BY-124L Kingdom Animalia II
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Phylum Echinodermata
- Echinoderms
- water vascular system used for feeding, locomotion, respiration, and sensory perception
- Tube feet – small appendages along canal
- some can regenerate
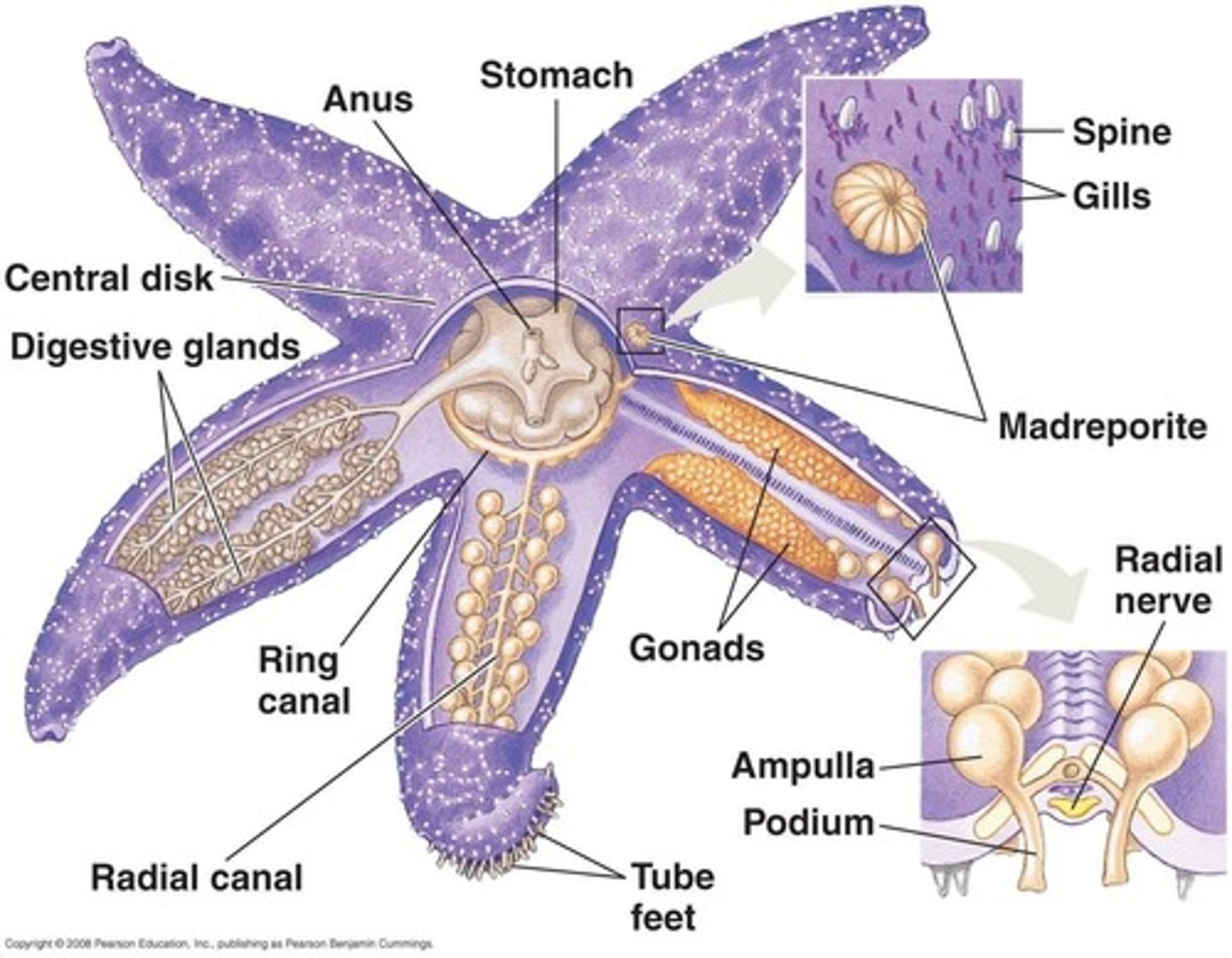
Phylum Echinodermata Organization
- Tube in Tube body plan
- bilateral symmetry
- organ level organization
- deuterostome
- coelomate
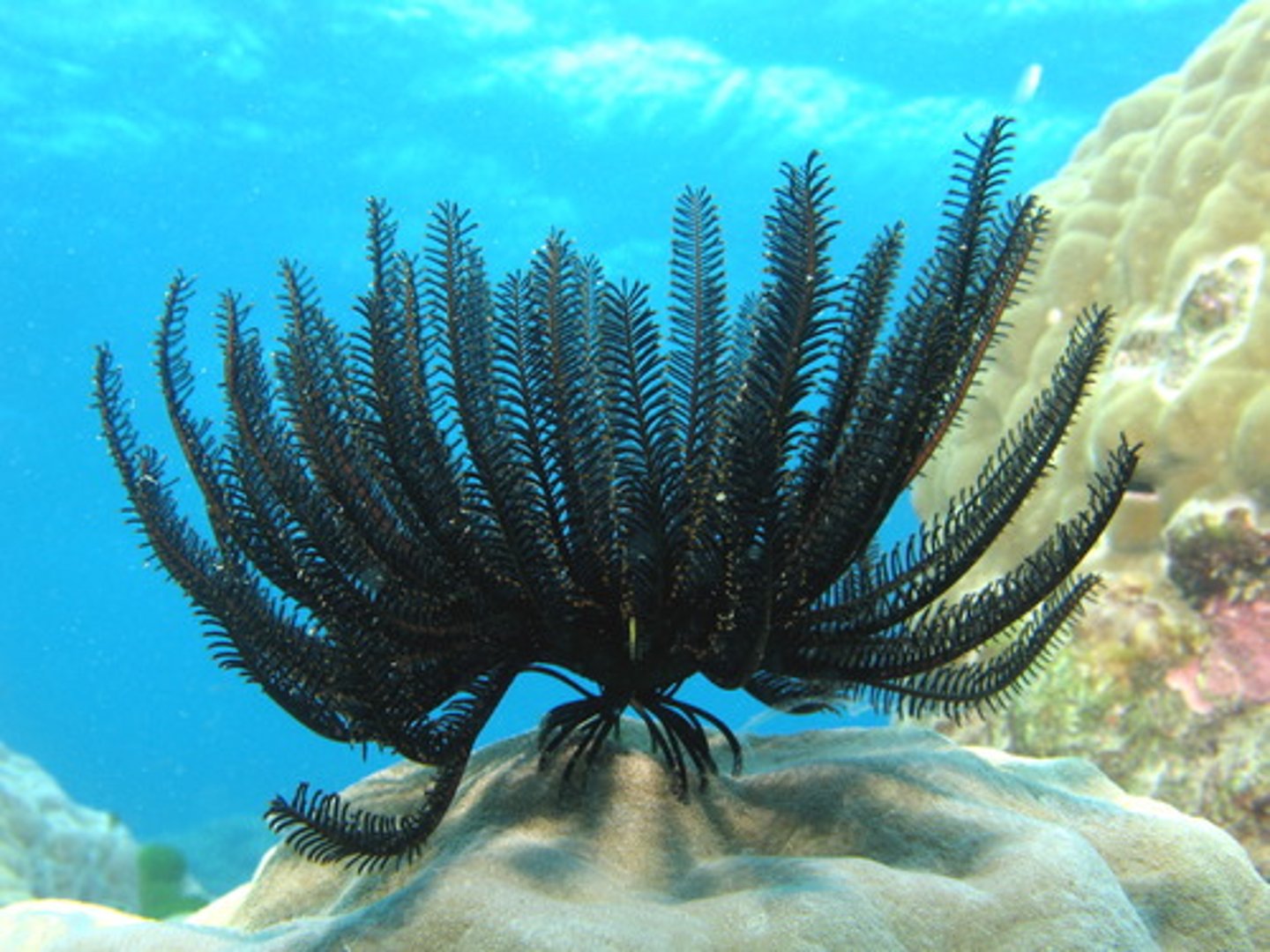
Phylum Echinodermata - Class Crinoidea
- feather stars and sea lilies
- oldest and most primitive echinoderms
- mouthparts UPWARDS

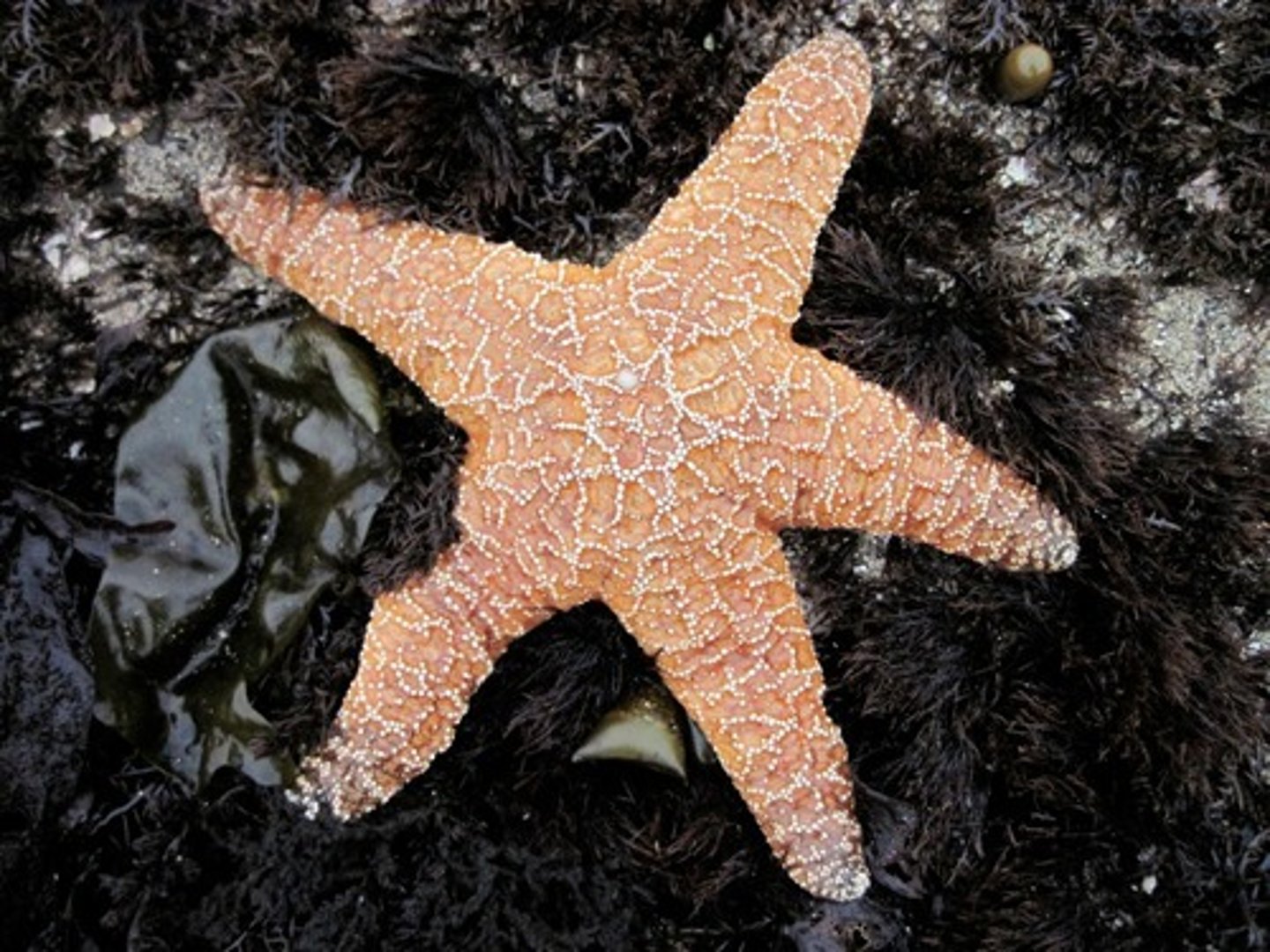
Phylum Echinodermata - Class Asteroidea
- sea stars
- suckers on tube feet
- mouth pointed DOWNWARDS
- capable of regeneration

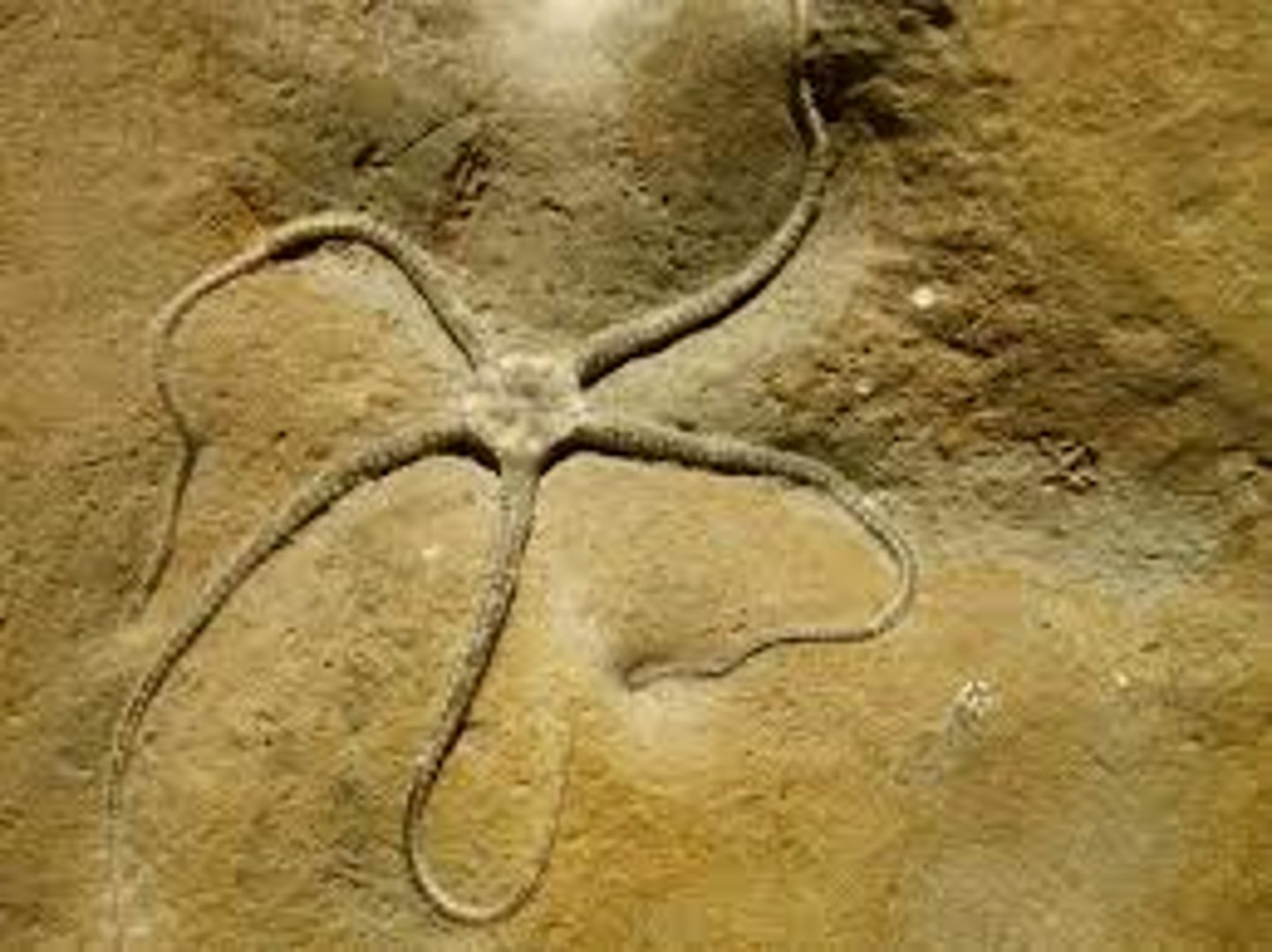
Phylum Echinodermata - Class Ophiuroidea
- Brittle Stars
- slender armed sea stars

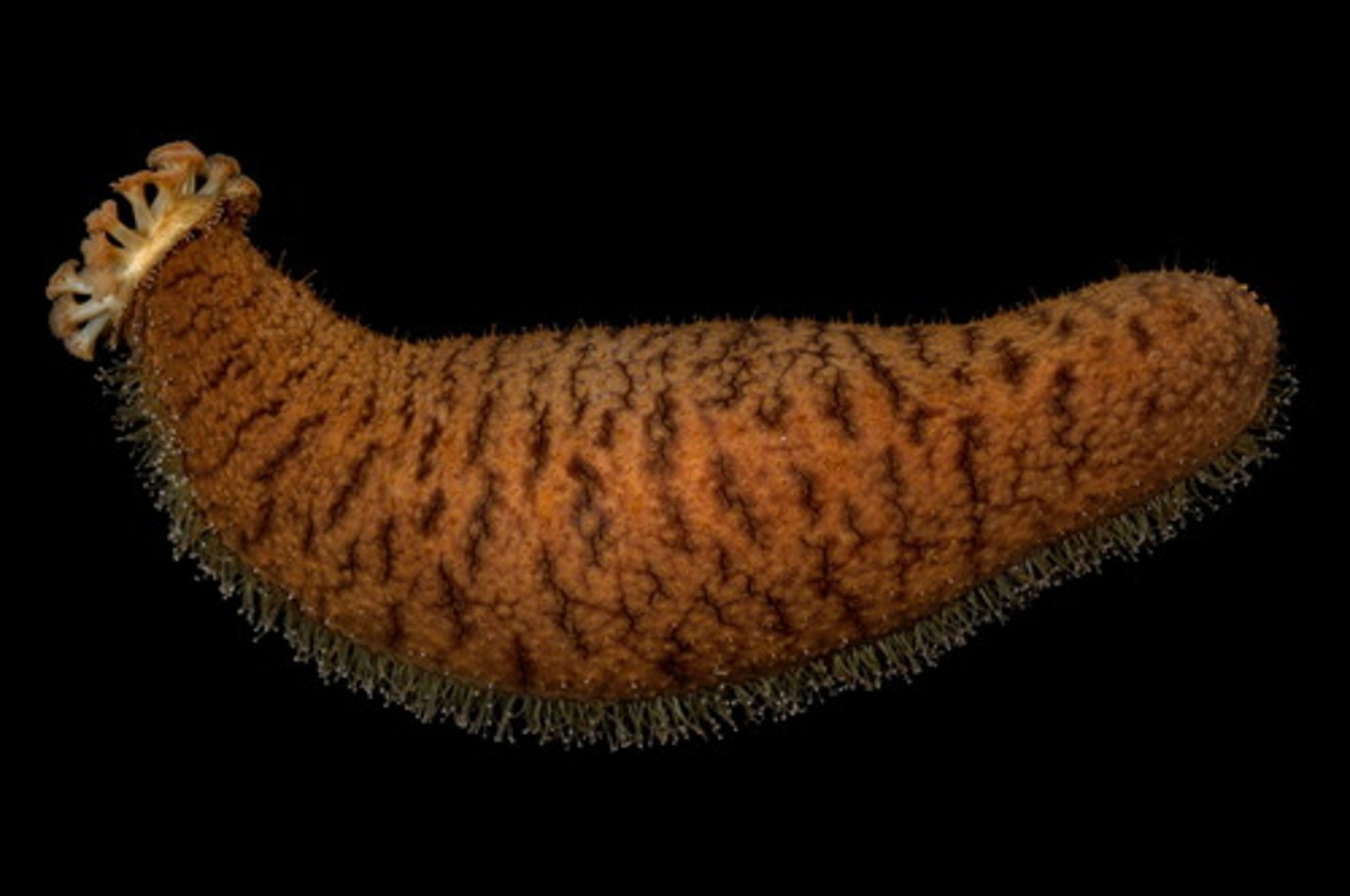
Phylum Echinodermata - Class Holothuroidea
- Sea Cucumbers
- Defense mechanisms include evisceration(throws up guts)

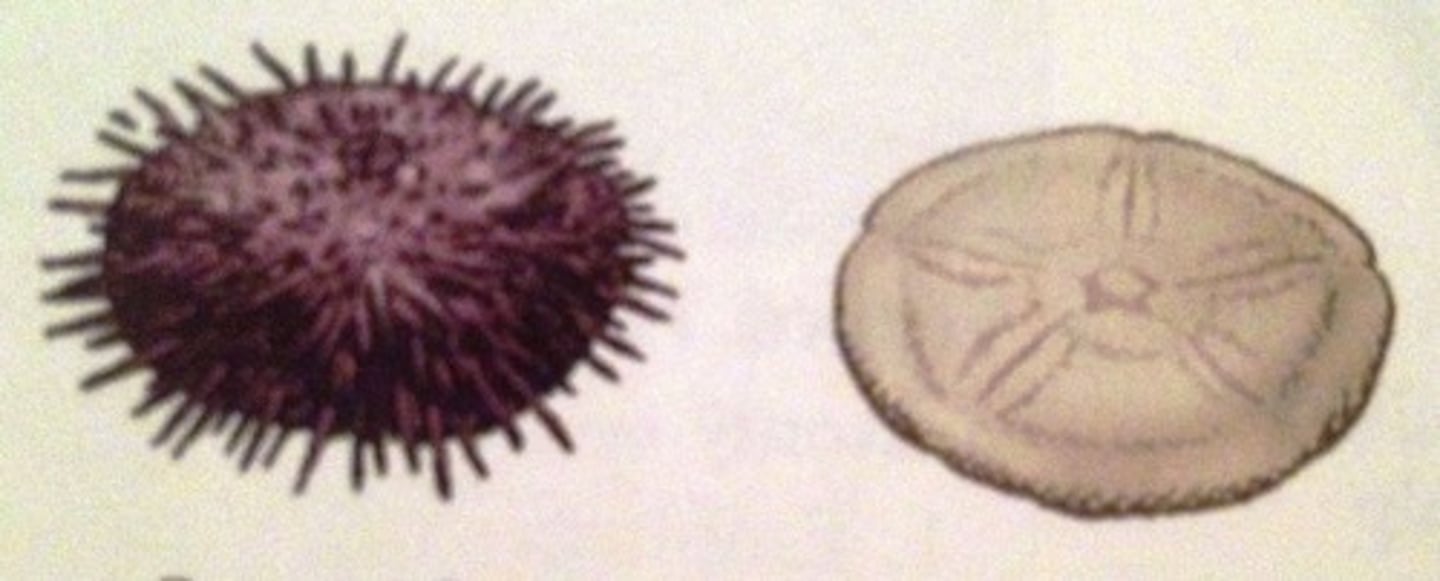
Phylum Echinodermata - Class Echinoidea
- Sea Urchins and Sand Dollars
- Regular echinoids (urchins) have plates of same size and shape
- Irregular echinoids (sand dollars)have plates of different sizes and shapes

Phylum Hemichordata
- Acorn worms
- have 2/4 chordate characteristics
--- gills / pharyngeal gill slits
--- dorsal nerve cord
Phylum Hemichordata Organization
- tube in tube body plan
- bilateral symmetry
- organ level organization
- deuterostome
- coelomate
Phylum Chordata
- Chordates
- 4 characteristics:
-- Pharyngeal gill slits
-- Notochord
-- Muscular, post-anal tail
-- Dorsal, hollow nerve chord
Phylum Chordata Organization
- tube in tube body plan
- Bilateral Symmetry
- Organ-level organization
- Deuterostome
- Coelomate
- Segmented
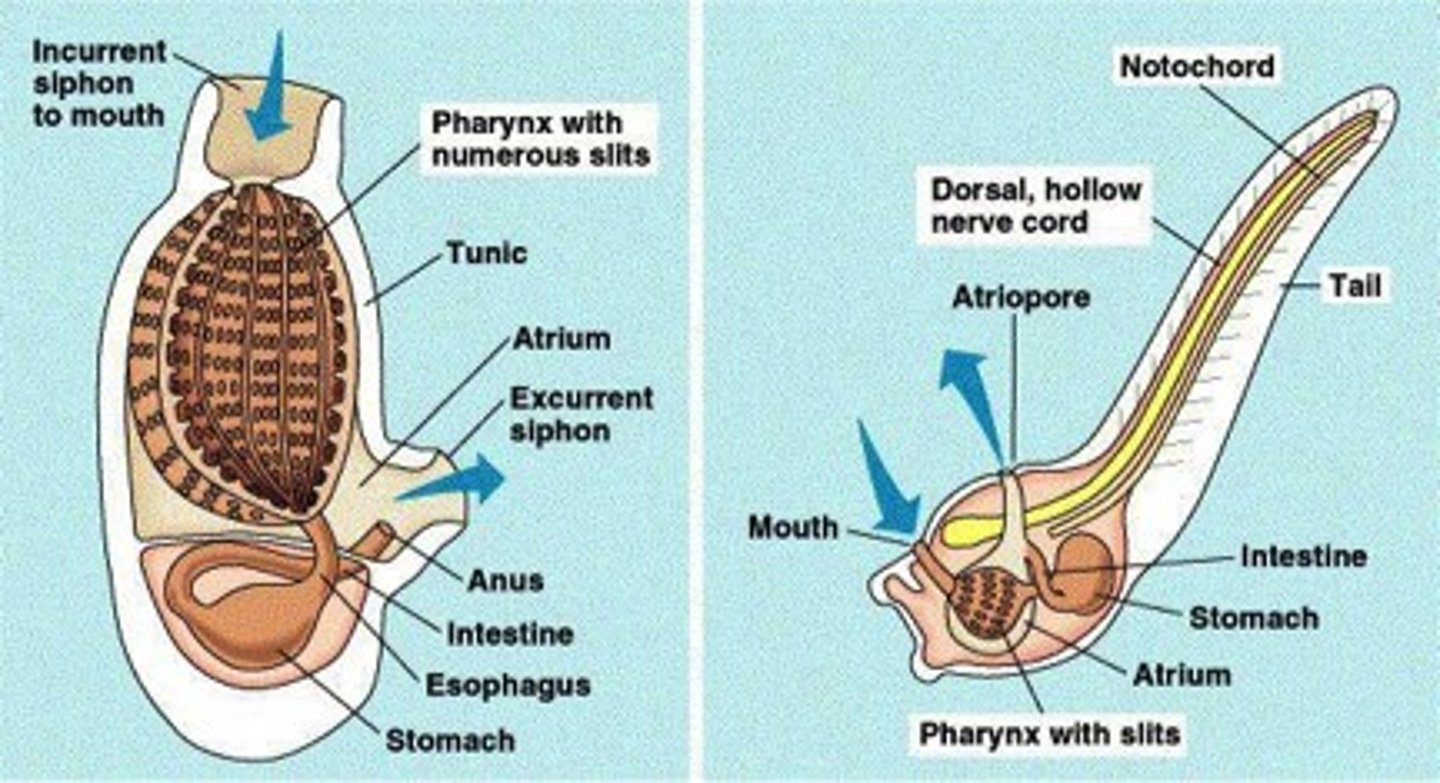
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Urochordata
- Tunicates and Sea Squirts
- adults are sessile
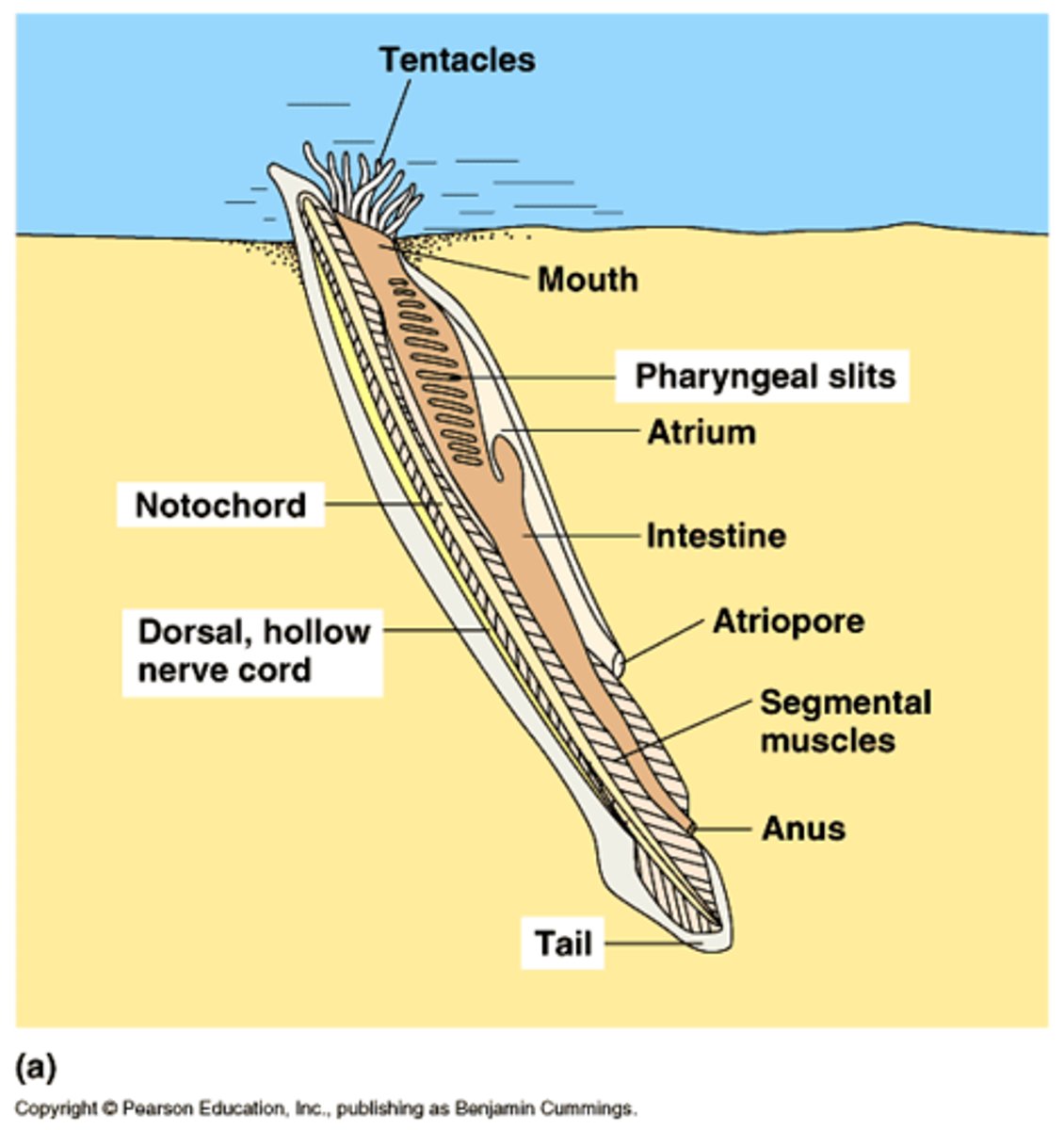
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Cephalochordata
- Lancelets
- “Cephalo” = head
- all 4 chordate characteristics are present in adult
- Segmentation
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata
- vertebrates
- "Cranium" = brain box (cranium around brain)
- Backbone replaces the notochord during development

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Grouping Pisces - Class Myxini
- Hagfish
- Jawless fish
- Cartilaginous skeleton
- 2-chambered heart
- defense mechanism is to produce slime and tie body into a knot

Grouping Pisces - Class Cephalospidomorphi / Hyperoartia
- Lampreys
- jawless fish
- parasitic on fish
- cartilaginous skeleton
- 2 chambered heart
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes
- Gnathostomes = jaw-mouth
- JAWED FISHES – developed hinged jaws
- Have lateral line down body – used to detect vibrations in water
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - Class Placodermi
- Armored Fish
- All are extinct
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - Class Chondrichthyes
- Cartilaginous Fish – Sharks, Skates, Rays, Chimaeras
- Possess cloaca – common opening for urinary, digestive, and reproductive systems
- Internal fertilization:
-- Oviparous – eggs hatch OUTSIDE body
-- Ovoviviparous – has eggs but they hatch INSIDE body (“fake live birth”)
-- Viviparous – has physical connection to parent (REAL live birth)
- "Ovi” = egg; “Viv” = Live
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - Class Osteichthyes
- Bony Fish
- Skeleton contains calcium– phosphate
- Possess an operculum gill covering
- 2-chambered heart
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - Class Osteichthyes - Subclass Sarcopterygii
- Fleshy-finned fish (lobe-finned fish)
- Lungfish
- Tiktaalik - "amphibian-like" fish:
--- primitive lungs & ribs for breathing
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - Class Osteichthyes - Subclass Actinopterygii
- Ray-finned fish
- Most common fish like goldfish, bass, catfish, trout, moray eel, sea horse
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Amphibia
- Amphibians
- 3-chambered heart
- ectothermic
- 4 limbs
- lungs
- water for reproduction
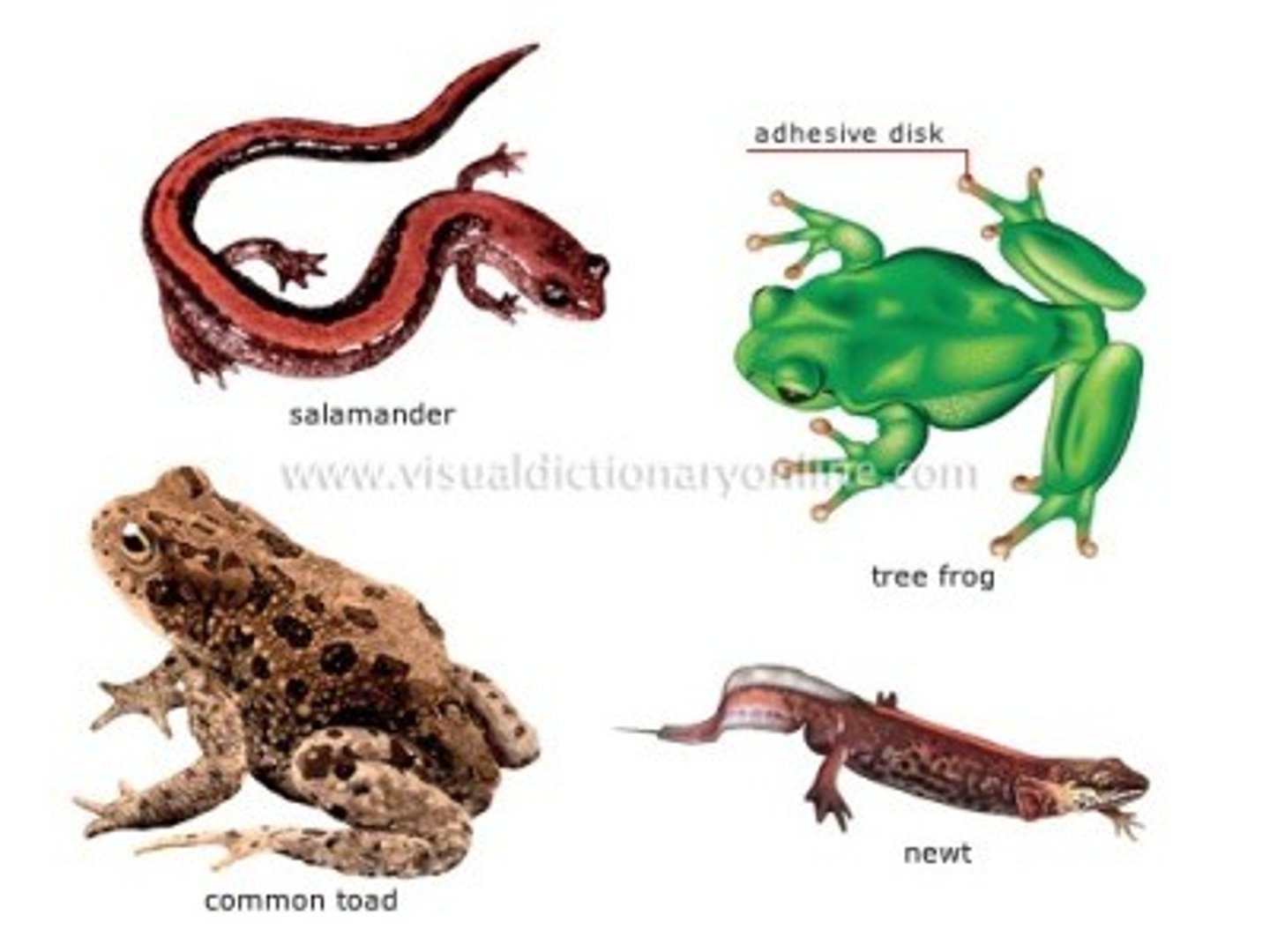
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Amphibia - Order Anura
- Frogs and Toads (Anura = no tail)
- Undergo metamorphosis --> little to no neoteny
- frogs: smooth, moist skin
- toads: more adapted for drier environments with bumpy, dry skin

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Amphibia - Order Urodela
- Salamanders and Newts
- Neoteny is the retention of juvenile characteristics as an adult

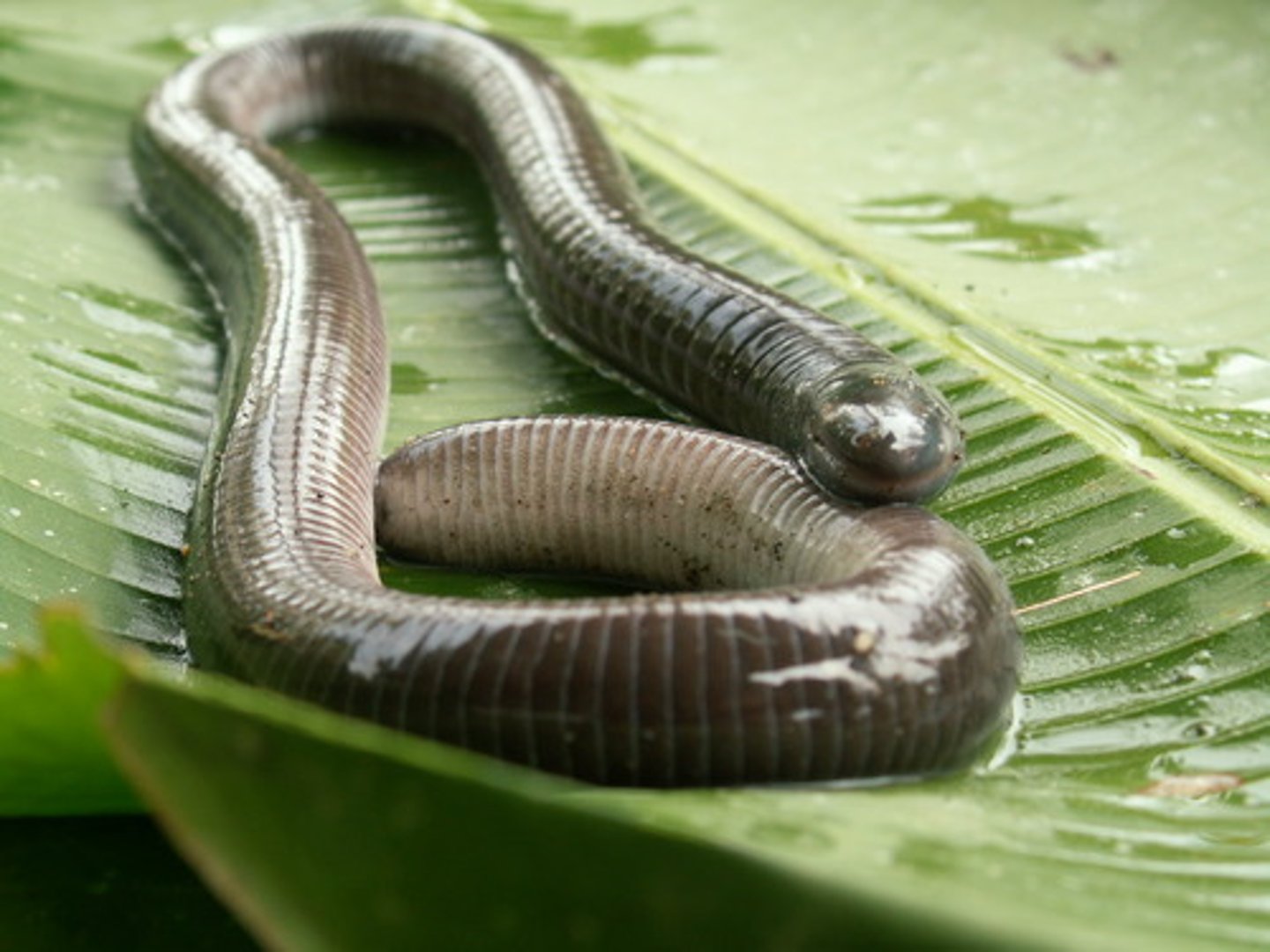
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Amphibia - Order Apoda
- Caecilians (apoda = no leg)
- Legless amphibians that look like giant worms

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Reptilia
- Reptiles
- Ectothermic
- 3 chambered heart
- Adaptations for land made by reptiles: amniotic egg
--- Amnion – protects the embryo from desiccation
--- Allantois – acts in waste removal
--- Chorion – acts in gas exchange
--- Yolk sac – provides food to the embryo
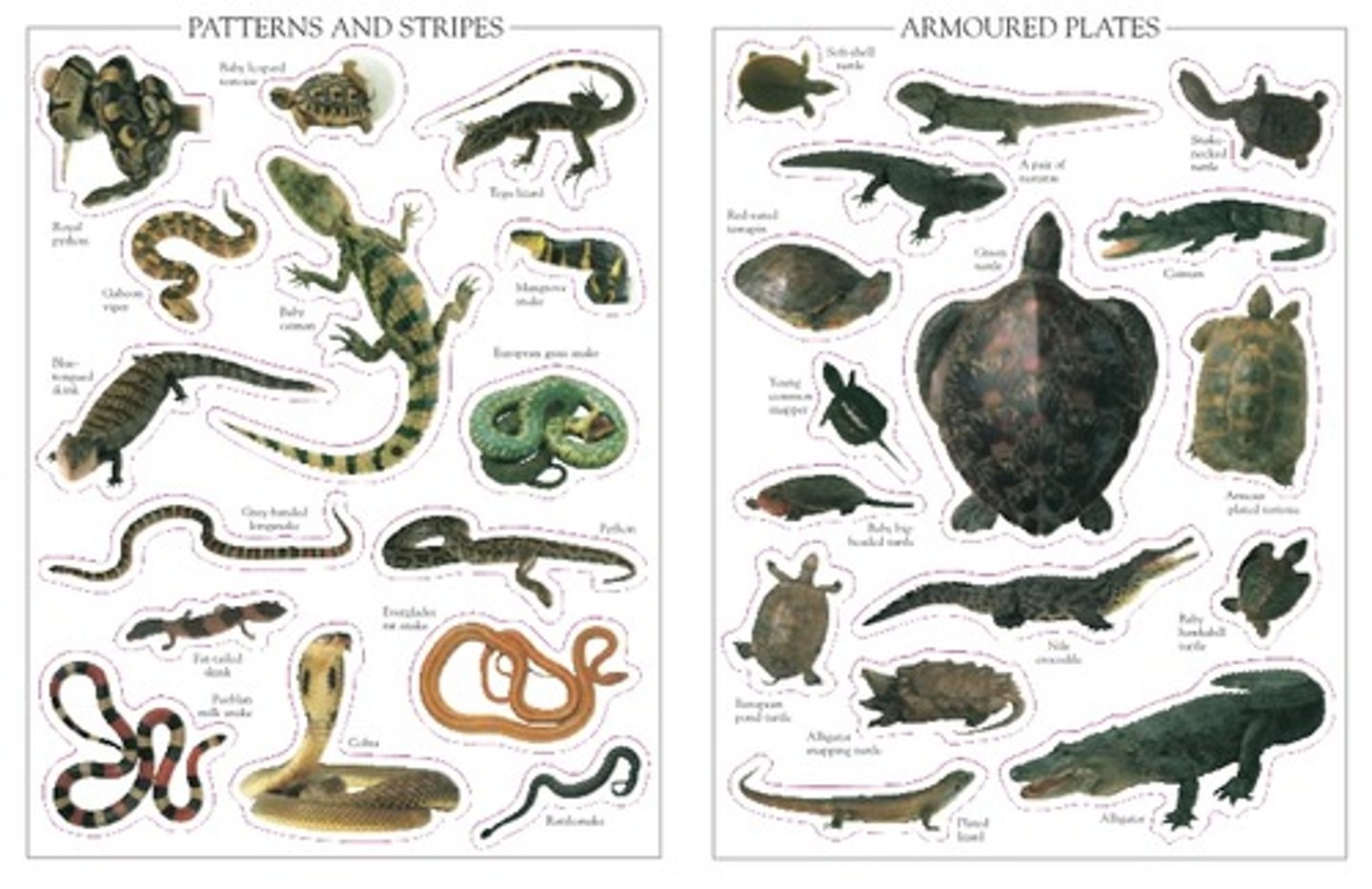

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Order Chelonia
- Turtles and Tortoises
- Turtles can be aquatic
- Tortoises are strictly terrestrial
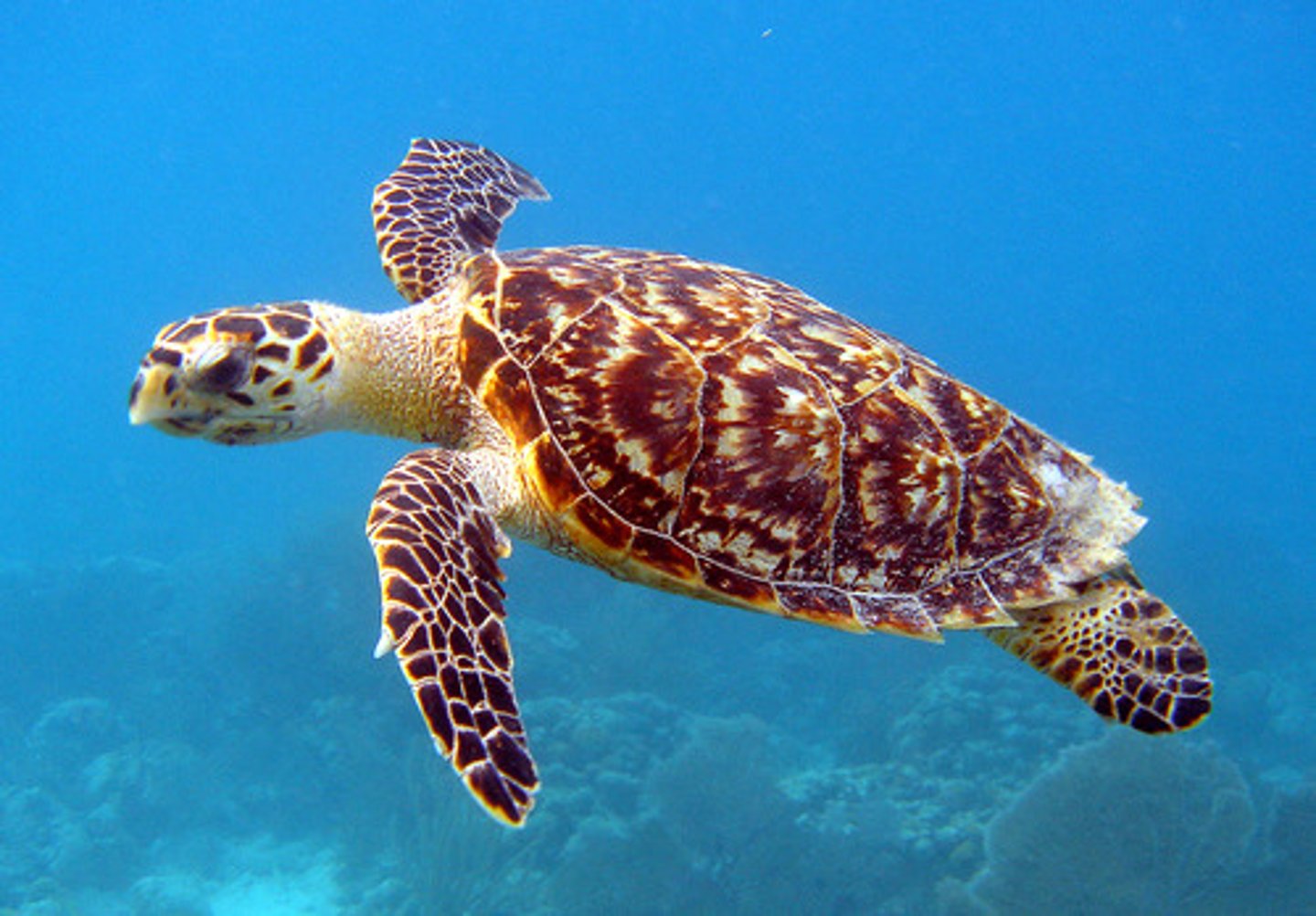

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Reptilia - Order Rhychocephalia
- Tuatara
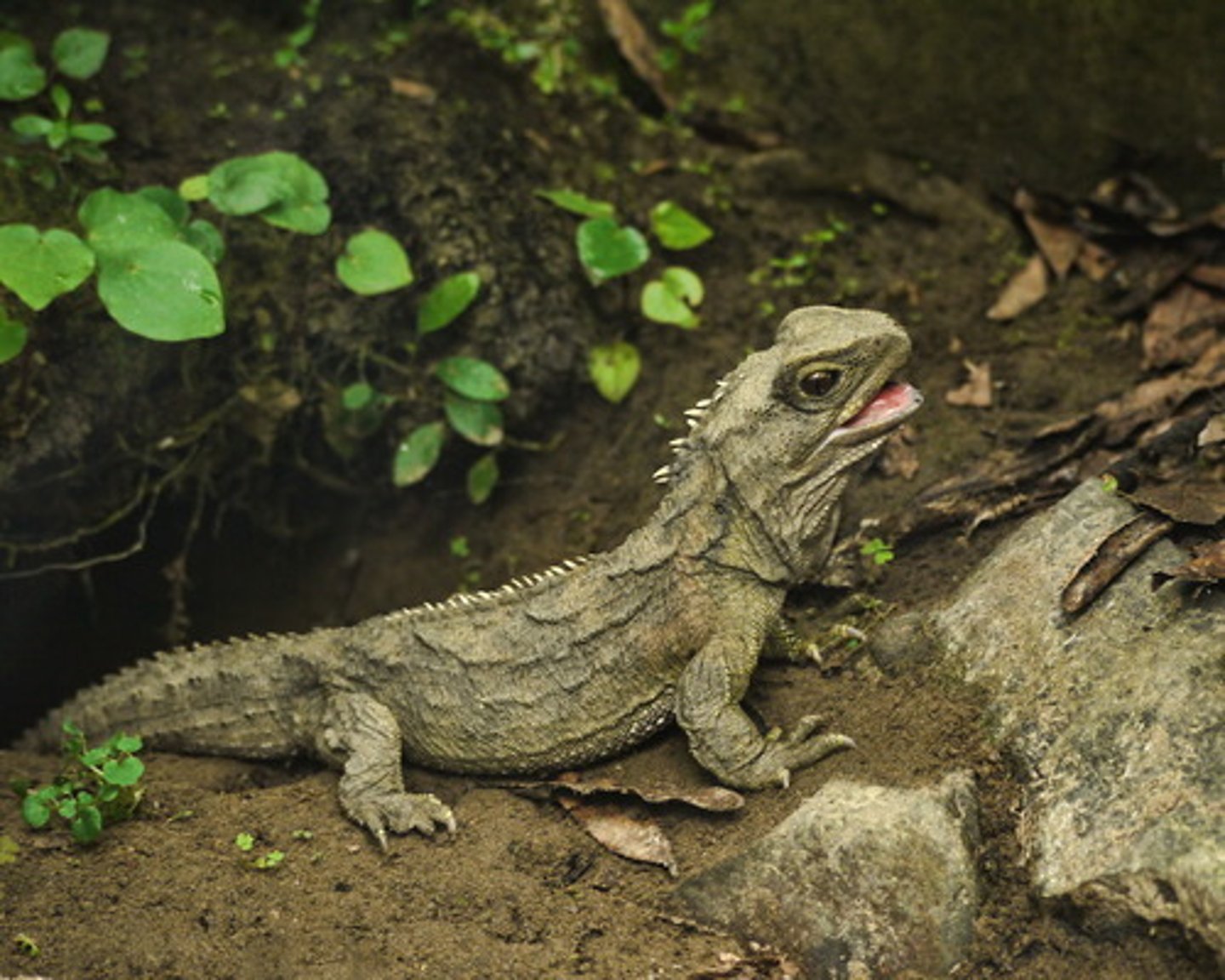

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Reptilia - Order Squamata
- Lizards and Snakes
- Snakes are highly adapted lizards that lost their legs
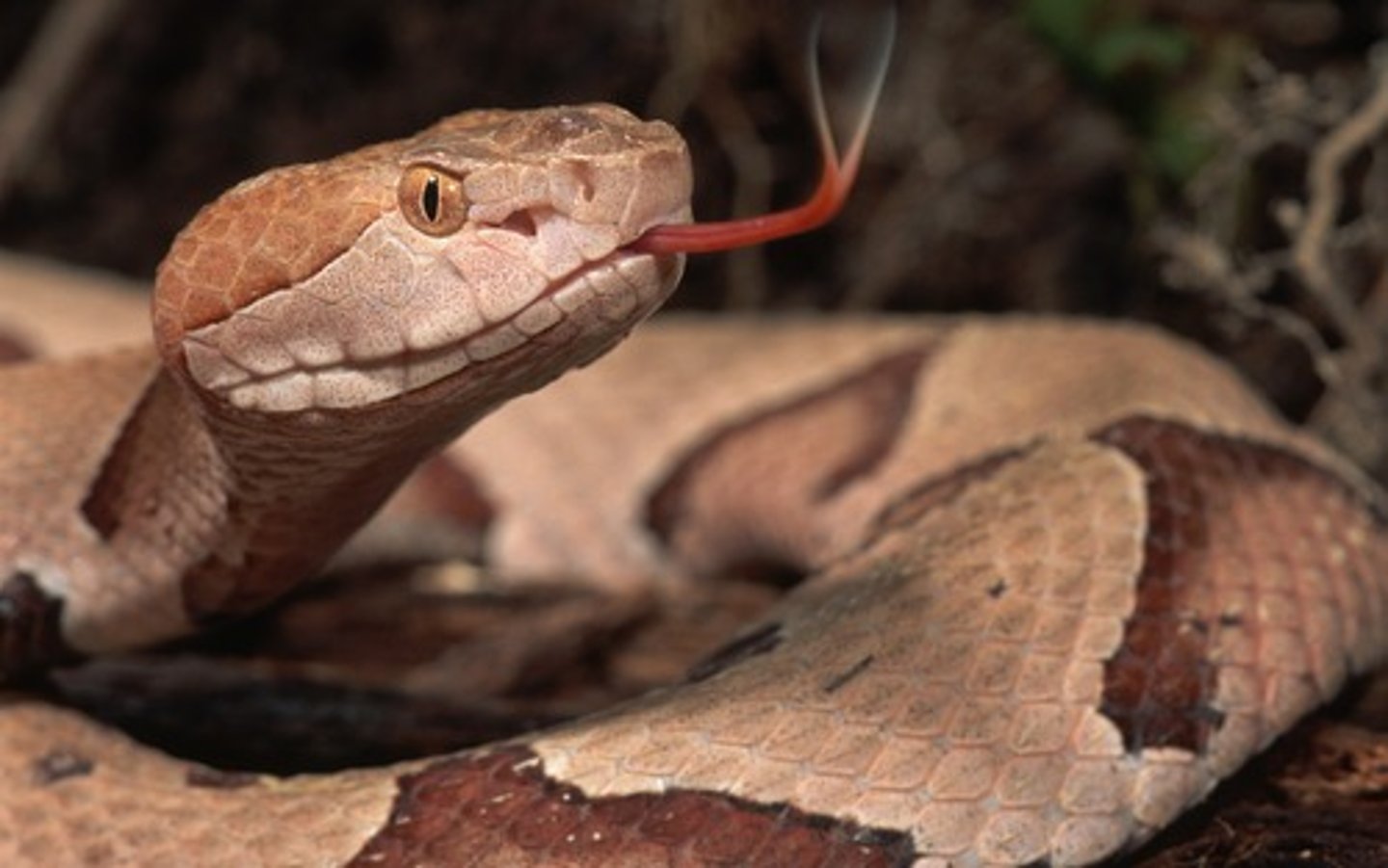

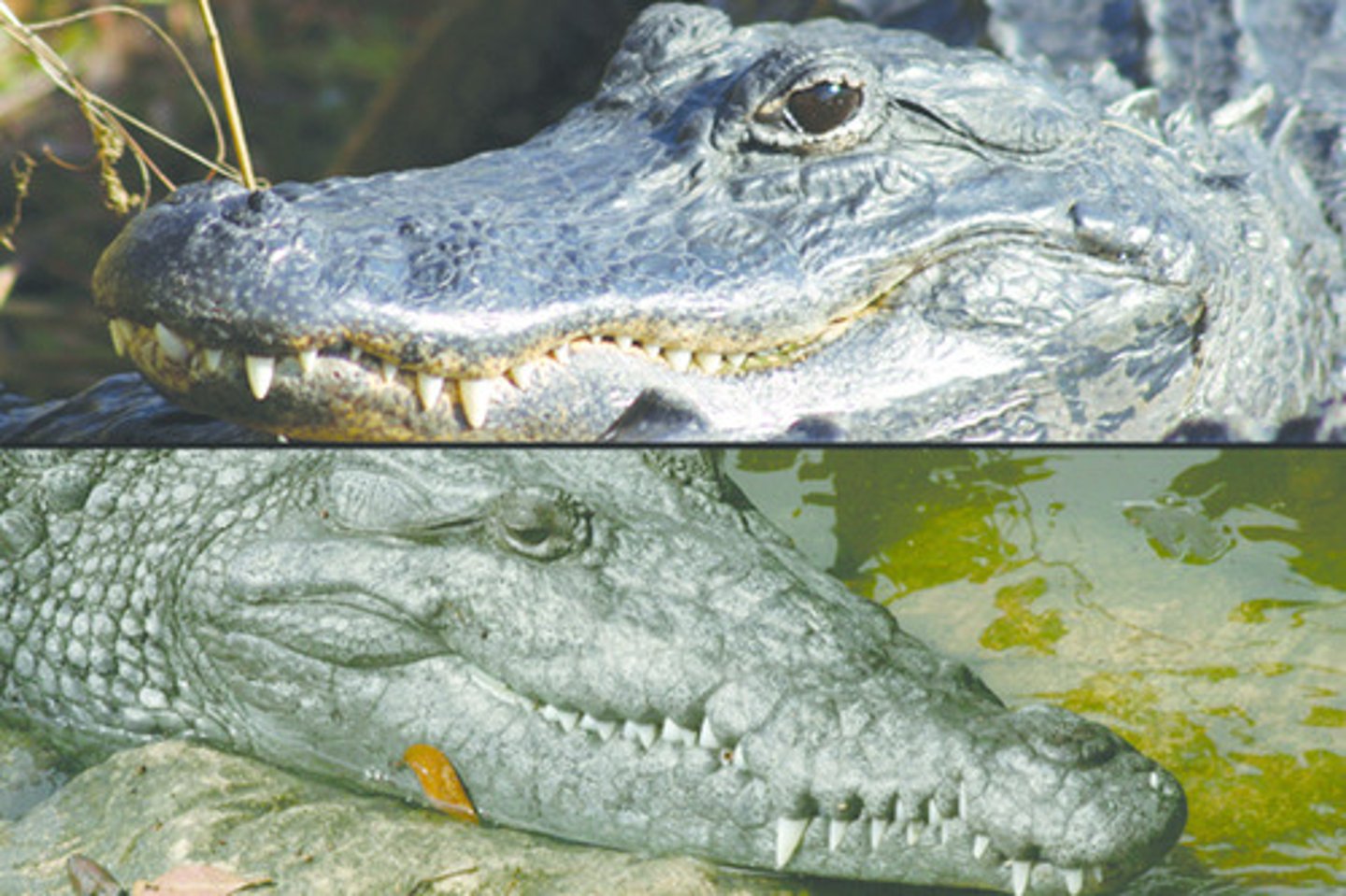
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Reptilia - Order Crocodilia
- Crocodiles, Alligators, Caimans and Gharials
- Crocodiles have a 4-chambered heart
- First signs of parental care

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Aves
- Birds
- 4 chambered heart
- Air sacs in lungs for better gas exchange
- Endothermic – able to maintain a constant bodytemperature due to heat from metabolism

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Mammalia
- Mammals
- 4-chambered heart
- Endothermic
- 3 bones of the middle ear: Malleus, incus, stapes
- Hair made from keratin
- Mammary glands, sweat glands (nipples)

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Mammalia - Order Monotremata
- Platypus and echidnas
- Primitive egg-laying mammals

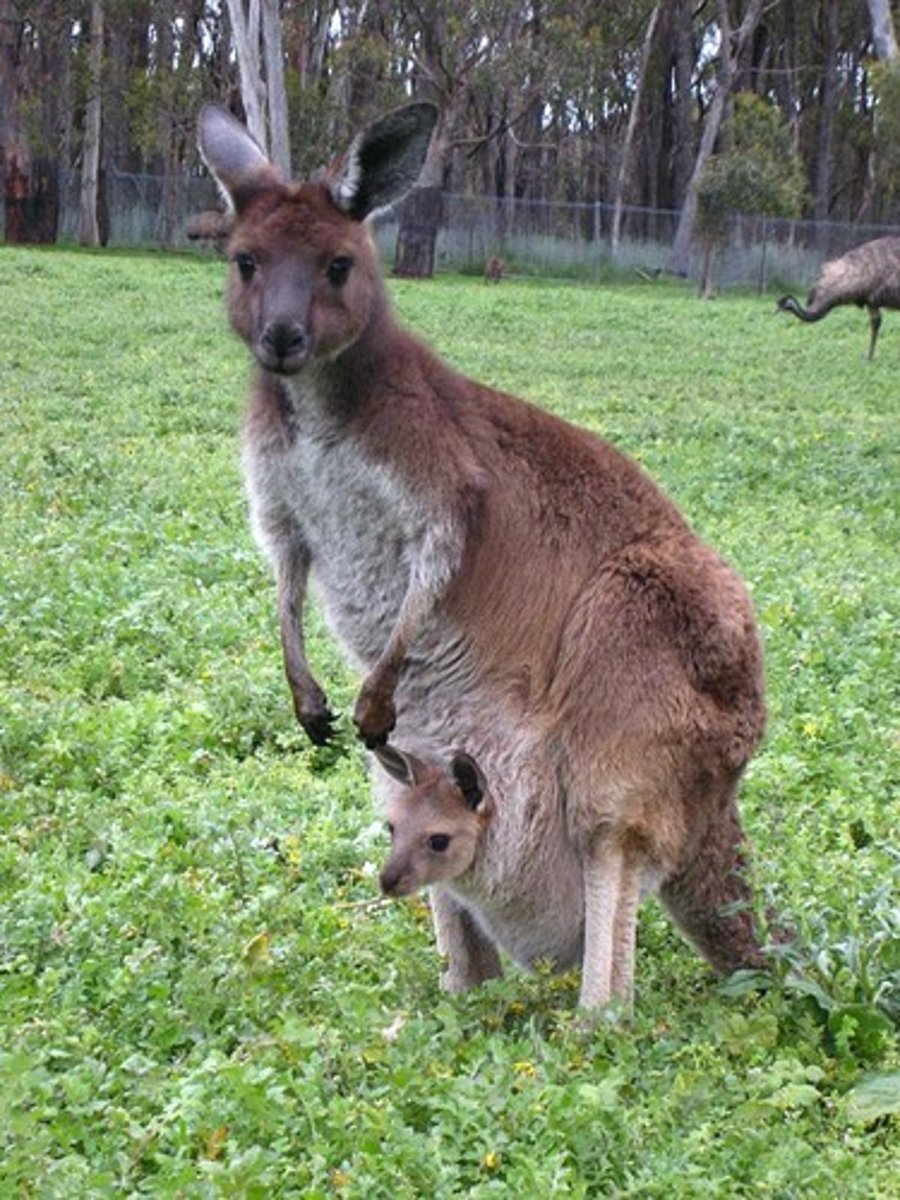
Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Mammalia - Order Marsupialia
- Kangaroos, opossums
- Give birth, but embryo is immature so it must complete development in the pouch

Phylum Chordata - Subphylum Craniata - Gnathostomes - (Grouping Tetrapoda) - Class Mammalia - Grouping Placentals
- Advanced mammals, mother nourishes embryo via the placenta
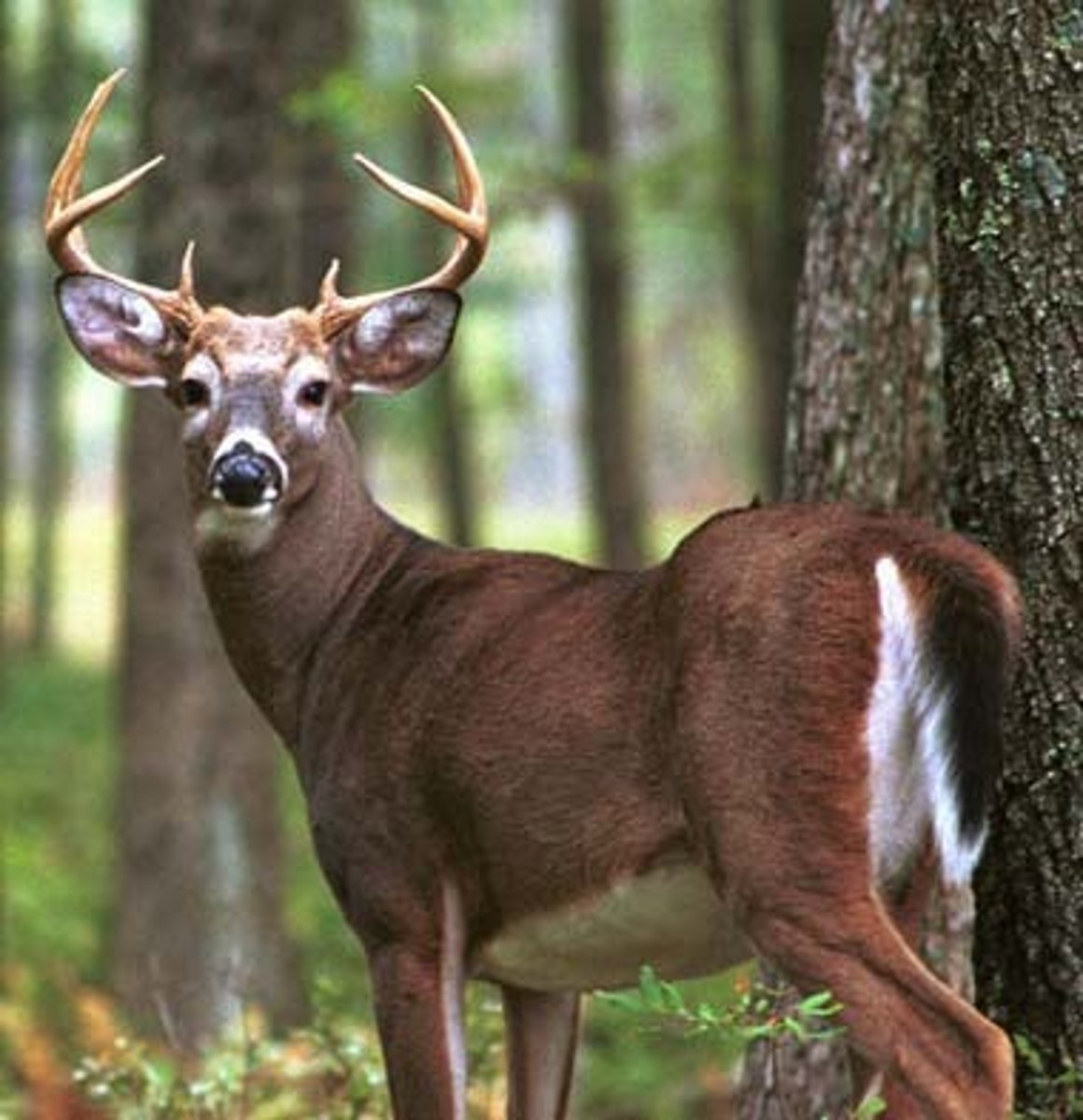

Grouping Placentals - Order Artiodactyla
- Even-toed ungulates - sheep, cattle, pigs, deer
Grouping Placentals - Order Perissodactyla
- Odd-toed ungulates - Horses, zebras, rhinos
Grouping Placentals - Order Carnivora
- Cats, dogs, bears, wolves
Grouping Placentals - Order Cetacea
- Whales, dolphins
Grouping Placentals - Order Chiroptera
- bats
Grouping Placentals - Order Xenarthra
- sloths, armadillos, anteaters
Grouping Placentals - Order Eulipotyphla
- Moles and shrews
Grouping Placentals - Order Lagomorpha
- rabbits and hares
Grouping Placentals - Order Primates
- Monkeys, lemurs, apes, humans
Grouping Placentals - Order Proboscidea
- elephants
Grouping Placentals - Order Rodentia
- Beavers, squirrels, and porcupines
Grouping Placentals - Order Sirenia
- Manatees