Biology 005A UCR Final
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Electronegativity
The atoms strength on tug. Depends on distance between nucleus and valence shells (closer-stronger), and the configuration of valence shells (electron accepts=stronger). C and H have almost equal electronegativity.
Periodic Table (in terms of electronegativity)
Elements increase in electronegativity as they move to the right of the table and up the table.
Hydrogen Bonds
The attraction between 2+ hydrogen atoms (in a polar molecule) to nearby negative charge. Attraction between partial positive and partial negative charges.
Acids
Substance that increases hydrogen ion (H+) in concentration of a solution. Strong acids: HCL, H4So4, and HNO3—>H+ and Cl-, H+ and HSo4, H+ and NO3.
Bases
A substance that reduces the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. Or molecule that accepts a proton. Ex: NaOH—> Na+ and OH-.
pH scale
pH=negative log of the [H+]. The lower the pH, higher # of of hydrogen ions, higher pH, lower # of hydrogen ions.
Questions to ask to determine how a functional group will impact the molecular function
Is it Polar
Is it Non-Polar
Is it an acid or negatively charged?
Is it a base or positively charged?
Hydroxyl Group
Polar
Not nonpolar
Not negatively charged
Not positively charged, or base
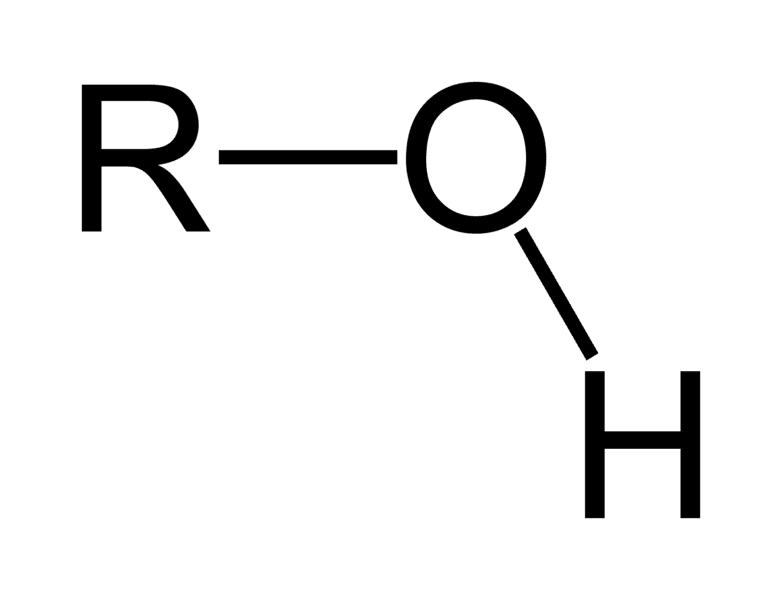
Carbonyl Group
Polar
Not nonpolar
Not negatively charged or acid
not positively charged or a base
Carboxyl Group
Polar
Not nonpolar
Yes negatively charged or acid
Not positively charged or base
Amino Group
Polar
Not nonpolar
Not negatively charged or acid
Yes positively charged or base (base)
Methyl Group
Not polar
Nonpolar
Not acid or negatively charged
Not base or positively charged
Phosphate Group
Polar
Not nonpolar
Acid or negatively charged
Not base or positively charged.
Proteins
Important for functions of living things. Ex: Hemoglobin —> oyxgen around blood + transports it. Ex: Insulin—> regulates metabolism
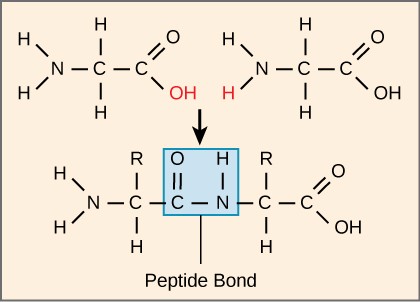
Dehydration Synthesis
Combine amino acids and create a polypeptide by taking an h20 out.
Primary Structure (Proteins)
Primary protein structure-sequence of amino acids. Outcome: polypeptides. Bonds: Covalent.
Secondary Structure (Proteins)
Outcome: Alpha helix (local structures), beta pleated sheet. Bonds: hydrogen bonds between atoms in the backbones of polypeptides.
Tertiary Structure (Proteins)
Van der Waals hydrophobic interactions. Includes nonpolar side chains. Forces: Hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, disulfide bridges, ionic bonds. Outcome: 3d shape of protein.
Quaternary Structure (Proteins)
Outcome: Folded proteins w/multiple polypeptides. Forces: Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interaction, disulfide bridges, ionic bonds.
Denaturation
Process in which protein loses its 3d structure. Causes proteins to denature: Heat above 50 degrees C disturbs H-bonds. Alcohols form H bonds and disrupt the intramolecular bonds. Salts of heavy metals form strong bonds w/acid r-groups. Alkaloid Reagents combine with charged r-groups, disrupting ionic bonds.
Carbon numbering
The first carbon is the one connected to 2 oxygens, then the next numbers follow the ring clockwise.
Monosaccharides—> Disaccharides
Glucose undergoes dehydration synthesis to form a glycosidic linkage.
Polysaccharides
Used to store energy for later use, and for cellular structure. Function determined by: individual monosaccarides, how they are linked, # of carbons and what number carbons are being linked.
REDOX reactions
Reduction: gaining electrons. Oxidation: losing electrons. FADH2—> Reduced. FAD—>Oxidized.
Mitochondria
Cellular respiration occurs here. Includes membrane (outer, innermembrane), cristae (integral membrane proteins-ETC), Ribosomes and DNA.
Endosymbiosis Hypothesis
The theory is that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from an ancestor of Alpha Proteobacteria. Evidence includes the double membrane, ribosomes, DNA, and binary fission.
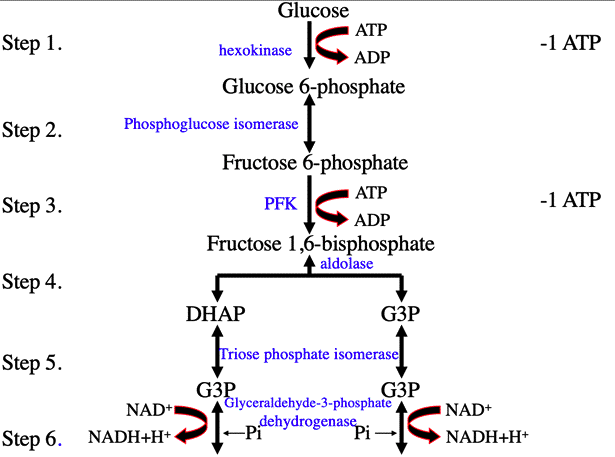
Glycolysis
INPUTS: Glucose, 2 NAD+, 2 ATP
OUTPUTS: 2 ATP (net gain), 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate
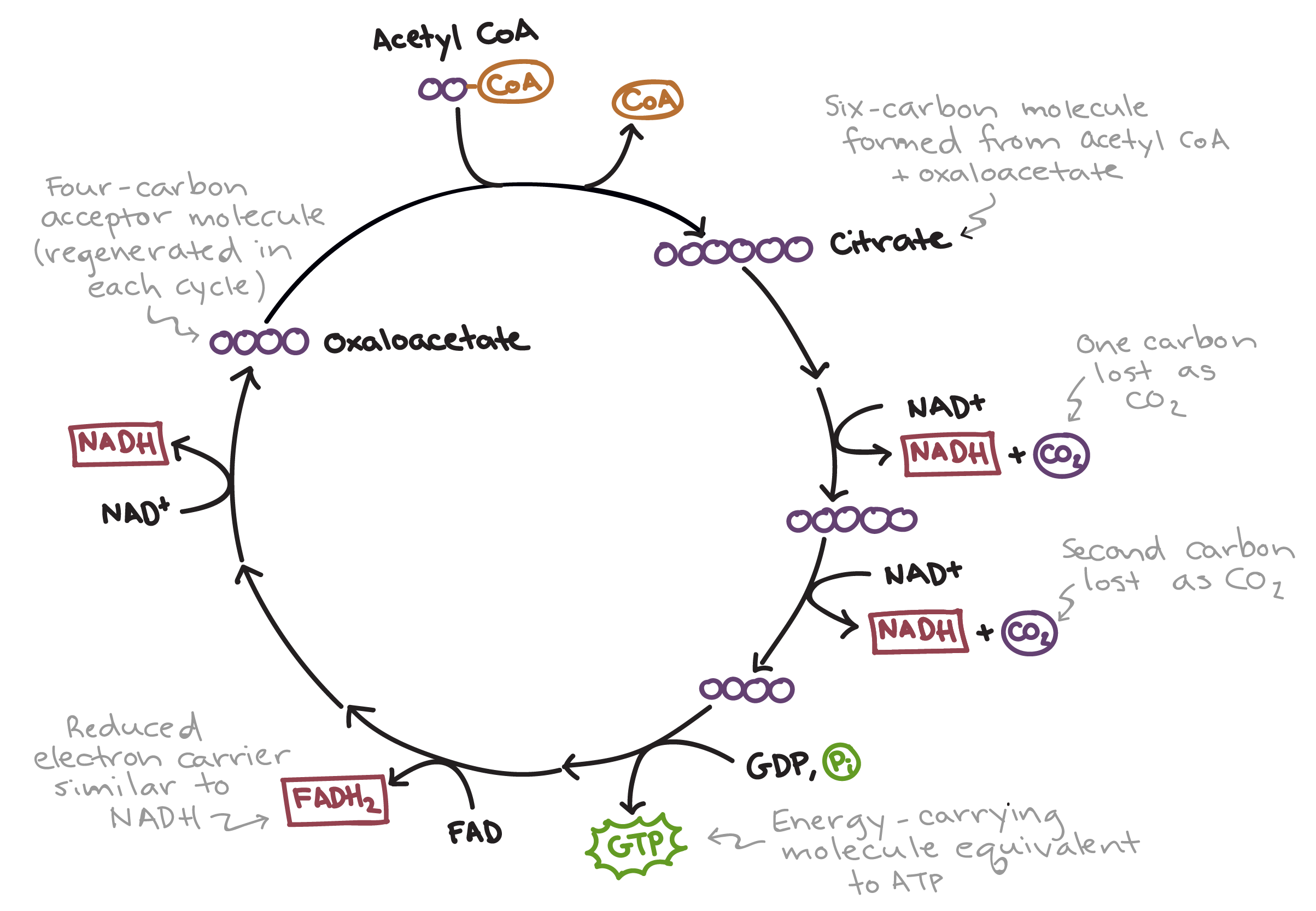
Citric Acid Cycle
INPUTS: Acetyl-CoA
OUTPUTS: carbon dioxide (CO2), NADH, FADH2, and ATP (or GTP)
Chloroplast Membranes
3 membranes: Outer membrane, inner membrane, thylakoid (ETC, ATP Synthase)
Stroma
Fluid that fills the internal space of the chloroplast
Cyanobacteria
Free-lining prokaryotic bacteria, pigments (Chlorophyll A, Careteroids), preform photosynthesis independently.
Chloroplasts
Found within the cells of plants and algae, include chlorophyll A, Carotenoid, and Chlorophyll B. Preform photosynthesis on plant cells.
Electron Transport Chain
a series of protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that facilitates the transfer of electrons from electron carriers (like NADH and FADH2) to oxygen, ultimately producing ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Its located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Fermentation
Process used to remake NAD+ for glycolysis
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Occurs when there is not enough O2 present. Glucose turns into 2 pyruvate through glycolysis, then 2 lactate. Reverts back when oxygen is regained.
Photosynthesis
Light dependent reactions that create energy in light harvest. Leads to the calvin cycle.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Visible light is 400 nm to 700 nm
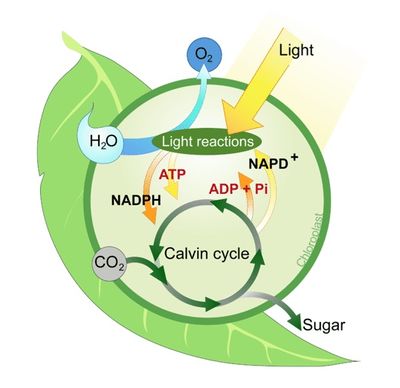
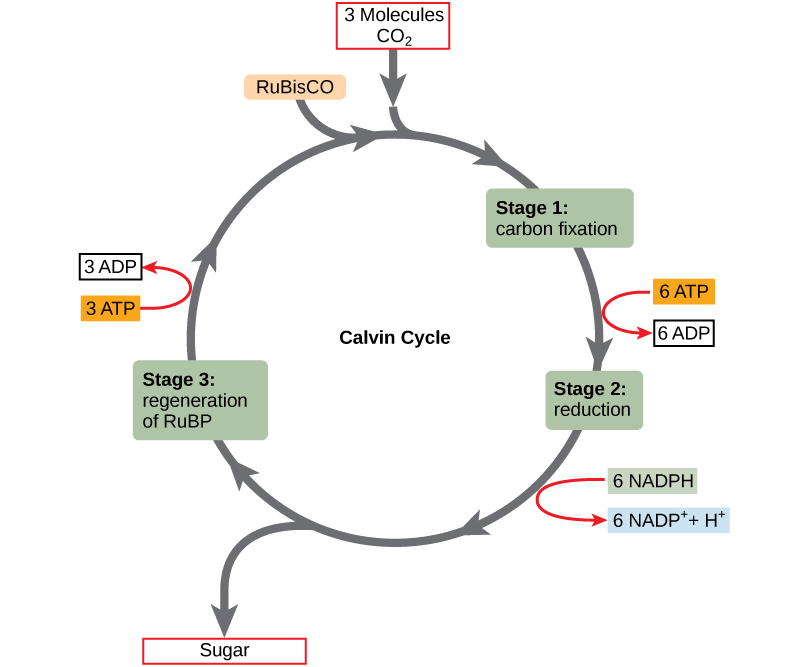
Calvin Cycle
Light reactions. INPUTS: Light, H2O, NADP+, ADP
OUTPUTS: O2, NADPH, ATP.
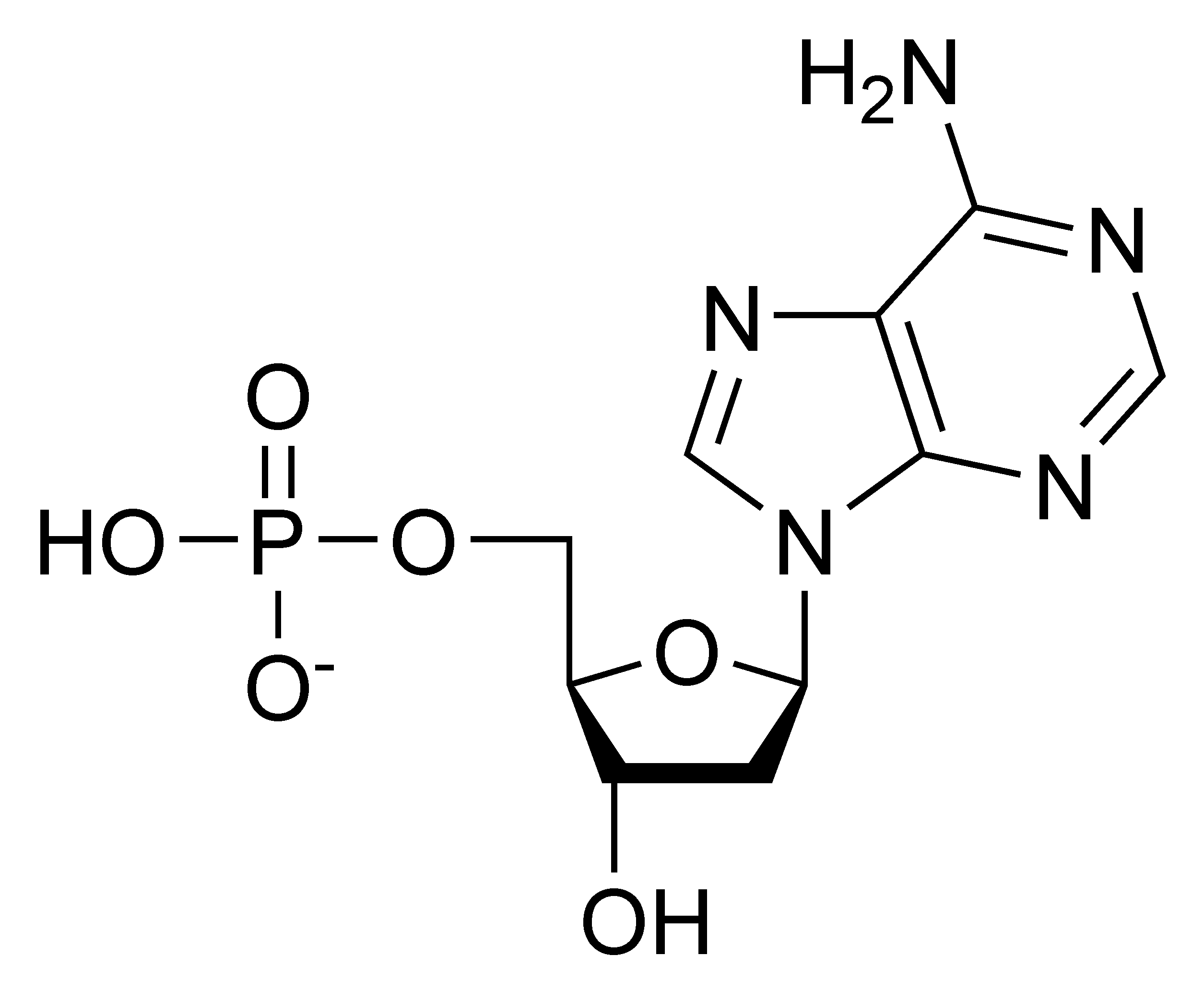
Components of Nucleotides
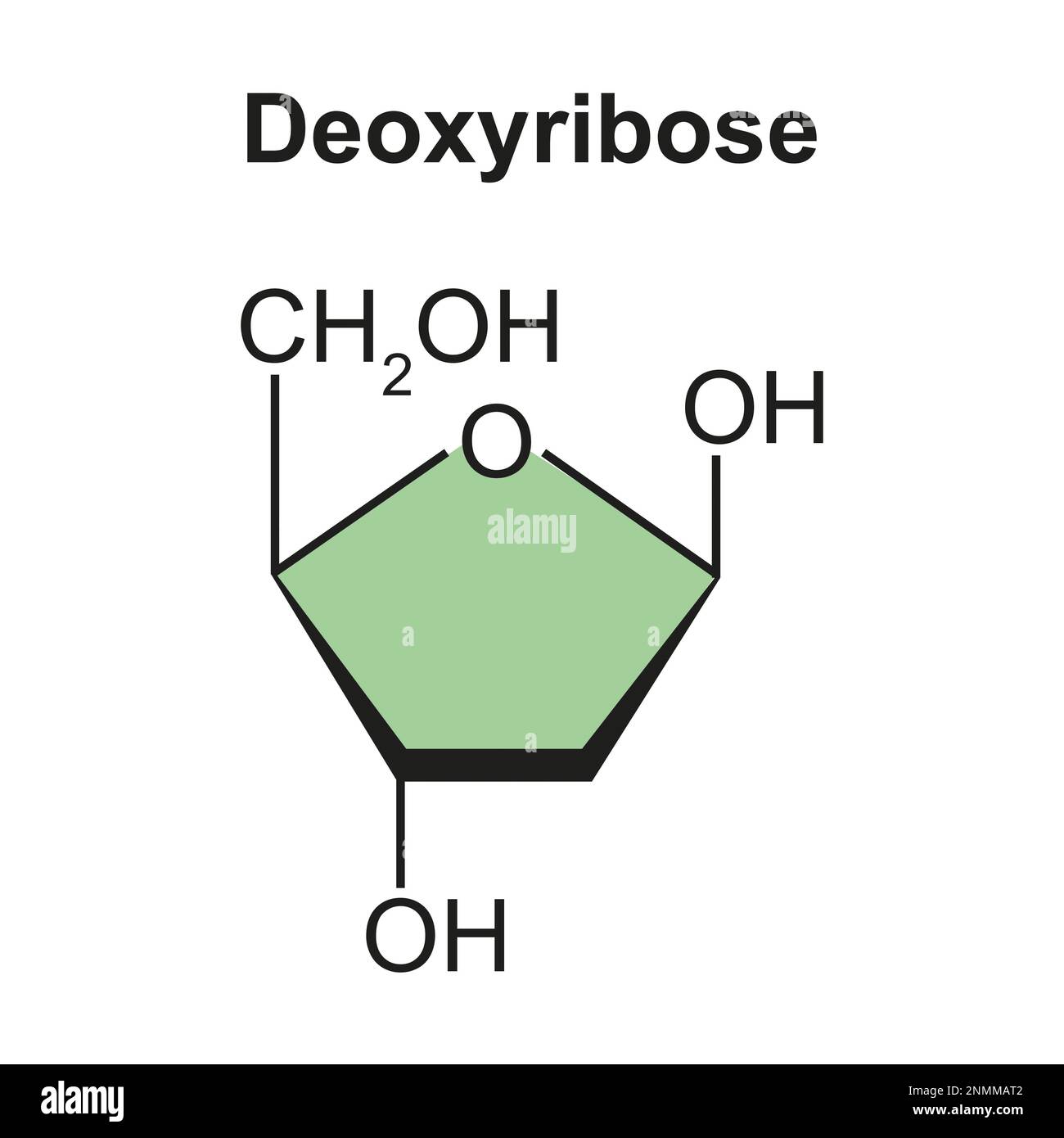
Have 3 main components: phosphate group, nitrogenous base, and sugar connected at first ribose or dioxyribose).
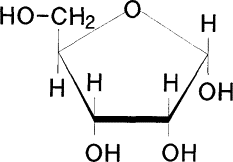
Ribose
Dioxyribose
Pyrimidines
Include Cytosine, and Thymine. Both have single rings.
Purines
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G). Have two rings.
Nucleotide bonding rules
Adenine pairs to Thymine, and Cytosine pairs to Guanine. Are bonded through hydrogen bonds.
Gene
Sequence of Nucleotides that encodes an RNA.
Genome
All of the DNA of an individual.
Histones
Consist of 8 polypeptides, they compact DNA by having the dna wrap around 1.6x. Compacts DNA by 40,000x.
Transcription
Process by which an RNA leaves the nucleus and a copy is made of DNA.
In what direction is DNA “read” in?
Always the 3’-5’ direction
In what direction is RNA “read” in?
Always the 5’-3’ direction. RNA is antiparallel to DNA.
Regulatory Gene
Present in Prokaryotic genes, encodes for proteins that control expression of structural genes. Located in the first part of the DNA.
Operator
Present in Prokaryotic genes, and is a segment of DNA that a repressor (protein that regulates) can bind to. Located after the promoter.
Promoter
In Eukaryotic gene structure, and is a region of DNA where the RNA polymerase binds.
Enhancer
In Eukaryotic gene structure, and is a region of DNA that binds to transcription factors (protein). Increases the likelihood of RNA polymerase coming in (binding).
Silencer
In Eukaryotic gene structure, and is a region that can bind to transcription factors, decreasing the likelihood of RNA polymerase binding to the promoter.
5’ UTR
In Eukaryotic gene structure, located in the first part of what is made. It is the untranslated region, so no amino sequence is coded from it, it helps the RNA attach to the ribosomes and plays a role in the mRNA leaving the nucleus.
Exon
In Eukaryotic gene structure, and is the coding sequence, resulting the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide.
Intron
Removed before RNA leaves the nucleus.
3’ UTR
Untranslated region, stability of mRNA and addition of poly A tail. mRNA leaves the nucleus.
Chlorophyll A
The key light capturing pigment that participates directly in light reactions.
Carotenoids
Hydrocarbons that are various shades of yellow + orange because they absorb violet + blue-green light
What happens when chlorophyll comes in contact with light?
It becomes “excited” by the light. When a molecule absorbs photons of light. one of the molecules electrons is elevated to an orbital w/ more potential energy.
ETC in Photosynthesis
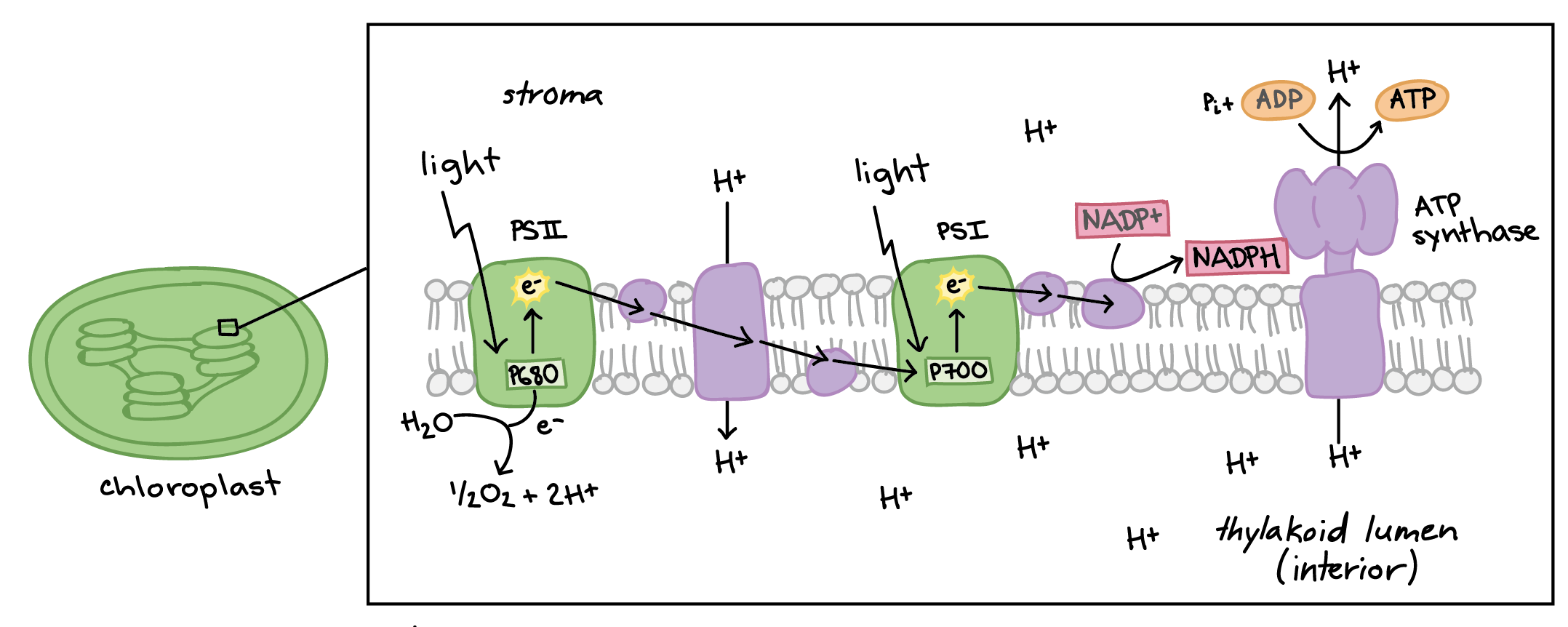
Photosystems
Photosystem I→ Chlorophyll A=P68- (actually the second photosystem to be discovered)
Photosystem II—> Chlorophyll B= P700 (the first photosystem discovered).
mRNA
Messenger-takes message from DNA and brings it to the ribosome. It contains a sequence that will tell ribosomes what amino acids should be in the polypeptide.
tRNA
Transfer- bring amino acids to the ribosome.
rRNA
Ribosomal-component of ribosomes.
Secondary Structure of RNA
Primary: Covalent bonds between nucleotides.
Secondary: Local structures/interactions (molecules are close).
Tertiary: Fully folded RNA- H bonded and Van Der Waals interactions.
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that is responsible for catalyzing bonds between strands of nucleotides of RNA, and breaks hydrogen bonds temporarily between strands of DNA (come back together due to partial charges).
What are different mechanisms by which signaling molecules can lead to changes in cells?
Making proteins, activating enzymes, secretion of products, stimulating cell division
What is the role of cyclin and cyclin dependent kinases in cell division?
Cyclins activate cyclin dependent kinases which are enzymes that cause the cell to move foward in the cell cycle or repress movement through the cell cycle.
when would p53 be made? what is the mechanism by which P54 regulated the cell cycle?
P53 would be made in situations of cellular stress. P53 is a transcription factor that increases transcription of P21. P21 activates a cyclin-CDK complex which removes phosphate groups from RB allowing it to attach to the transcription factor E2F serving as a co-repressor of cell-cycle genes.
When would Myc be made? How does Myc affect the cell cycle?
MYC would be made when an organism experiences wounding or needs to grow. Myc causes transcription of genes required for DNA synthesis. transcription of genes required for DNA synthesis
What are major functions of the different types of cytoskeleton?
Microtubule: Separates sister chromatids during cell division
Microfilament (actin): cell structure, works with myosin for cell movement
Myosin: Contraction and movement within cells
Intermediate filament: assembly of nuclear envelope
how does the cytoskeletal structure of muscle and neuron cells facilitate their function?
Muscle cells: Contractile assemblies made of actin and myosin pull on intermediate
filament to lead to contraction of cells and tissues.
Neuron: Axons are stabilized by microtubule and intermediate filament. Export and
import of neurotransmitters is facilitated by actin.
What is the difference between cohesin and the synaptonemal complex?
Cohesin: attaches sister chromatids
Synaptonemal complex: Holds homologous chromosomes together during crossing over.
If you had a cell that did not have a functional copy of the SPO 11 gene, what would the outcome be?
No recombination of chromosomes
What is the difference between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids? Where in Meiosis do homologous chromosomes separate? Where do sister chromatids separate?
Homologous chromosomes: different versions of chromosomes-separate during meiosis I
Sister chromatids: duplicated chromosomes-separate during meiosis II.
What is the function of the following proteins in DNA replication?
Helicase, Topoisomerase, Primase, and DNA polymerase
Helicase: breaks hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
Topoisomerase: Unwinds supercoiling of DNA
Primase: Make primer (usually RNA) that starts a new DNA strand replica7ng
DNA Polymerase: Add nucleo7des to the 3’ end of a growing DNA strand
SS Binding protein: Stabilizes single stranded DNA once helicase has broken H bonds between the strands.
Why is there a leading and lagging strand in DNA replication?
Because DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides the 3’ end of a DNA molecule one grows as helicase opens the strands (leading strand) but one strand copies away from helicase (lagging strand). Therefore, the lagging strand is built in pieces (Okazaki fragments).
How are duplicated chromatids attached to each other after DNA synthesis? When do they seperate?
Duplicated chromatids are attached by a protein called cohesin. They seperate after metaphase of mitosis.
What are two mechanisms by which double stranded DNA breaks can be repaired?
Non-homologous end joining and homology directed pair.
What are three potential functions of steroids?
Hormones, bile acids, membrane fluidity regulation
What are two ways that membrane fluidity is regulated? How do each of those regulatory mechanisms work?
Membrane phospholipid composition: more saturated fatty acids lead to more rigid
membrane and more unsaturated fatty acids lead to more fluid membrane. Cholesterol maintains intermediate membrane fluidity- the rings increase rigidity while the tail increases membrane fluidity.
What is the role of the following components of the nuclear pore?
Cytoplasmic filament: Interact with the cytoskeleton
Nucleoporins: Controls movement of substances in and out of the nucleus
Nuclear basket: mRNA export from the nucleus
For a protein that is made in the rough E.R, explain the process of translation.
In the cytoplasm: Translation complex assembles, translation begins with the first 15-30 amino acids. Signal polypeptide attaches to signal particle. Translation complex moves to the ER and attaches to the docking protein integral to the ER.
How are molecules targeted from the ER to the golgi
Molecules are packed into vesicles. On the surface of those vesciles is COPII proteins that target the vesciles from the ER to the golgi.
Explain the function of the following proteins in targeting vesciles from the golgi to their destination. Clathrin, V-Snare, T-Snare.
Clathrin: Protein that facillitates formation of vesciles off of the golgi.
V-Snare: Protein that is embedded in vesicles that targets the vesicles to its destination where its companion T-Snare is embedded in a membrane.
T-Snare” protein embedded in the membrane of the vesicle target location.