The American Journey Chapter 4: English Colonies In An Age of Empire
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
CHAPTER 4.1
How did the colonies became indispensable for Great Britain?
Colonies supplied raw materials unavailable in Great Britain.
Mercantilism
British economic system to improve its competitve position in trade.
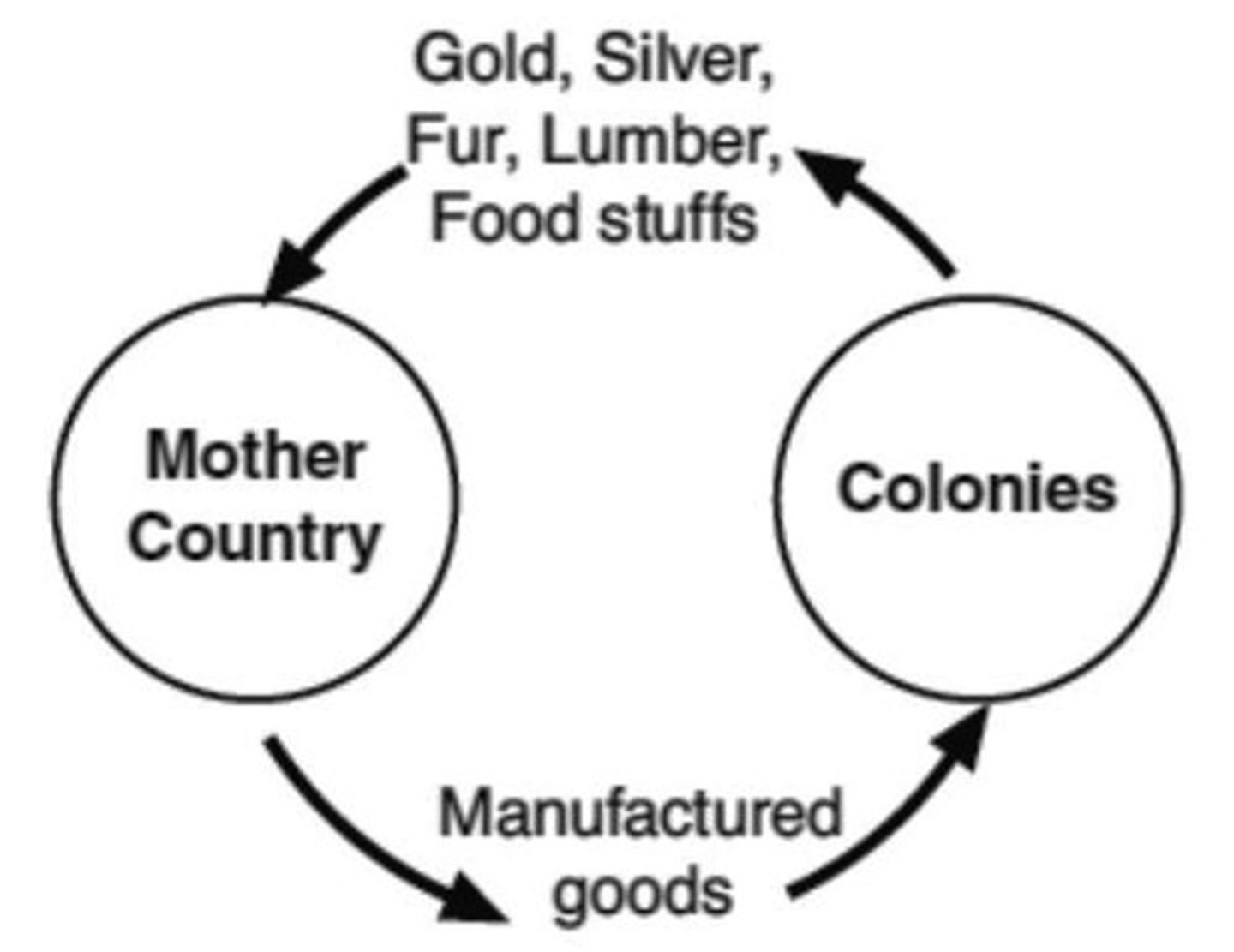
British regulations to imprive trade and commerce:
1. Navigation Acts of 1651 and 1660
2. Staple Act of 1663
Navigation Act of 1651 and 1660
- Aimed at ending Dutch Empire dominance in overseas trade
- All trade conducted in English colonial ships
At least half of the ship crew must be Englishmen or colonists
Staple Act of 1663
- Taxed products
- European goods myst be passed through England before shipped to the colonies
- Enumerated products should be shipped only to England and other English colonies.
British Web Trade route
Vessels carried goods and people from Great Britain, Europe, and West Africa to the colonies and returned to GB with raw materials
How did the colonists sink into debt?
Colonials imported more than exported. Imbalance. British merchants extended credit to colonists so they could buy British products.
Colonists sank into debt and realized they depended on European goods.
How did colonist life transformed in order to look like their fellow British?
They tries to asssimilate their culure, houses, manners, minds, like the British.
Goods and houses
Remodeled to recreate an English environment. Big. More kitchens and private bedrooms
Did all colonists remodel their houses?
No. Some still lived in places where they cooked, ate, and slept.
Manners
Many Americans imported "courtesy books" that contain rules of polite behavior.
Women sent to boarding schools.
The First Great Awakening
The rise of spiritual diversity, new protestant religions, and new ideas in the colonies during the 1730s and 1740s. People were encouraged to think for themselves and not follow the popular will.

Effects of First Great Awakening
It minimized the supreme authority of the Anglican Church.
People found more freedom of speech and comfortableness in the new religions.
CHAPTER 4.3
What did the First Great Awakening encourage?
Individual choice, individualism and poltiical resistance.
How interested was the new King of England, Charles II, on the American colonies?
He did not show interest besides economic matters.

Who became king after Charles II?
His brother James II (1685)

How did King James II restrict the colonists' rights?
--He combined colonies into 4 large provinces.
--Appointed governors under his control
--He attempted to establish the Dominion of England (all colonies combined into one large province governed by his royal appointee)
What stopped James II from establishing all the previous restrictions on the colonies?
The Glorious Revolution

The Glorious Revolution
Netherland king William of Orange took over England and destituted James II.
While William of Orange overthrew James II at England, who did the colonists overthrew at the Americas?
The governor appointed by James II, Edmund Andros
Effects of the Glorious Revolution
--Colonist no longer elected their governor
--Voters no longer had to be church members
--Religious toleration extended to all protestants at the colonies.
Salem Witchcraft Trials
Massachusetts, during the gap of the governor, overthrown and the arrival of a new one, colonists did not have a government.
Witchcraft accusations during this gap led to the execution of accused "witches".
Legacy of the Glorious Revolution
While the English Parliament was concentrated on the economy and the Bill of Rights (which limited king's power), the colonies were left alone.
This allowed colonies to evolve and grow.
CHAPTER 4.4
Competition of land, trade and resources between:
Great Britain, France, and Spain.
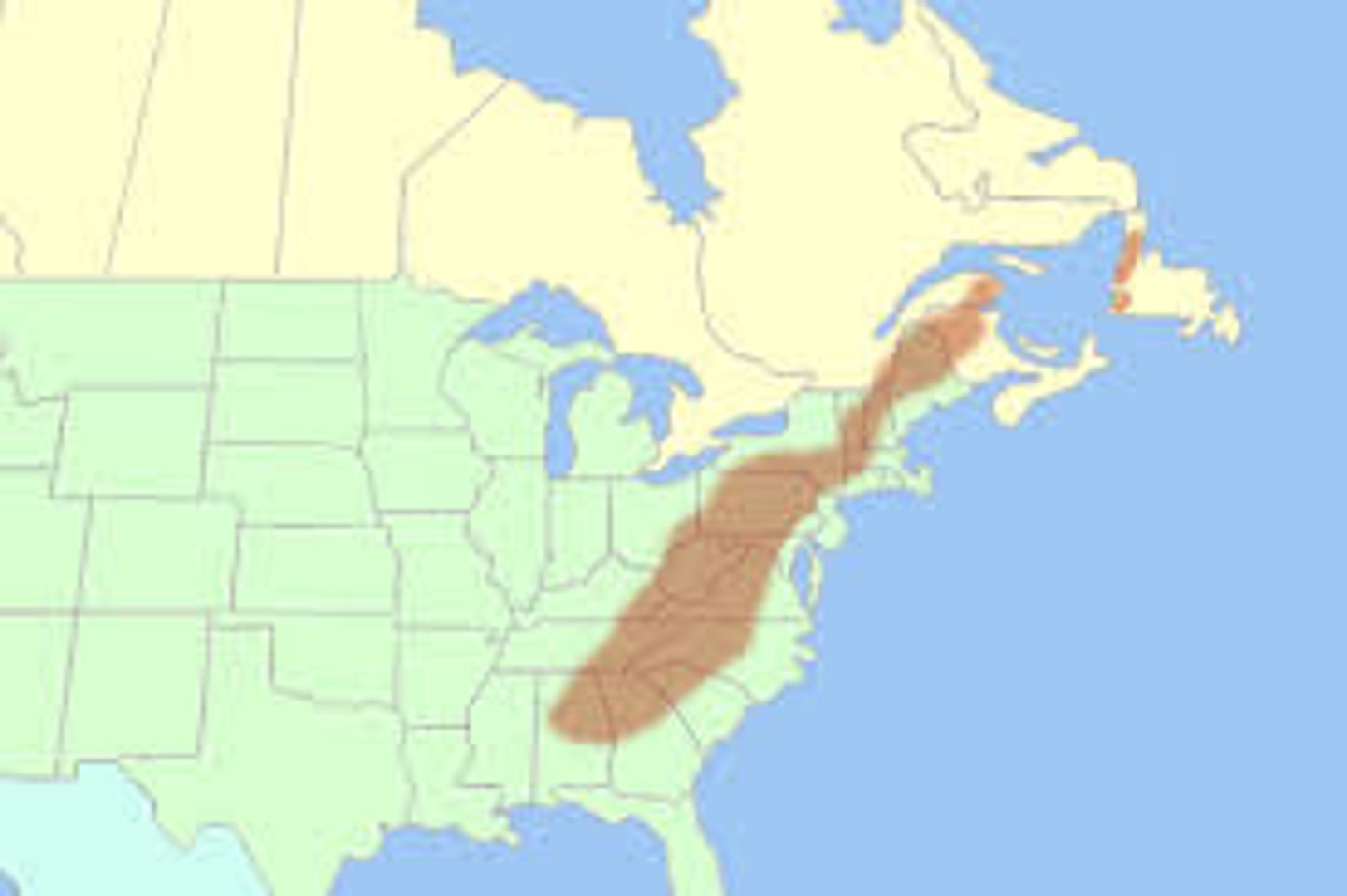
Backcountry expansion
Scots-Irish and English colonies expanded their boundaries towards the Appalachian Mountains and settled with farms and plantations.
Colonists expansion alarmed Indians who lived there and constantly had to move.
The Appalachian Mountains
Area from Pennsylvania to Georgia known as the backcountry. Many Indians lived here.
The Spanish in Texas and California
Spanish moved to both states but met with French/Indian resistance.
With few settlers, Spain left Texas and moved to California.
French along the Mississippi and Louisiana
French expansion followed the Mississippi. First Illinois settlers were fur traders. French expansion depended on Indian alliances. French Louisiana continued being a diverse Indian territory.
CHAPTER 4.5
Whihch four wars shaped the colonial society during the 18th century?
1. King William's War
2. Queen Anne's War(Spanish Seccession)
3. King George's war(Austrian Succession)
4. French and indian War (7 years war)
King William's War (1689-1697)
Results for Great Britain
Reestablished balance of power between England and France.

Queen Anne's War (1702-1713)/Spanish Succession
Results for GB
Britain acquired Nova Scotia

King George's War (1744-1748)/Austrian Succession
Results for GB
GB returned Louigsborg to France
British settlers began moving westward
Weakened Iroquois neutrality

French and Indian War 1754-1763 (Seven Years' War)
Resolts for GB
Britain acquired Canada and all French territory east of Mississippi.
Britain gained Florida from Spain.
