Theme 4 - Microbial growth
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Microbial growth
Increases in the number of cells not cell size
Colonies
Group of cells large enough to be seen
What are the physical requirements for microbial growth
Temperature
PH
Osmotic pressure
What are the chemical requirements for microbial growth
carbon, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorous
Trace elements
Oxygen
Organic growth factor
What pH do most bacteria grow in
6.5 and 7.5
Acidophilus
Grow in acidic environments
What pH do moles and yeasts grow in
5 and 6
Osmotic pressure
Hypertonic environments or an increase in salt or sugar cause plasmolysis
What requires high somatic pressure ( 30% salt)
Extreme or obligate halophiles
What tolerates high osmotic pressure ( 2% salt )
Facultative halophiles
Why is carbon required
energy source
Chemoheterobtrophs use organic carbon sources
Autotrophs use CO2
Why is nitrogen required
can be used for nitrogen fixing from atmosphere
NH4+ and NO3-
In amino acids and proteins and most bacteria decompose proteins
Why is sulfur required
Amino acids - thiamine and biotin
Bacteria decompose proteins
SO42- or H2S
What is phosphorus required for
In DNA, RNA, ATP and membranes
PO43-
What are trace elements required for
inorganic elements in small amounts
Enzyme cofactors
Fe, Cu, Zn
What are organic factors
Vitamins, amino acids, purines and pyrimidines that cannot be synthesised by themselves and are obtained from the environment
Biofilms
Microbial communities attached to a surface and form slime or hydrogels. Communicate through quorum sensing
What criteria is important for growing microorganisms
correct nutrients for growth
Sufficient moisture
Adjusted pH
Suitable level of O2
Sterile
Incubated in correct temp conditions
Culture medium
Nutrients prepared for microbial growth in the lab
Sterile
No living microbes
Inoculum
Introduction of microbes into medium
Culture
Microbes growing in/on culture medium
Agar
Complex polysaccharide that is used as a solidifying agent for culture media
What temperature does the agar solidify
40
What temperature does agar liquify
100
Chemically defined media
Exact chemical composition is known
Complex media
Slightly varies per batch, extracts and digests of yeasts, meat or plants
Anaerobic culture methods
Contain chemicals that combine oxygen then use heat to drive off oxygen
Special Culture techniques
Some bacteria will not grow in culture and can only grow inside cells
Capnophiles
Microbes that grow better at high CO2 concentrations
Differential media
Distinguishes colonies
Enrichment media
Favours growth of desired microbes
Selective media
Encourage desired microbes to grow and suppress unwanted microbes
Pure cultures
Contains only one species or strain of bacteria
Colony
A population of cells that arise from a single cell or spore or from a group of attached cells called a colony-forming unit
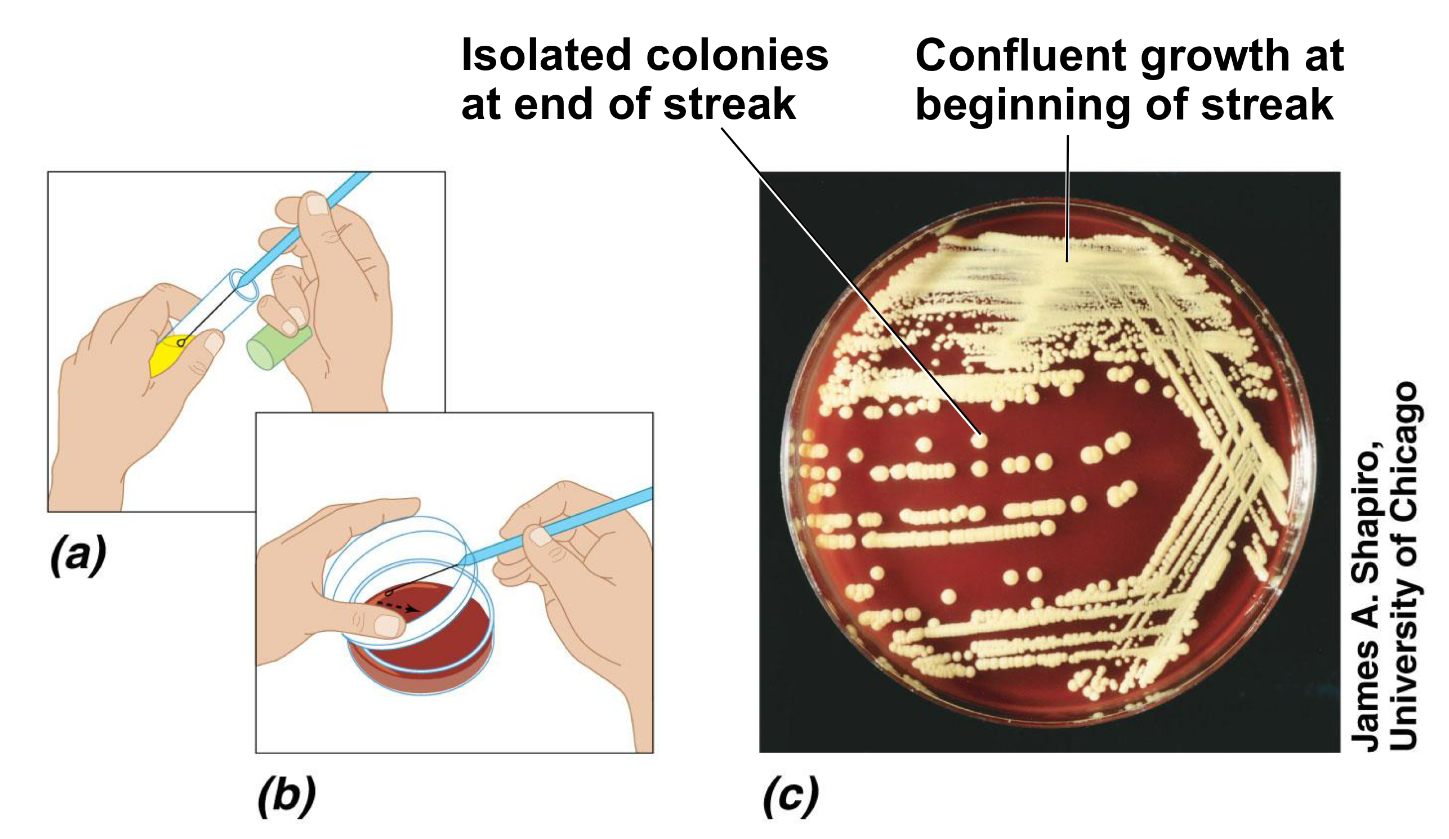
What is this method called
Streak plate method
Types of preserving bacterial cultures for a long term
deep-freezing
Lyphilization, freeze-dying,
Name the growth phases of bacteria
Lag phase
Log phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
Lag phase
Intense activity for preparing for population growth, but no increase in population
Log phase
Logarithmic or exponential, increase in population
Stationary phase
Period of equilibrium, microbial deaths balance production of new cells
Death phase
Population is decreasing at a logarithmic rate
What are the direct methods to measure microbial growth
plate counts
Filtration
Direct microscopic count
MPN
What are indirect methods used to measure the microbial growth
turbidity
Metabolic activity in
Dry weight
What are the advantages and disadvantages of plate counts
A: count viable cells
D: can take a long time, cells can form clumps
How do you calculate the number of bacteria on a plate count
Number of colonies on plate * reciprocal of dilution of sample = number of bacteria/ml
Advantages and disadvantages of direct microscopic count method
A: no incubation required
D: count dead cells, motile bacteria is difficult to count, need high concentration of cells
Turbidity
Measurement of cloudiness with spectrophotometer
Metabolic activity
Amount of metabolic product is proportional to the number of bacteria
Dry weight
Bacteria are filtered, dried and weighed then used for filamentous organisms