BIO Reproductive system and Biotechnology
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
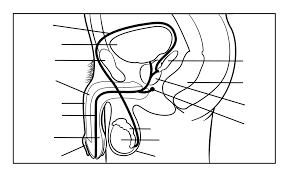
Name all the parts of the male reproductive organs
testis
scrotum
epididymis
sperm duct
seminal vesicle
urethra
erectile tissue
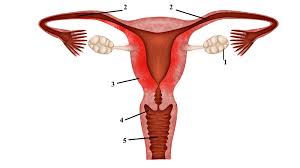
Name all the parts of the female reproductive organs
vagina
cervix
oviduct
endometrium
uterus
clitoris
List 4 roles of testosterone
Increased muscle mass
Deepening of voice
Enlargement of penis
Production of sperm cells
Explain how the sperm cell production is controlled
Testosterone is controlled by a feedback mechanism
FSH and LH increase → Testosterone increases
Increased testosterone → decreased FSH and LH
Decreased FSH and LH → decreased testosterone
Outline the short term effects of AAS (Anabolic Aandrogenic Steroids)
Increased male secondary sexual characteristics
Sperm production
Body hair
Growth of testicles and penis
Voice deepening
Outline the long term effects of AAS (Anabolic Aandrogenic Steroids)
Addiction
Growth of breast tissue(male) too much testo → estrogen
Increased risk of heart attacks, heart muscles grow → higher blood pressure
testicles will shrink and produce less sperm → infertility
Explain what happens during the menstrual cycle
1. Menstruation + follicular phase
Day 1-13
Mens. - Rupture of extra tissue(no fertilisation), decrease in estrogen and progestrone
Follicie devel. - FSH levels incr. → a follic develop in the ovary. FSH incr. stimulates estrogen prod. in the ovaries
Estrogen stimulates growth of endometrium
2. Ovulation
Day 14
Estrogen stimulates the increase of LH.
LH in hig levels stimulates ovulation, the release of amatured egg into the oviduct
3. Luteal phase
Day 15-28
The empty follicle forms, corpus luteum
Corpus luteum produces:
Progestrone + Estrogen = growth and maintenance of the endometrium
Prog. and Estr. inhibit FSH and LH to make sure no other egg is developed or released during this cycle
If no fertilisation → corpus luteum breaks down and Prog. + Estr. levels decrease → menstruation
Explain how a gel electrophoresis is carried out
Used to seperate DNA fragments by size
Samples are placed in a gel, which seperates the molecules based on size, and electrical current make the DNA samples move
Smaller samples move quicker towards the positive pole (DNA is negatively charged)
How are fragments of DNA are seperated in gel electrophoresis
Gel acts like a molecular sieve, with smaller pores(kind of like a mesh in the gel that the molecules have to travel through) in higher concentration gels. Smaller DNA fragments can navigate through the pores more easily and move faster, while larger fragments move more slowly.
Electric field causes the negatively charged DNA fragments to migrate through the gel towards the positive electrode.
Staining and Visualization: The stained gel allows for the visualization of DNA fragments, which appear as distinct bands. Each band corresponds to DNA fragments of a specific size.
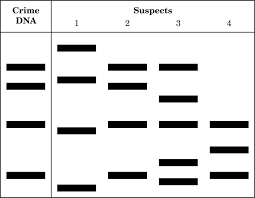
The following part of a DNA profile was used as evidence in a criminal investigation. DNA profiles of two suspects labelled S1 and S2 were compared to the DNA profile taken from the scene of the crime labelled E.
Analyse the profiles to determine which suspect that was present at the crime scene.
What is a primer?
List the criteria of life
Metabolism → Chemical reactions inside a cell. Anabolic reaction=building new molecules from smaller molecules(grow), Catabolic reaction=breaking down molecules to create ATP(move).
Excreation → getting rid of waste product left over from the metabolic reaction.
Reproduction →create offspring sexual or asexual way.
Homeostasis → keeping a constant internal environment
Response →ability to react to stimuli
Nutrition → take in nutrients for gaining energy and building blocks. Autotrophs=make energy on their own, Heterotrophs=need to eat others to get energy and building blocks
Growth →to build new molecules and get bigger/more cells
What is a stem cell?
It is:
a cell that is undifferentiated
first stem cell in a multicellular organism is called a zygote
can dicide a tremendous amount of times and form new stem cells or differentiated cells
role is to replace dead cells (blood and skin cells) and growth
Stem cells can be divided into 3 different groups, what are those three groups called and what defines them?
Pluripotent stem cell → Embryonic stem cell, can be differentiated into any body cell. Source → Blastocyst (5-6 weeks after fertilisation), produced in lab through IVF and leftovers are often used for research.
Induced pluripotent stem cell → Differentiated cells that are programmed in a lab to become a Pluripotent stem cell. Source → Skin cells or blood cells, you can use any differentiated stem cell, patients own cells can be used to repair a tissue.
Adult stem cell/Multipotent stem cell → Can differentiate into a limited amount of cells related to their tissue. Source → Bone marrow
There are 2 types of transport, name them
Passive transport → no energy required, transport from high concentration to low concentration in order to balance the conc. differences. Simple diffusion = right through the membrane + Facillitated diffusion = through protein channels
Active transport → Require ATP. Transport from low concentration to high. Endocytosis and exocytosis and protein pump.
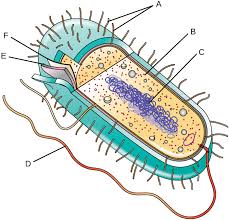
Name all the parts in a prokaryotic cell
A) Pilli/Pillus
B) Ribosomes
C) Nucleoid
D) Flagellum
E) Cell wall
F) Cell membrane
Extra: a layer outside of cell wall is the capsule
Name all the Biomolecules
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids
What is the monomer of Carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
What is the polymer of Carbohydrates?
Polysaccharides
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen
What is the function of Carbohydrates?
Energy, cell to cell communication
What is the monomer of Lipids?
Fatty acids, Glycerol
What is the polymer of Lipids?
Fats (triglycerides), Steroids, Phospholipids
What is the function of Lipids?
Long term energy storage, Insulation,