Redox
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Give the formulas for hdrochloric,sulfuric,nitric and ethanoic acid
HCL
H2SO4
HNO3ds
CH3COOH
What element do all acids contain?
Hydrogen
What happens when you dissolve an acid in water?
It releases hydrogen as an H+ ion
H+ Ion is simply a proton
What happens when an acid molecule disassociates (splits)?
Releases H+ ion
Releases a negative ion
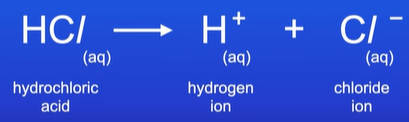
Define a strong acid and give examples?
Acid that completely ionises(splits) in aqueous solution
Every acid molecule donates a H+ ion to water
E.g. HCL, H2SO4,HNO3
Why is ethanoic acid a weak acid?
Only partially dissociates
Only a small percentage of the acid molecules dissociate
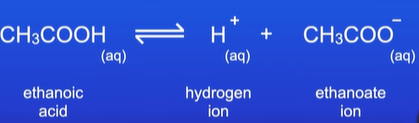
Why does ethanoic acid partially disassociate?
O-H bond is not easily broken as it is less polarized
CH3OOCH dissolving in water is reversible reaction, so some H+ ions recombine with CH3OOC- to reform CH3COOH
What makes a chemical a base?
A base can neutralise an acid to produce a salt
4 examples of bases
Metal oxide
Metal hydroxide
Metal carbonate
Ammonia
What products are forms when a metal carbonate reacts with an acid
salt
water
carbon dioxide
What is an alkali?
Base that dissolves in water
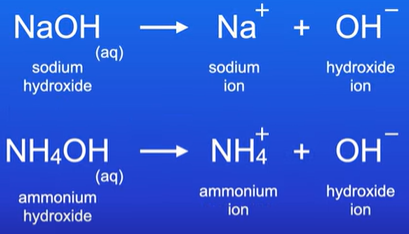
What happens when sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water?
soluble in water
It will make a sodium hydroxide solution
This solution is an alkali
All group 1 metal hydroxides are soluble in water and can form alkalis
What happens when ammonia is dissolved in water?
Its a gas that is soluble in water
Produces ammonium hydroxide which is an alkali
What is the key feature of all alkalis?
In solution they release hydroxide ions OH-
Summarise a neutralisation reaction
OH- + H+ → H2O
What is a redox reaction?
An oxidation and reduction reaction has taken place
Involves a transfer of electrons from the reducing agent to the oxidising agent
Explain oxidation and reduction (in terms of oxygen)
Oxidation= Oxygen has been gained by an atom
Reduction= Oxygen has been lost by an atom
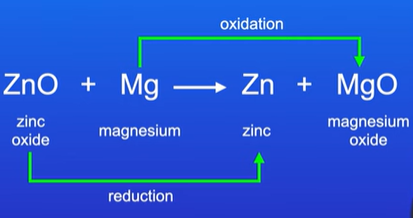
Oxidation and reduction (in terms of electrons)
OIL RIG
Oxidation= Losing electrons
Reduction = gaining electrons
Write the half equations from the reaction
ZnO + Mg → Zn + MgO
Figure out what is being oxidised and reduced in terms of oxygen first
Write the ionic equation and cancel out the spectator ions
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e- oxidation
Zn2+ + 2e- → Zn Reduction
How do you figure out the reducing and oxidising agent?
Reducing agent is being oxidised (Mg)
Oxidising agent is being reduced (Zn)
What do oxidation numbers (states) tell us?
How electrons are lost or gained in a reaction
The change in the oxidation state of an element is used to identify whether it has been oxidised or reduced
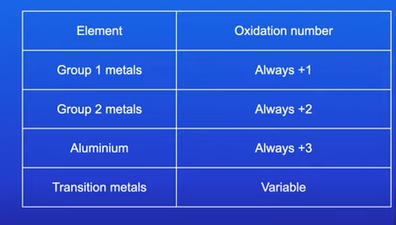
What is the oxidation numbers for pure elements?
0
E.g. Fe, Na, Cl2, O2, S8 = all have an oxidation number of 0
When an element chemically reacts with another element, then the oxidation numbers will no longer be 0
Oxidation states for non metals when they react with other elements?
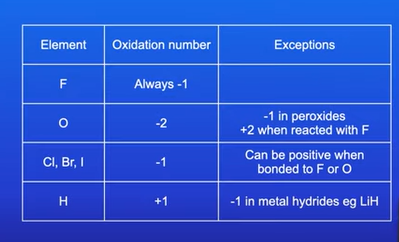
Oxidation states of metals when they react with other elements
What must all of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in a compound add up to?
The total charge of the compound
Oxidation states in H2O
H2O molecule has a charge of 0
Hydrogen has a +1 charge. There’s 2 hydrogens so the oxidation sate of H is +2
Oxygen has a an oxidation state of -2
+2 + -2 = 0
Workout the oxidation state for Phosphorous in H3PO4
Hydrogen has +1 charge. There’s 3 so = +3
Oxygen has a -2 charge. There’s 4 so = -8
This means the charge of the compound is -5.This is not true as the compound has no overall charge
So the oxidation of Phosphorous must be 5
Workout the oxidation state of Mn in MnO4-
The overall charge of this compound is -1
Oxygen has a charge of -2.Theres 4 so -8
To add up to -1, Mn must have a charge of +7
How can oxidation numbers be used to show oxidation and reduction in a reaction?
First assign oxidation states to all atoms in the reaction
When the oxidation number of an atom has increased, this shows oxidation has occurred
When the oxidation of a number decreases, this shows reduction has occurred
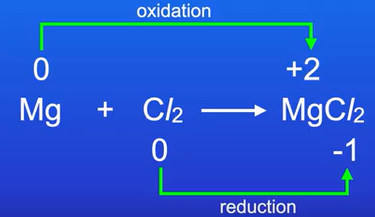
Using oxidation states, workout what has been oxidised and reduced in the reaction
Mg + Cl2 → MgCl2
Mg and Cl2 are unreacted atoms so the oxidation state for both is 0
In MgCl2, Mg has an oxidation state of +2 and Cl has an oxidation state of -1. (despite there being 2 atoms of Cl, only oxidation state for one atom will be written)
Mg was oxidised
Cl was reduced
How do you make a full redox equation from half equations?
Balance the electron charge for both equations
Combine the equations
Cancel out the same stuff on both sides