Final exam 1
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Mechanism of Bromocriptine
Dopamine agonist —> stops cAMP and decreases transcription of prolactin
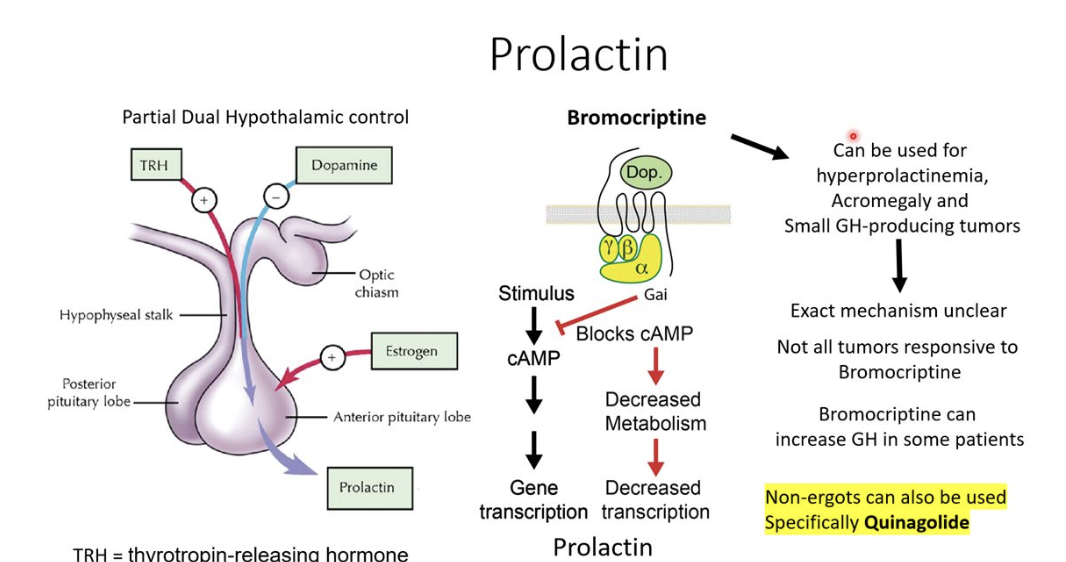
Use of bromocriptine
Used for hyperprolactinemia
Acromegaly
Small GH producing tumors
How does prolactin modulate GnRH and Estrogen
Prolactin can negatively affect GnRH, which will in turn decrease FSH and LH production, which can decrease estrogen production
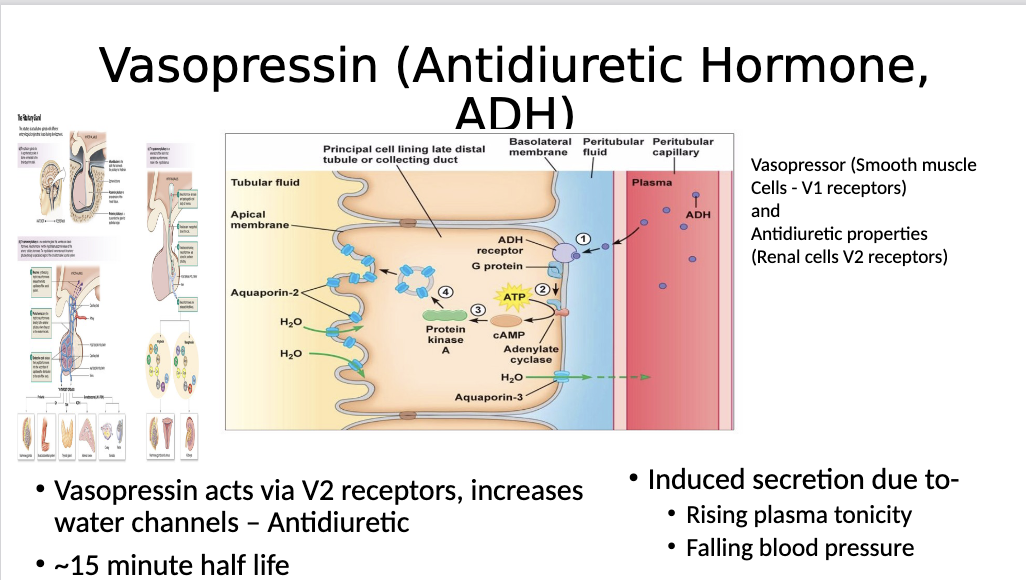
Does vasopressin induce water retention or water elimination?
Goal of vasopressin is to increase BV:
Therefore, we would increase water retention via
Controls aquaporin tubes via GPCR cAMP
ADH binds to its receptor in the collecting ducts. When the blood delivers vasopressin -> triggers cAMP - moves tubes to the membrane and water is reabsorbed into the body
A 7-year-old boy underwent successful chemotherapy and cranial radiation for Treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia. One month after the completion of therapy, the patient presented with excessive thirst and urination plus hypernatremia. Laboratory testing revealed pituitary diabetes insipidus. To correct these problems, this patient is likely to be treated with which of the following?
A. Corticotropin
B. Desmopresin
C. hCG
D. Menotropins
E. Thyrotropin
HYPERnatremia = high salt
We want to reabsorb water yes? How do we do that? Vasopressin analogue IE increase water reabsorption via desmopressin
Vasopressin antagonists
Conviaptan and Tovaptan
What 2 hormones are released by the posterior pituitary
Oxytocin and Vasopressin
Oxytocin receptors activate:
GPCR, triggers IP3 and phospholipase C —> increase influx of calcium —> stimulates muscle contraction
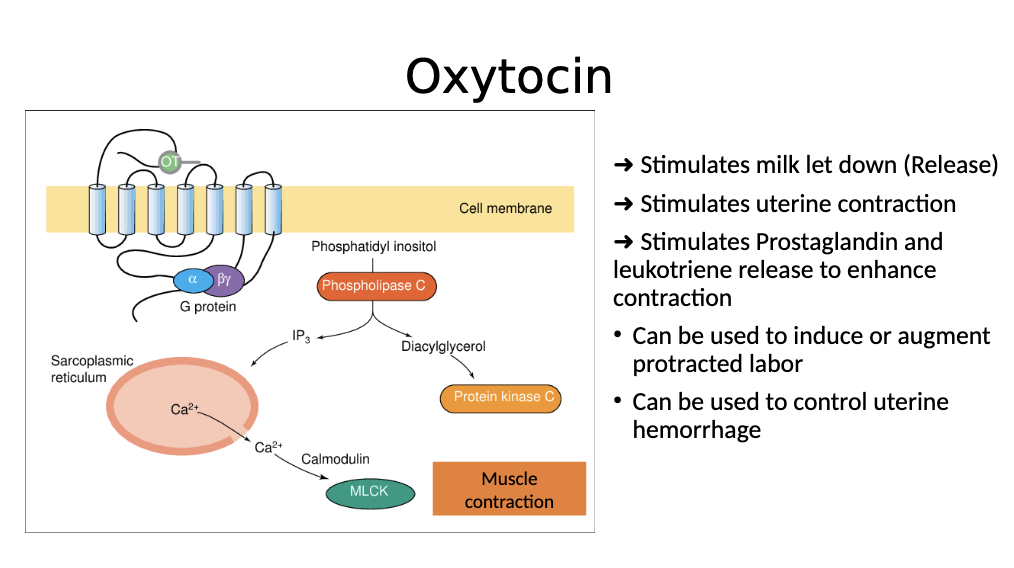
Oxytocin leads to
Milk stimulation, uterine contraction
Prostaglandin and leukotriene release
Induce labor
Oxytocin antagonist
Atisoban
Nifendipine is a CCB used for this purpose but is controversial
Vasopressin MOA?
ADH binds to the receptor and activates adenylyl cyclase → cyclic AMP → protein kinase a → movement of aquaporins to the apical membrane (the side with the pee). This allows for more water to move out of the collecting duct back into the blood for reabsorption. (Diuretics block this and make us pee to lower BP)
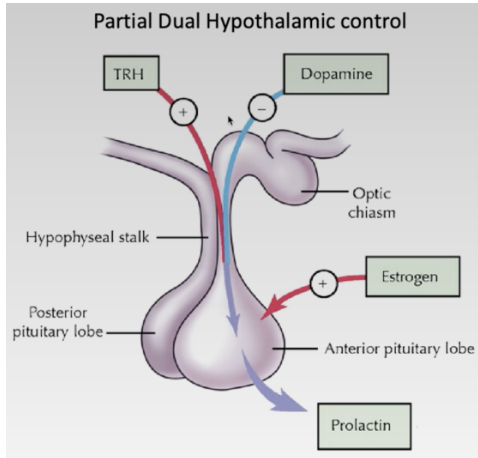
Role of prolactin?
Principle hormone for lactation, stimulated by circulating estrogen, progestin, corticosteroids, and insulin
Mediators of prolactin
Prolactin does not have a direct hypothalamic releasing hormone, but it can be regulated by other hormones
TRH can increase prolactin
Estrogen can increase prolactin
Dopamine can block prolactin
Excess prolactin leads to:
Fertility problems (alters feedback mechanism of estrogen and can alter ovulation, as estrogen excess can lead to GnRH inhibition)
Loss of libido
Causes of prolactin secretion:
PRL stimulation in primary hypothyroidism or adrenal insufficiency
Increase PRL production can occur via pituitary tumors or PCOS
Pregnancy
Hepatic insufficiency or renal failure (reduced clearing of prolactin)
Effect of opiates and neuroleptics on dopamine:
These typically inhibit dopamine release. If dopamine typically negatively affects prolactin release, then removing the inhibitor allows for less downregulation of dopamine and thus increase dopamine levels. (hyperprolactinemia is a side effect of antipsychotics)
Effect of bromocriptine on prolactin?
Bromocriptine is a dopamine agonist
Dopamine activates gai to block cAMP production. This decreases the transcription of prolactin and suppresses prolactin release
This reduces prolactin expression
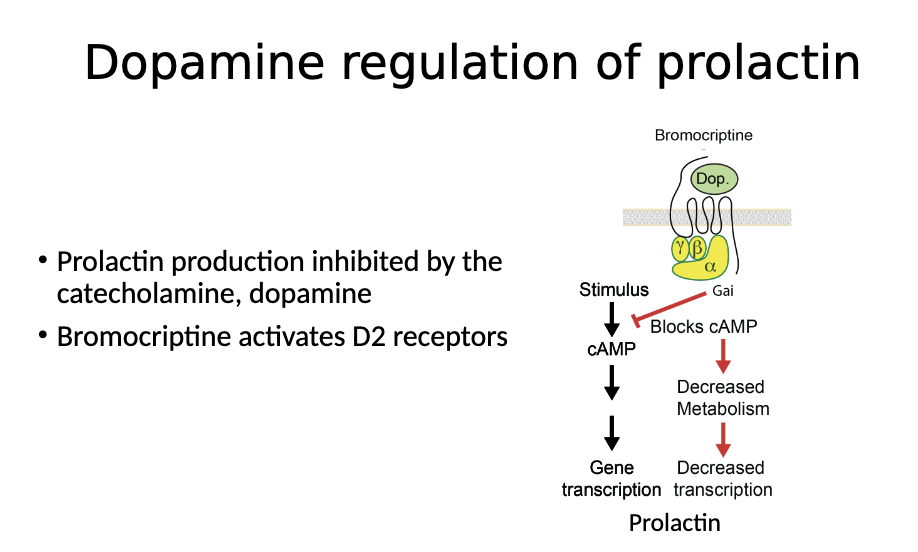
Therapeutic use of bromocriptine
Dopamine receptor agonists reduce PRL
Can shrink pituitary prolactin secreting tumors
Examples of dopamine agonists:
Bromocriptine, cabergoline (ergot derivative)
Quinagolide, pramipexole, ropinirole (nonergot) ← antiparkinson treatment, give them dopamine and anticholinergics
What neurohormone is released in the anterior pituitary but acts directly on its target organs?
Prolactin
How is oxytocin activated?
Activates GPCR, which activates Phospholipase C → IP3 pathway → , which results in release of calcium, which leads to muscle contraction. This releases milk and stimulates uterine contraction and stimulates prostaglandin and leukotriene release
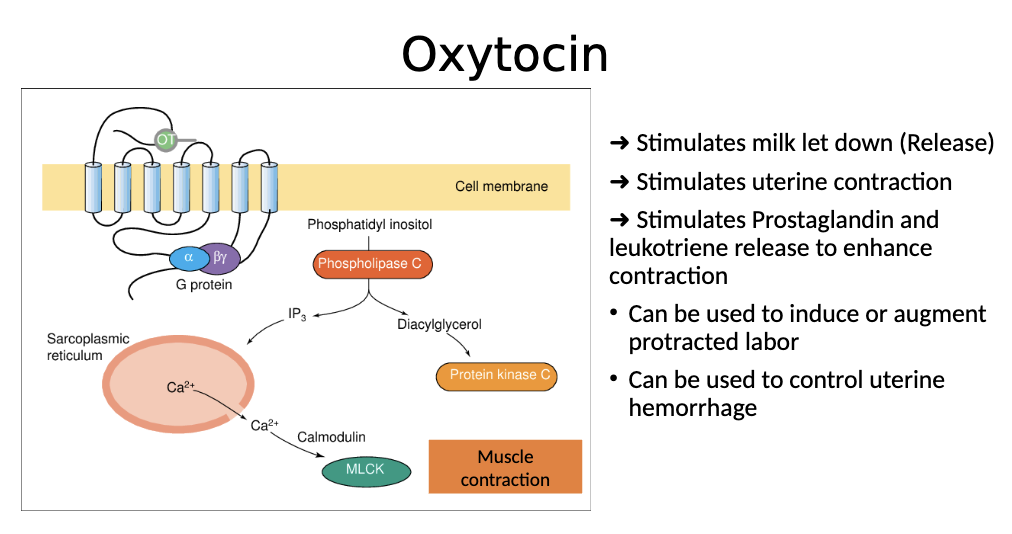
Therapeutic use of oxytocin
Release milk, induce labor
Can be used to control uterine hemorrhage
What is a physiological trigger that will release vasopressin
Release is triggered by rising tonicity (high salt in the blood will trigger the reabsorption of water) or falling BP
Released by the kidney to increase water retention
ADH activates a GPCR adh receptor. This enhances cAMP to activate PKA, which triggers the movement of aquaporins (water channels) to move to the apical membrane. This induces water reabsorption to increase BP
Modified vasopressin analogue:
Desmopressin, long lasting analog and more selective to V2
Desmopressin therapeutic use:
Can be used to treat mild hemophilia A
Diabetes Insipidus (inability to control water levels in the blood due to pituitary insufficiency)
Use for vasopressin antagonists
Used in hyponatremia, antagonize the binding of add to the receptor and block the reabsorption of water. This increases excretion and increases the tonicity of the blood by removing the water volume to concentrate the blood with more salt
What hormones are released by the anterior pituitary?
GH, TSH, ACTH, LH, FSH, Prolactin
What hormones are released by the hypothalamus?
GnRH, TRH, GHRH, CRH, Dopamine, Somatostatin
What 2 hormones are produced in the posterior pituitary?
ADH and Oxytocin
What 2 hormones activate the JAK/STAT pathway?
Prolactin, GH
Key functions of growth hormone
Carbohydrate and lipid metabolism
Lean body mass and bone density
Growth during adolescence
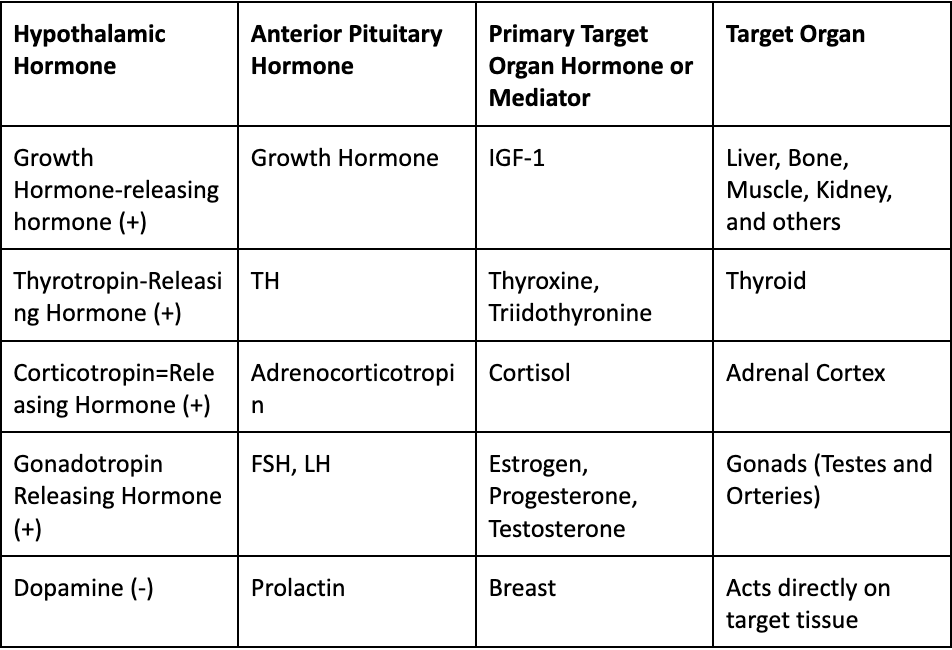
Axis of GH?
Hypothalamus releases GHRH
Stimulates anterior pituitary to release GH
Stimulates Liver, Bones, or Muscles to release IGF-1
Growth hormone agonist
Somatostatin - Growth Hormone Agonist
Mecasermin - Recombinant IGF-1
Clinical use of growth hormone antagonist?
Acromegaly, when too much growth hormone is produced
Examples of growth hormone antagonists?
Pegvisomant - Growth Hormone receptor antagonist
Somatostatin analogues - Octreotide, Lanreotide
D2 Receptor agonists (due to negative feedback of dopamine on GH) - Bromocriptine
Somatostatin analogues
Octretide, Leuprolide
Examples of gonadotropins
FSH, LH, hCG
All gonadotropins exert their effects on what kind of receptors?
GPCR
What is the role of FSH in women?
Follicle support and development
What hormones play a role in steroidogenesis for women?
FSH and LH
What is the role of FSH in men
Regulation of spermatogenesis
What is the role of LH for men?
Regulation of androgen production
Name 3 therapeutic forms of FSH
Follitropin Alpha
Follitropin Beta
Urofollitropin
Complete the following chart:
FSH and LH are dimeric gonadotrophic hormones. FSH binds a _______ and induces transcriptional changes in the cell by activating ______.
A. Dimer of receptors, Calcium channels
B. G protein–coupled receptor, Calcium channel
C. G protein–coupled receptor, cyclic AMP
D. Dimer of receptors, JAK/STAT signaling
E. G protein–coupled receptor, JAK/STAT signaling
C. G protein-coupled receptor, cyclic AAMP
The only ones that are JAK/STAT are Prolactin and GH
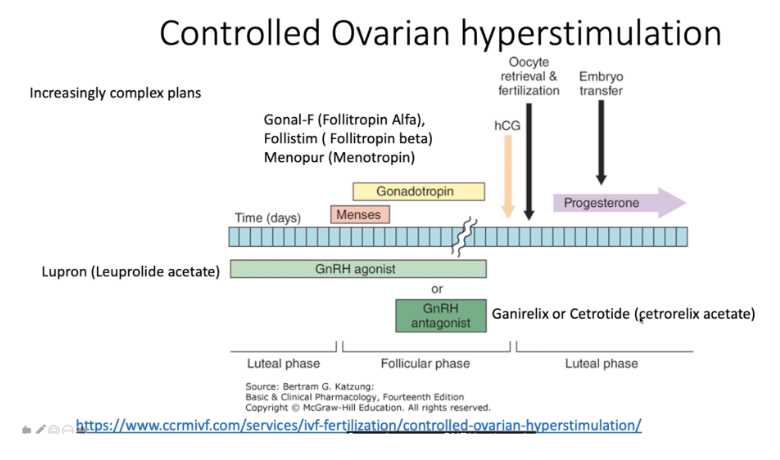
Why does a continuous dose of GnRH agonist block steroid hormone expression in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation?
A. High blood GnRH agonist concentration blocks LH activity in the ovaries.
B. Continuous GnRH activation triggers GnRH receptors degradation
C. GnRH agonists inhibit gonadotropin activity.
D. Continuous GnRH agonist administration shrinks the ovaries.
Why does a continuous dose of GnRH agonist block steroid hormone expression in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation?
A. High blood GnRH agonist concentration blocks LH activity in the ovaries.
B. Continuous GnRH activation triggers GnRH receptors degradation
C. GnRH agonists inhibit gonadotropin activity.
D. Continuous GnRH agonist administration shrinks the ovaries.
Pulsatile GnRH increases fertility, as it can lead to hormone surges and increase in steroidogenesis. By providing a continuous dose of hormones, you downregulate the amount of receptors that are available to respond to FSH and LH
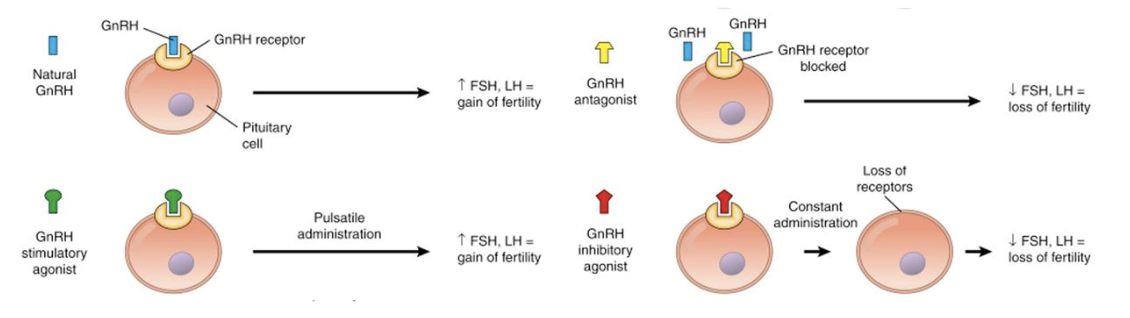
Which of the following drugs are alternative GnRH analogues?
Aberelix
Nafareline
Goserelin
Leuprolide
Degarelix
A. 1 & 5
B. 2 &4
C. 2 & 3
D. 2, 3, & 4
E. All of the above
* These are activators that drive down regulation
Which of the following drugs are alternative GnRH analogues?
Aberelix
Nafareline
Goserelin
Leuprolide
Degarelix
A. 1 & 5
B. 2 &4
C. 2 & 3
D. 2, 3, & 4
E. All of the above
Relix = GnRH antagonists
* These are activators that drive down regulation
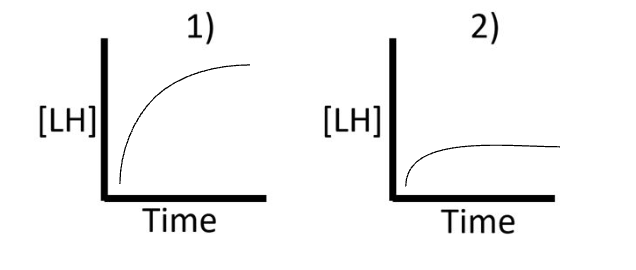
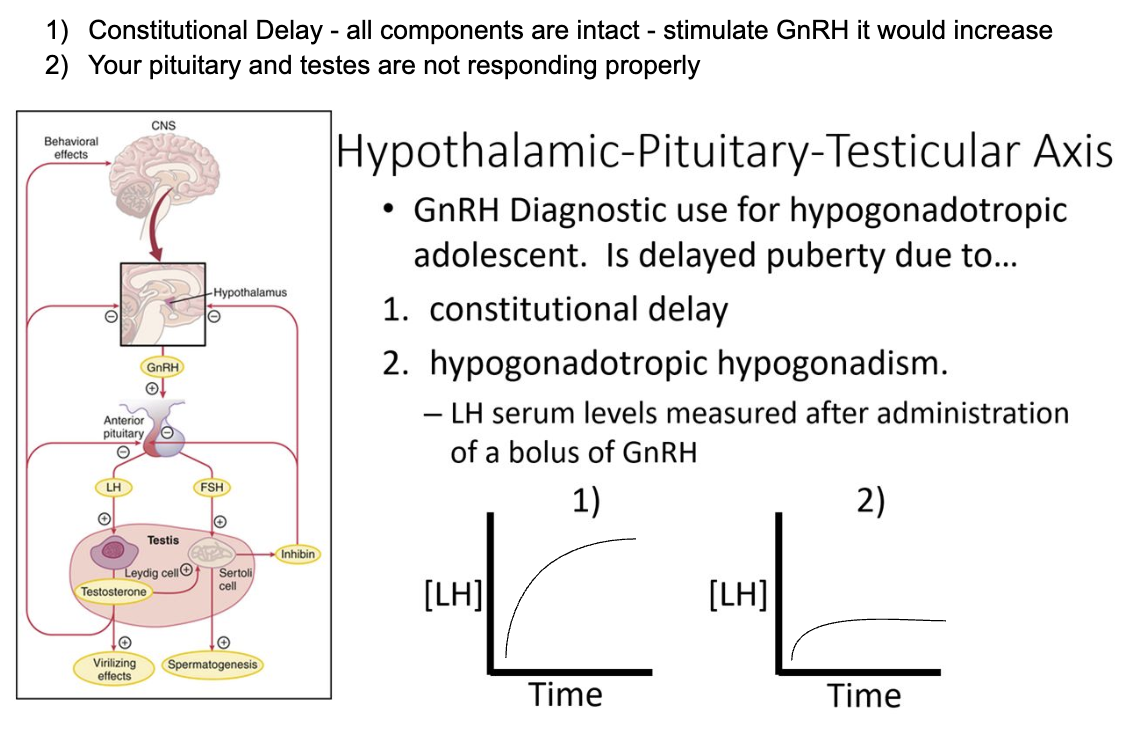
Which graph would be seen in LH serum levels for a constitutional delay in LH?
1) Administration of GnRH would lead to an increase in LH levels if the parts are working
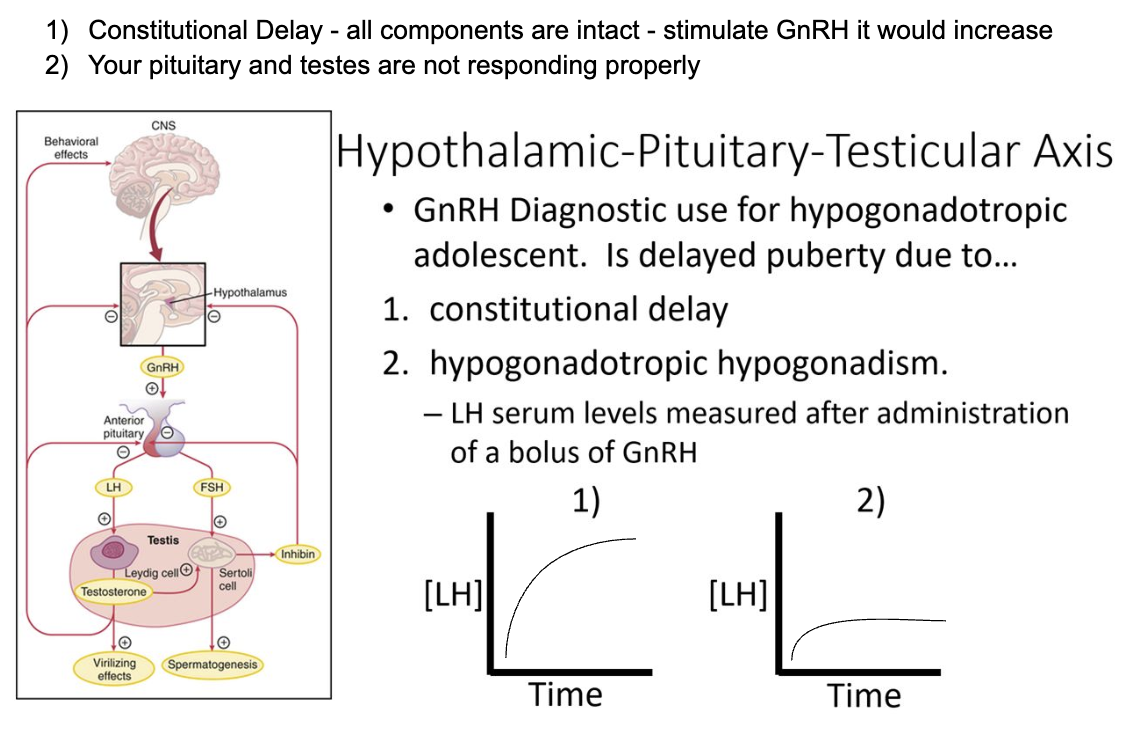
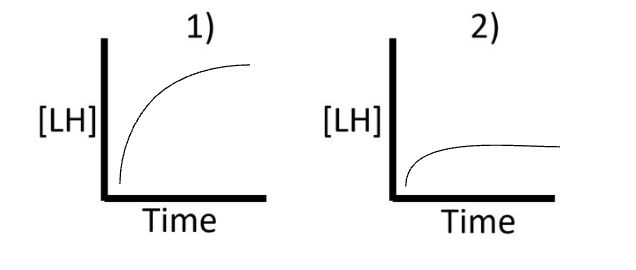
Which graph would be seen in LH serum levels for hypogonadotropic hypogonadism?
2) Administration of GnRH would have minimal effect of LH levels because the parts are not responding properly
Growth hormone antagonists can be used to treat acromegaly, by blocking the GH pathway. Which of the following is NOT a Growth hormone antagonists??
A. Bromocriptine
B. Lanreotide
C. Octreotide
D. Pegvisomant
E. Somatropin
Growth hormone antagonists can be used to treat acromegaly, by blocking the GH pathway. Which of the following is NOT a Growth hormone antagonists??
A. Bromocriptine - D2 agonist
B. Lanreotide - Somatostatin agonist
C. Octreotide - Somatostatin agonist
D. Pegvisomant - Growth hormone antagonist
E. Somatropin - growth hormone analogue
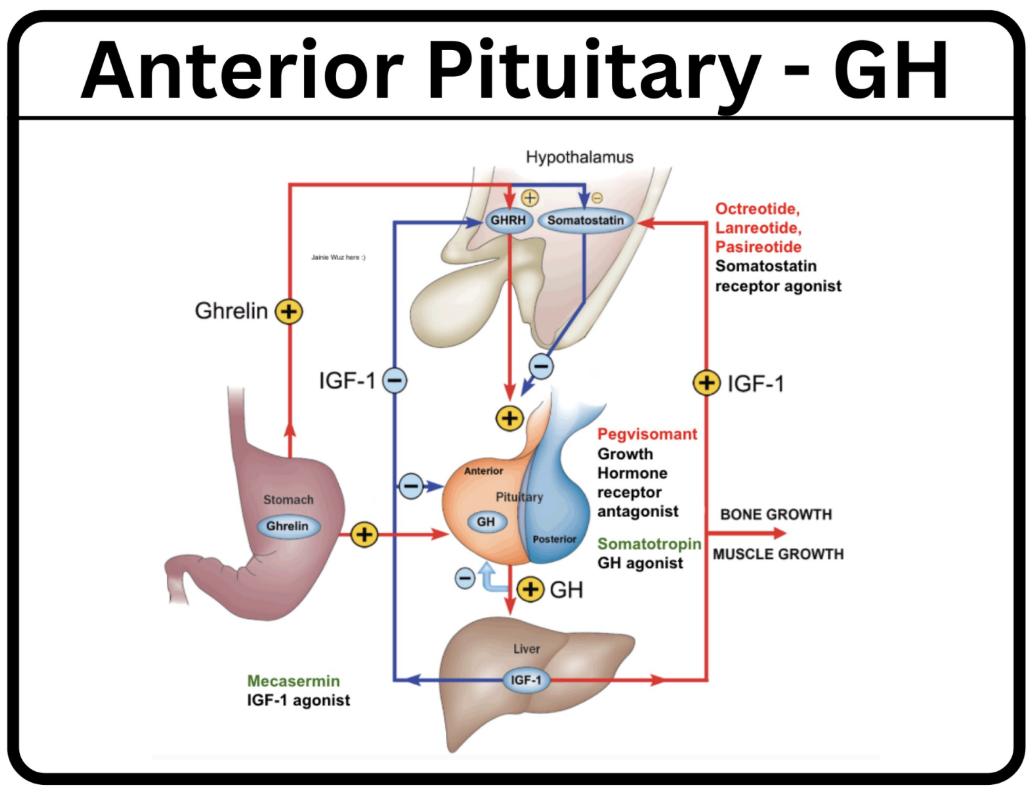
Bromocriptine and Pegvisomant are all antagonists for which endocrine pathway?
A. They suppress ACTH release
B. They suppress growth hormone release
C. They suppress Follicle Stimulating hormone release
D. They suppress thyroid stimulating hormone release
Bromocriptine and Pegvisomant are all antagonists for which endocrine pathway?
A. They suppress ACTH release
B. They suppress growth hormone release
C. They suppress Follicle Stimulating hormone release
D. They suppress thyroid stimulating hormone release
Bromocriptine is a D2 agonist - dopamine can have inhibitory effects on GH
Pegvisomant is a GH receptor antagonist
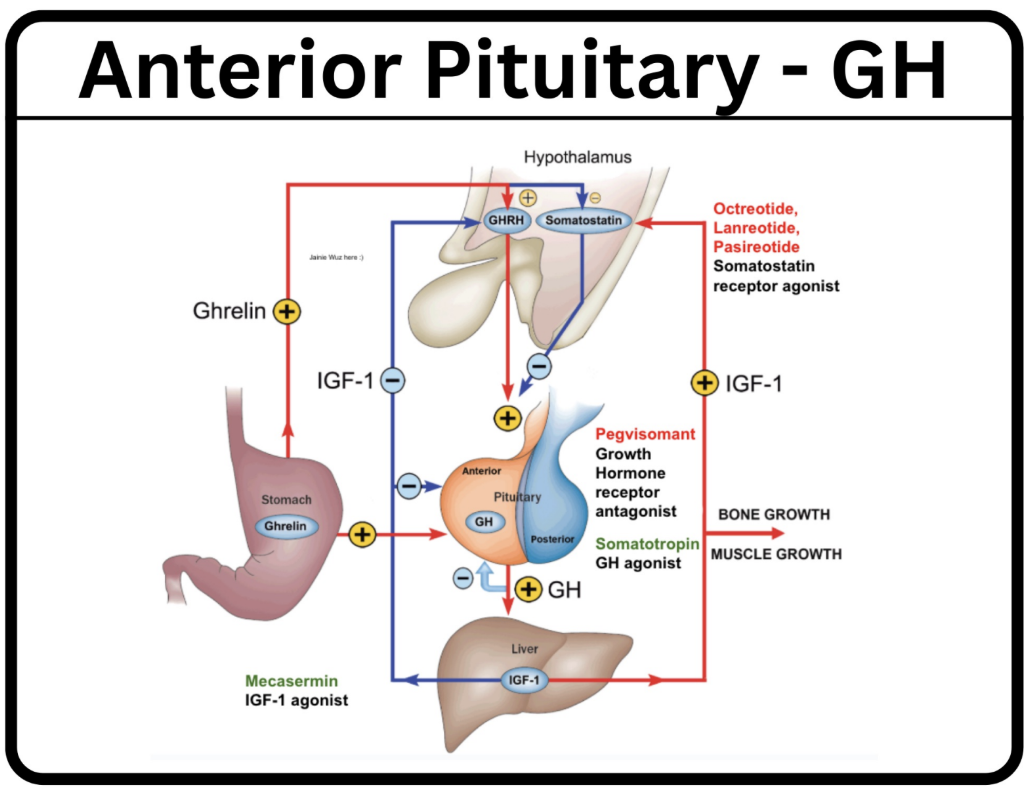
Clinical uses for somatotropin
Somatotropin is a GH agonist
It can be used for disease related to GH deficiency
Genetic Disease associated with short stature
HIV Wasting
Use of mecasermin
treatment for children irresponsible to GH
Clinical use of growth hormone antagonists?
Acromegaly or GH secreting tumors; used for defective IGF-1 negative feedback loop
Therapeutic use of gonadotropins
Fertility, controlled ovarian hyperstimulation
Explain the gonadal axis
Hypothalamus releases GnRH
GnRH stimulates the release of LH and FSH
FSH is used for follicle development → produces estrogen to select the best follicle
LH surge is used for ovulation
Follicle expels the oocyte for implantation and awaits fertilization
Leftover sac is corpeus luteum, which releases progesterone and more estrogens to develop the lining
If no pregnant (hCG), drop in hormones initiates the restarting of the cycle
Examples of LH analogs
Lutropin alfa
Therapeutic use of LH
In combination with follitropin alfa for follicular development
Diagnostic use for distinguishing between retained testis (undescended) from retracted in prepubertal boys
use of hCG
Excreted in the urine and produced by the human placenta
Choriogonadotropin alfa can be used in the final follicular development stage or development
Pulsatile GnRH ____ and Sustained GnRH ____
Pulsatile GnRH stimulates gonadotropin release, and sustained GnRH inhibits FSH and LH release
GnRH analogues:
Gonadorelin, Leuprolide, Goserelin, histerelin, narfarelin, triptorelin
GnRH antagonists:
Ganirelix, Cetrorelix, and Degarelix inhibit FSH and LH secretion by binding to GnRH receptors
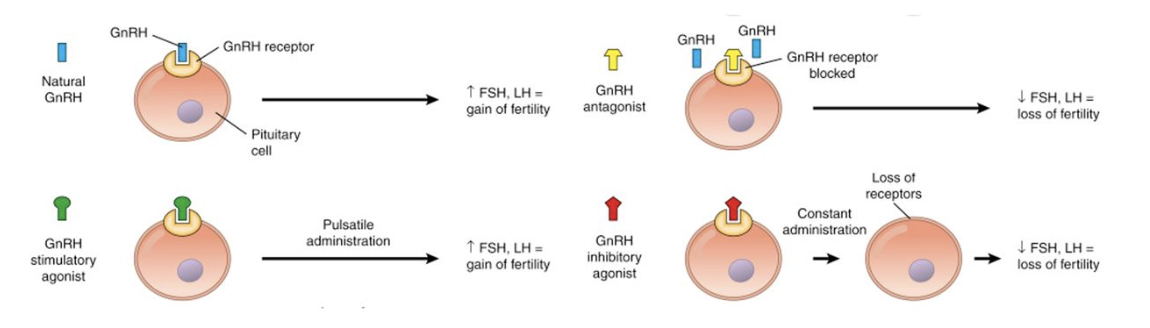
Clinical use of GnRH and analogous:
Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation suppresses the LH surge and increases mature oocyte number
Ovarian suppression in endometriosis; helps reduce fibroid size to reduce progesterone and estrogen production
Prostate cancer in men
Central precocious puberty - GnRH agonists to suppress FSH to delay development of secondary sexual characteristics
How does fertility treatment work?
Via long GnRH agonist protocol, which seeks to use GnRH to suppress the LH surge alongside the use of FSH to help enhance follicle development to create a large amount of oocytes
GnRH antagonist will help block the LH surge to help alongside FSH to enhance oocyte development
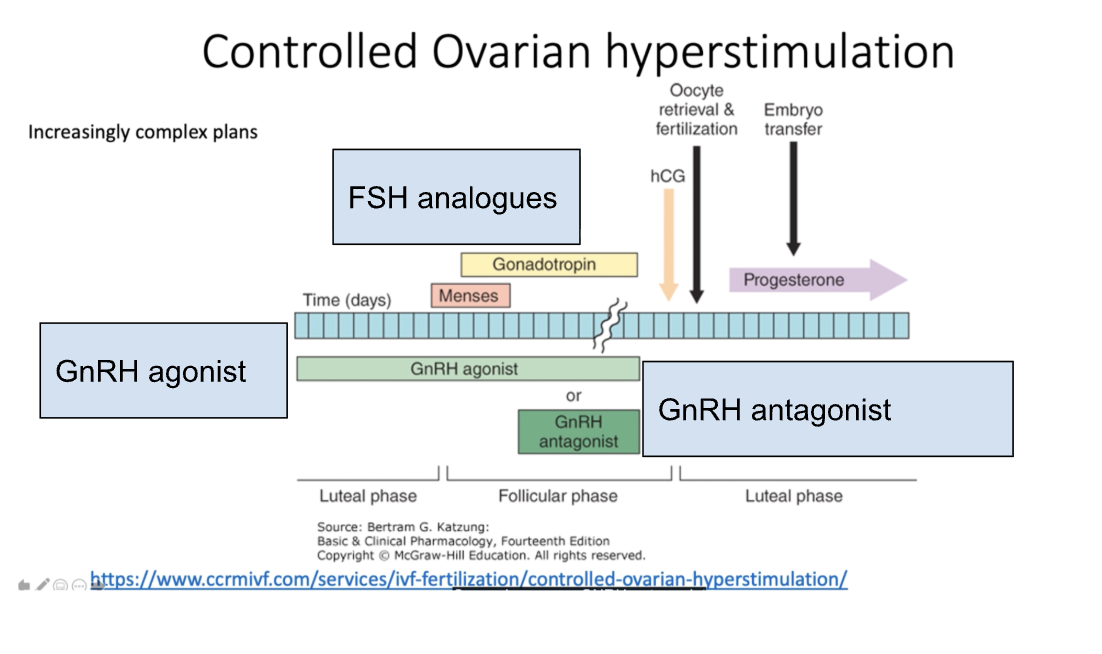
Fill in the respective drugs to the chart
Role of FSH and LH in the testes:
LH stimulates androgen production
FSH stimulates spermatogenesis
Name a Growth hormone (GH)
Somatropin
Somatropin
Recombinant form of GH
Acts through GN receptors to increase IGF-1 production
Somatropin uses
- Replacement in GH deficiency
- increased final adult height in children with certain conditions associated with short stature
- wasting in HIV infection
- short bowel syndrome
Name a IGF-1 agonist
Mecasermin
Mecasermin
Recombinant form of IGF-I that stimulates IGF-I receptors
Mecasermin uses
Replacement in IGF-1 deficiency that is not responsive to exogenous GH
Somatostatin analogs
- Octreotide
- Lanreotide
Octreotide
Agonist at somatostatin receptors
Octreotide uses
- Acromegaly and several other hormone-secreting tumors
- acute control of bleeding from esophageal varices
Lanreotide
Somatostatin analog similar to octreotide; available as a long-acting formulation for acromegaly
Growth hormone receptor antagonist
Pegvisomant
Pegvisomant
Blocks GH receptors
Pegvisomant uses
Acromegaly
Gonadotropins: Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) analogs
- Follitropin alpha
- Follitropin beta
- Urofollitropin
- Menotropins (hMG)
Follitropin alpha
Activates FSH receptors
Follitropin alpha uses
- Controlled ovulation hyperstimulation in women
- infertility due to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in men
Follitropin beta
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) analog recombinant product with the same peptide sequence as follitropin alpha but differs in its carbohydrate side chains
Urofollitropin
FSH analog, human FSH purified from the urine of postmenopausal women
Menotropins (hMG)
FSH analog, extract of the urine of postmenopausal women; contains both FSH and LH activity
Gonadotropins: Luteinizing hormone (LH) analogs
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Choriogonadotropin alfa
- Lutropin
- Menotropins (hMG)
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Agonist at LH receptors
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) uses
- Initiation of final oocyte maturation and ovulation during controlled ovarian stimulation
- male hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Choriogonadotropin alfa
LH analog recombinant form of hCG
Lutropin
LH analog recombinant form of human LH
Menotropins (hMG)
LH analog extract of the urine of postmenopausal women; contains both FSH and LH activity
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs
-Leuprolide
- Gonadorelin
- goserelin
- buserelin
- histrelin
- nafarelin
- triptorelin
goserelin
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs
buserelin
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs
histrelin
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs
nafarelin
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs
triptorelin
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs
Leuprolide
Agonist at GnRH receptors
Leuprolide uses
- Ovarian suppression
- controlled ovarian stimulation
- central precocious puberty
- block of endogenous puberty in some transgender early pubertal adolescents
- advanced prostate cancer
Gonadorelin
synthetic human GnRH