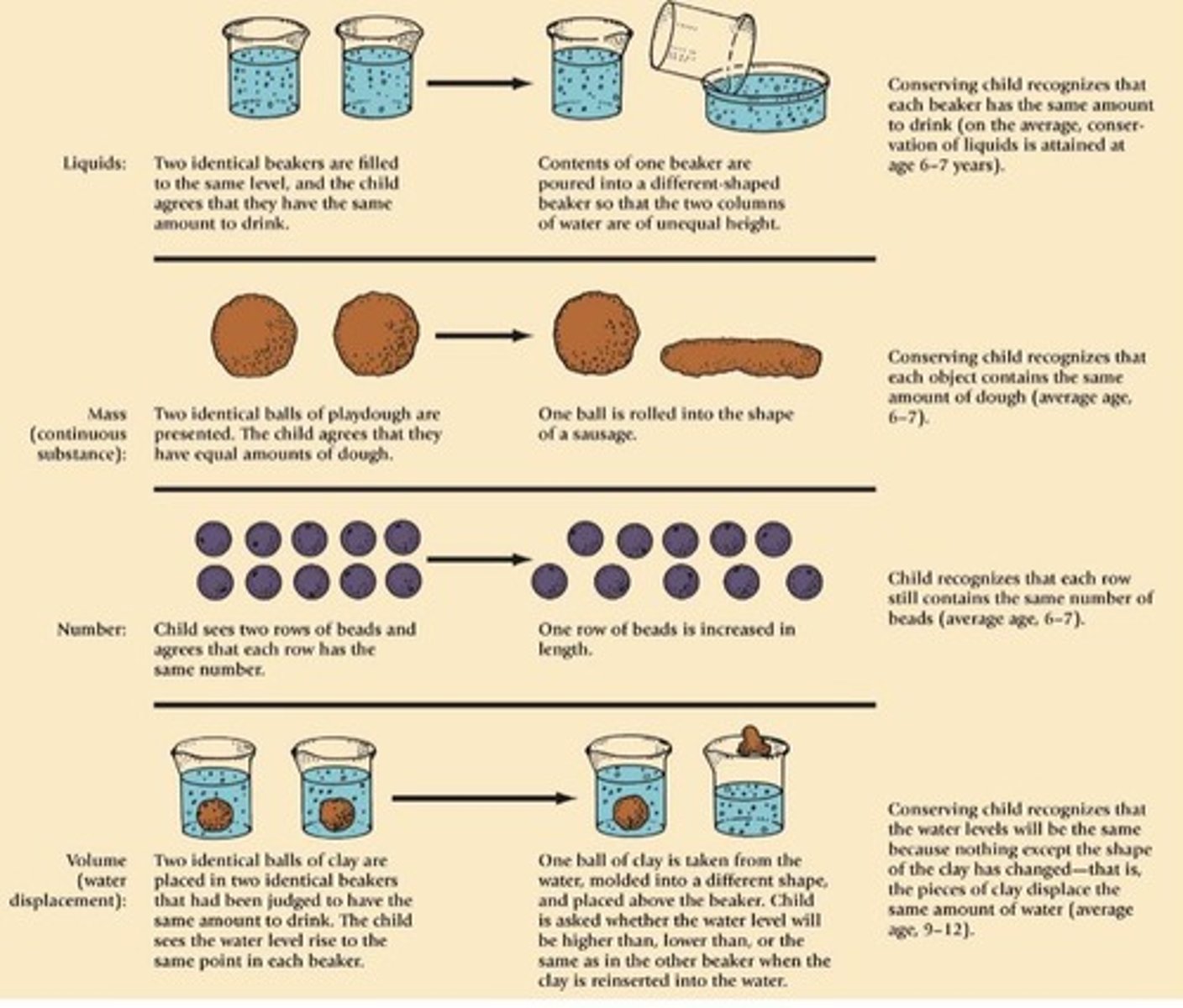
Conservation of length task
Understanding that length remains unchanged despite spacing.
Animism
Attributing life to inanimate objects.
Egocentrism
Seeing the world solely from one's own perspective.
Mountain task
Test revealing children's egocentric viewpoints.
Theory of Mind
Understanding others' mental states and perspectives.
False-belief task
Test assessing understanding of others' beliefs.
Concrete Operational Stage
Ages 7-11, logical operations applied to concrete experiences.
Balance Beam Task
Task requiring weight counting and distance assessment.
Formal Operations Stage
Adolescence and beyond, abstract and hypothetical reasoning.
Piaget's Theory
Foundation of cognitive development discipline.
Competence/performance distinction
Difference between ability and demonstration of skills.
Neo-nativists
Theorists believing infants possess innate knowledge.
Violation of Expectations
Infants' surprise at impossible events indicating reasoning.
Renee Baillargeon
Researcher studying infants' understanding of physical laws.
Zone of Proximal Development
Difference between independent and guided learning.
Scaffolding
Tailored support based on learner's competence.
Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory
Cognitive development driven by social interactions.
Collaborative Learning
Learning enhanced through group interactions.
Information-Processing Models
Mind compared to a computer for processing information.
Input
Information received through attention and perception.
Storage and retrieval
Encoding and recalling information.
Software
Applying information to solve problems.