All Cellular physiology lectures
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
States of Matter
Solids are compact and have a definitive shape
Liquids, definitive volume and take shape of the their container
Gases have neither a shape nor a volume
Element definition
a substance which cannot be split into a simpler substance by using basic chemical procedures
26 elements in human body
Major = C, O, H, H
Minor
Atom definition
Atom is the smallest chemical unit of a molecule
It has a nucleus which contains protons and neutrons
Electrons move around the nucleus in an electron shell or orbit
Atomic number = no. of protons in nucleus
Atomic mass number = no. of protons + neutrons
Isotope definition
An isotope is when an atom exists as one or more species having the same atomic number BUT only differ in their number of neutrons and therefore their atomic mass differ.
Carbon-14 helps solve ancient mysteries! (USES OF ISOTOPES)
Scientists use carbon dating (based on the isotope Carbon-14) to determine the age of ancient fossils and artifacts.
Electrons
The number of electrons in the orbit equals the number of protons within the nucleus of the atom.
Atoms have net charge of zero
Electrons can occupy any position in a certain volume of space: orbital
1st orbital = 2 electrons
2nd + 3rd orbital = 8 electrons
4th orbital = 18 electrons
Ions
Atoms of an element can gain or loose electrons forming an ion
Ionisation is process of loosing or gaining electrons (eg Ca2+)
Molecule vs compound
Molecule: is formed when two or more atoms share electrons (eg H2O)
Compound: substance that contains atoms of two or more different elements (eg H2O and NaCL)
Chemical bonds
Chemical bonds: forces that hold together the atoms of a molecule or a compound
This bond is depended on the valence electrons
Ionic Bond
Ionic bonds = results when valence electrons from one atom are completely transferred to a second atom (no sharing of electrons), Ionic compound = anion + cation
atom 1 loses its electrons (more protons)
Ions are formed ( + or – charged molecules)
Cations = +ve charge and move towards -ve pole (cathode)
Anion = -ve charge and moves towards +ve pole (anode)
Ionic bonds easily dissociate (separate) and the ions are attract polar water molecules and hydration spheres are formed around each ion
In the body: found in teeth and bones where they give strength
An ionic compound which breaks apart in solution is called an electrolyte
Covalent Bonds
definition: occur when atoms share valence electrons
single, double and triple bonds
non-polar (no -ve or +ve sides), polar (a -ve and +ve side)and hydrogen bonds (where H bonds w N, F or O,, WEAKER THAN CONVALENT BONDS)
Functions of hydrogen bonding folding/ bending of long organic molecules (eg proteins)
✓ bonds 2 strands of DNA
✓ surface tension
✓ capillary action
What is an Atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It is the basic building block of all substances. Atoms consist of three main subatomic particles:
Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus.
Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also in the nucleus.
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels.
Properties of Atoms

Types of Chemical Bonds
Covalent Bonds
Definition: A covalent bond forms when two atoms share electrons.
Occurs Between: Typically between nonmetals.
Types: Can be single, double, or triple bonds depending on how many electrons are shared.
Example:
H₂ (Hydrogen gas): Each hydrogen shares one electron to form a single bond.
H₂O (Water): Oxygen shares electrons with two hydrogens.
Ionic Bonds
Definition: An ionic bond forms when one atom donates an electron and another accepts it, creating oppositely charged ions that attract.
Occurs Between: Typically between a metal (which loses electrons) and a nonmetal (which gains electrons).
Example:
NaCl (Table Salt): Sodium (Na) donates an electron to chlorine (Cl), forming Na⁺ and Cl⁻.
Hydrogen Bonds
Definition: A hydrogen bond is a weak attraction between a hydrogen atom (already covalently bonded to an electronegative atom like oxygen or nitrogen) and another electronegative atom.
Occurs Between: Molecules, not atoms directly.
Important In: Water properties, DNA structure, protein folding.
Example:
H₂O Molecules: The slightly positive hydrogen of one water molecule is attracted to the slightly negative oxygen of another water molecule.
What is a compound?
A compound is a substance that contains atoms of two or more different elements bonded together. The body mainly uses organic and inorganic compounds.
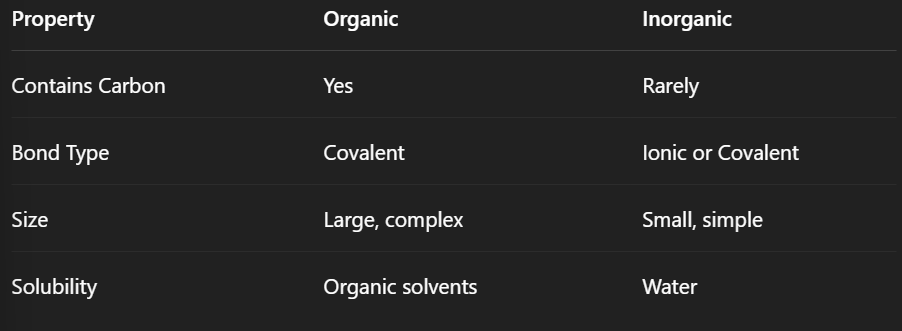
What is an organic compound?
Always contains carbon and usually hydrogen
Bonds are covalent
Large and complex molecules (e.g., proteins, glucose, DNA)
Examples: CH₄ (methane), C₆H₁₂O₆ (glucose)
What is an inorganic compound?
Usually does not contain carbon
Simple structures
Includes water, salts, acids, and bases
Examples: H₂O, NaCl, HCl
Compare organic and inorganic compounds.
What makes water a polar molecule?
Uneven electron sharing causes partial charges:
Oxygen is partially negative
Hydrogen is partially positive
Enables hydrogen bonding and makes water a good solvent for polar/charged substances
Define cohesion and adhesion in water.
Cohesion: Attraction between water molecules (surface tension)
Adhesion: Attraction to other substances (e.g., capillary action in plants)
What is an acid, a base, and a neutral solution?
Acid: Releases H⁺ ions; pH < 7
Base: Accepts H⁺ ions; pH > 7
Neutral: H⁺ = OH⁻; pH = 7
What does the pH scale measure?
Measures H⁺ ion concentration
Scale ranges from 1 (acidic) to 14 (basic)
Blood pH: 7.35–7.45 (slightly basic)
What is a buffer system?
Resists changes in pH
Converts strong acids/bases into weak ones
Example: Bicarbonate buffer in blood
Low pH: HCO₃⁻ + H⁺ → H₂CO₃
High pH: H₂CO₃ → HCO₃⁻ + H⁺
What are monosaccharides?
Simple sugars with 3–7 carbon atoms
Examples: Glucose, fructose, galactose
Form disaccharides and polysaccharides via dehydration reactions
What are disaccharides and how are they formed?
Two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond
Formed by condensation (removal of water)
Examples:
Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose
Lactose = Glucose + Galactose
Maltose = Glucose + Glucose
What are polysaccharides?
Long chains of monosaccharides
Insoluble, tasteless
Example: Starch (turns blue with iodine)
What are lipids and their properties?
Organic, hydrophobic compounds (18–25% body mass)
Insoluble in water; soluble in nonpolar solvents
Includes fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
What are fatty acids?
Long hydrocarbon chains with -COOH group
Saturated: All single bonds
Unsaturated: One (mono) or more (poly) double bonds
Used in energy, membranes, hormones
What are triglycerides?
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids (via dehydration)
Main form of stored energy (fat)
Solid = fat, Liquid = oil
Excess nutrients stored as triglycerides in adipose tissue
Water – The Most Important Inorganic Compound
Why it's important:
Acts as a solvent for many biological reactions
Participates in chemical reactions (e.g. hydrolysis, dehydration)
Regulates body temperature
Provides lubrication (e.g. in joints, between organs)
Water’s Key Properties

Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic Substances
Hydrophilic (water-loving):
Polar or ionic compounds
Dissolve easily in water
Examples: sugars, salts
Hydrophobic (water-fearing):
Non-polar compounds
Do not dissolve in water
Examples: oils, animal fats
Acids, Bases, and Neutral Solutions – Definitions
Acids:
Release H⁺ ions in solution
Proton donors
Example: HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻
Bases:
Remove H⁺ from solution (or release OH⁻)
Proton acceptors
Example: NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻
Neutral Solution:
Equal concentrations of H⁺ and OH⁻
Pure water is neutral (pH 7)
What elements make up proteins?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. Proteins make up 12–18% of body mass.
What is the monomer (building block) of proteins?
Amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, and their sequence determines the protein's structure and function.
What is a peptide bond?
A covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another.
How are amino acids joined to form proteins?
By dehydration synthesis (removal of water)
Form a peptide bond (covalent bond)
Two joined amino acids = dipeptide
Many joined = polypeptide
100 amino acids = protein
What are conjugated proteins? Give examples.
Proteins combined with non-protein groups:
Glycoproteins = protein + carbohydrate
Lipoproteins = protein + lipid
Hemoglobin = protein + iron pigment (heme group)
Used in cell membranes, hormone transport, oxygen delivery, etc.
List major functions of proteins in the body.
Structure (e.g., collagen, keratin)
Enzymes (biological catalysts)
Transport (e.g., hemoglobin, carrier proteins)
Immunity (e.g., antibodies)
Hormone receptors and signaling
Energy source (when necessary)
What are nucleic acids?
Macromolecules that store and transmit genetic information. Two types: DNA and RNA.
Made of nucleotides.
What are the components of a nucleotide?
Nitrogenous base (A, T, G, C, or U)
Pentose sugar (deoxyribose or ribose)
Phosphate group
What are the nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA?
Purines (2 rings): Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines (1 ring): Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U)
In DNA: A, G, C, T
In RNA: A, G, C, U (no T)
Describe the structure of DNA.
Double-stranded helix
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Base pairing:
A with T
G with C
Bases are complementary and held by hydrogen bonds
What sugar is found in DNA?
Deoxyribose, a 5-carbon sugar with one less oxygen than ribose.
What is RNA and how is it different from DNA?
Single-stranded
Sugar: ribose
Base uracil (U) replaces thymine (T)
RNA is shorter and more versatile than DNA
Name the three types of RNA and their functions.
mRNA (Messenger RNA) – carries genetic code from DNA to ribosomes
tRNA (Transfer RNA) – brings amino acids during translation
rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) – forms part of the ribosome and catalyzes protein synthesis
What is the function of DNA?
Stores genetic instructions for protein synthesis
Passes hereditary information to the next generation
Controls cellular activities via gene expression
What is the role of RNA in the cell?
Acts as the intermediary between DNA and protein synthesis
Helps decode the genetic instructions into functional proteins
What are the 3 main parts of a cell?
Plasma Membrane – outer boundary, regulates entry/exit of substances.
Cytoplasm – fluid-filled space with organelles (site of biochemical reactions).
Nucleus – control center of the cell, contains DNA and RNA.
What is the plasma membrane made of and what are its functions?
Structure: Phospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic heads, hydrophobic tails), proteins, carbohydrates.
Functions:
Selective permeability
Cell signaling via receptors
Maintains cell shape & integrity
Clinical link: CFTR mutation (Cystic Fibrosis), abnormal channels
Define cilia, where they are found, and their function.
Definition: Tiny hair-like extensions of plasma membrane.
Function: Move substances across the surface or assist in signaling.
Locations:
Respiratory tract (move mucus)
Fallopian tubes (move egg)
Brain ventricles (move CSF)
Clinical relevance: Impairment may lead to respiratory issues or infertility.
Define flagella and describe its function in humans.
Definition: Long, whip-like extensions of plasma membrane.
Function: Motility – enables sperm cells to swim toward the egg.
Impairment: Affects fertility due to impaired sperm movement.
What are microvilli and what is their function?
Definition: Finger-like projections that increase surface area.
Function: Absorption of nutrients and ions.
Locations:
Small intestine (nutrient absorption)
Kidney tubules (ion reabsorption)
Exercise relevance: Enhance nutrient uptake post-exercise; endurance training can increase their density.
What is the cytoplasm composed of and what are its roles?
Components:
Cytosol (fluid)
Organelles
Cytoskeleton (microtubules + microfilaments)
Functions:
Metabolism (glycolysis, protein synthesis)
Structural support
Transport within cell
What is the cytoskeleton and what are its components/functions?
Components:
Cytosol (fluid)
Organelles
Cytoskeleton (microtubules + microfilaments)
Functions:
Metabolism (glycolysis, protein synthesis)
Structural support
Transport within cell
What is the cytoskeleton and what are its components/functions?
Microtubules: Cell shape, mitosis (spindle fibers), transport, motility
Microfilaments: Cytokinesis, movement, shape changes, endo/exocytosis
Function: Organizes cytoplasm, supports organelles, responds to exercise stress
What is the centrosome and why is it important?
Structure: Pair of centrioles + pericentriolar material
Function:
Organizes microtubules
Essential for mitosis and cell division
Exercise relevance: Supports muscle repair and neurogenesis through proper division and cell adaptation
What are lysosomes and what do they do?
Definition: Membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes
Functions:
Breakdown macromolecules & damaged organelles (autophagy)
Entire cell destruction (autolysis)
Exercise link:
Helps in muscle recovery by removing damaged mitochondria/proteins
Involved in fat metabolism during endurance
Regulates inflammation
What are lysosomes and what do they do?
Structure: Inner & outer membranes, cristae, matrix, own DNA (maternally inherited)
Function:
ATP production via aerobic metabolism
Fat & carb oxidation
Exercise relevance:
Endurance training improves mitochondrial efficiency
Affects fat burning and glycogen sparing
What are ribosomes and what is their role?
Structure: Two subunits (made of rRNA + proteins), found free or on ER
Function: Protein synthesis (translate mRNA → protein)
Exercise relevance:
Essential for muscle hypertrophy
Ribosomal biogenesis increases post-resistance training
Supports enzyme/protein production for recovery
What is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and what are its two types?
Rough ER: Ribosome-studded; site of protein synthesis
Smooth ER: No ribosomes; lipid/steroid synthesis, Ca²⁺ storage
Exercise role:
ER remodeling for protein demand
Manages inflammation, protein handling, and muscle repair
What does the Golgi apparatus do?
Structure: Flattened sacs (cisternae), vesicles enter from ER side and exit toward membrane
Functions:
Protein/lipid modification & packaging
Forms lysosomes and secretory vesicles
Exercise role:
Handles muscle repair proteins
Regulates calcium for contractions
Aids in immune and hormonal response to training
What is the nucleus and what are its key components?
Nucleus stores genetic info.
Nucleolus produces ribosomes.
Controls protein synthesis and exercise adaptation.
How does cell structure relate to exercise physiology?
Microvilli absorb nutrients for energy and repair
Mitochondria power endurance
Ribosomes/ER/Golgi synthesize muscle repair proteins
Centrosomes enable regeneration
Lysosomes recycle waste and reduce inflammation
All adapt to training stress for better performance and recovery
What is the primary function of the nucleus?
It contains genetic material (DNA and RNA), acting as the blueprint for the cell’s function.
What surrounds the nucleus and what is its purpose?
The nuclear envelope; it is a double membrane with nuclear pores that regulate exchange of materials between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
What are nuclear pores and what do they allow through?
Openings in the nuclear envelope; they allow RNA to exit but not DNA
What is chromatin?
DNA wrapped around histone proteins inside the nucleus.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Pairs of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent, that carry similar genetic information. Similar structure, function and shape.
How many chromosomes do somatic cells contain?
46 chromosomes (22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes).
How many chromosomes do gametes contain?
23 chromosomes (haploid), with ova always contributing an X, and sperm either X or Y.
What is gene expression?
The process by which DNA is used to synthesize proteins via transcription and translation.v
What is transcription?
The process of copying DNA into RNA in the nucleus.
What enzyme is essential for transcription and what does it do?
RNA polymerase; it breaks hydrogen bonds in DNA to copy the template strand into RNA.
What happens to RNA after transcription?
Introns are removed, exons are spliced together, and it is modified (5’ cap and poly-A tail) to become mature mRNA.
Where does translation occur?
In the cytoplasm, at ribosomes.
What are the three stages of translation?
Initiation, elongation, and termination.
What happens during initiation of translation?
The ribosome assembles around the mRNA and the first tRNA (carrying methionine) binds to the start codon.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
It brings amino acids to the ribosome based on mRNA codons.
What happens during termination?
A stop codon is reached, and the newly synthesized polypeptide is released.
What is mRNA?
What is tRNA?
What is rRNA?
Transfer RNA; it decodes mRNA and delivers amino acids.
Messenger RNA; it carries genetic instructions from DNA to ribosomes.
Ribosomal RNA; a structural part of ribosomes where proteins are synthesized.
Cell - Main Parts
Plasma Membrane – Outer boundary, selectively permeable, regulates cell’s interaction with the environment.
Cytoplasm – Gel-like content between membrane and nucleus; contains organelles.
Nucleus – Spheroid body containing DNA & RNA, controls cell function.
Mitochondria – Structure & Exercise Role
Structure: Double membrane, inner folds (cristae), central matrix, contains their own DNA (called mitochondrial DNA from maternal inheritance)
Function: ATP production (through aerobic metabolism), energy production
Exercise Relevance:
Fuels endurance sports
Fat/carbohydrate oxidation
Enhanced with training
Ribosomes – Structure & Function
Referred to as PROTEIN FACTORIES as they translate mRNA into polypeptide chains.
Structure: composed of two subunits (rRNA + proteins), free or bound to ER.
Function: Translate mRNA → proteins.
Exercise Relevance:
Muscle protein synthesis (hypertrophy)
Enhanced by amino acid intake
Ribosomal biogenesis = key to training adaptation
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – Types, Function + Exercise role
Rough ER: Has ribosomes; involved in protein production (e.g., glands).
Smooth ER: No ribosomes; site for enzymic reactions in steroid hormone production
ER adaptations in muscle cells during exercise:
ER expands and remodels to handle stress.
Improves protein folding, calcium storage, and lipid synthesis.
Inflammatory signaling is upregulated for repair, but must be tightly regulated.
These changes support muscle repair, reduce damage, and boost endurance over time.
Golgi Apparatus – Structure & Role
Structure: Flattened sacs (cisternae), vesicle entry from ER, exit to membrane.
Functions:
Involved in Protein modification & packaging
Involved in Lysosome/vesicle formation
Hormone & cytokine processing
Exercise Relevance:
Hormonal + immune responses
Protein synthesis + muscle repair
Protein sorting + transport
Adaptation to exercise induced stress
What is the nucleus and what does it contain?
The nucleus is a large spheroid organelle that contains the cell's genetic material (DNA and RNA). It also contains the nucleolus, where ribosomes are produced.
What is chromatin?
DNA wrapped around histone proteins; found inside the nucleus
What is the nucleolus and its function?
A substructure inside the nucleus where rRNA is synthesized and combined with proteins to form ribosomes.
What are somatic cells vs. gametes in terms of chromosomes?
Somatic cells (2n): 46 chromosomes (22 pairs + XX or XY)
Gametes (n): 23 chromosomes (ova = always X; sperm = X or Y)
What are homologous chromosomes?
One chromosome from each parent that form a pair with the same genes in the same order.
List and describe the 3 types of RNA.
mRNA – Messenger RNA: carries code from DNA to ribosomes.
tRNA – Transfer RNA: brings amino acids during protein synthesis.
rRNA – Ribosomal RNA: forms part of the ribosome structure.
Where does transcription occur?
In the nucleus.
Replication definition
DNA can also replicate itself during cell division to ensure that genetic information is passed on to daughter cells.
Steps in transcription?
Double helix DNA unzips and unwinds
enzyme RNA polymerase breaks the hydrogen bonds between paired DNA bases
2 separate DNA strands are formed
One DNA strand is used as a template
mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are synthesized.
mRNA is processed (introns removed, exons joined, ends modified).
Mature mRNA exits the nucleus.
What happens during initiation?
Ribosome assembles around mRNA and first tRNA (with methionine, start codon AUG).
What happens during elongation?
Codons of mRNA are read; tRNA brings amino acids; polypeptide chain grows.
What happens during termination?
Stop codon enters ribosome (UAG, UAA, or UGA); polypeptide is released and folds into its functional shape.
What is the purpose of cell division?
To produce new cells with identical (mitosis) or half (meiosis) genetic material.
Describe the phases of the cell cycle/division.
Interphase: Period between cell divisions
G1: Cell grows, organelles replicate
S: DNA replication
G2: Final preparations for division
M phase: Mitosis or Meiosis
2 different types of cell division
Mitosis: Cell division of somatic (body) cells
Meiosis: Cell division of the gametes (egg and sperm cells)
What are the stages of mitosis?
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
→ Produces 2 diploid daughter cells (46 chromosomes each
What are key features of meiosis (reduction division)
2 divisions: Meiosis I and II
Crossing over in Prophase I
Ends with 4 haploid cells (23 chromosomes each)