EPH3022 Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Health Policies at EU Level and Global Health Europe
Last updated 2:51 PM on 12/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
1
New cards
What is health policy analysis about?
1. Assessing a situation to see if it's a problem (= systems mapping)
2. Analyzing a problem and understand its drivers (= systematic analysis/approach)
3. Engaging stakeholders to set political agendas (= stakeholder analysis; is this feasible? does it have a solution?)
4. Leveraging science to implement solutions (= how can we use evidence to solve policy problems?)
2
New cards
A good policy problem analysis includes...
1. Clearly articulated policy problem → Who? What is the measure? Statistics (scope of the problem)?
2. A broad & systematic search of policy drivers was conducted → Ex. behavioural change wheel, policy triangle, stakeholder triangle
3. The interconnections between the various drivers were explored and illustrated → Justify why!
4. Most relevant points for intervention in the problem are identified → Mention if the country's plan makes sense or not (and why)
3
New cards
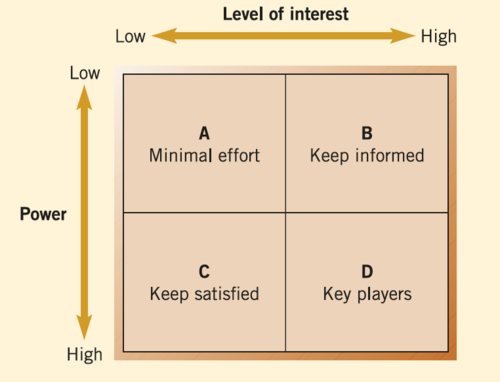
A good stakeholder analysis includes...
1. A broad and systematic brainstorm is conducted to identify stakeholders → Say something about stakeholders mentioned and the stakeholders that are not mentioned but should be
2. Stakeholders' power, interests & positions (positive/negative) are explored and illustrated → Power depends on the stakeholder's position; the level of interest might contain a catch on governmental level
3. Create a power-interest matrix to identify a policy advocacy strategy → Visually draw the square with power (high/low) + level of interest (high/low) etc.
4
New cards
A good policy evaluation includes...
1. Key objectives/measures for the proposed policy are identified → They should be measurable!
2. Key sources of data are highlighted → What kind of data is important; from what sub-populations?
3. Appropriate study designs to collect and analyze the data are proposed → What are the threats to validity? What can go right/wrong?
4. The insights of the evaluation are used to inform a new cycle of EIPM → Evidence informed policy making; what would you do? Justify with examples and integrating theory from the course
5
New cards
What statistical analysis should be used for ex-ante experimental study?
Differences between primary and secondary outcome measures; t-test to compare means in control and intervention group
6
New cards
What statistical analysis should be used for longitudinal observational study?
ANOVA to compare groups and means
7
New cards
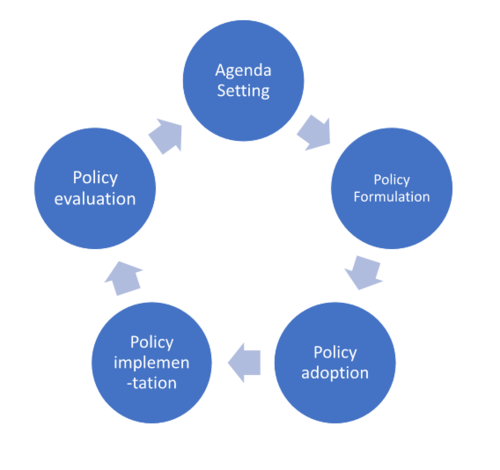
The 5 components of a policy cycle/process are...
1. Agenda setting
2. Formulation
3. Policy adoption
4. Policy implementation
5. Policy evaluation
8
New cards
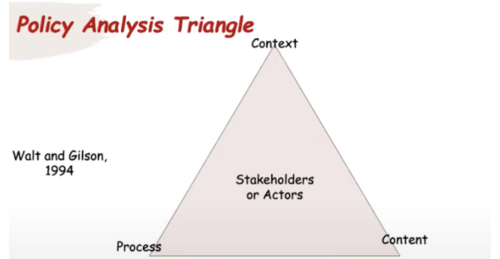
Explain the policy analysis triangle
Context → systemic factors — political, economic, social or cultural, both national and international — which may have an effect on health policy
Content → substance of a particular policy which details its constituent parts
Process → how policies are initiated, developed, negotiated, communicated, implemented, and evaluated
Actors →short-hand term used to denote any participant in the policy process that affects policy, including individuals, organisations, groups and even the government
Content → substance of a particular policy which details its constituent parts
Process → how policies are initiated, developed, negotiated, communicated, implemented, and evaluated
Actors →short-hand term used to denote any participant in the policy process that affects policy, including individuals, organisations, groups and even the government
9
New cards
What is decentralisation? What are its three forms?
Decentralisation → shifting of defined power from central to local level of the public system with the aim of increasing the effectiveness and efficiency of health care system
1. Deconcentration → shifting of limited managerial authority
2. Delegation → massive leadership/managerial autonomy except financial decision making authority
3. Devolution → political decentralization
1. Deconcentration → shifting of limited managerial authority
2. Delegation → massive leadership/managerial autonomy except financial decision making authority
3. Devolution → political decentralization
10
New cards
What does the Kingdon/garbage can model entail?
* Aims at explaining the agenda-setting process → chaotic
* Three streams:
1. Problem stream (problems)
2. Policy stream (solutions)
3. Politics stream (politics)
* Issues get on the agenda (a policy window is created) when a problem is recognised, a solution is available, and the political climate makes the time right for change
* Three streams:
1. Problem stream (problems)
2. Policy stream (solutions)
3. Politics stream (politics)
* Issues get on the agenda (a policy window is created) when a problem is recognised, a solution is available, and the political climate makes the time right for change
11
New cards
Distinguish democratic systems and explain them
* Liberal democratic → relatively stable political institutions with considerable opportunities for participation through elections, political parties, interest groups and 'free media'
* Egalitarian-authoritarian → monolithic (ex-Soviet states, China); closed ruling elite, state-managed popular participation; intent to be egalitarian; well-developed social security systems/healthcare financed and delivered almost exclusively by the state as a fundamental human right
* Traditional-inegalitarian → rule by traditional monarch, few opportunities for participation (Saudi Arabia), health policy in private sectors with the elite using facilities in other countries as the need arises
* Populist → more tribal (no commitment to the population, focus on personal interests); a single rule or dominant political parties, highly nationalist, leadership tends to be personalised
* Authoritarian-inegalitarian → military governments involve varying degrees of oppression (sub-Saharan Africa, Afghanistan after the Taliban), health policy reflects the interests of a narrow elite
* Egalitarian-authoritarian → monolithic (ex-Soviet states, China); closed ruling elite, state-managed popular participation; intent to be egalitarian; well-developed social security systems/healthcare financed and delivered almost exclusively by the state as a fundamental human right
* Traditional-inegalitarian → rule by traditional monarch, few opportunities for participation (Saudi Arabia), health policy in private sectors with the elite using facilities in other countries as the need arises
* Populist → more tribal (no commitment to the population, focus on personal interests); a single rule or dominant political parties, highly nationalist, leadership tends to be personalised
* Authoritarian-inegalitarian → military governments involve varying degrees of oppression (sub-Saharan Africa, Afghanistan after the Taliban), health policy reflects the interests of a narrow elite
12
New cards
Explain the innovation attributes by Rogers (1995)
Potential adopters of policies evaluate an innovation based on specific characteristics (pros and cons)
* Relative advantage → does it add to what I'm currently doing?
* Compatibility → does it fit within my organisation?
* Complexity → is it easy for me to use=
* Trialability → can I try it out first?
* Observability → can I observe its effectiveness?
* Relative advantage → does it add to what I'm currently doing?
* Compatibility → does it fit within my organisation?
* Complexity → is it easy for me to use=
* Trialability → can I try it out first?
* Observability → can I observe its effectiveness?
13
New cards
Explain why an ex-post evaluation is useful
* For evidence-based policymaking in other countries
* To examine whether policies have the intended effect and how they can be improved
* To identify possible unintended consequences
* To identify groups that do not benefit (as much) and need more or something else
* For situations in which policy is reversed and later reconsidered
* To examine whether policies have the intended effect and how they can be improved
* To identify possible unintended consequences
* To identify groups that do not benefit (as much) and need more or something else
* For situations in which policy is reversed and later reconsidered
14
New cards
What is included in ex-post evaluation?
* Policy problem evaluation →WPR model (what's the problem represented to be) refers to the fact that policy 'constructs' problems in a certain way by integrating particular facts and values; studying problematisation gives insights into underlying assumptions of policy and uncover 'silenced' assumptions; six questions need to be asked
* Process evaluation → examining how well a policy is being implemented or delivered
* Time trend analysis → examining trends in outcome measures before and after policy implementation, with cross-sectional monitoring data that is representative for the general population
! Advantage: showing the impact of policies on the population level
! Disadvantage: changes in outcomes measures may not be caused by the policy; there may be anticipatory and delayed effects
* Quasi-experimental study → examining changes in outcome measures in a country/region where a policy is implemented and comparing this to changes in outcome measures in a country/region where the policy is not implemented
* Longitudinal observational study → examining changes in outcome measures among the same group of people before and after the implementation
* Economic evaluation → he comparative analysis of interventions/policies in terms of their cost and consequence
* Process evaluation → examining how well a policy is being implemented or delivered
* Time trend analysis → examining trends in outcome measures before and after policy implementation, with cross-sectional monitoring data that is representative for the general population
! Advantage: showing the impact of policies on the population level
! Disadvantage: changes in outcomes measures may not be caused by the policy; there may be anticipatory and delayed effects
* Quasi-experimental study → examining changes in outcome measures in a country/region where a policy is implemented and comparing this to changes in outcome measures in a country/region where the policy is not implemented
* Longitudinal observational study → examining changes in outcome measures among the same group of people before and after the implementation
* Economic evaluation → he comparative analysis of interventions/policies in terms of their cost and consequence
15
New cards
What is the behaviour change wheel/implementation theory?
Michie (2011) defines 6 main groups of behaviour; determinants tell us whether a person adopts a certain behaviour and the intervention fits to the relevant determinants
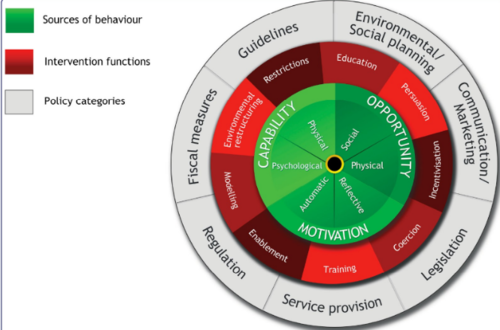
16
New cards
What statistical analysis should be used for an economic evaluation?
Comparative analysis of intervention/policies in terms of their cost and consequence (cost benefit, cost effectiveness, and cost utility analysis)
17
New cards
What statistical analysis should be used for a quasi-experimental study?
Regression analysis to see relationship between two variables (if it makes sense → policy is good)
18
New cards
Who are the main stakeholders involved in tobacco policy-making?
* Manufacturers, advertisers, public relation companies, vendors, government officials with tobacco industry stocks and lobbyists
* Customers – retailers, wholesalers and distributors. Adult consumers. Governments and regulators. Scientific and public health communities.
* Customers – retailers, wholesalers and distributors. Adult consumers. Governments and regulators. Scientific and public health communities.
19
New cards
What are the tobacco industry’s main tactics of interference?
* They fund political campaigns, ask for a seat at negotiation tables and __draft sample legislation(link is external)__
* They exaggerate their contribution to economies in terms of tax income and employment
* They discredit proven science and conduct their own biased studies or set up front groups as self-claimed “grassroots” movements to stir up public controversy and muddy the waters on topics such as second-hand smoke and novel tobacco products, with tobacco industry research frequently quoted in the media
* They exaggerate their contribution to economies in terms of tax income and employment
* They discredit proven science and conduct their own biased studies or set up front groups as self-claimed “grassroots” movements to stir up public controversy and muddy the waters on topics such as second-hand smoke and novel tobacco products, with tobacco industry research frequently quoted in the media
20
New cards
What are the main arguments provided by the tobacco industry?
* To resist taxation → claim that illicit trade and smuggling raise in a high-tax context (this has been debunked)
* To delay legislation → participating in meetings and proposing their own drafts for tobacco products bills or laws
* Government representatives, decision-makers or policymakers have been previously working for the industry or have been hired by the tobacco industry, which might be perceived as a conflict of interest according to the WHO
* To delay legislation → participating in meetings and proposing their own drafts for tobacco products bills or laws
* Government representatives, decision-makers or policymakers have been previously working for the industry or have been hired by the tobacco industry, which might be perceived as a conflict of interest according to the WHO
21
New cards
How to counter tobacco industry interference?
* Coordination across government ministries and public agencies → governments must end the endorsement of industry activities by public officials and reject any non-binding agreements that have been passed with the tobacco industry
* End any incentives provided to the tobacco industry and promote full transparency with respect to their ties with the industry, including disclosure of interest regarding physical and virtual meetings where tobacco companies are represented
* The tobacco industry should also be obligated to provide any information about its business, and especially with respect to lobbying and marketing activities with governments, that would provide a more accurate picture of their intentions and the extent of their influence
* End any incentives provided to the tobacco industry and promote full transparency with respect to their ties with the industry, including disclosure of interest regarding physical and virtual meetings where tobacco companies are represented
* The tobacco industry should also be obligated to provide any information about its business, and especially with respect to lobbying and marketing activities with governments, that would provide a more accurate picture of their intentions and the extent of their influence
22
New cards
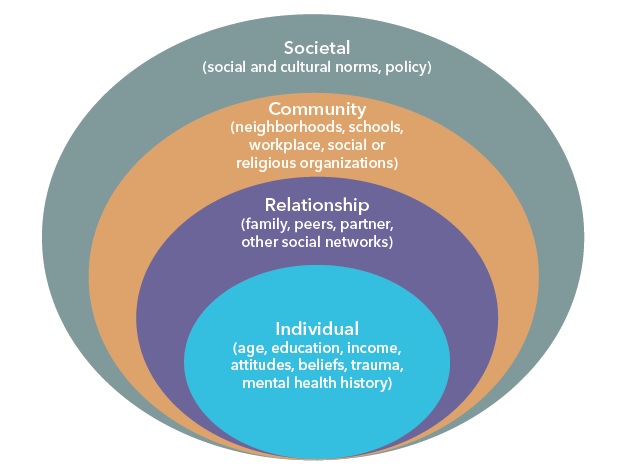
Explain the sociological-ecological model
Categorizes determinants in individual, interpersonal, organizational, societal and policy drivers