MCHE 3920 Week 4: Sheet Metal Skeleton
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Bending and matched die forming
Sheet metal forming methods fall btw 2 extremes:
matched die forming
complex, expensive, double curved parts, high volumes
Bending
simple, cheap, single curved parts, small volumes
blanking
precedes processed, cuts sheet metal to size
yield stress
want to keep stress below
exceed, bend the metal
in SMF, need to ________ yield stress in order to ________
anisotropy, isotropic
sheet metals have ________, but we assume ________
springs
interatomic bonds act like:
return to original shape
For no PERMANENT deformation, load removal makes material:
yield stress, crystal lattice
at the ________, dislocations begin to form in the ________
0.2% offset method
when hard to find yield stress from test, use ________
slip planes, slip
dislocations move along ________, where one part of lattice ________ relative to the other
strain/work hardening
slip planes hinder each s.t. it take more stress to keep deforming material
alpha (degree), R (radius); tension, compression; Neutral axis; thinner, thicker
Minimum Bending Radium (MBR) model assumptions: all deforms take place in zone defined by ________ and ________; metal deformation has same behavior in ________ as in ________ (anti-symmetric s-s curve); ________ does not change in length; metal outside NA becomes ________, inside becomes ________
original, actual, necking
Recall that stress is calculated using ______ area; if it was calculated using ______ (or instantaneous) area, stress would continue to increase in the _______ region.
true stress
calculating stress w time-varying area
unloading, parallel
If the load is reduced or removed, the material will follow a linear _____ curve that is ______ to the elastic portion of the curve.
fracture strain
The __________ is an indication of the amount of material elongation at failure.
smaller; yields; accommodated; uniform stress; more; bending; deformation
MBR caveats: can bend metal w/ ______ radius than predicted. There is a transition zone outside of the bend in which material ______ somewhat, meaning some deformation is ______ by this region. materials in bending DO NOT have ______, so can deform ______ than what tensile test suggest. in ______ tests, ______ concentrated in small volume
springback, removal
After bending the sheet metal, there will always be some amount of ______ associated with the ______ of the elastic strain.
beyond
If we can predict the amount of springback in a part, we can account for it by bending the part ______ the desired ending angle.
E, yield strenght, stress-strain
The amount of springback is proportional to the ratio of _____ to _______ (E + σ_y). Energy stored in the part is equal to the area under the _______ curve.
scaling laws
Hard to predict springback exactly, but if it is known in a reference case, we can use _________ to predict what it will be if we changed the thickness or the bending radius.
air bending
single curved parts: deforms part by predetermine bend angle w/o contacting die
Bottoming
sandwiches part btw punch and die
wipe bending
part is bent as a cantilever by a moving punch
roll bending
used to make cylinders
rollers, adjustable rolls
roll bending: Sheet metal is passed relatively slowly over turning _______ while ________ are moved with each pass to gradually deform the sheet part.
shape
In roll forming: A strip of metal is fed through a series of rollers that progressively _____ a cross-section.
good, high
in roll forming: _____ tolerance control, but initial investment is _______.
thin-walled sections, solid shapes
roll forming: Usually used with __________, but not __________ (typically extruded).
negative deformation (contraction)
Multi-axis bending: when tension is applied in one direction, positive deformation is accompanied by _______ in the other 2 directions
multi-axial deformations
poission’s ratio relates:
volume, plastic deformation
we assume ______ stays constant during ____________
v-0.5, e1+e2+… = 0 (true strains)
plastic Poission’s ratio:
e1, forming
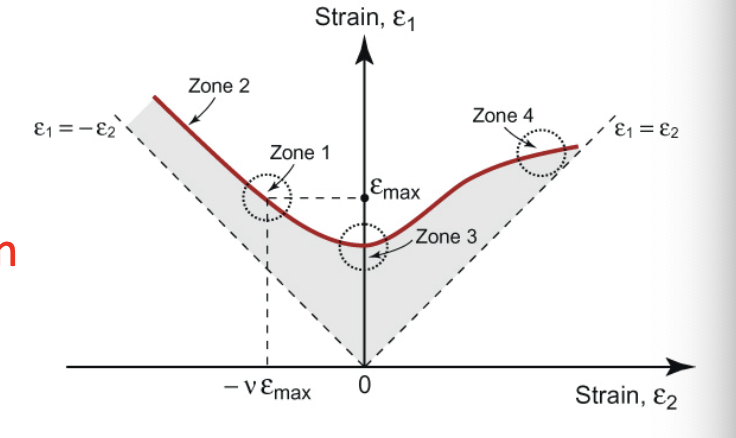
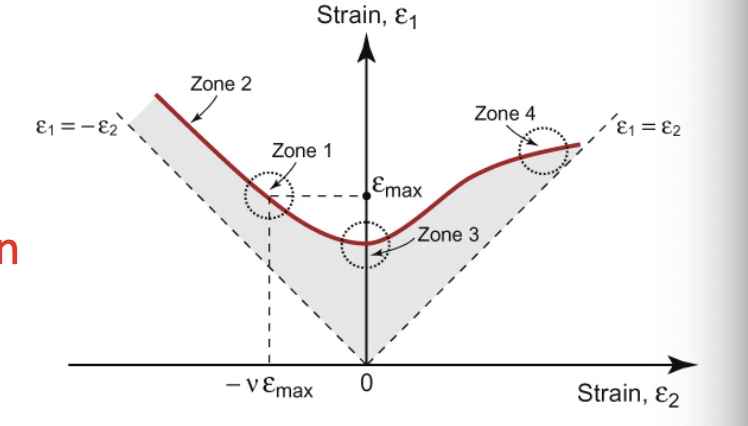
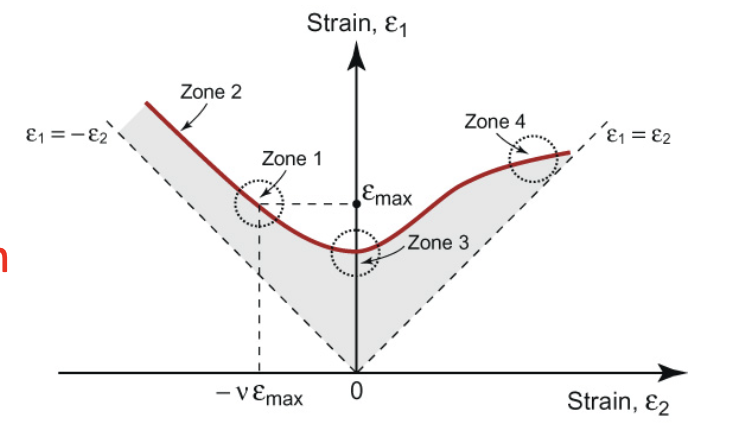
Forming Limit Diagram: applied stress is ________, so tensile test data can’t determine ______ limits
various
use FLD to show _______ combos of strain in two axes
true strains
plotted strains are what in an FLD?
e1; e2, perpindicular; not applicable, e1>e2; will fail
FLD: _____ is direction w/ largest tensile strain; _____ is _____ direction and can be in T or C; areas below dashed lines are _____ because _____; ABOVE THE FLD, THE MATERIAL _____
e1+e2+e3=0
how to solve for e3
-vplasticemax, Zone 1
for an FLD, if we only apply one load (e1=emax), e2=_____, which is denoted _____
transverse, higher, Zone 2
for an FLD, if greater compressive strain in _____ direction- there is now a _____ strain-to-failure in principle direction (_____)
transverse, reduced, Zone 3
for FLD, if we prevent deform. in _____ direction, then strain-to-failure is _____ (_____)
higher than emax
for an FLD, if tension applied in both directions, strain-to-failure is _______
out-of-plane and in-plane
2 directions for springback in double curved parts:
stiff, springback
highly double curved parts (hemispherical bowls eg) are usually _____ enough to resist ______
hammering/panel beating
process where a part is placed on leather sandbag and shaped with a rounded mallet
pressurized wheels
smooths out hammer marks from hammering
double curved parts (pans, cans, cooking pots)
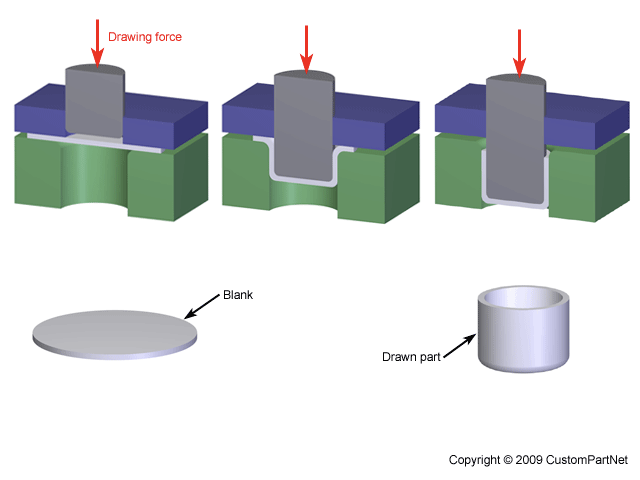
deep drawing is used for
deep drawing
consists of die, blank holder, punch
plastic region
Deep drawing works best if material has a large _________
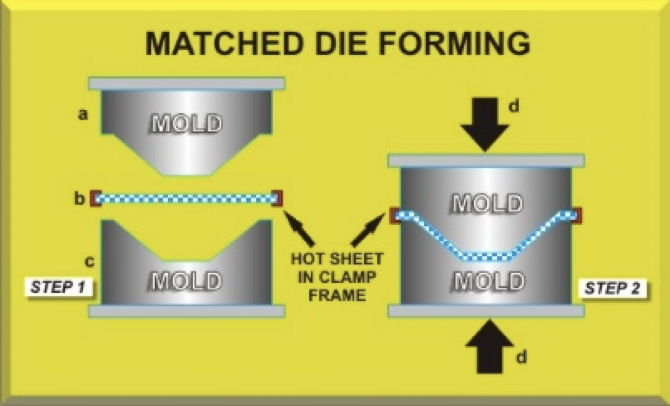
matched die forming
method for double-curved parts that is similar to deep drawing, except underside of the blank is fully supported by lower die
matched die forming
Method for double-curved parts used in automotive industry
sequential die forming
when done on a single line w/ each die doing a portion of forming
Rubber forming
method for double-curved parts similar to matched die forming, but lower die is a compliant material
lower die does not have to match upper die
what makes rubber forming easier to manufacture?
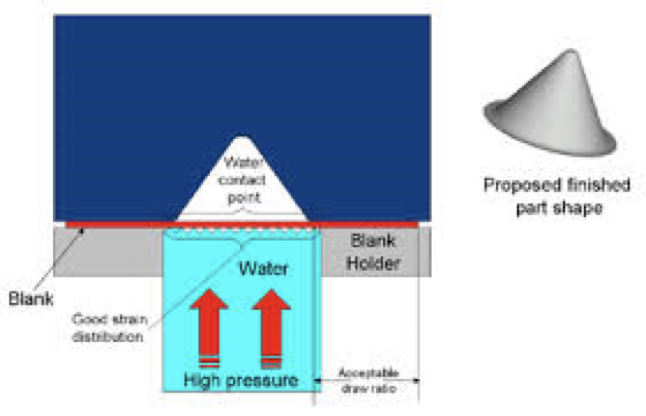
hydroforming
Method for double-curved parts where instead of a punch, high pressure water forces the sheet into the die
expand outward
what does hydroforming causes tubes to do?
fast, tight
hydroforming is ________ and allows ______ tolerances