IB Geography: Leisure, Sport and Tourism
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Leisure
Any freely chosen activity or experience that takes place in non-work time (IB definition)
Sport
A physical activity involving a set of rules or customs. The activity may be competitive (IB definition)
Tourism
Travel away from home for at least one night for the purpose of leisure (IB definition).
Recreation
A leisure time activity undertaken voluntarily and for enjoyment (IB definition)
Mass tourism
Large-scale tourism when flights, accommodation, tours and transfers are booked together and often part
of a group.
Sustainable tourism
Tourism that conserves primary tourist resources and supports the livelihoods and culture of local people. It attempts to have a low impact on the environment and local culture, while helping to generate future employment for local people. The aim is to bring about a positive experience for local people, tourism companies and tourists.
Ecotourism
Responsible travel to fragile, pristine and usually protected areas that strive to be low impact and (often) small scale (alternative to mass tourism)
Heritage tourism
Tourism based on historic legacy as its main attraction e.g. natural landscape, historical buildings.
Honeypot
A location that attracts a large number of tourists. Gruyères in Switzerland would be considered a honeypot location.
(Economic) Leakage
Money that is generated in a country but then leaves the country. Money that is lost from a tourist destination. For example, a large number of TNCs operating in a country may send the money earned back to their home country e.g.Intercontinental or Hilton.
Multiplier effect
When an initial amount of spending (investment in services/facilities for example) leads to increased spending by tourists and so results in an increase in national income greater than the initial amount of spending. For example, investment in tourism helps create more jobs and generate demand for locally produced goods (food etc); more income is earned which enters the local economy
Sports tours
Trips that either go to play sport or view sport. Trips to the football World Cup or Olympics are becoming
much more common.
Primary tourist/recreational resources
Refer to pre-existing attractions for tourism or recreation (i.e. not built specifically for the purpose) including climate, scenery, wildlife, cultural and heritage sites, and indigenous people (IB definition)
Secondary tourist/recreational resources
Refer to accommodation, catering, entertainment and shopping (developed with tourism in mind) (IB definition)
Those resources developed with tourism in mind
Tourist attractions
Climate (Maldives, Mediterranean), Landscape (New Zealand), Culture (Cambodia), Sport (surfing in Australia, Olympic Games)
Tourism deterrents
Hazards (earthquakes), Political unrest (Greece, Sri Lanka), Disease (SARS in East Asia), exchange rate (reduced spending power)
Butler's Tourism Model
Tourist areas development in six main stages: (1) exploration; (2) involvement ; (3) development; (4) consolidation; (5) stagnation; (6) decline or (6) rejuvenation
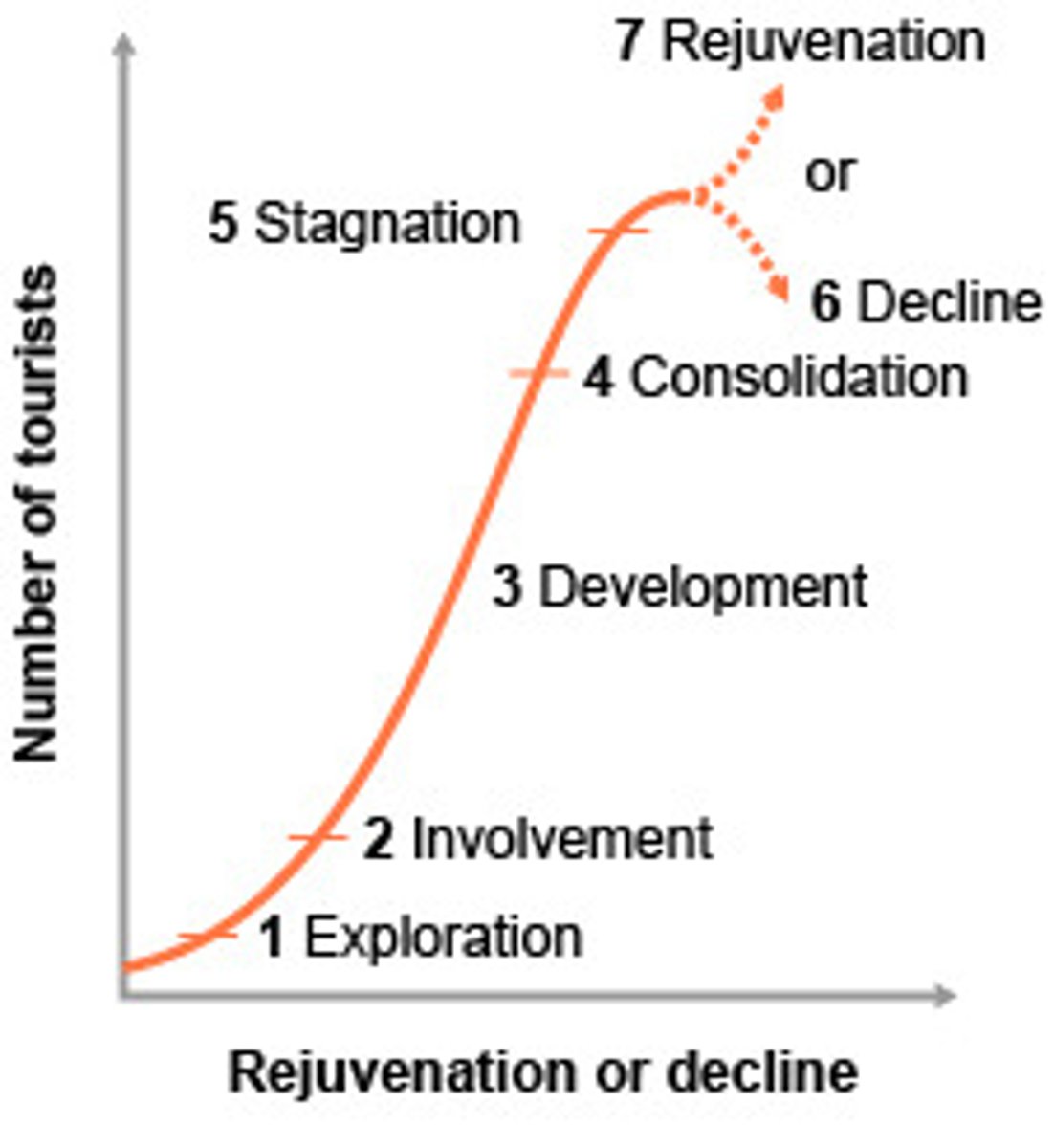
Carrying capacity
The maximum number of visitors/participants that a site/event can satisfy at one time.
Environmental carrying capacity
The maximum number before the local environment becomes damaged (IB definition)
Perceptual carrying capacity
The maximum number before a specific group of visitors considers the level of impact, such as noise, to be excessive. e.g. young mountain bikers may be more crowd-tolerant than elderly walkers (IB definition)
Urban regeneration
Improving an area that has been experiencing a period of decline e.g. in East London, deindustrialisation contributed to a period of decline. This area was selected as the primary venue for the Olympics and this has contributed to regeneration within this area
Gentrification
The process of an area being improved by the people that live there. Young professionals might move into an area that is deprived (houses will be cheaper). As the income of the professionals increases they might make improvements to their house and local facilities e.g. park areas. The income of the professionals may also attract new businesses like restaurants. The movement of higher economic groups into an area
Social sustainability
means benefiting local people long-term. This might be done through infrastructure improvements, provision of affordable housing or job creation
Economic sustainability
means benefiting the economy long term. It might mean increasing the income of an area, keeping inflation low or eliminating debt
Environmental sustainability
means reducing the impact on the environment. It might be using renewable energy, developing public transport or reforesting areas
Sports Hierarchy
when the best teams are promoted to a higher division and the worst teams are relegated to a lower division. Generally there are more teams playing at the lower division and fewer teams playing in the higher division
Sports Leauge
when an organization coordinates a group of individual clubs that play each other
Sphere of influence
The average distance people are willing to travel to get to a particular service (such as a stadium)
Threshold population
The minimum population required for a service to be offered.
Factors Affecting Patterns of Distribution of Leisure Facilities
Natural: Space, physical characteristics
Economic: Land value, advertising, socio-economic standards (rich people and golf)
Social: historical location, land use of surrounding area, accessibility
Sustainability
meeting the demands of the present without compromising future generations