AP Bio - Ch.4: Tour of the Cell
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Plasma membrane, cytosol, chromosomes, ribosomes
All Eukaryotic cells have these
Nucleus
houses most of the DNA
Enclosed by the nuclear envelope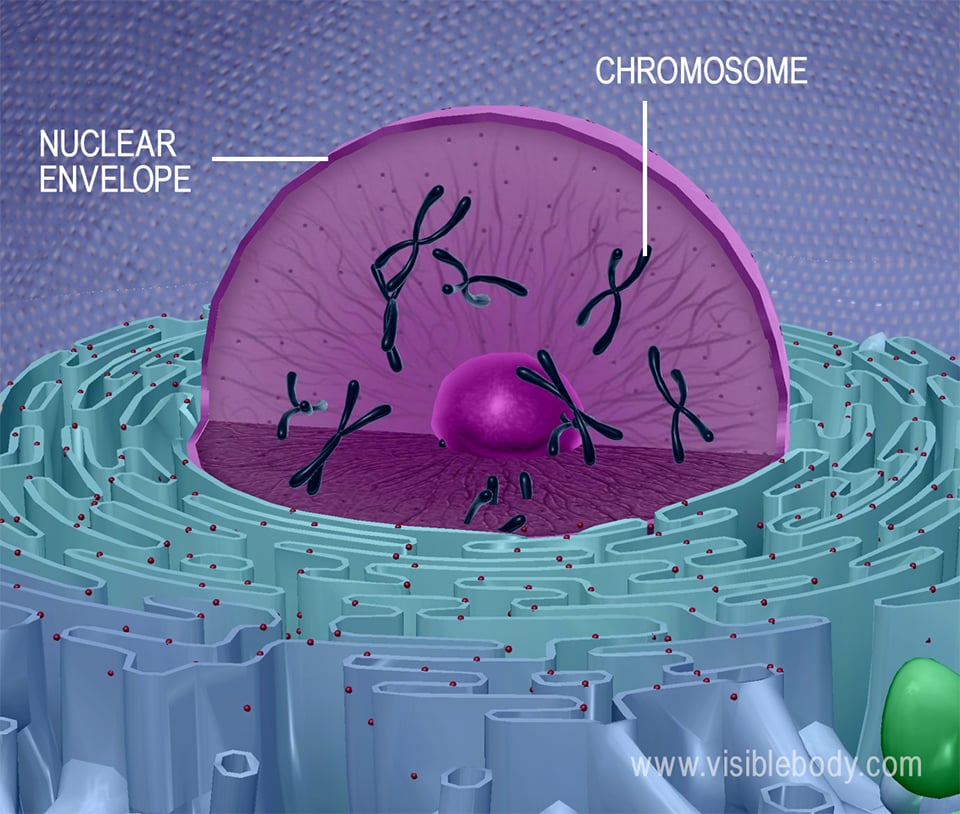
Chromosomes
contains genetic material. Sub-unit of DNA
appears as:
chromatin: DNA + protein complex
nucleoli: where RNA is synthesized and rRNA + proteins are assembled → ribosomes
Nuclear envelope
Encloses the nucleus and perforated with pores to filter in traffic in cytoplasm
has inner + outer membrane
lined by nuclear lamina inside → made of protein filaments → maintain shape
outer membrane is continuous with endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes
utilizes DNA to make proteins
primary parts (rRNA and protein) assembled in the nucleoli
free ribosomes → proteins in cytosol
bound ribosomes → proteins that are attached to ER
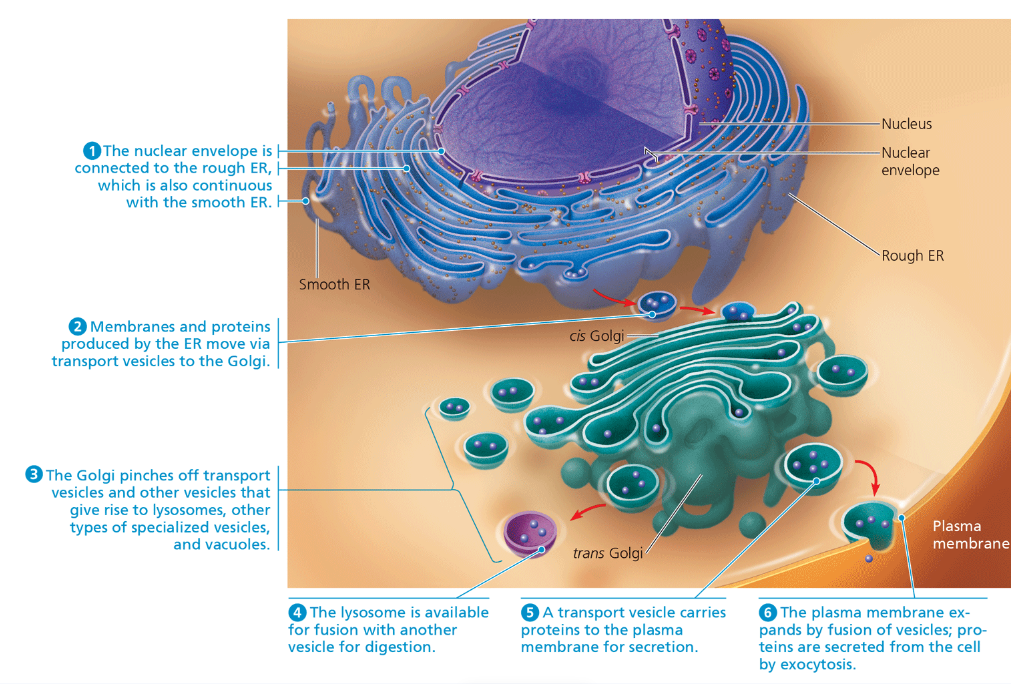
endomembrane system
Involves the entirety of the membranes (including organelles) in and surrounding an eukaryotic cell. In charge of: synthesizing proteins, metabolizing lipids, and detoxifying
Includes:
nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
lysosomes ← (not found in plant cells)
vesicles and vacuoles
plasma membrane
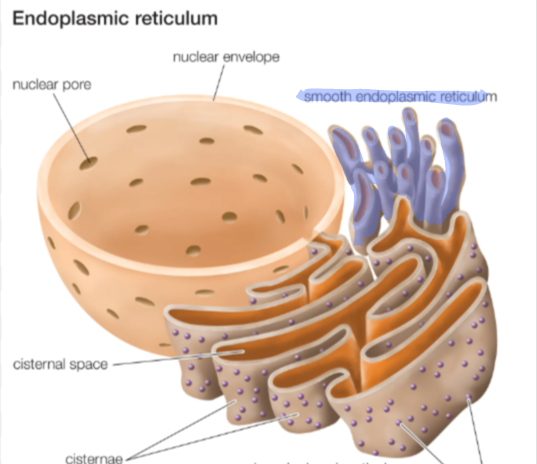
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
ER that lacks ribosomes. Synthesizes lipids and detoxifies drugs and poisons
(more poisons = higher detoxification rate)
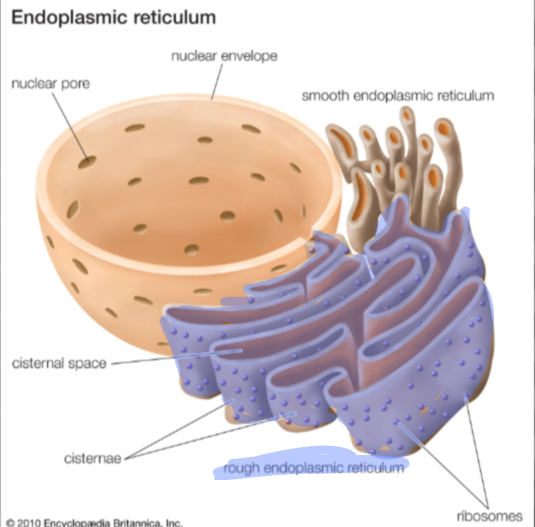
rough endoplasmic reticulum
ER embedded with proteins. Responsible for synthesizing secretory proteins (glycoproteins), and membranes (a membrane factory)
helps separate and package secretory proteins and their products into vesicles
helps expand plasma membrane of the cell itself
Golgi Apparatus
Flattened membranous sacs (cistarnae) that receives, modifies and transfers the products of the ER 
Lysosomes
Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that hydrolyze (digest) cell food
Hydrolyzes in two ways:
phagocytosis — engulfs cell to digest components (food vacuole)
autophagy — fuses with damaged components to digest them to be reused
recycles the cells’ own organelles and macromolecules
Mitochondria
site of cellular respiration: metabolic process that uses oxygen to drive intake of sugars to produce ATP.
“Power house of the cell” : responsible for providing energy for cellular processes
 Made up of:
Made up of:
inner and outer membrane
cristae — folding in inner membrane → increases SA:V ratio
matrix — compartment inside inner membrane
Chloroplast
site of photosynthesis: the conversion of solar energy into chemical energy  Made up of:
Made up of:
two membranes
thylakoids — flattened membranous sacs
granum — a stack of thylakoids
stroma — fluid outside of thylakoids
vacuoles
Membrane bound vesicle derived from Golgi and ER.
In plant cells: central vacuole — contains plant cells sap + responsible for their shape
peroxides
organelles that detoxify by transporting a hydrogen atom form a harmful substance
cytoskeleton
Network of fibers that stretch throughout the cytoplasm of a cell. Transports organelles through motor proteins, helps provide cell shape and alters plasma membrane to form food vacuole
Made up of:
microtubules: creates dyneins (motor proteins in cillia/flagellum)
typically grows out of the centrosome ← only found in animal cells
microfilaments: creates microvilli of cell and myosin (motor proteins in muscle cells contraction)
intermediate filaments: related to keratin (found in hair)
Cell wall
Extracellular structure of plant cells that protects a plant cells, helps maintain its shape, and prevents and excessive intake of water
Made up of (2) layers:
primary cell wall (innermost, thinnest wall)
middle lamella (thin layer rich with polysaccharides)

extracellular matrix
ECM. Meshwork of proteins and molecules (glycoproteins and carbohydrates) surrounding an eukaryotic cell.
Helps communicate the cell’s environment with the cell through binding at receptor proteins called integrins

Includes:
collagen — most abundant + forms strong fibers outside of cells
fibronectin — secreted by eukaryotic cells → binds to integrins
Plasmodesmata
Cell junctions found only in plants
An open channel through the cell wall, connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells
Tight junctions
Cell junctions found in animal cells
“Seals” and prevents leakage of liquids/water between cells
Desmosomes
Cell junctions found in animal cells.
Fastens the cells together in strong sheets (“rivet”)
Gap junctions
Cell junctions found in animal cells.
Provides cytoplasmic channels for cell (similar to a plant cell’s plasmodesmata) ; necessary for communication between cells in tissues.