Architectural Appreciation - W. Briar Jones - Test #3 Study Guide
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Gothic Architecture
- A-historical, asymmetrical
- Architecture in service of God
-Assembly of parts
-Designed out for each individual building
-Architecture adaptable to any situation
Renaissance Architecture
- Mathematics, Rational, Proportions, Universal order
- Not aspired to heavens, grounded to earth, human reason
- Symmetry
- Circle and square pure form
Renaissance 15th Century
- Began in Florence
- Authentic re-use of classicism, based in understanding of perspective, change size and proportions of columns, pediments, etc.
- Represent human intellect as much as the power of God
What is Humanism?
Philosophical system based upon the capacity of humankind for rational, objective thought and action; stresses human reason and is centered around human nature, interests, and ideals, as distinct from religious philosophies based on a higher God.
Human achievement separate from religious dogma
What is Renaissance?
The activity, spirit or time of humanistic revival of classical art, literature and learning originating in Italy in the 14th Century and extending to the 17th Century making the transition from the medieval to the modern world
What is Renaissance Architecture?
The various adaptations of Italian Renaissance architecture that occurred throughout Europe until the advent of Mannerism and the Baroque in the 16th and 17th Centuries, characterized by the use of Italian Renaissance forms and motifs in more or less traditional buildings
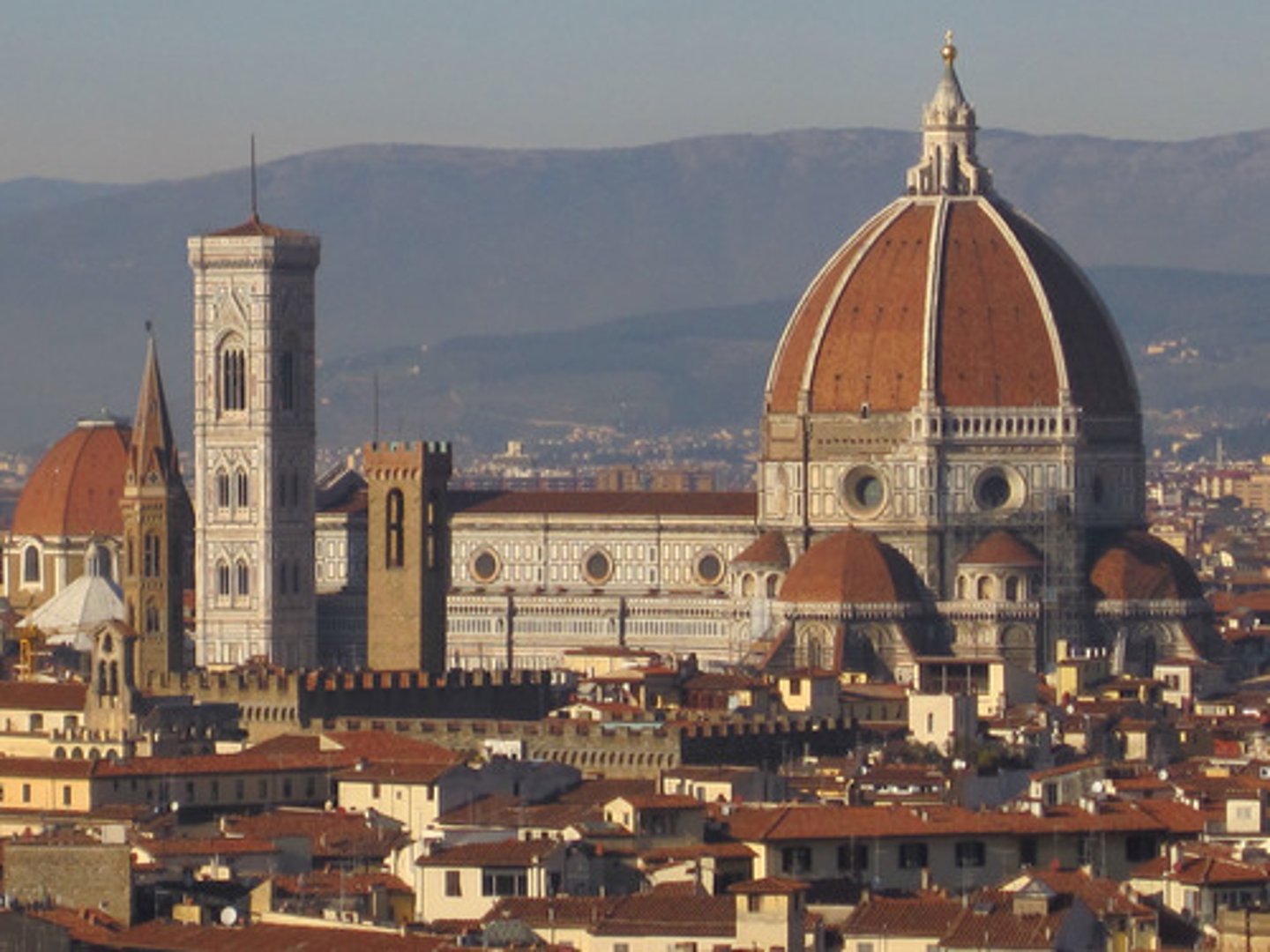
Who is Brunelleschi?
An architect, painter, sculptor, and goldsmith
Image of the Cathedral in Florence
Dome is witness to human achievement

What is Early Renaissance?
A style of Italian Renaissance art and architecture developed during the 15th century, characterized by the development of linear perspective, chiaroscuro, and in buildings, by the free and inventive use of classical details
Brunelleschi (Foundling Hospital)
Father of the Renaissance
Designed the First Renaissance building - Brunelleschi (Foundling Hospital) in Florence, Italy (1422). Has symmetrical forms, proportion relate from one element to another application scientific perspective

What is the “Duomo,” Dome of the Cathedral?
Located in Florence, Italy. Constructed between 1419-1436. Largest dome built since the Romans. Technical achievement in its construction (no “centering” - built to be self-supporting as it was constructed)
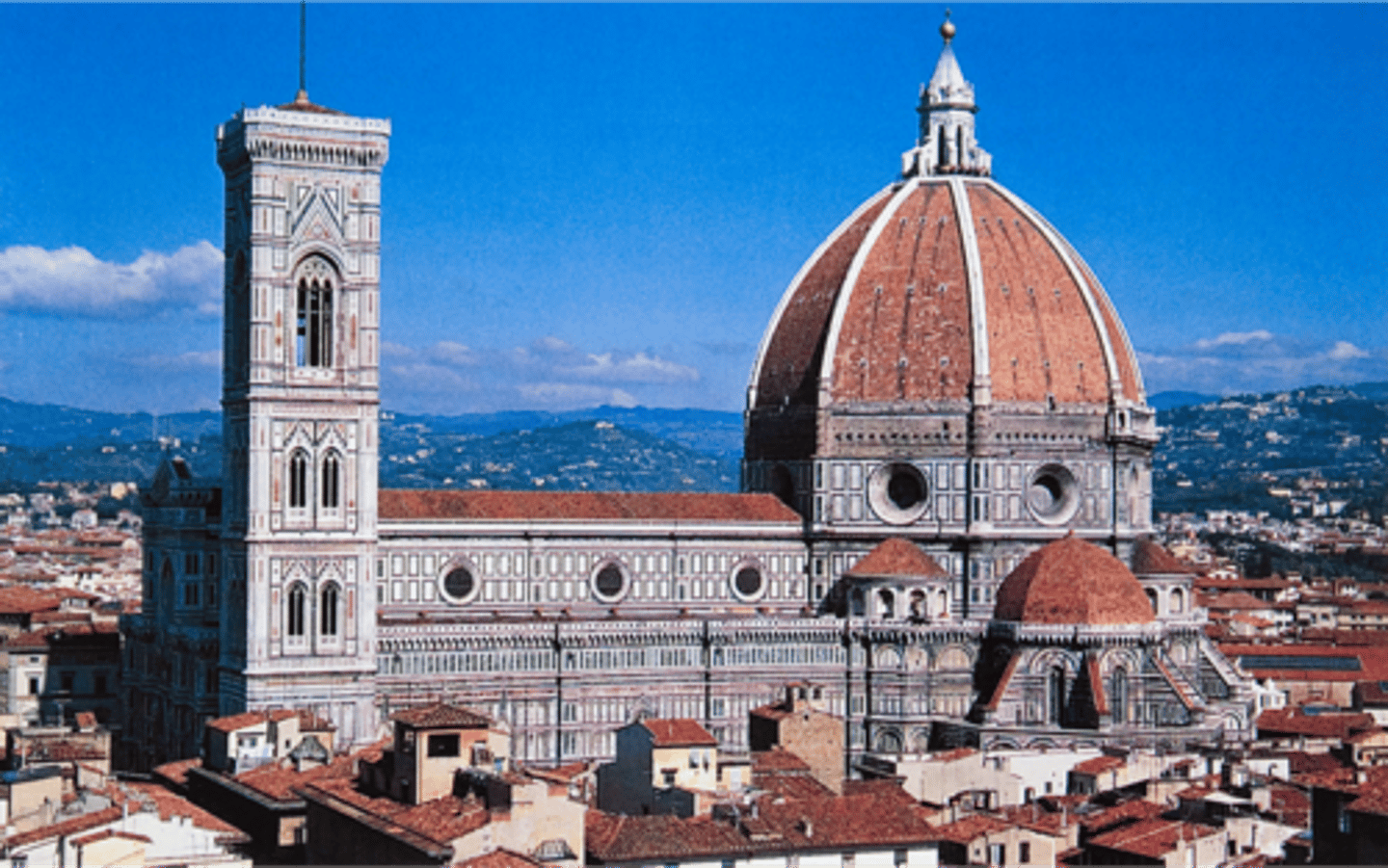

The Cathedral in Florence Employed What?
Ribs and double shells
_______ is Renaissance
Dome
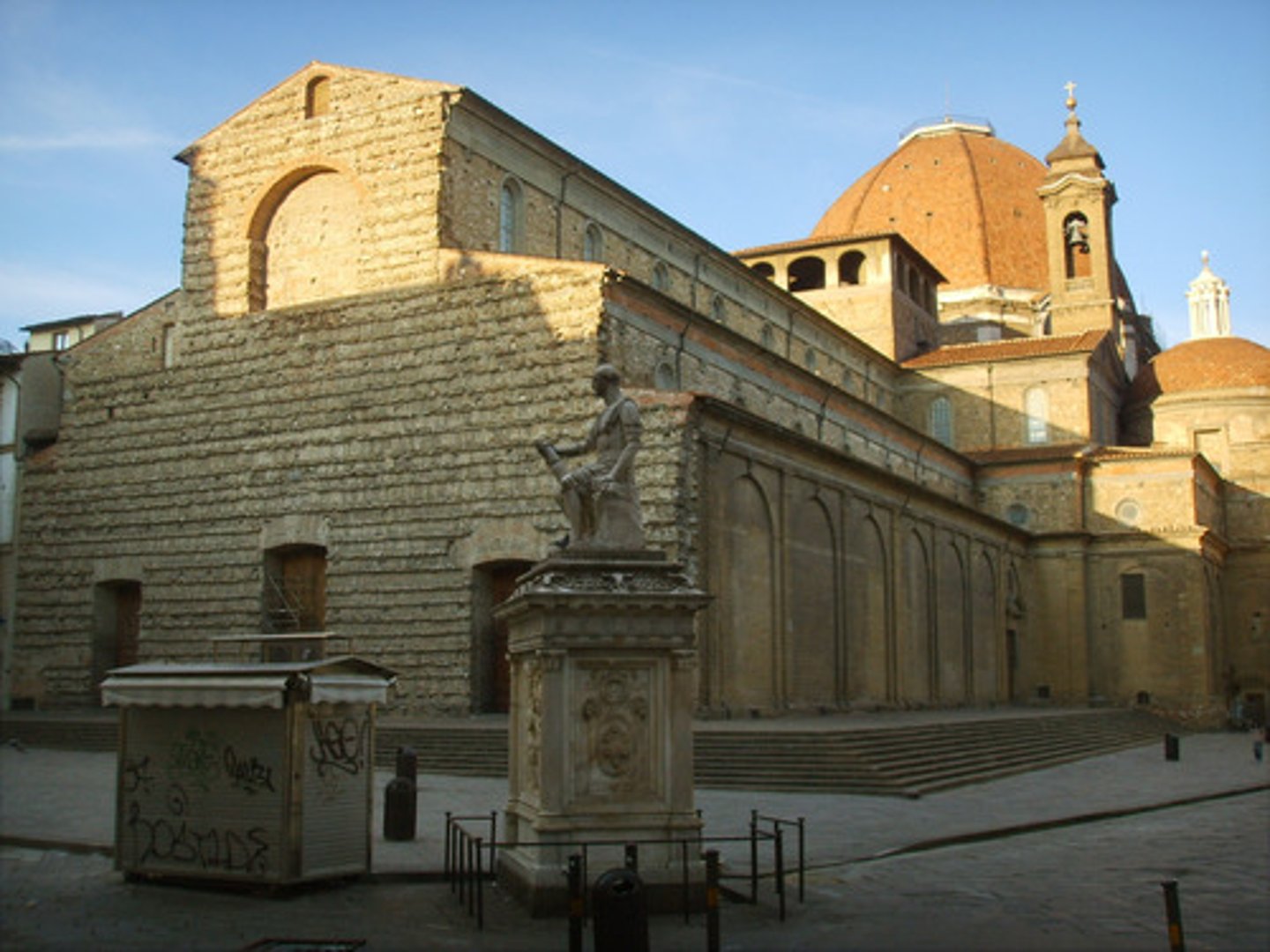
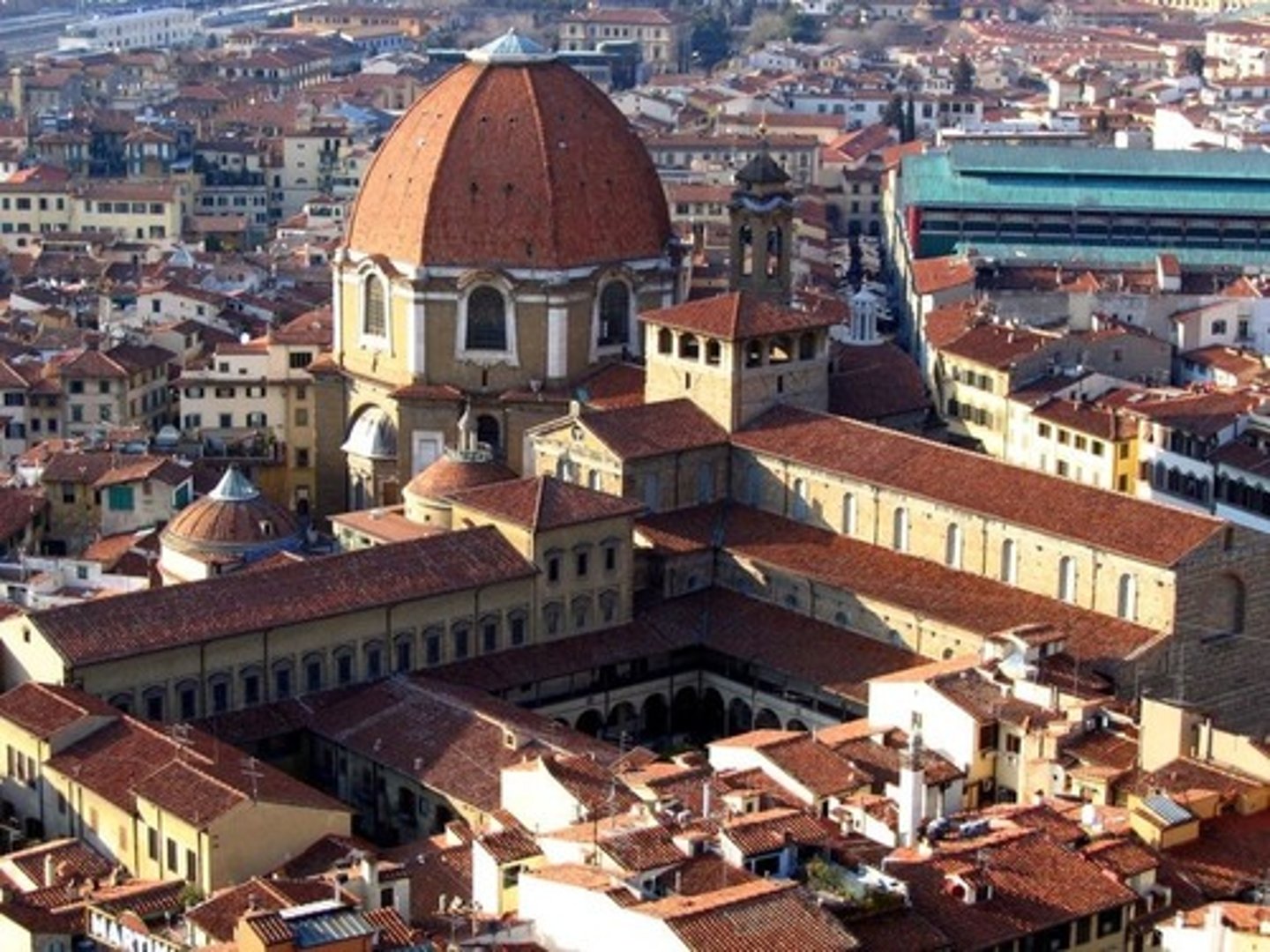
Church of San Lorenzo
Made by Filippo BRUNELLESCHI between 1418-1446

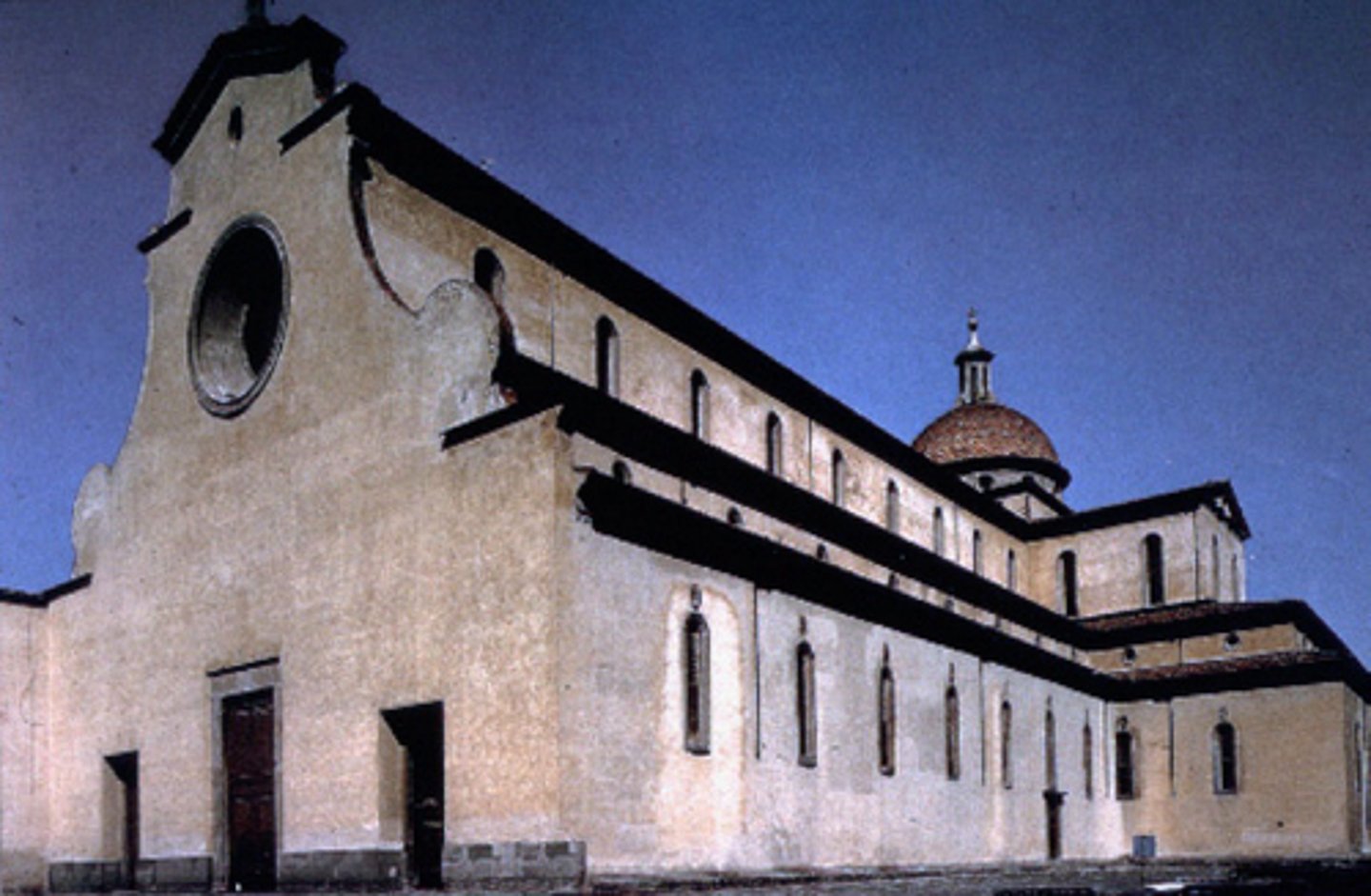
Church of S. Spirito
Made by Filippo Brunelleschi between 1436-4182. Proportions and style are fully realized (Volumes are CUBES and CONSTRUCTED PERSPECTIVE!)

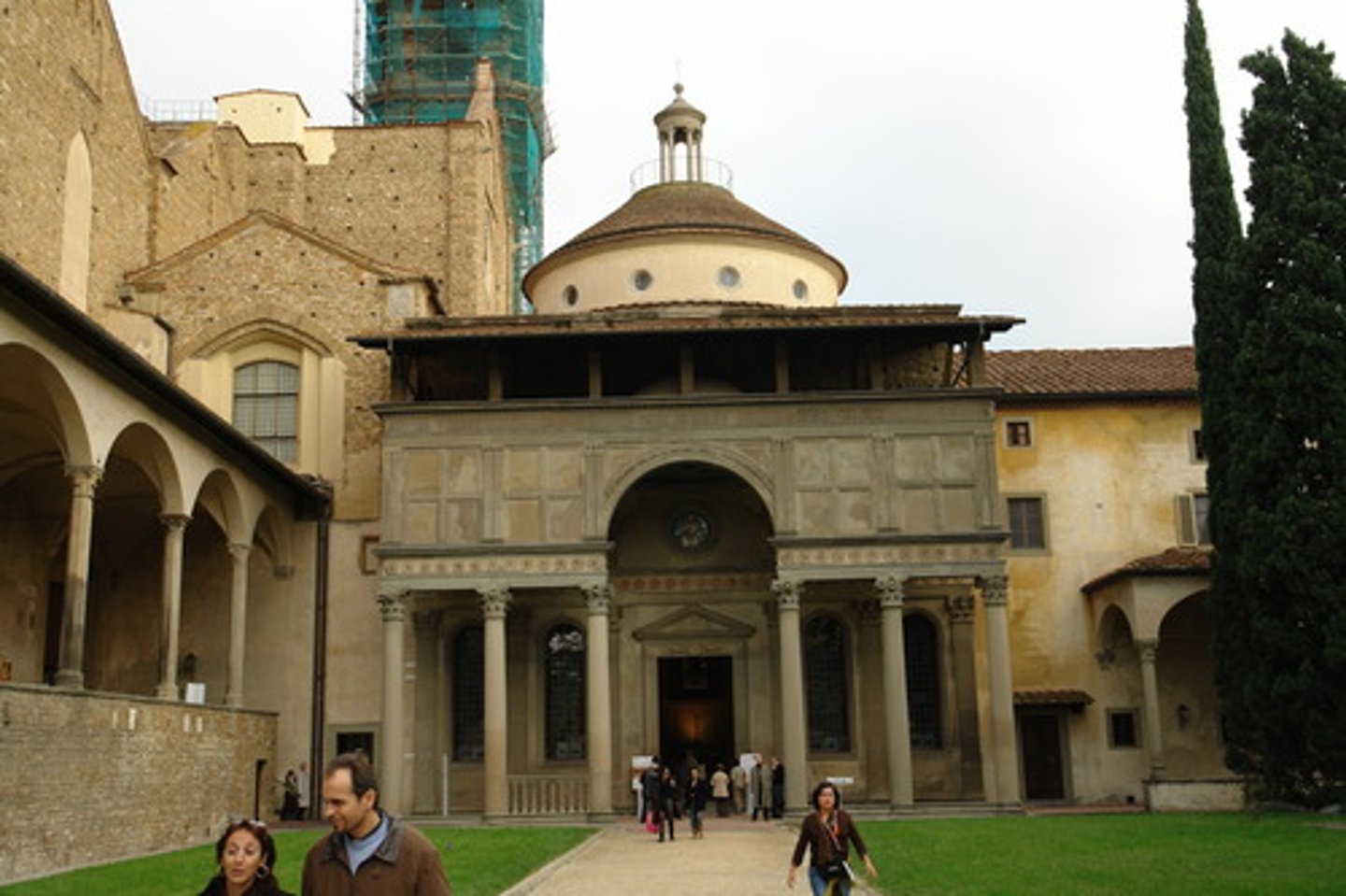
Pazzi Chapel
Made by Filippo Brunelleschi

Who is Vitruvius?
- Wrote “Bible” for Renaissance Architects
- Roman architect and theorist, active between -46 to -25
What did Vitruvius Write?
“The Ten Books on Architecture” which is the only complete book on architectural design. Had enormous influence on Renaissance architecture
What are the Two Thoughts from Vitruvius?
- “Firmness, Commodity, and Delight”
- Vitruvian Figure (believed Platonic forms were “eternally and absolutely beautiful." Circle and squares became basic design modules - based on whole number proportional relationships)
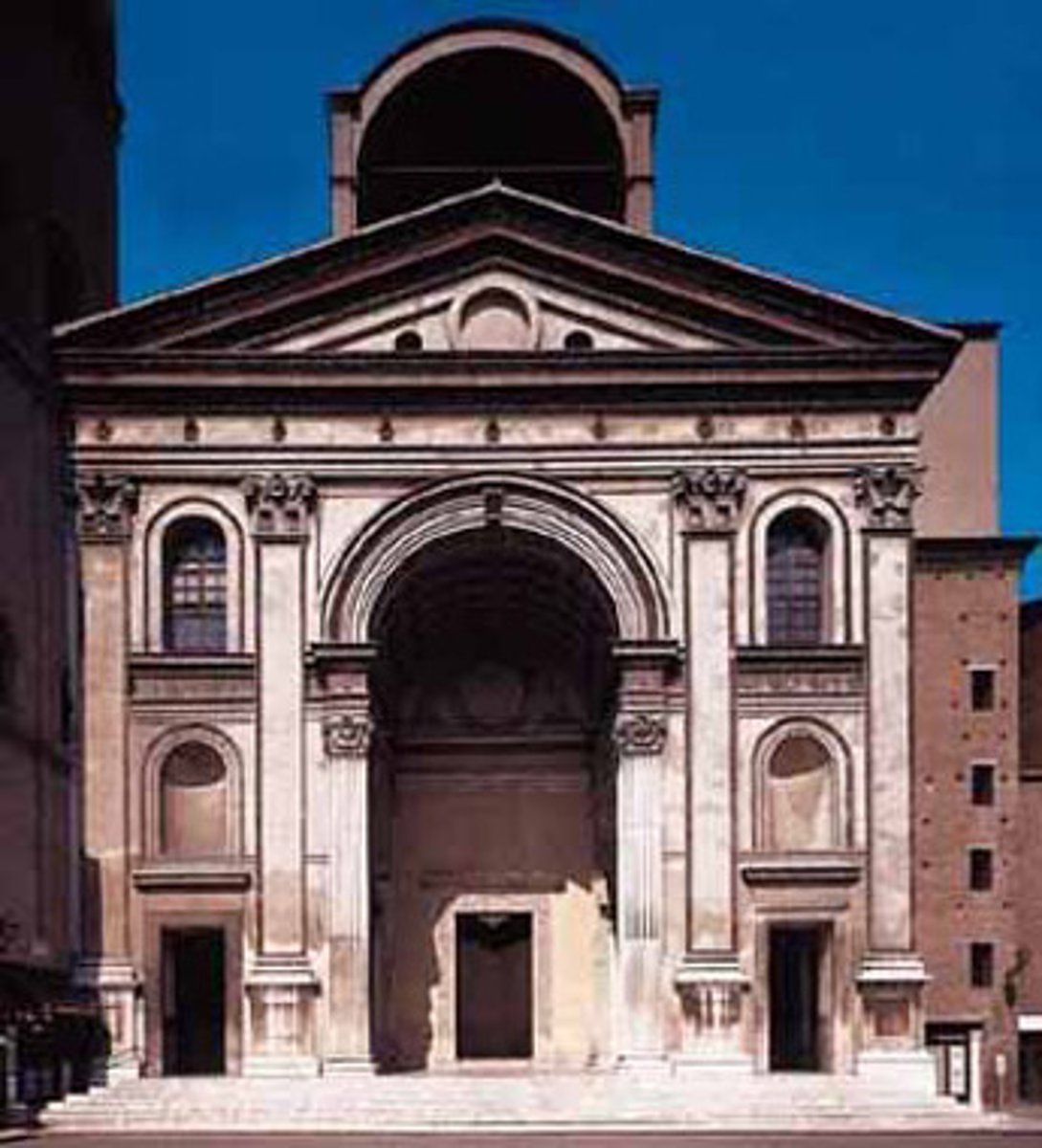
Church of Sant' Andrea
Made by Leon Battista ALBERTI between 1470-1490

Who is Leon Battista Alberti?
A theorist, historian, scientist and architect. Promoted architecture as intellectual activity. Wrote another TEN BOOKS on architecture modeled on Vitruvius’s Books
Ideal city of Sforzinda
Made between 1461-1462
Man is the center!
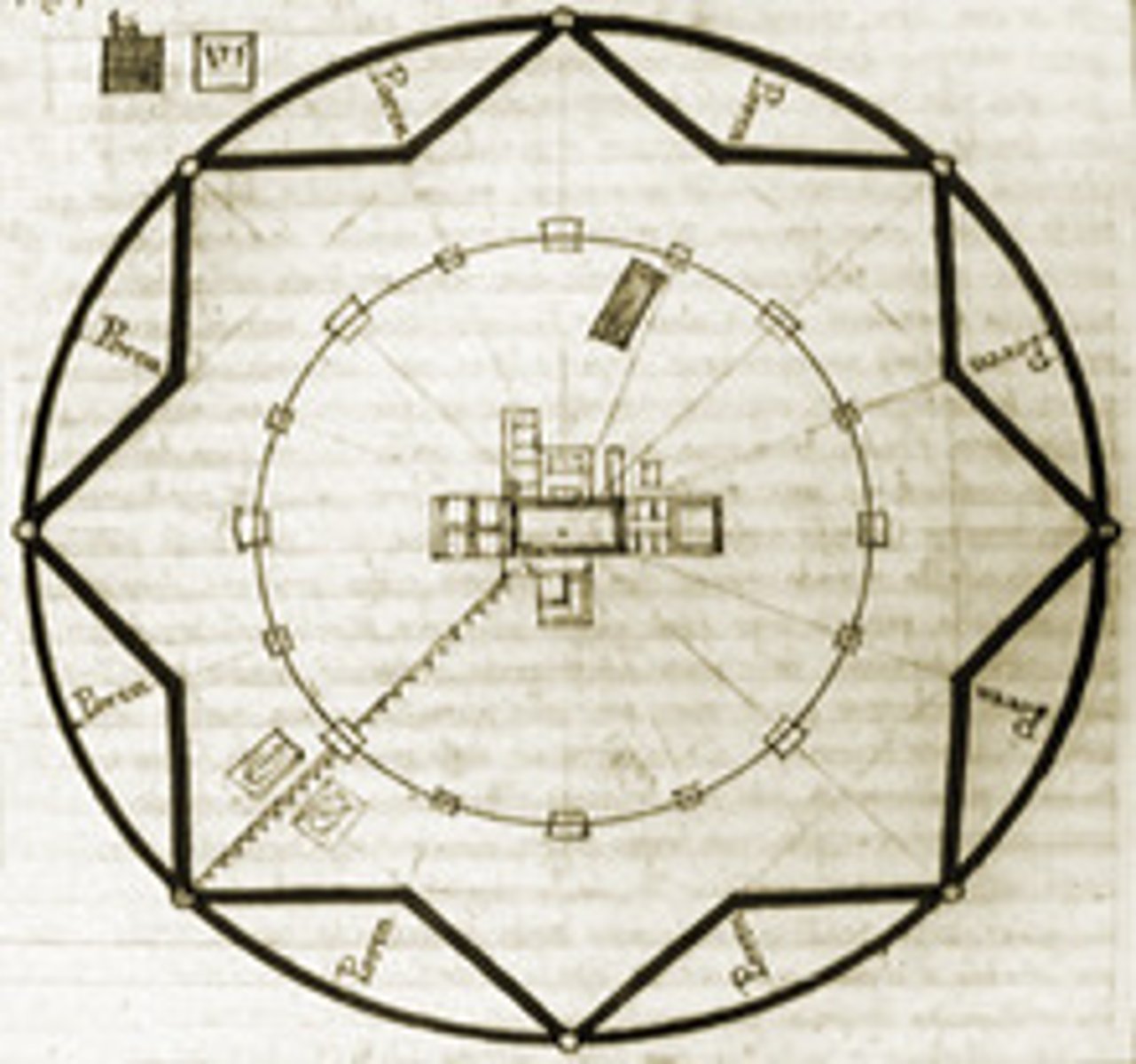
Villa Rotunda
Made around 1500 in Vicenta, Italy by Andrea PALLADIO. Supreme example of theoretically inspired design (completely symmetrical, elements all governed by proportional relationships, turned house into a temple)
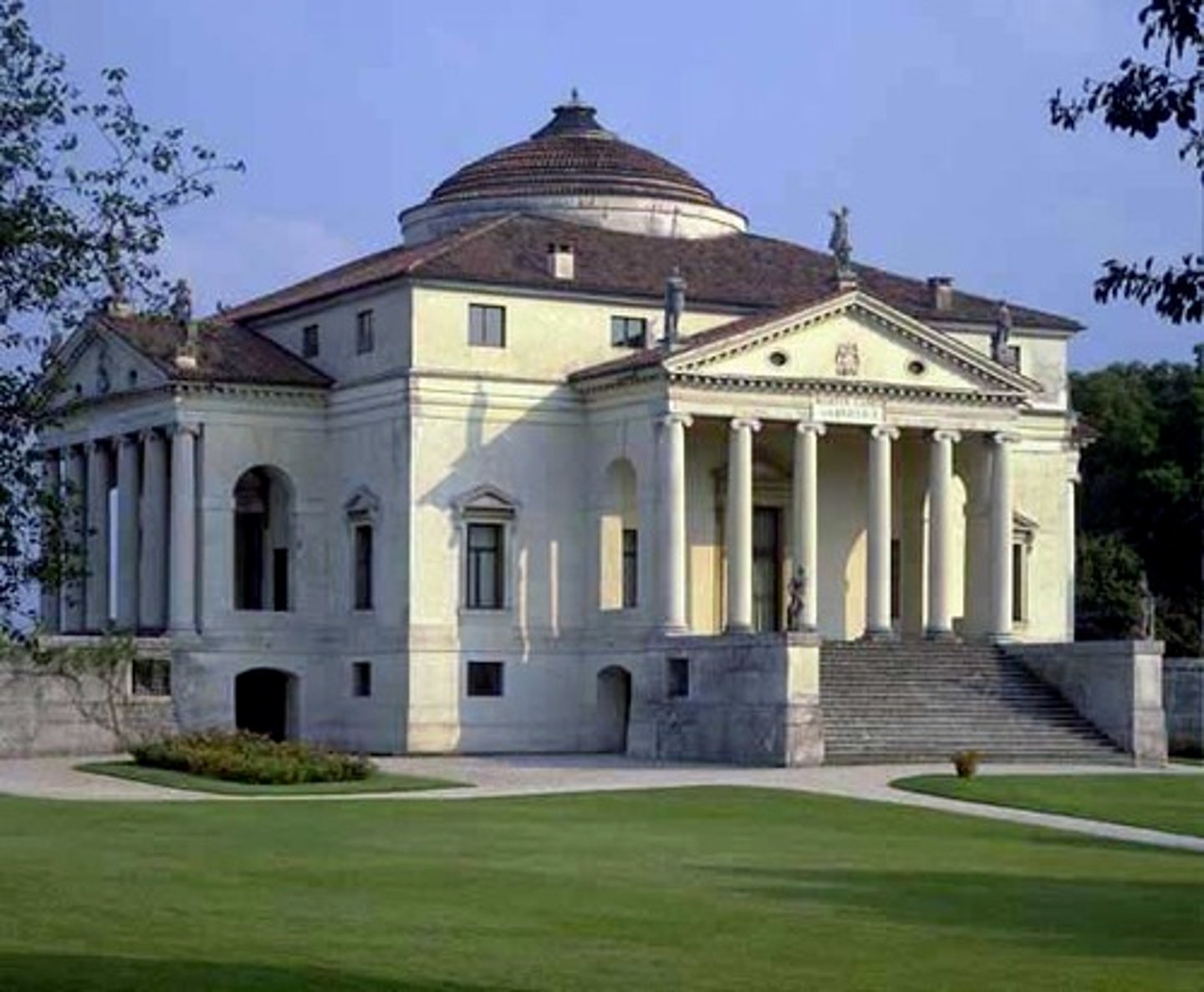

Who is Andrea Palladio?
Palladio wrote treatise on architecture (THE FOUR BOOKS OF ARCHITECTURE). Constructed villas between Venice and Vincenza in 1550
What is a Palazzo?
A city house
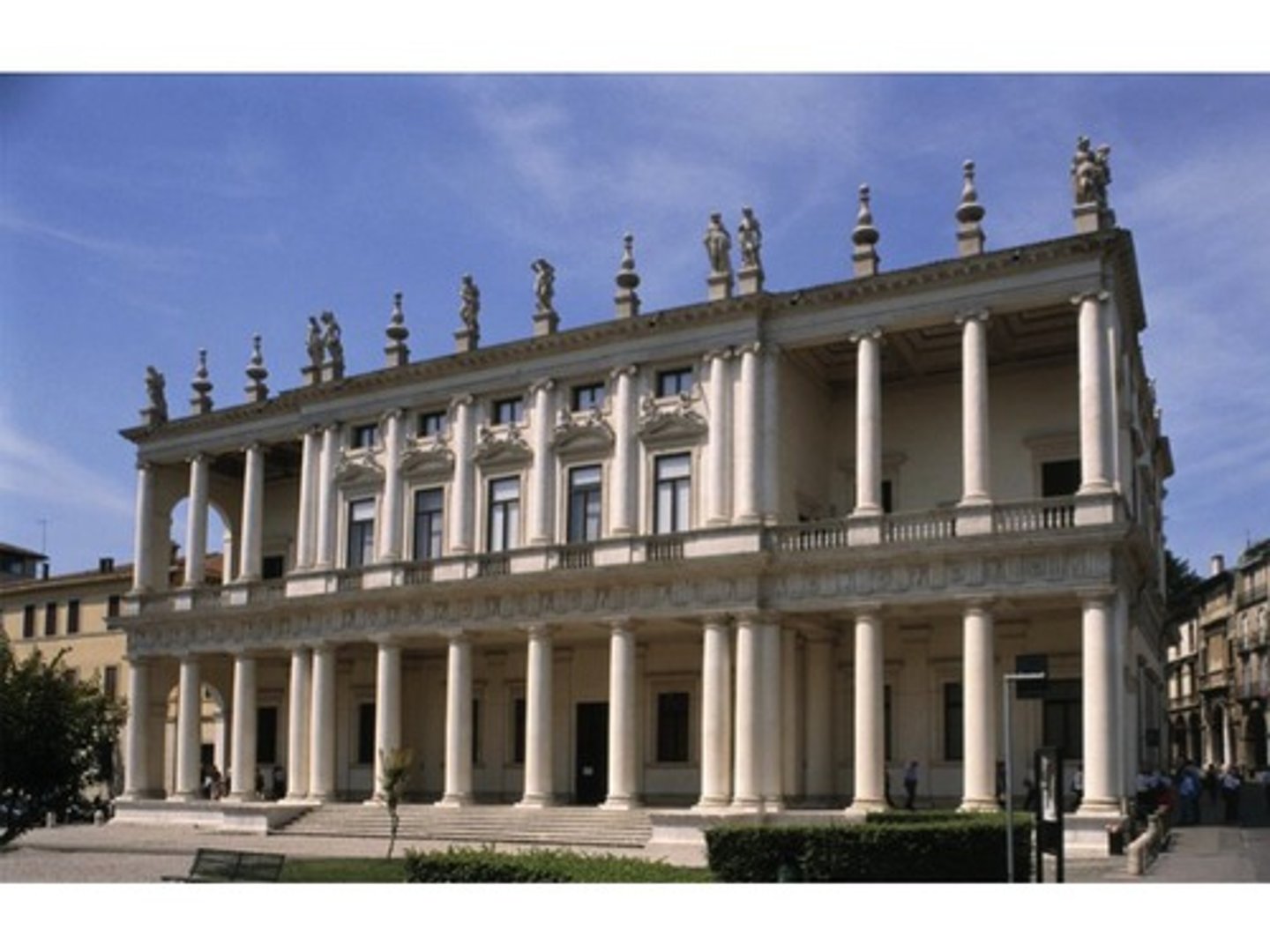
Palazzo Chiericati
Made by Palladio in Vincenza

What is a Piazza
Public square

What is High Renaissance?
A style of Italian Renaissance art and architecture developed during the late 15th century, characterized by an emphasis on draftsmanship, the illusion of sculptural volume in painting, and in building, by the imitative use of orders and compositional arrangements in the classical style, with great attention to the formulation of compositional rules after the precepts of Vitruvius and the precedents of existing ruins
The "Tempietto" of San Pietro
Made by Donato BRAMANTE in Montorio between 1500-1502
Full realization of the perfection in circular geometry
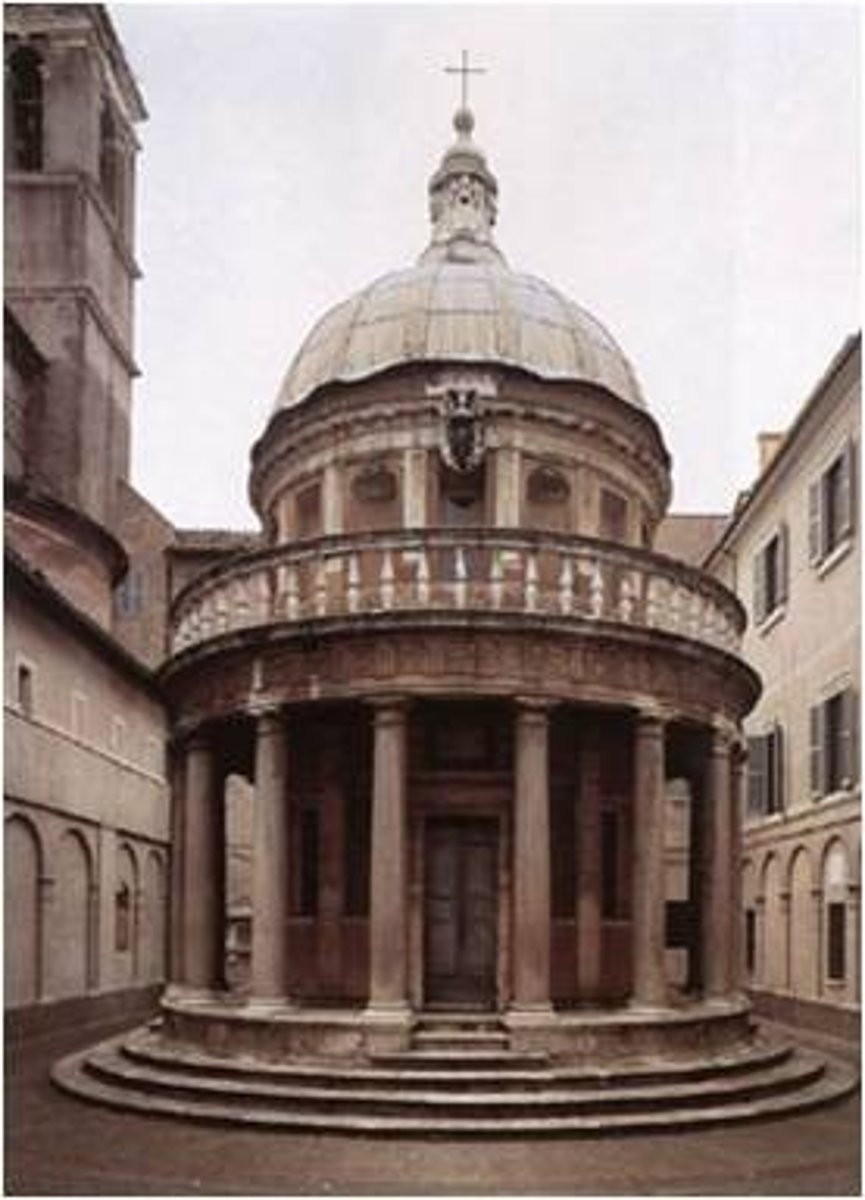

Who is Donato Bramante (1444-1514)?
Bramante was a close associate of Leonardo da Vinci. Early work in Milan but moved to Rome after French sack of Milan in 1499.
Designed the Tempietto in Rome that begun in 1502. Believed religious figure “Saint Peter” was killed (martyred) here. Meant to be an object, a picture, a marker
Who is Pope Julius II?
Introduced humanist ideals into the Papal court. Rome Queen city - consolidate temporal power. Return to glory from Roman antiquity
Who is Saint Peter's (1505-1612)?
- Made a magnificent new church of the crypt of Saint Peter
- Dome becomes an icon of “dome” often repeated
- Tomb for Pope Julius II would not fit in old basilica (almost 1100 years old in 1505)
- Bramante’s scheme was on a scale grander than any Roman structure (Building about the size of the Baths of Diocletian. Dome comparable to the Pantheon)
Bramante, Palazzo Caprini
Rome, ca. 1512

What is Mannerism in High Renaissance?
Inventive combinations of elements that purposefully play with classical rules. Proportions are exaggerated. Michelangelo, who lived between 1475-1564, rebelled against Renaissance decorum. Painter (painted ceiling of Sistine Chapel), sculpture (David, the Pieta), Laurentian Library
What is Mannerism?
A transitional style in European architecture in the late 16th century, particularly in Italy, characterized by the unconventional use of the classical elements. Complete challenge to Renaissance rules of order, proportion, and use of historic elements. The goal is to heighten physical experience of moving through space
Laurentian Library
Made in 1524, the vestibule is high and narrow and the design appears out of place with other Baroque architecture

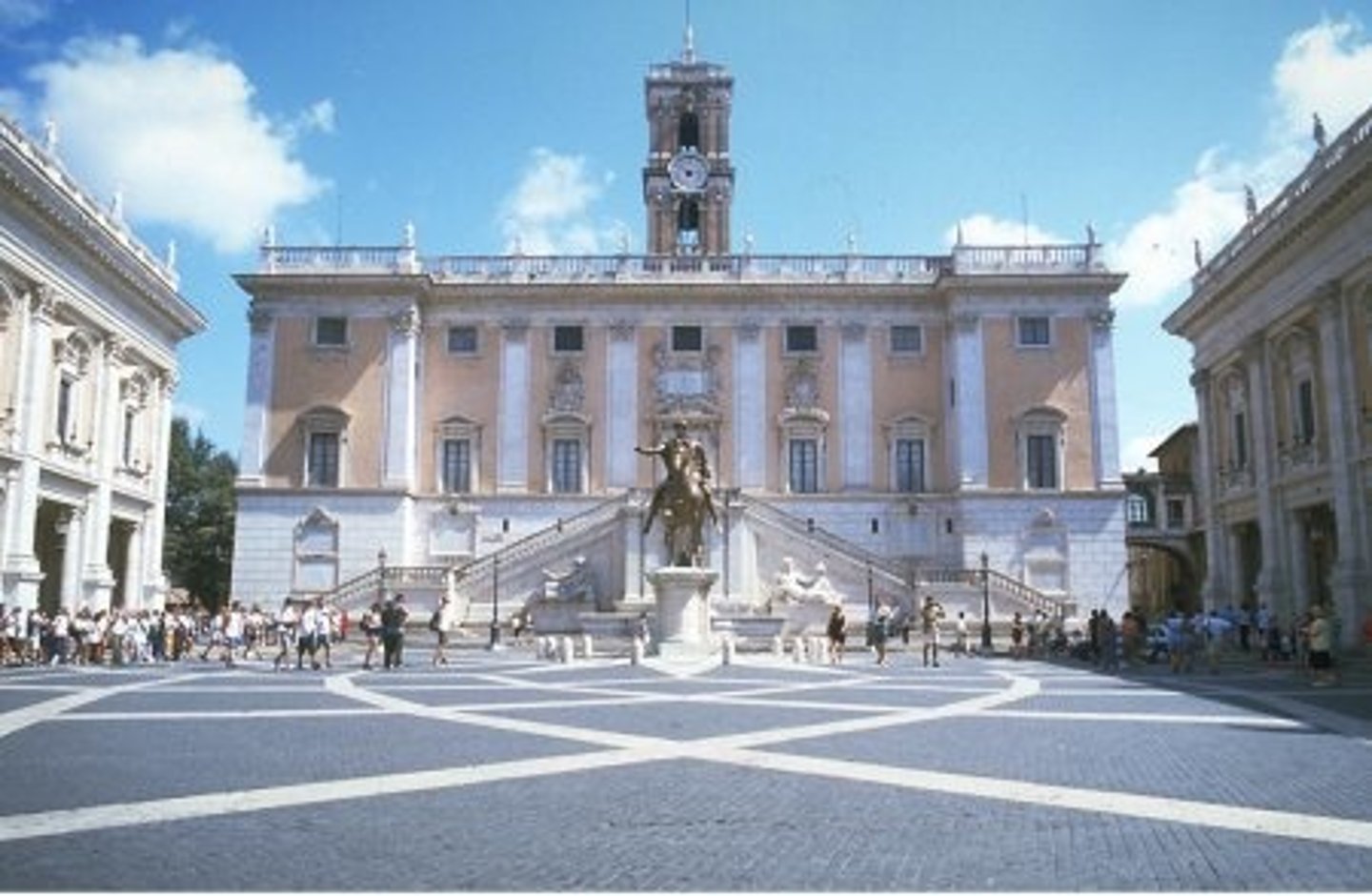
The "Campidoglio," Capitoline Hill 1536
Made on Capitoline Hill in Rome in 1536 by Michelangelo Buonarroti. Organization deviates from purity of Renaissance geometry (subtle tension of angled plan and oval plaza)

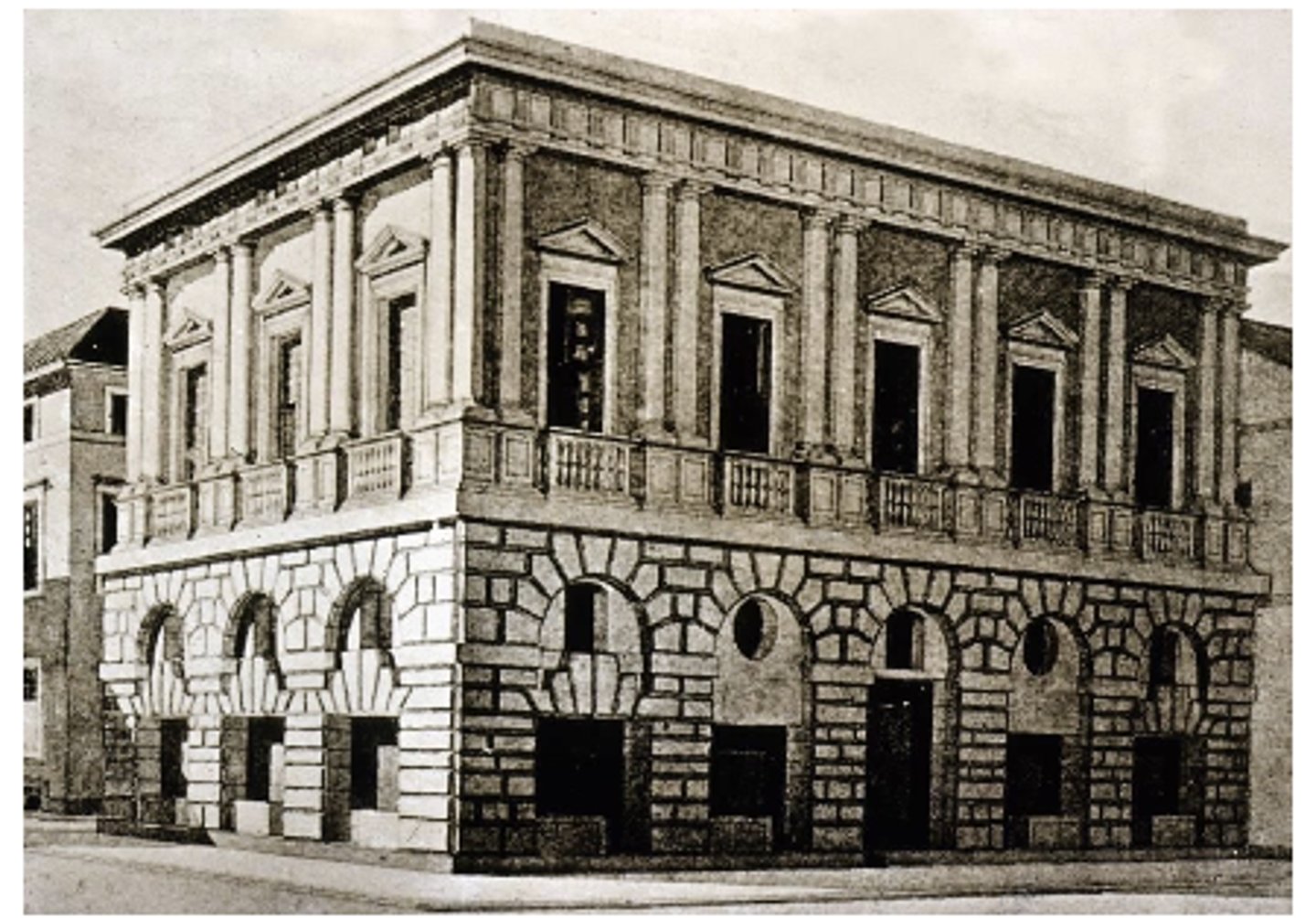
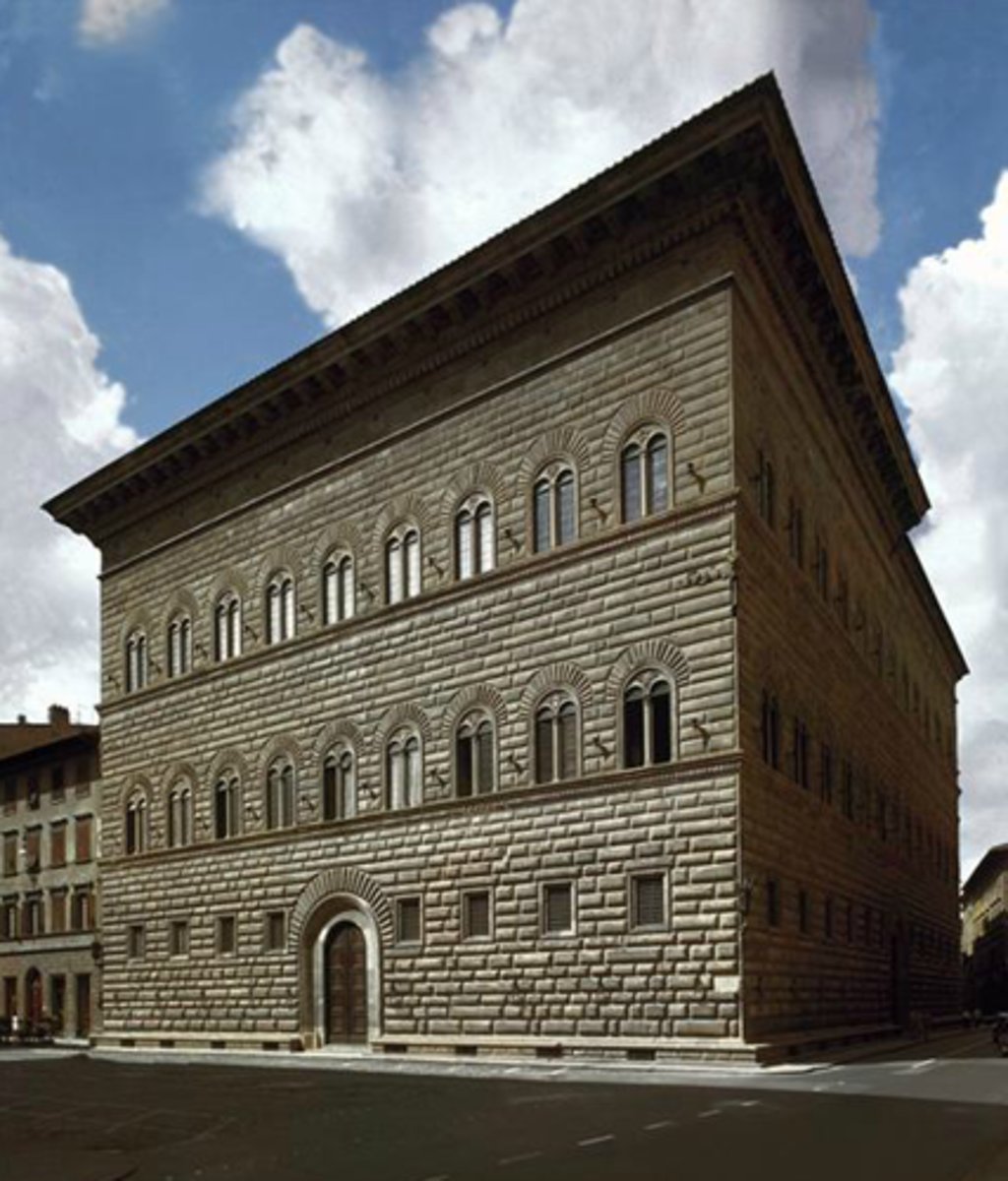
Palazzo Strozzi
Begun in 1489 and was made in Florence, Italy

Who is Inigo Jones?
From 1572-1652
Made the Queen’s House in Greenwich (begun 1616), using Balustrade which is a railing supported by balusters
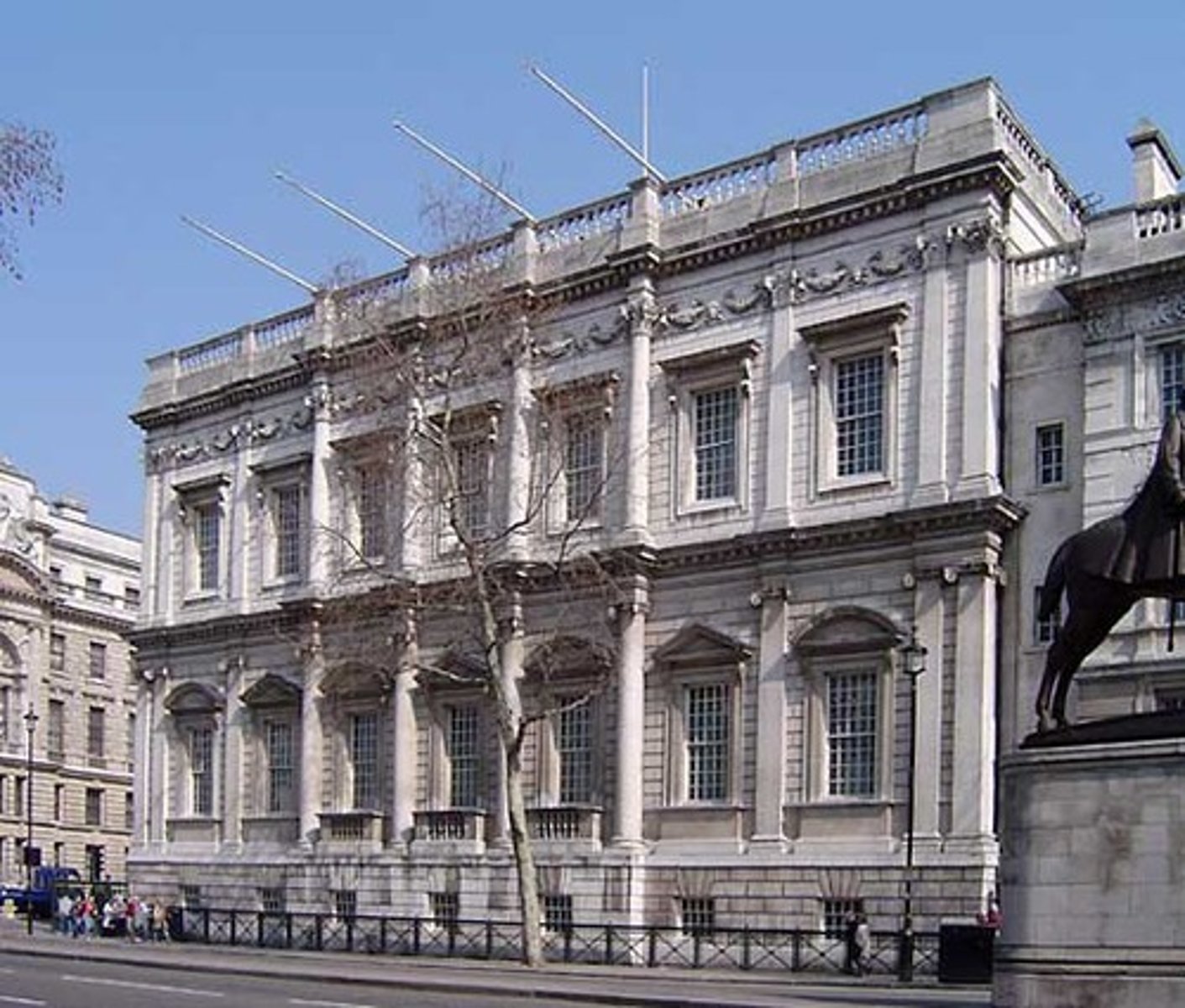
Made the Banqueting Hall of Whitehall, London (1619-1622)
Image of the Queen's House in Greenwich
Made by Inigo Jones
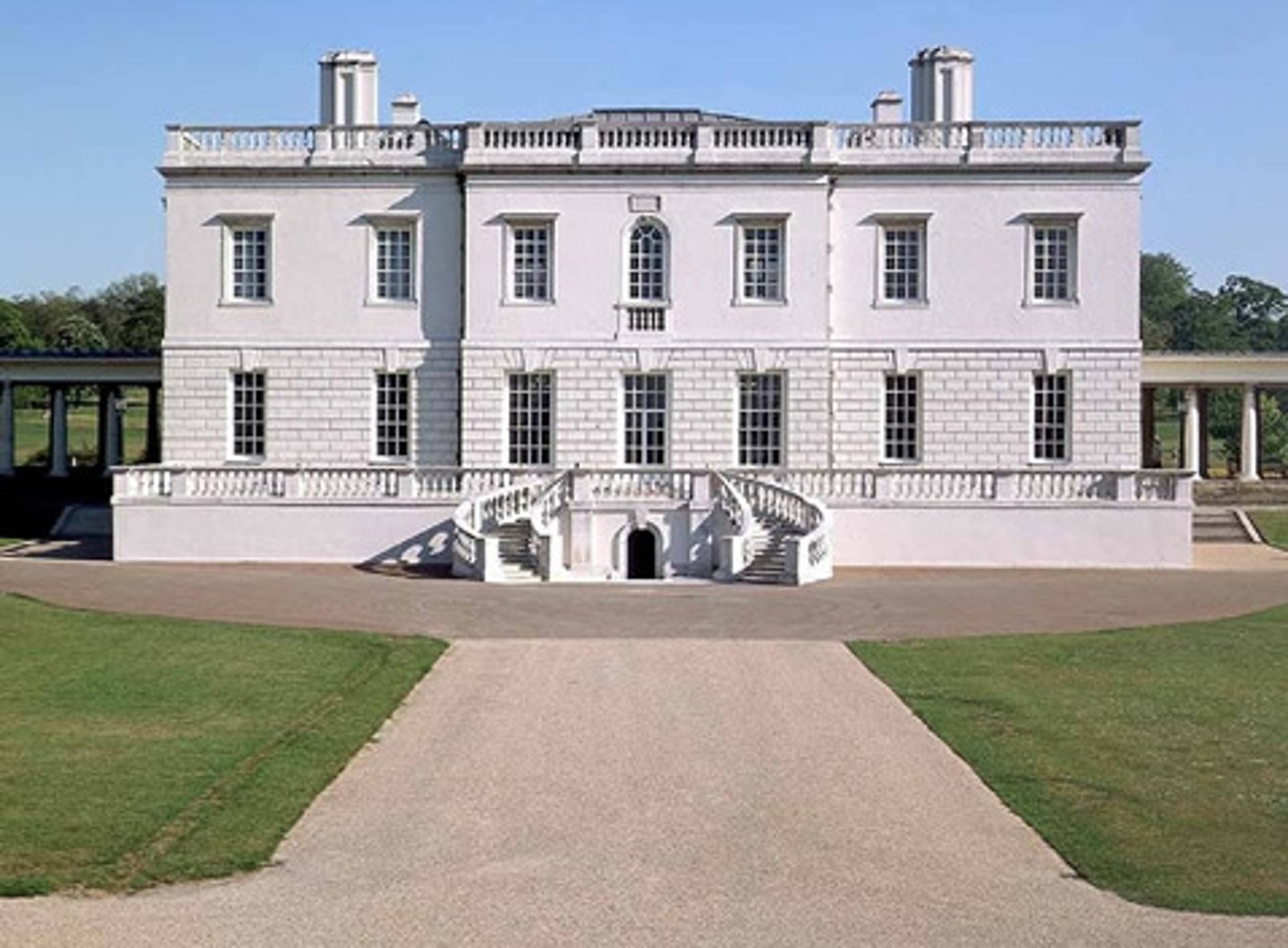

Image of the Banqueting Hall of Whitehall, London
Made by Inigo Jones

What is the Difference Between Baroque and Renaissance?
Renaissance engaged intellect, used pure forms, emphasized individual in isolation, made architecture for the wealthy, and made individual isolated buildings
Baroque engaged emotions, used illusionary effects, emphasized individuals as part of society, made architecture for all social classes, and made building designs to fit context
What is Baroque Architecture?
A style of architecture originating in Italy in the early 17th century and variously prevalent in Europe and the New World for a century and a half characterized by free and sculptural use of classical orders and ornament, dynamic opposition and interpenetration of spaces, and the dramatic combined effects of architecture, sculpting, painting, and the decorative arts
Who is Bernini and Borromini
Considered to be the Baroque of Rome. Reaffirmation of Catholic Churches after the Protestants led the Reformation. Made buildings to awe and convert. Wanted to make something greater than the individual. Wanted to reintroduce spiritual values (Counter Reformation)
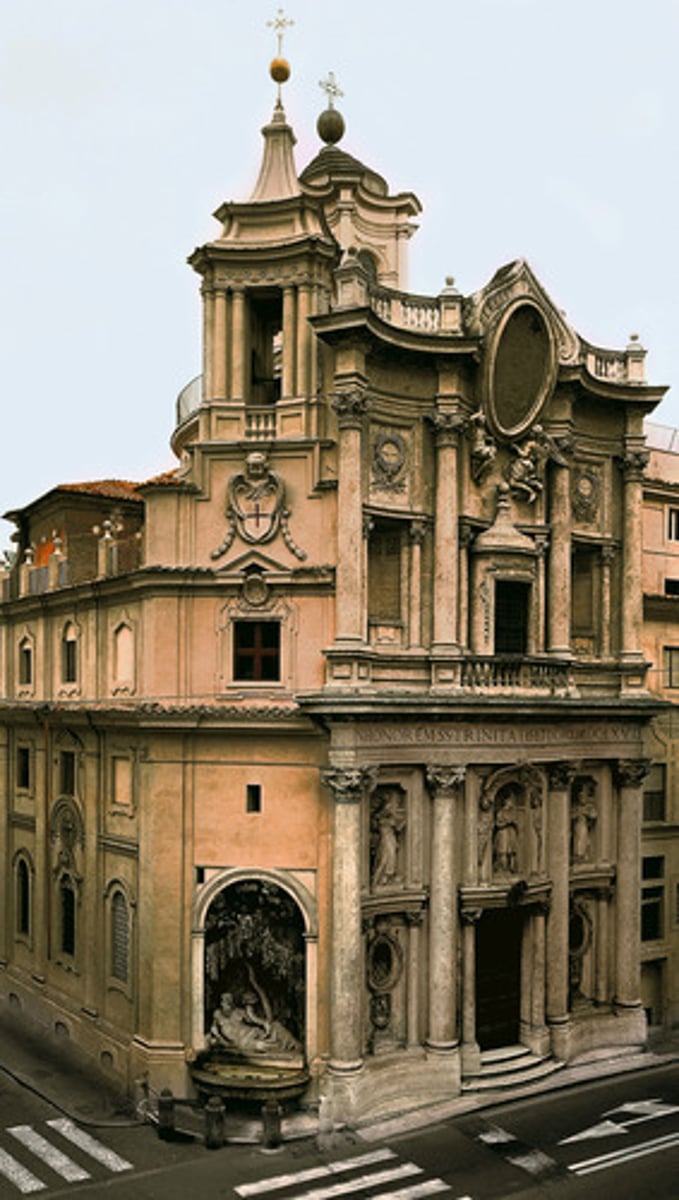
**Who Made the S. Carlo Alle Quattro Fontane in Rome?
Begun in 1634, Francesco Borromini built it. Bernini added colonnades.

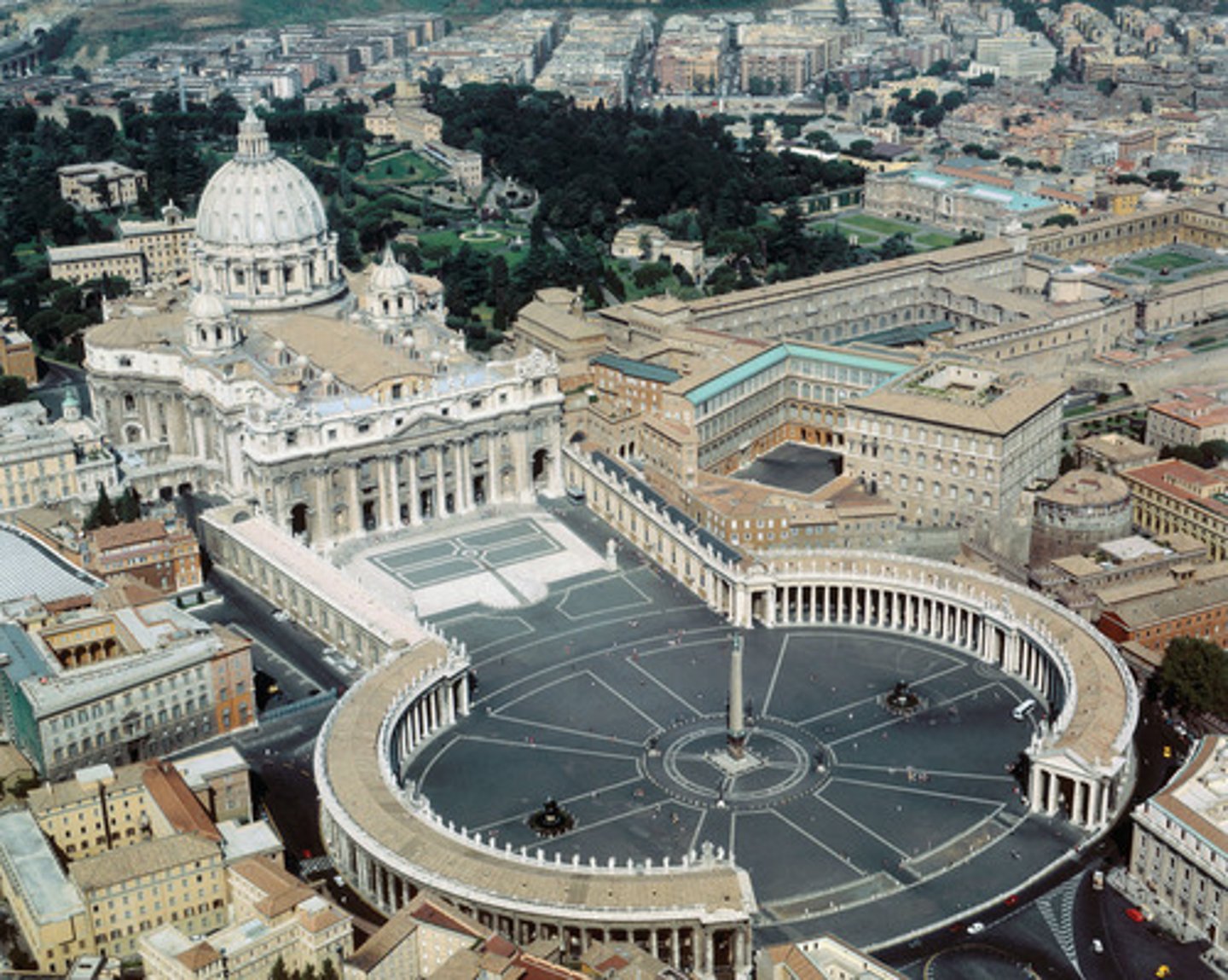
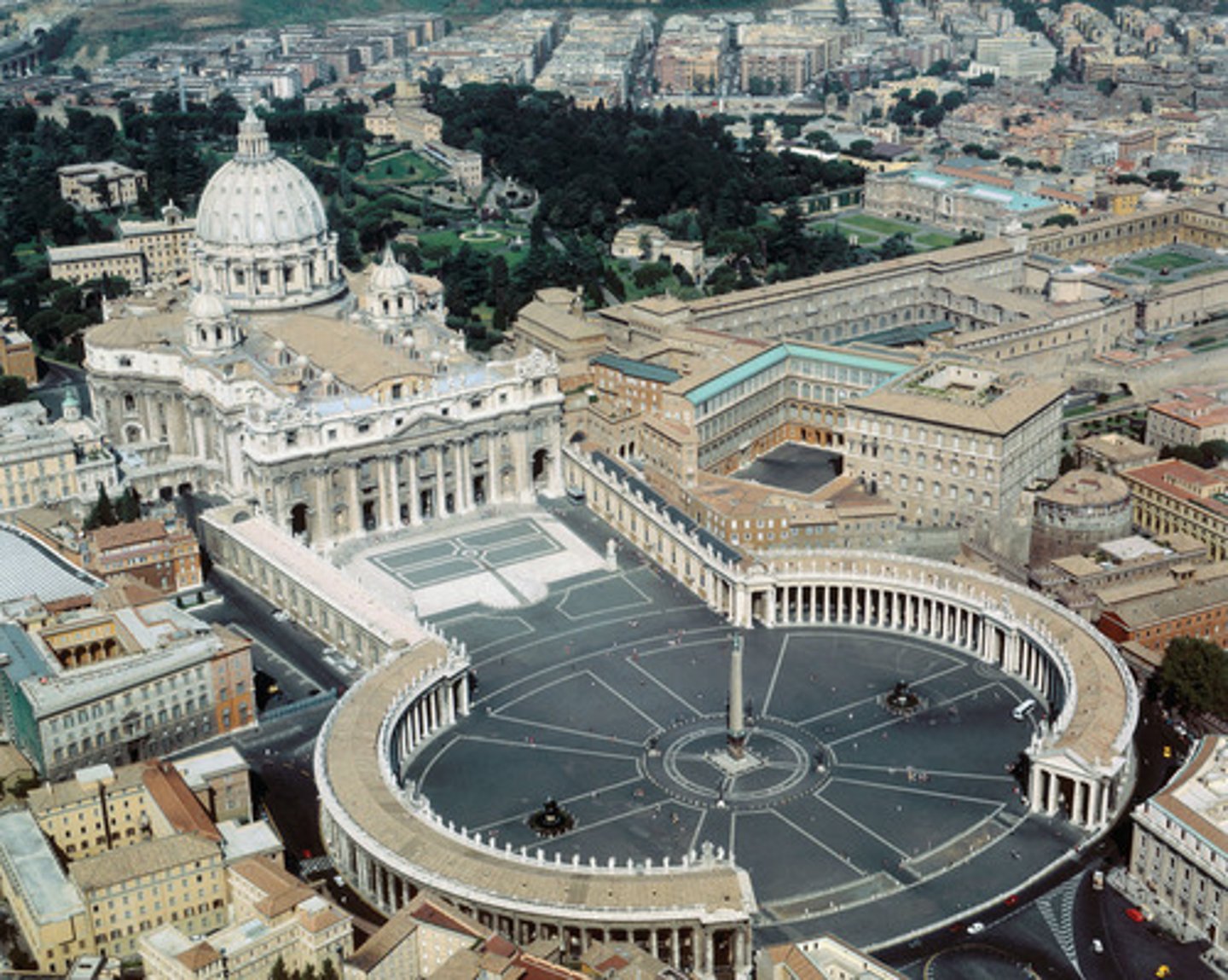
Piazza of St. Peter
Made by Gianlorenzo Bernini. Begun in 1656

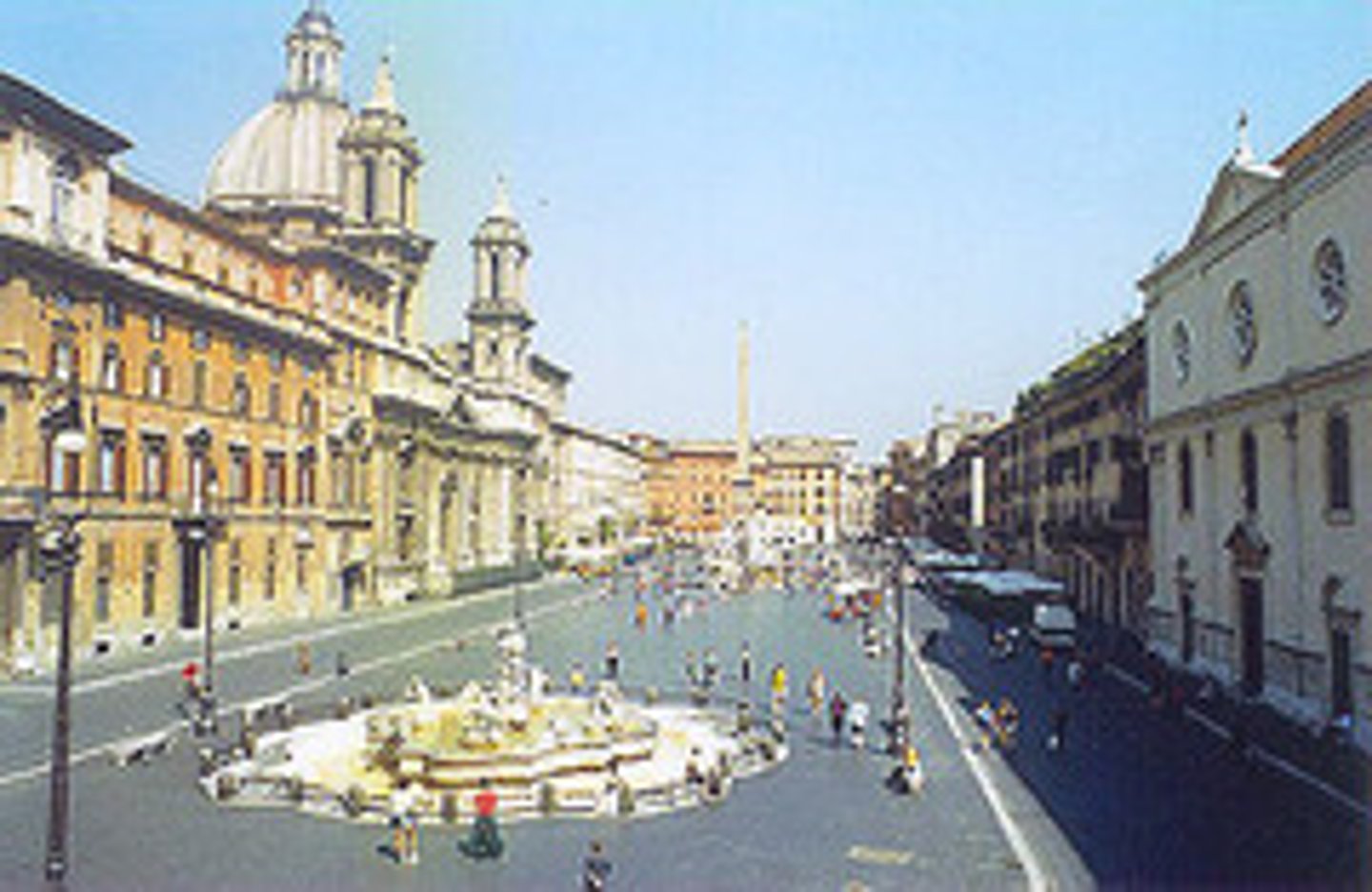
Piazza Navona, Rome
- Made by Bernini and Borromini, begun 1644
- Space dates to ancient Roman Circus

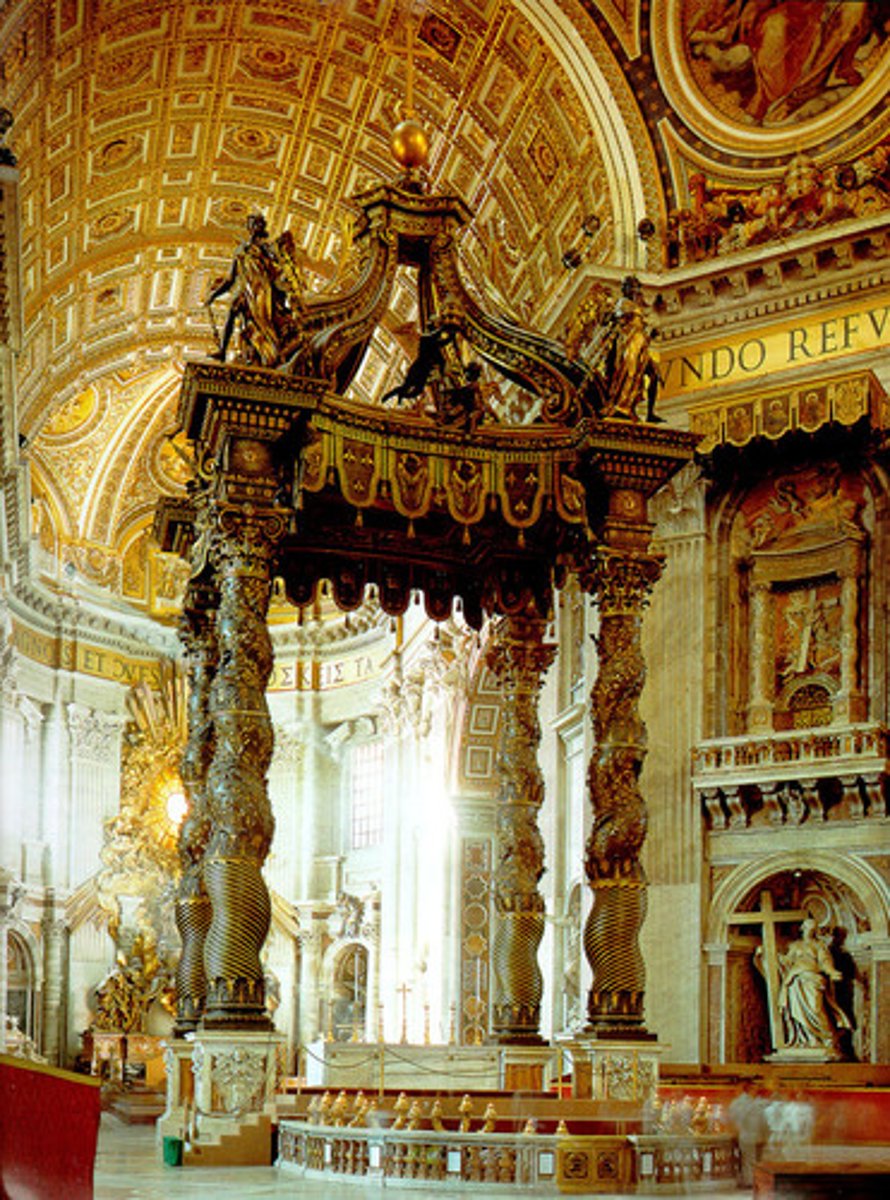
Baldacchino, St. Peter’s Rome
- Made by Bernini between 1624-1633
- Used an Aedicula

What is an Aedicula?
A canopied space intended to house a shrine or statue

What is the Fire of 1666 in London?
On September 2nd, 1666, a fire erupted and burned for three days destroying much of the city
Act of Rebuilding the City of London - example of an early building code
Sir Christopher Wren redesigned St. Paul’s Cathedral and over 50 other churches in London
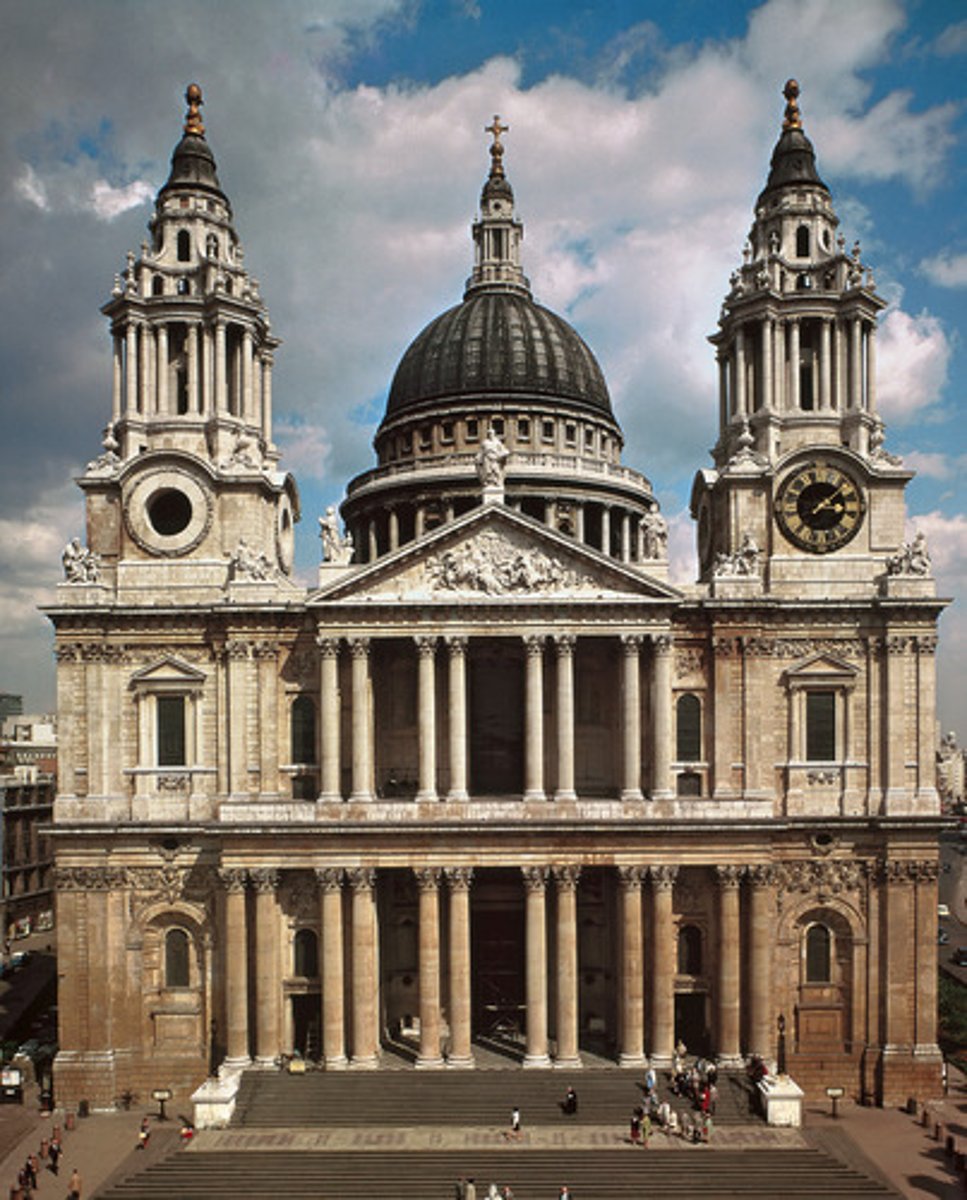
St. Paul's Cathedral, London
Made by Sir Christopher Wren between 1675-1709

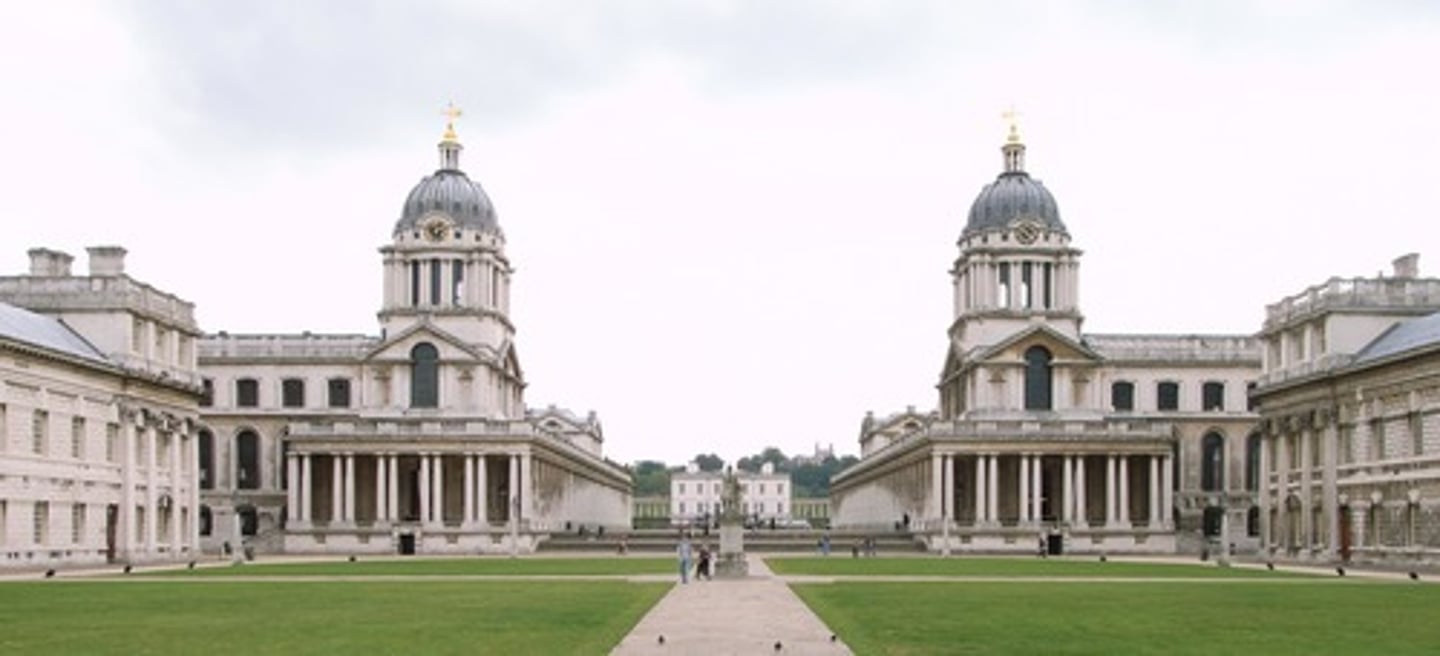
Royal Hospital in Greenwich
Made by Sir Christopher Wren between 1696-1702

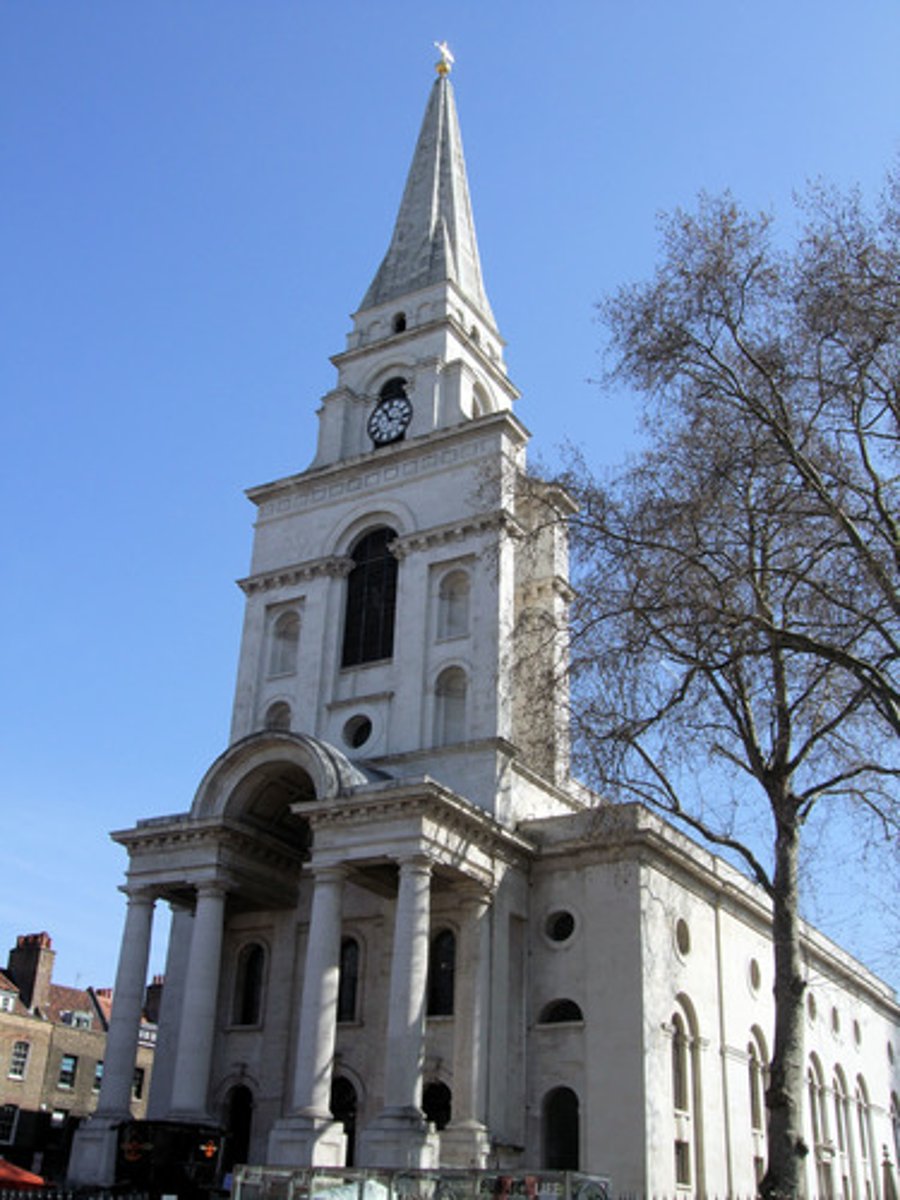
Christ Church, London
Made by Nicholas Hawksmoor between 1714-1729

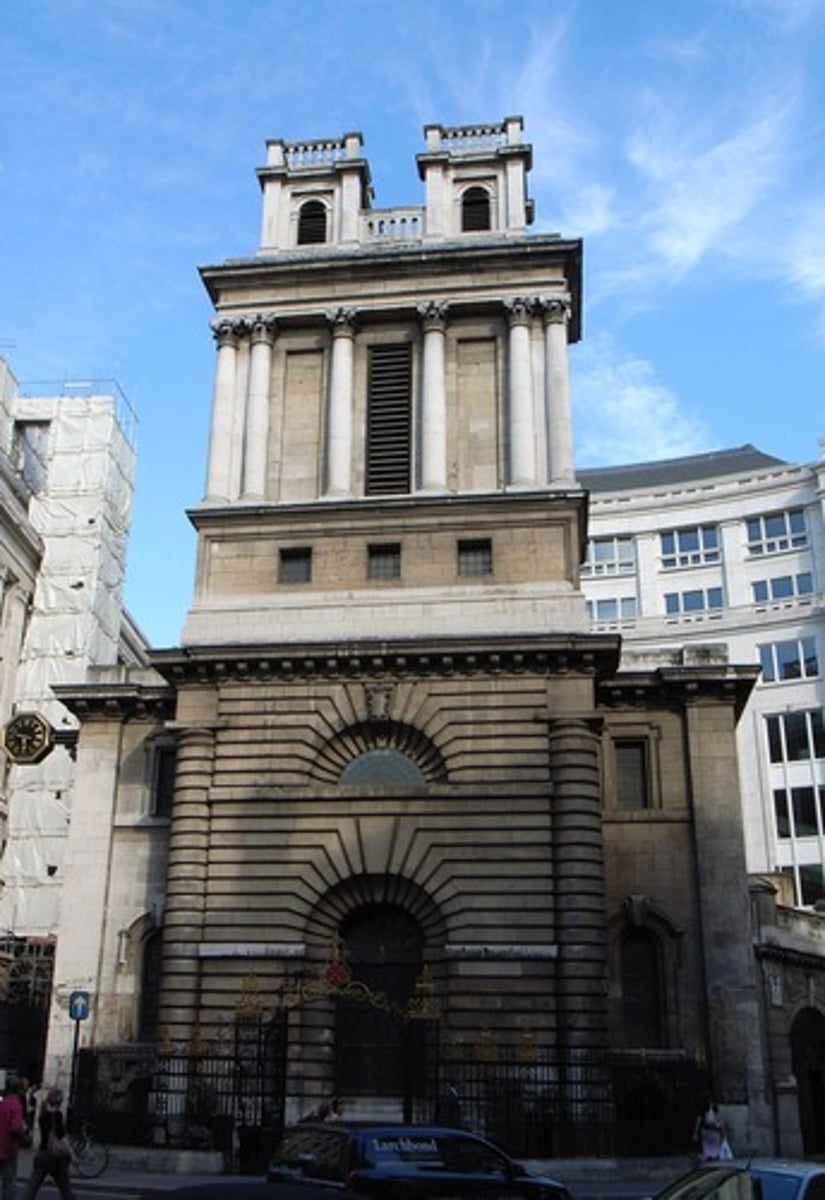
St. Mary Woolnoth, London
Made by Nicholas Hawksmoor between 1716-1724

Versailles
Located outside of Paris, France. Made by Baroque, which began in 1661. Louis 14th was a hunting lodge
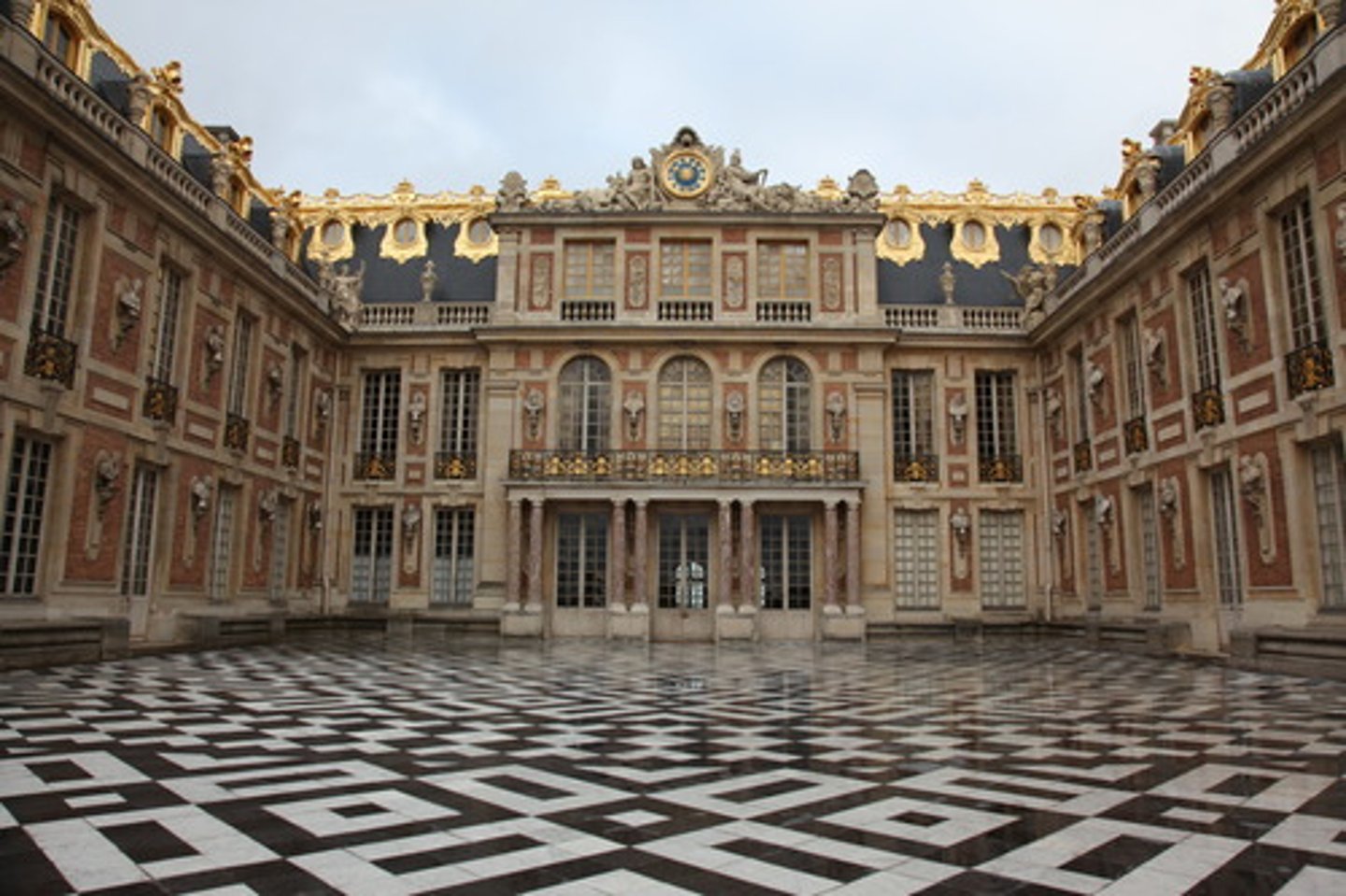

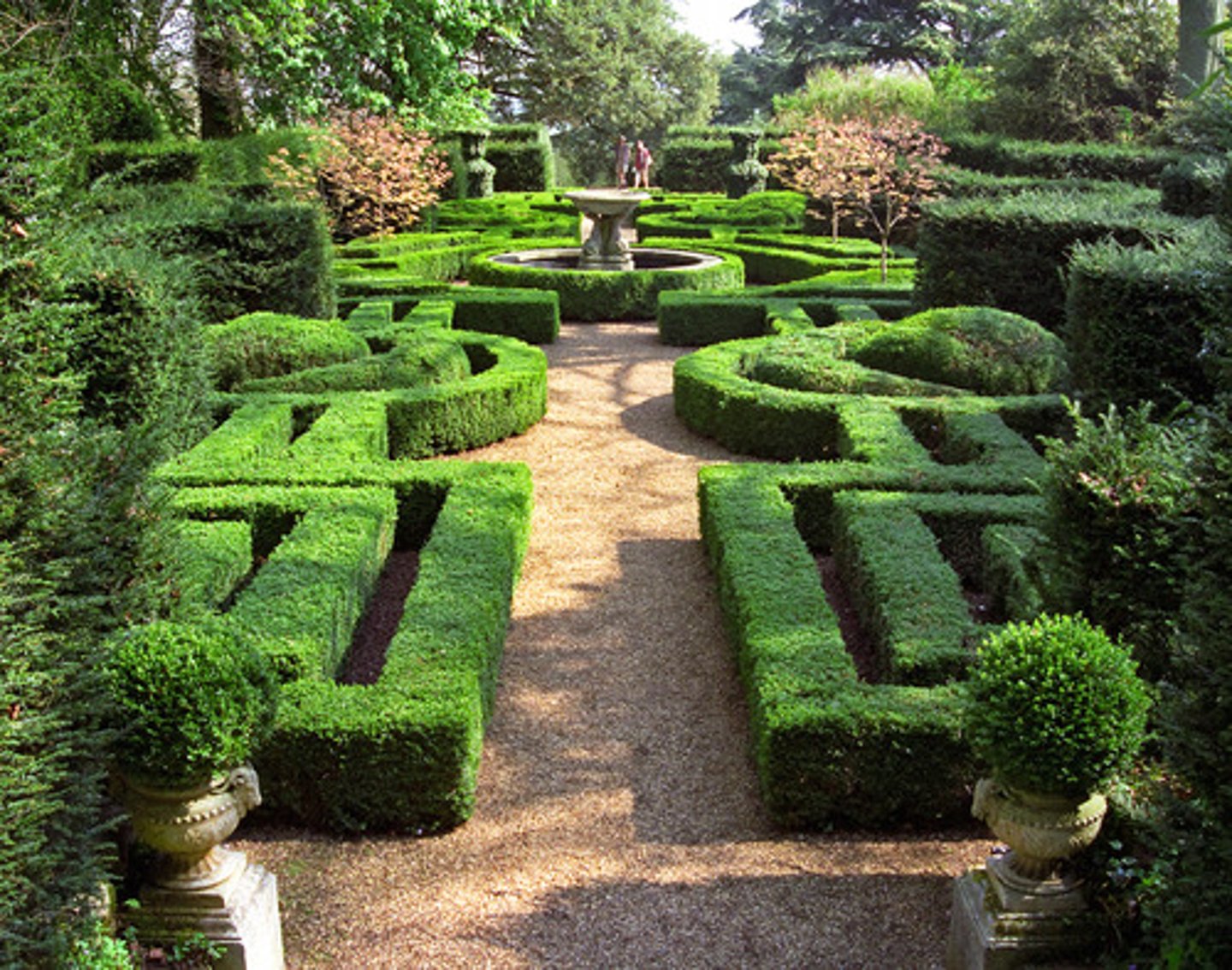
What is a Parterre?
Gardens that are geometrically organized. Extended baroque design of palace rooms into the landscape. Consisted of vegetation that is exotic to the region.

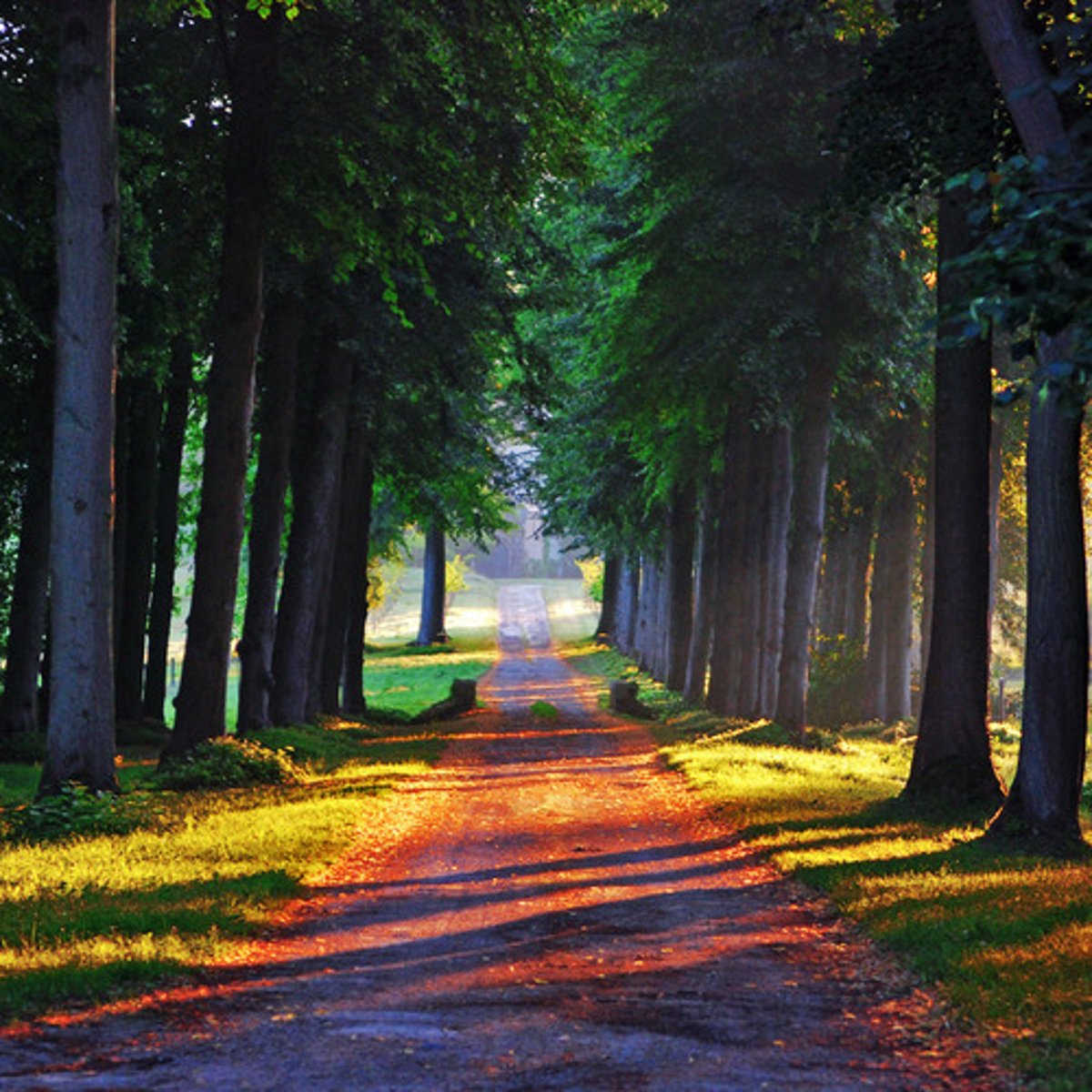
What are Allees?
A pathway lined with trees

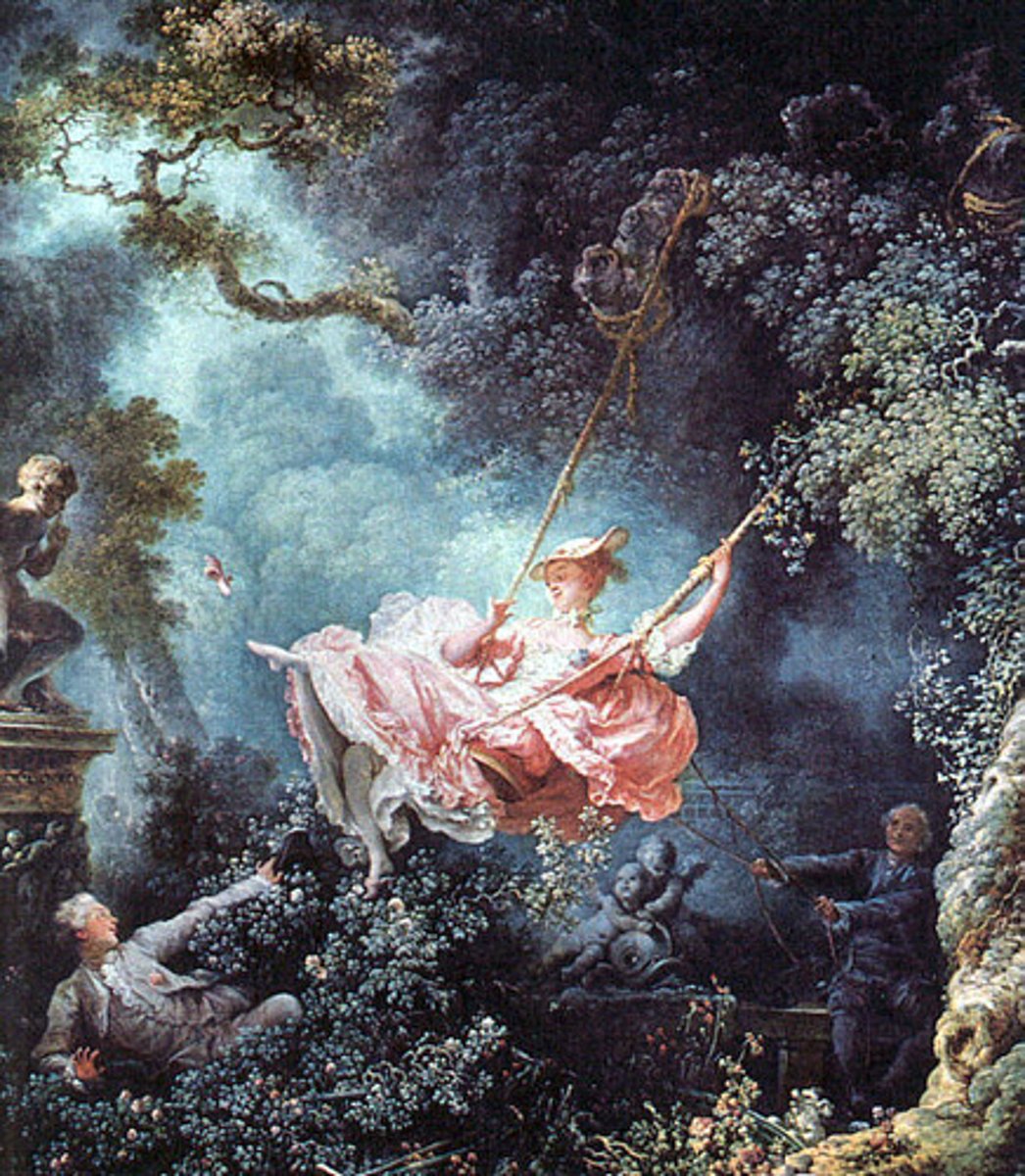
What is a Rococo?
A style of decorative art that evolved from the Baroque, originating in France about 1720 and distinguished by fanciful, curved spatial forms and elaborate, profuse designs of shellwork and foliage intended for a delicate overall effect

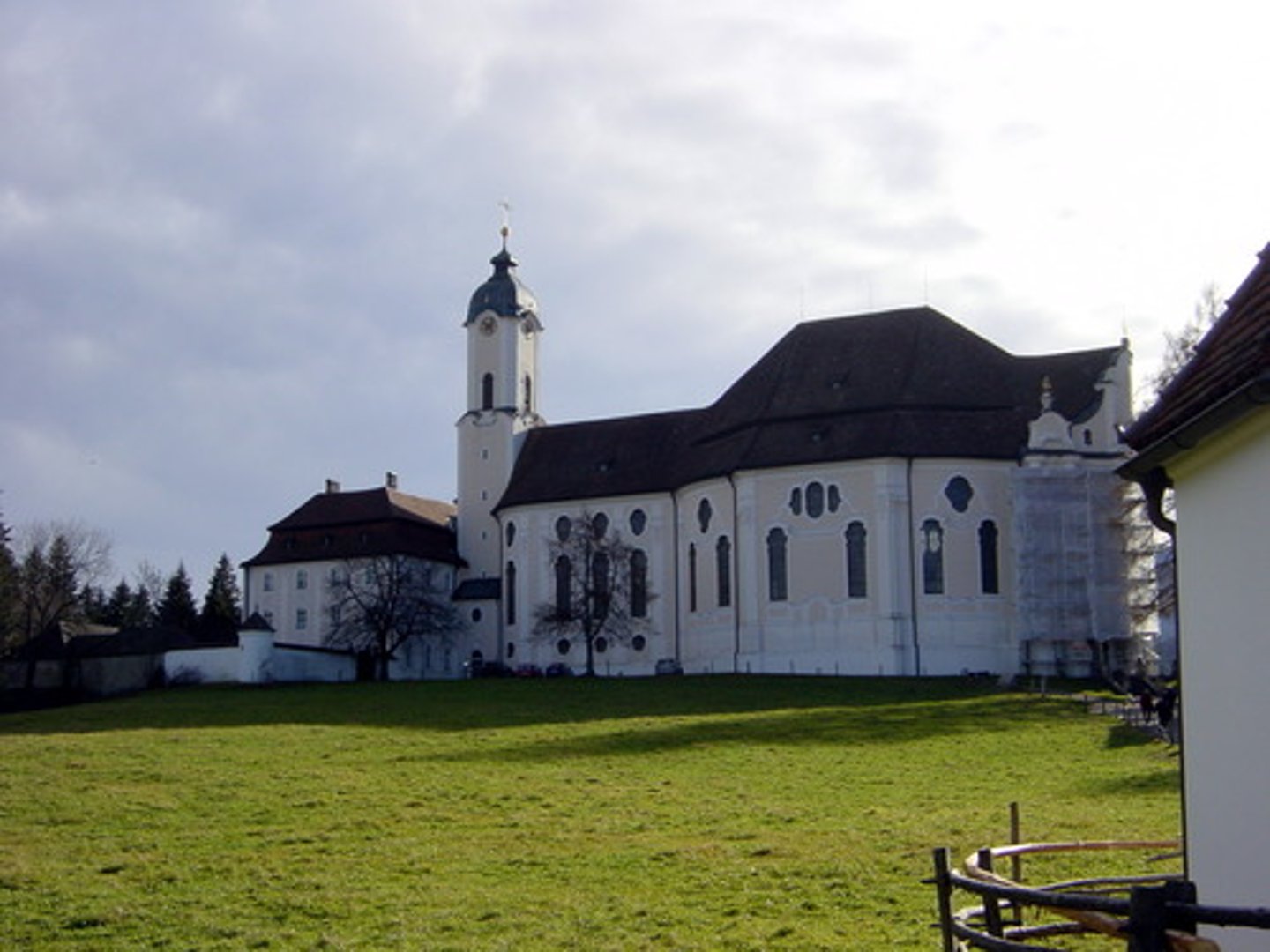
What is the Die Wies
A church in rural Bavaria, which is a Zimmerman Brothers design

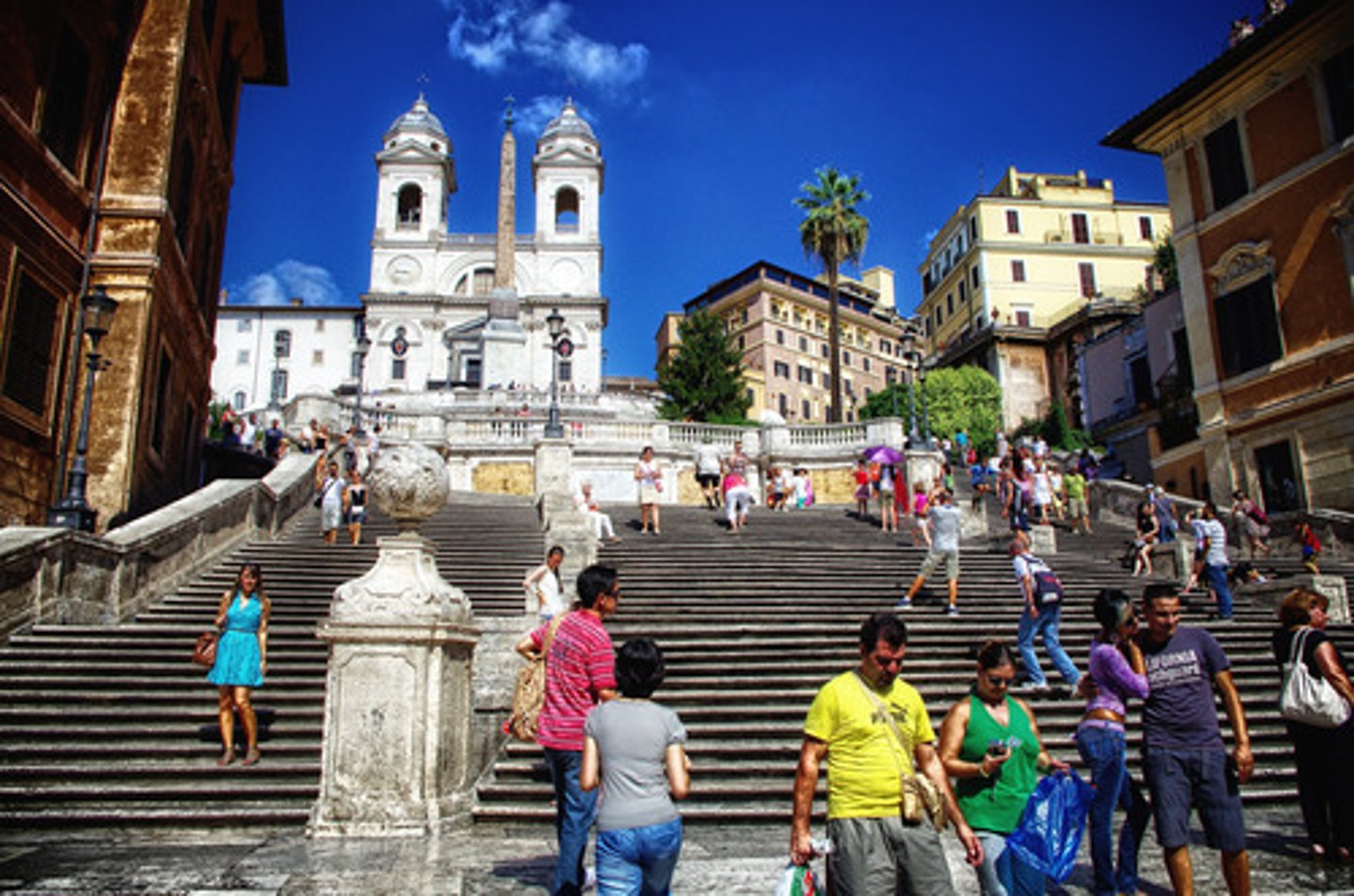
Spanish Steps, Rome
Built between 1723-1725

Industrial Revolution
Where the middle class emerges and cast iron is used as a building material
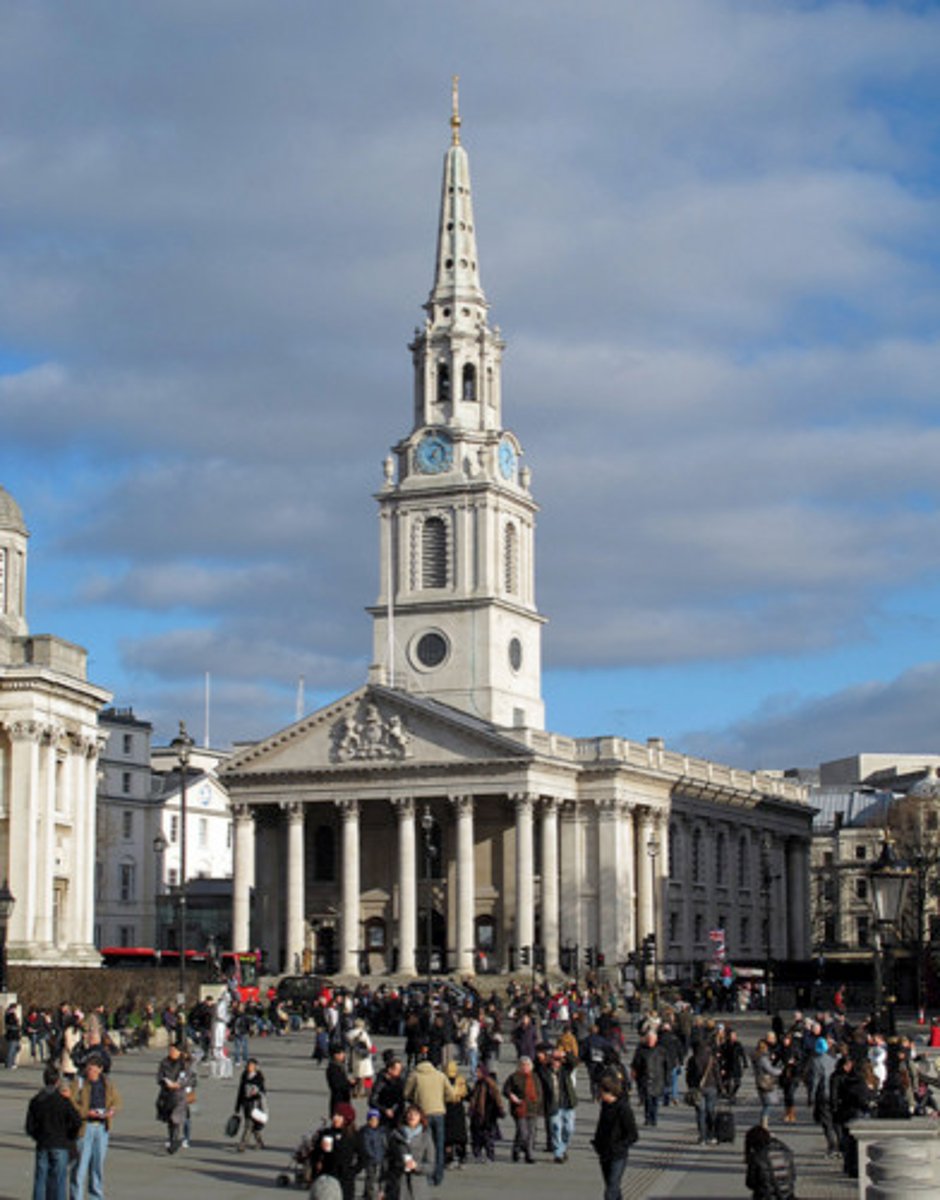
**St. Martin-in-the-Field
Made between 1722-1726 by James Gibbs whose design was copied throughout the US

What is the Federal Style?
Developed after the American Revolution (1780-1820). Copied from British architect Robert Adam (1728-1792)
Details: ellipse, circle in plan and elevation

Who is Benjamin Latrobe
An emigrating architect to the United States that is from London in 1796 and was acknowledged as the first professional architect
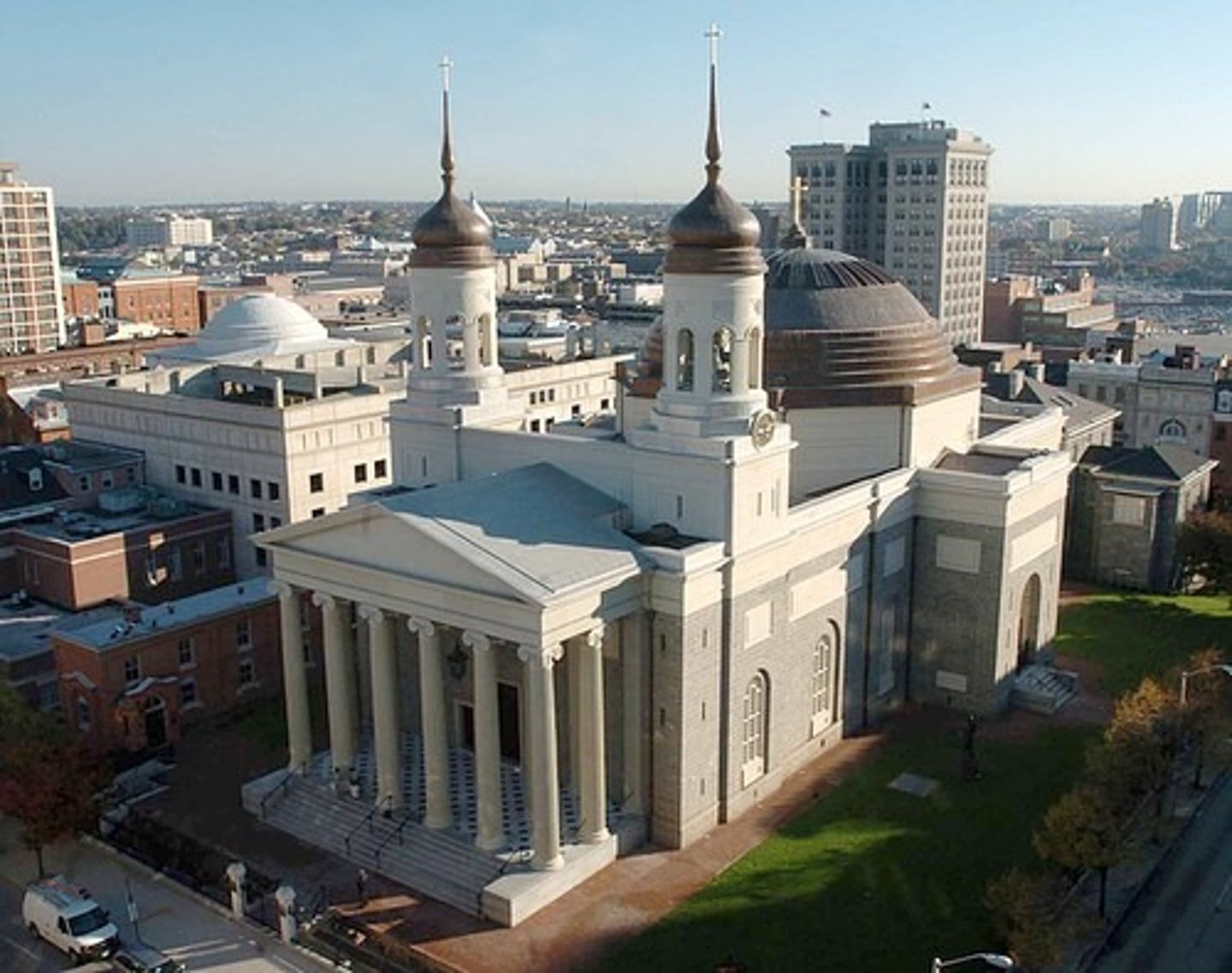
The Baltimore Cathedral
Based on work of John Soane which has vaults and domes

Who is Pierre Charles L’Enfant?
Designed plan of Washington DC
Social Class and Architecture
- 1700s
- Aspiring architects traveled west
- Sketched, took visual notes
- Used ancient Roman Greek architecture as motivation for architecture of their own time
Greek Revival Style
- Tennessee State Capital in Nashville, TN
- William Strickland (1845-1859)
- Stanton Hall in Natchez, MS (1857-1858)
- Minard Lefever - Asher Benjamin
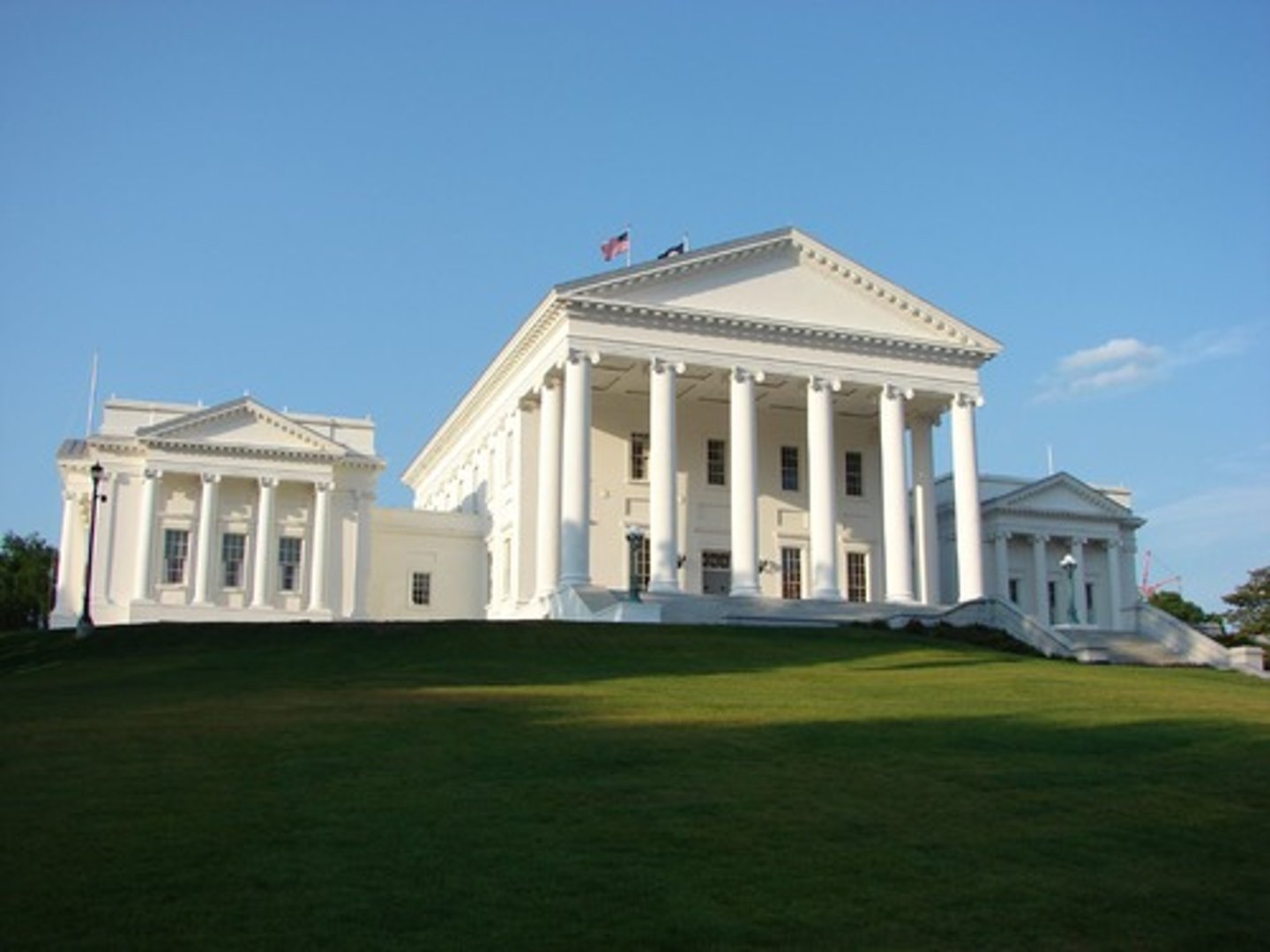
The Virginia State Capitol
Made by Thomas Jefferson between 1785-1789

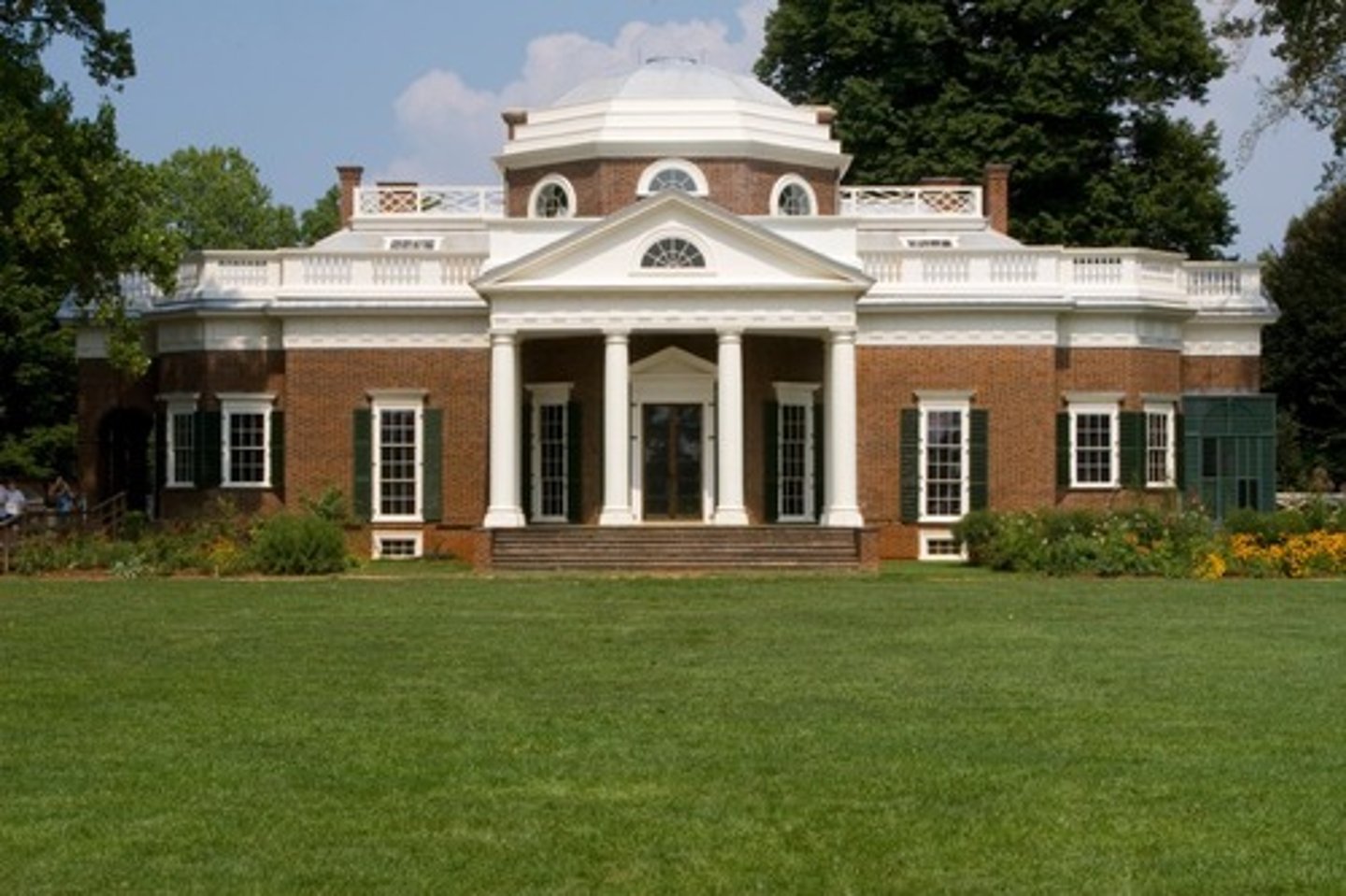
The Monticello
Made by Thomas Jefferson in 1770

University of Virginia
Made by Thomas Jefferson between 1817-1826
What is the Ecole des Beaux-Arts?
Established in Paris and was established in 1700. Educated Europeans through the 20th Century. Taught grand symbolic designs and gave academic, office, and construction site experience. Students work for national and municipal agencies. United State architecture schools are based upon this tradition.

Who is Charles-Nicolas Ledoux?
From 1736-1806 and believed that form speaks of function
Who is Viollet-le-Due?
He is the leading proponent of the Gothic Revival in France
What does the Term "Sublime Beauty" Mean?
"Sublime beauty" is a term coined by philosopher Edmund Burke in 1757
What is Romanticism?
goal to achieve sublime beauty
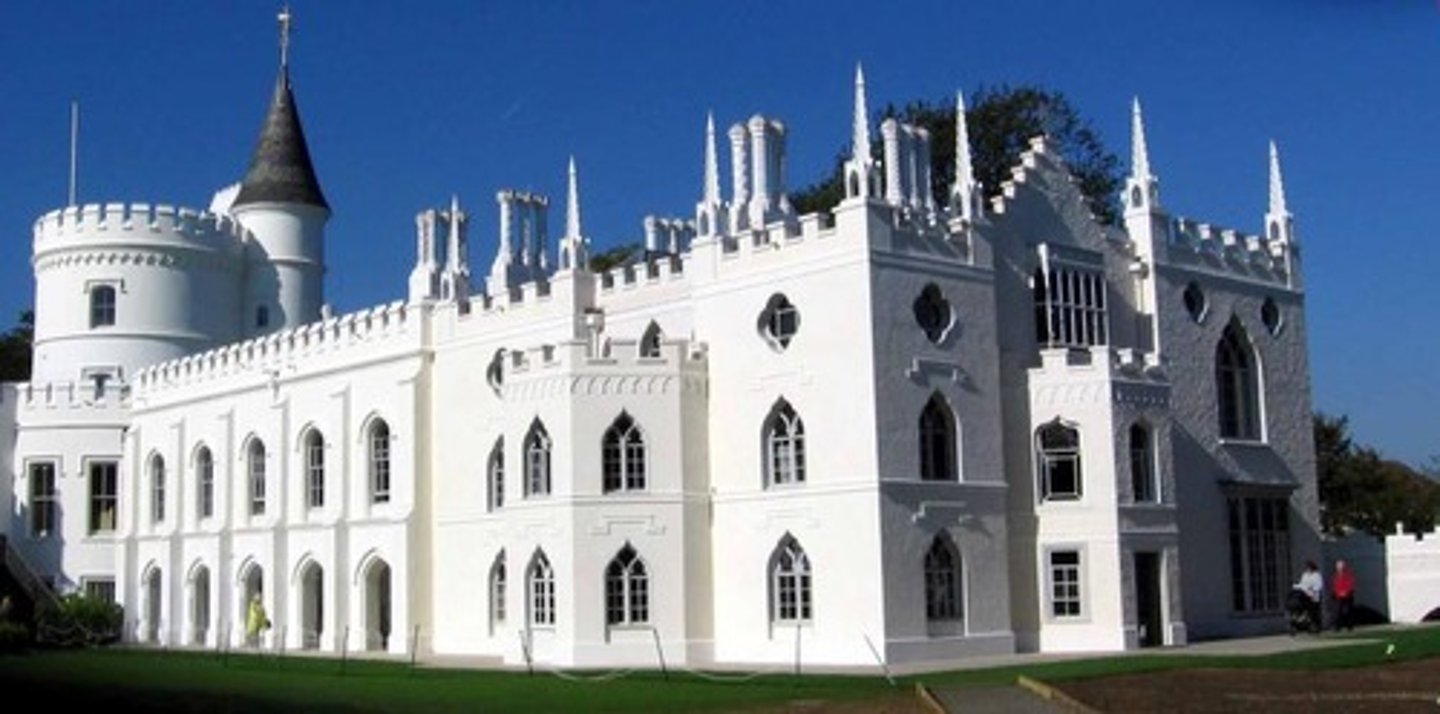
An Example of Gothic Revival is the _____________
Strawberry Hill
Image of Strawberry Hill

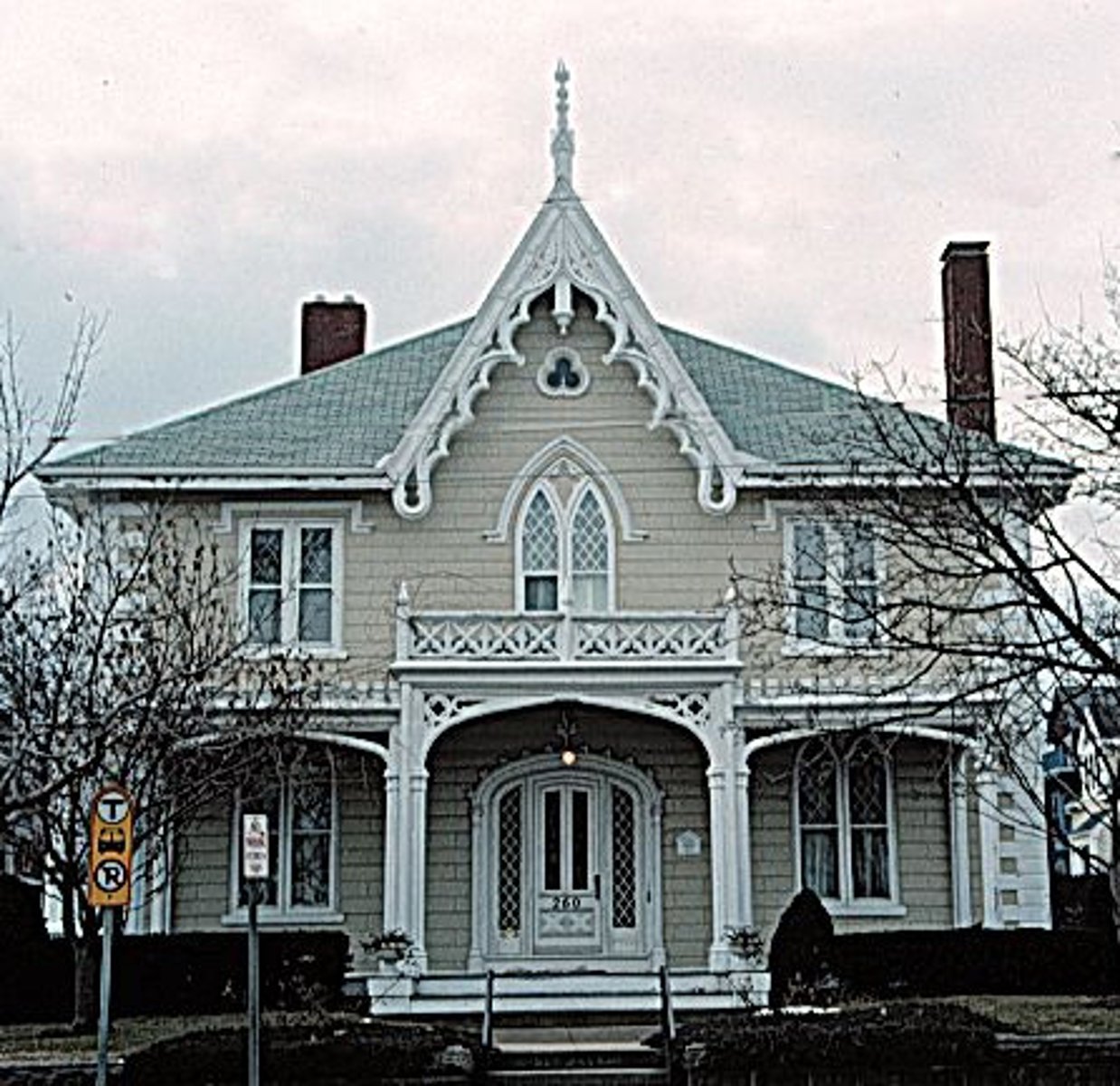
Carpenter Gothic

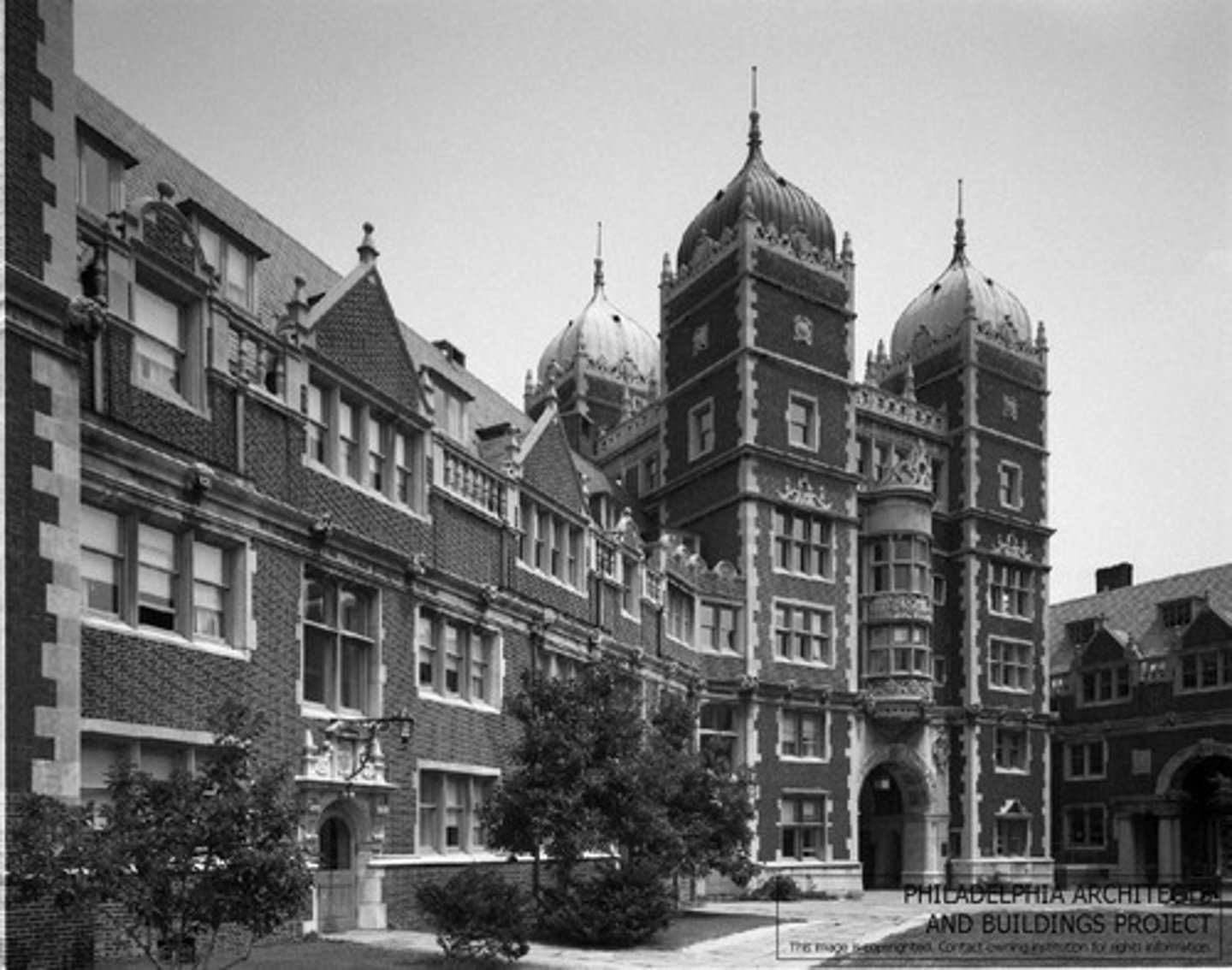
Collegiate Gothic

What is Picturesque?
Establishing a naturalistic feeling through irregular, asymmetrical compositions of building elements
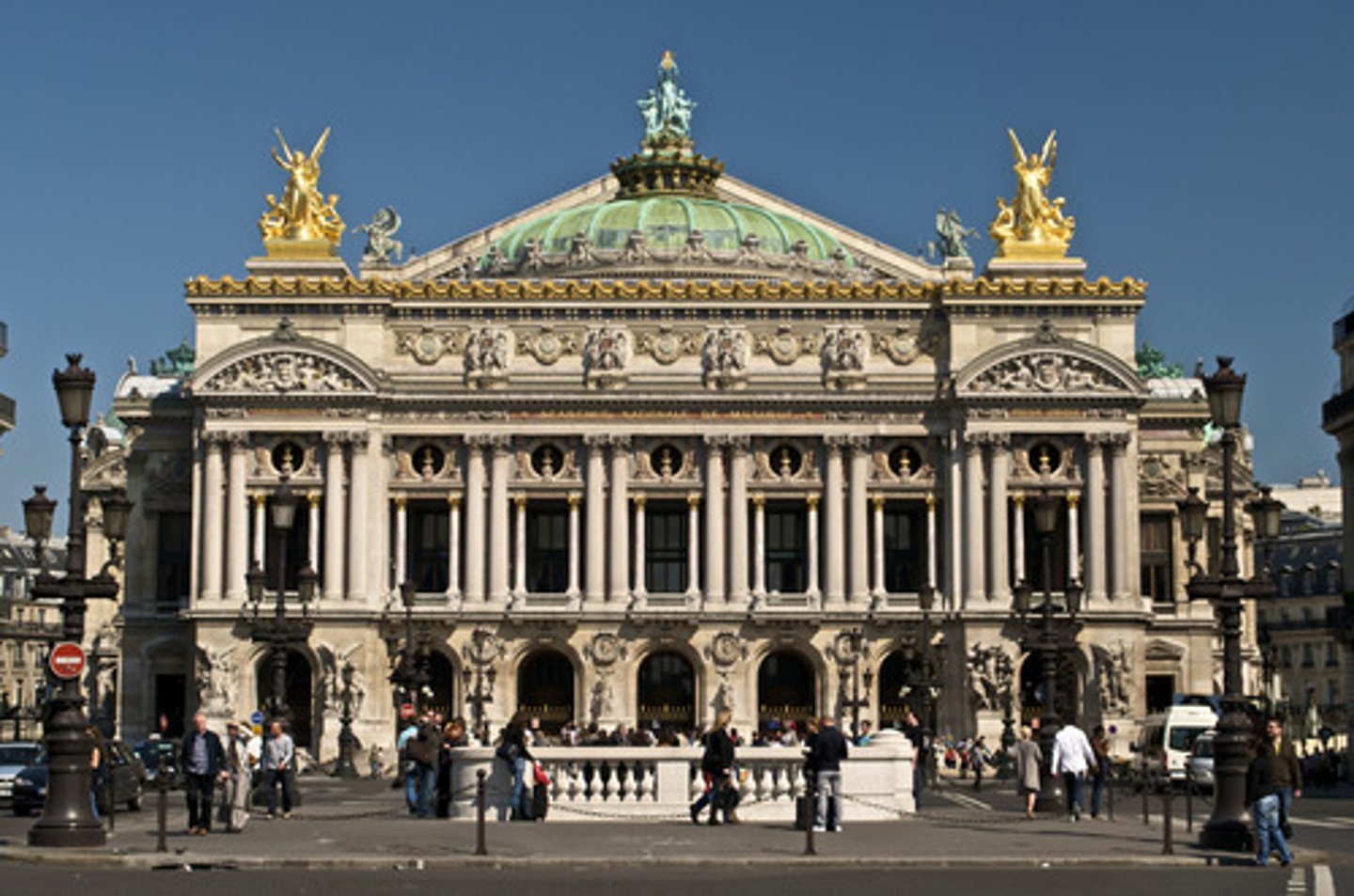
The Paris Opera House
Designed by Charles Garner who designed the building into a balanced hierarchy of spatial elements

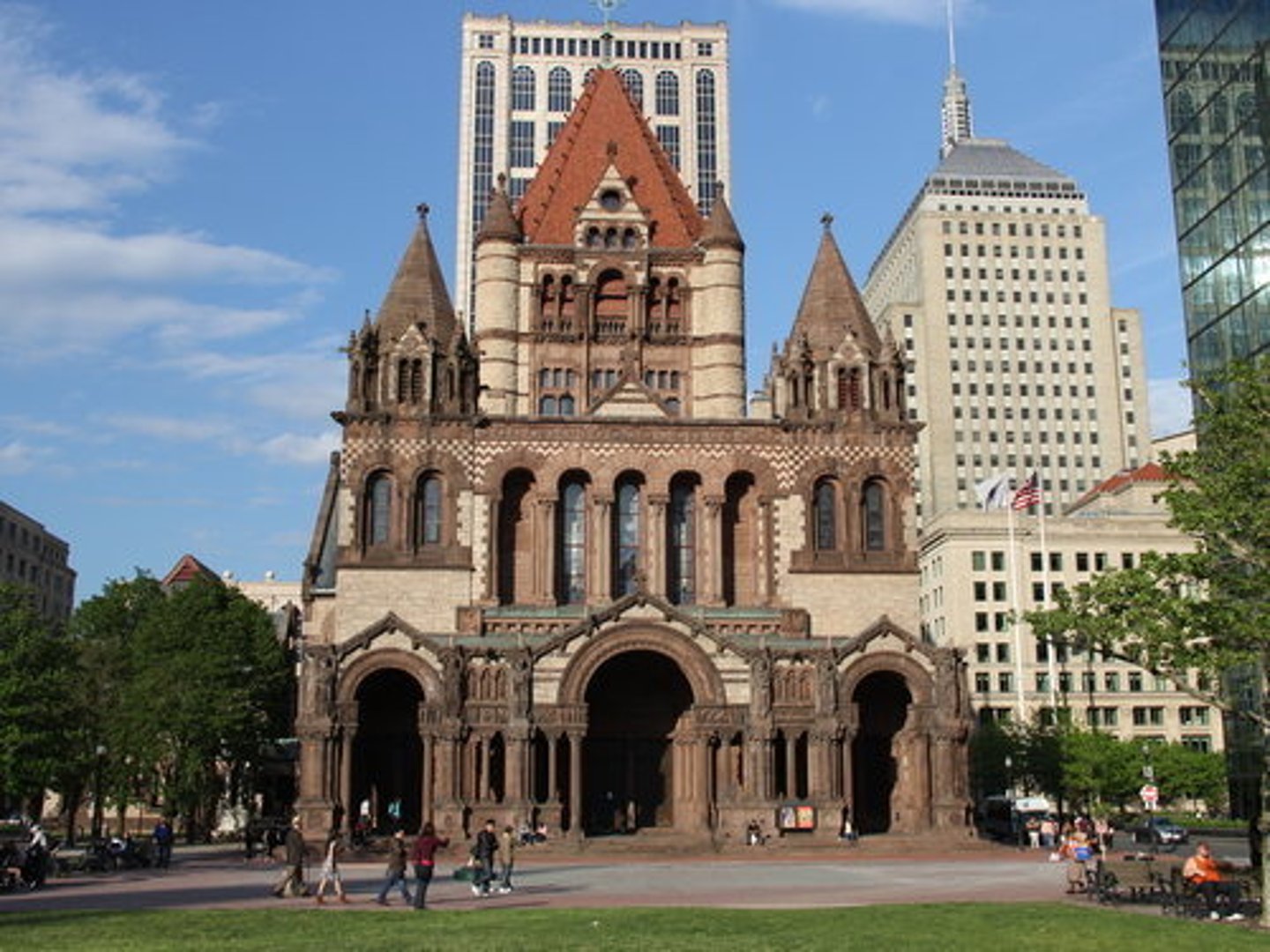
Who is Henry Hobson Richardson?
From Boston, he created the Trinity Church between 1872-1877
Image of Trinity Church
Created by H.H. Hobson between 1872-1877

What New Developments are from the 19th Century?
- Industrialization
- Urbanization
- Beginnings of “global” marketplace of goods, ideas
- Architects slow to embrace industrial materials
- DEBATE: historical styles vs new forms
- New building materials (cast iron, wrought iron, glass, steel) in industrial quantities
- Crowding cities - infrastructure problems
- NATIONALISM - want to establish identity through architecture using historical references
What are the Advances in Science and Construction During the 19th Century?
- Steel manufacturing
- Electricity and oil refining
- “People moving” - mass transit, elevators
How did Engineers Change Role of Architecture in the 19th Century?
- Engineering Design advanced structures
- Push limits of metal and glass
- Designed strong efficient structures
True or False: Were Buildings in the 19th Century the Largest since Roman Times?
True
What New Building Designs were Created in the 19th Century?
Railroad stations, covered public markets, asylums for mentally ill, housing for the industrial working class, libraries, universities, etc.
The Crystal Palace
Designed by Joseph Paxton (1851); For World's Fair, London
Critics and architects HATED IT because there were no historical references nor any decorations
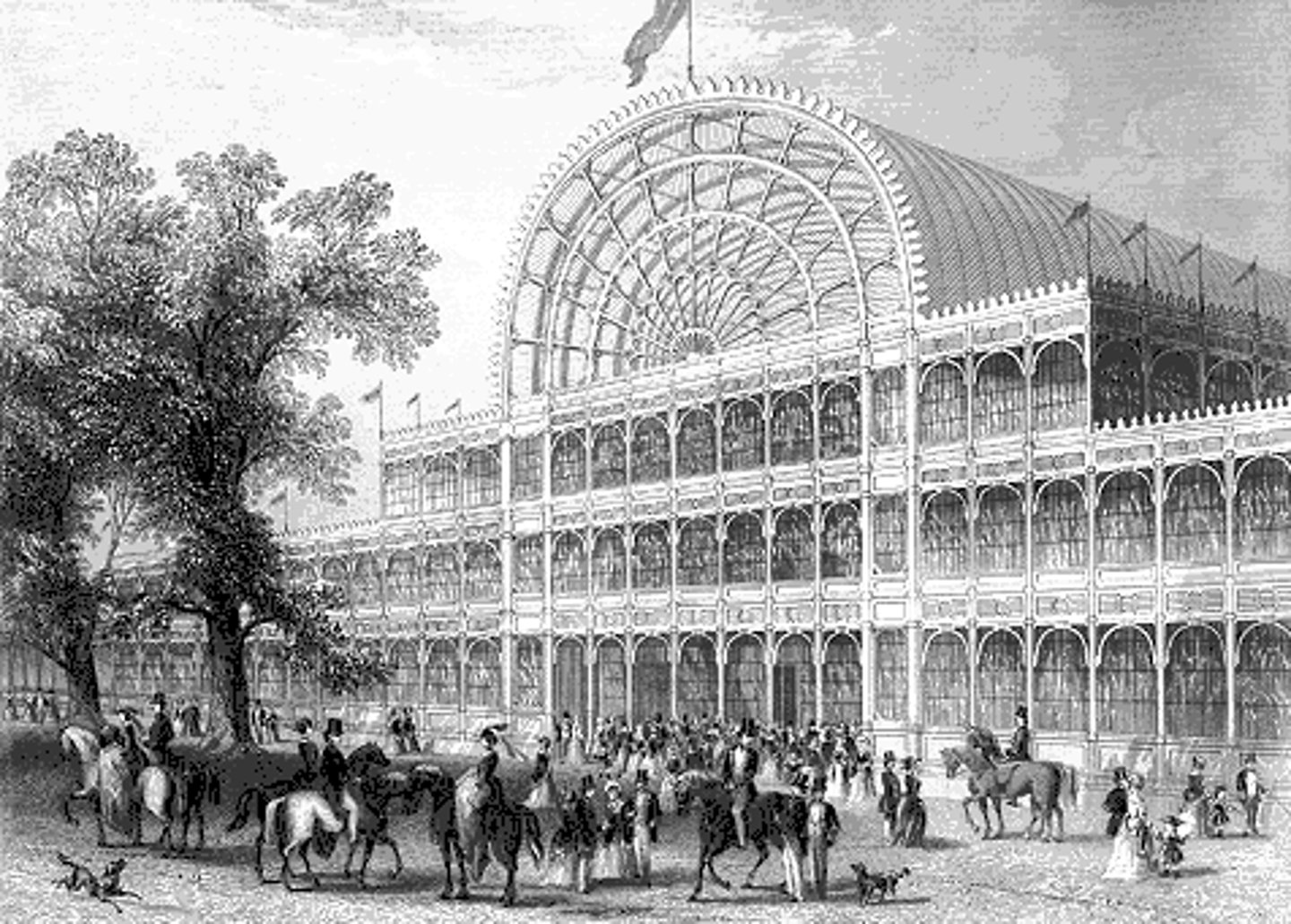

Who was Joseph Paxton?
Joseph Paxton was a horticulturalist - designed a “greenhouse” made of modular parts that could be disassembled and reassembled. Standardized, made from industrial manufacturing processes
What is the Brooklyn Bridge?
Designed by John Augustus Roebling between 1869-1883. It is a suspension bridge that uses tension

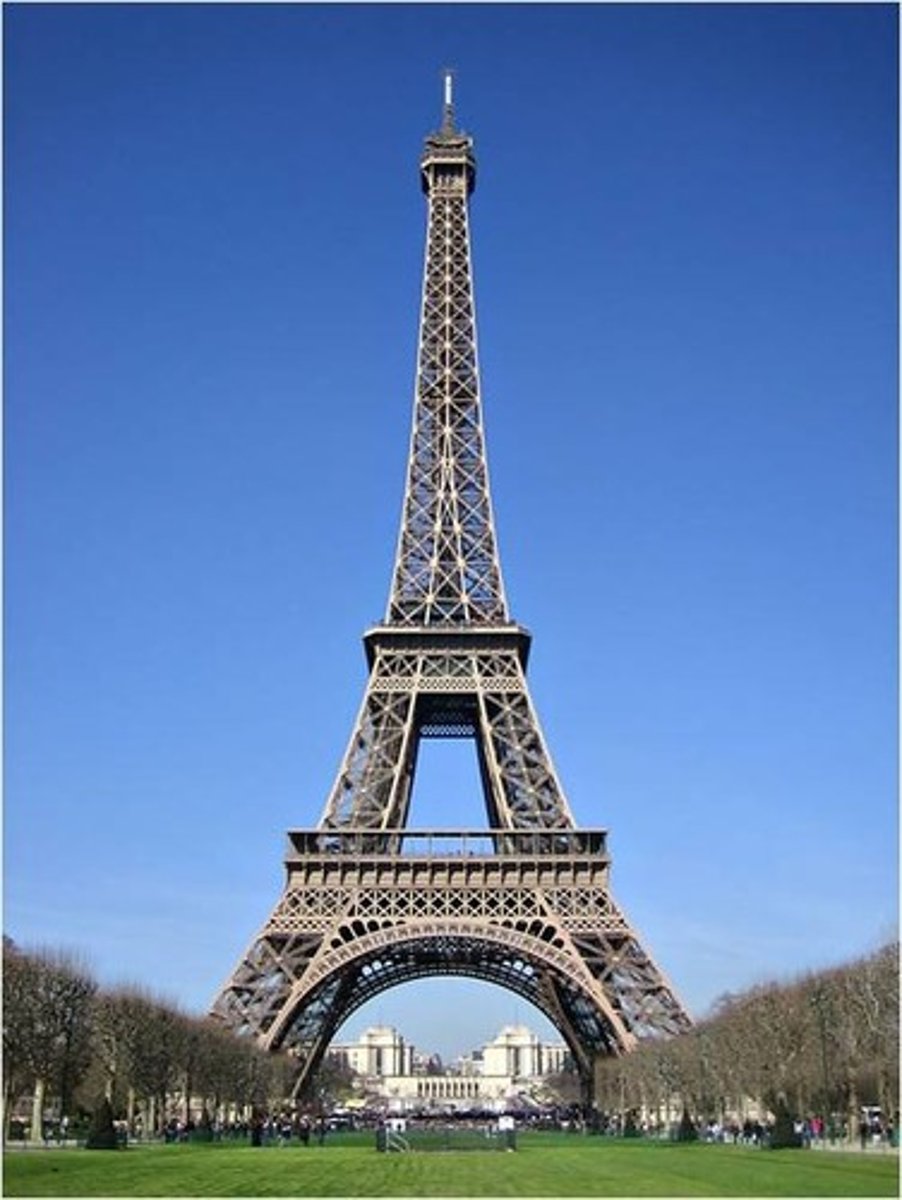
Who is Gustave Eiffel?
Constructed the Eiffel Tower in Paris in 1885. Constructed it with Iron

Why is Chicago so Important?
- Forefront of American architecture
- 1871 fire
- CHICAGO SCHOOL of architects
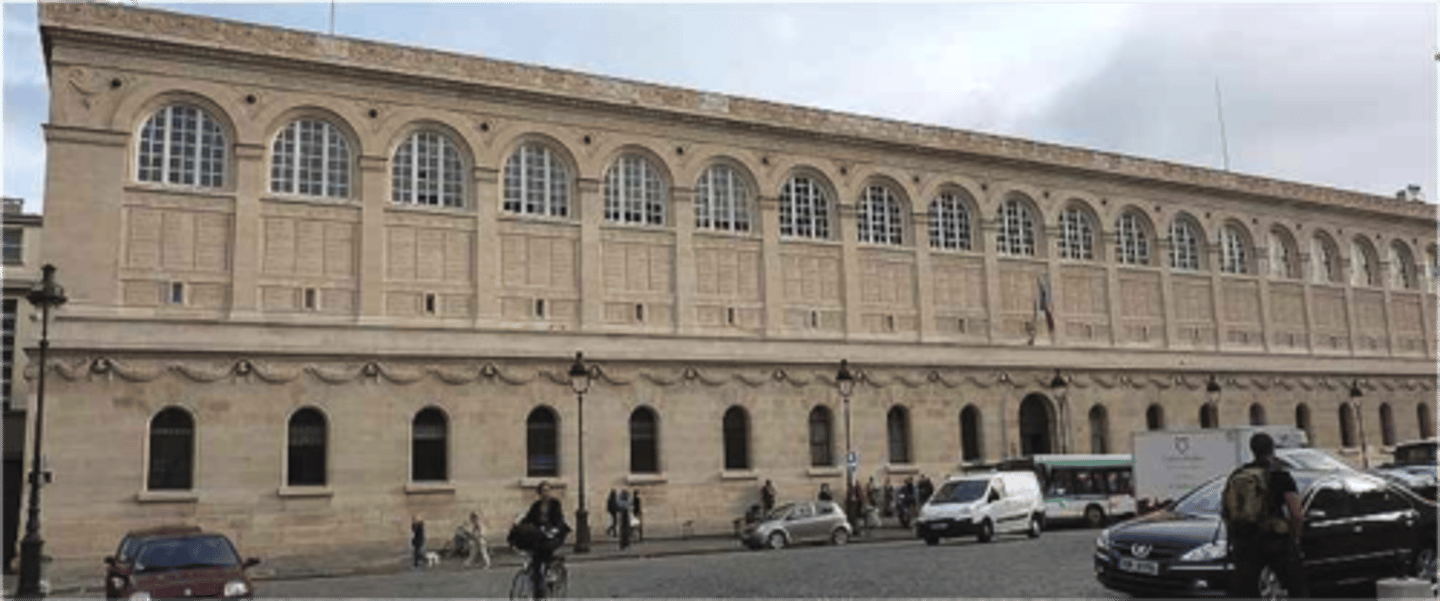
Who was Henri Labrouste?
Constructed the Bibliotheque Ste. Genevieve in Paris between 1842-1850. It was a symbolic train station and shaped cast iron into columns and arches supported the vaults and domes
Image of the Bibliotheque Ste. Genevieve in Paris
Made by Henri Labrouste between 1842-1850

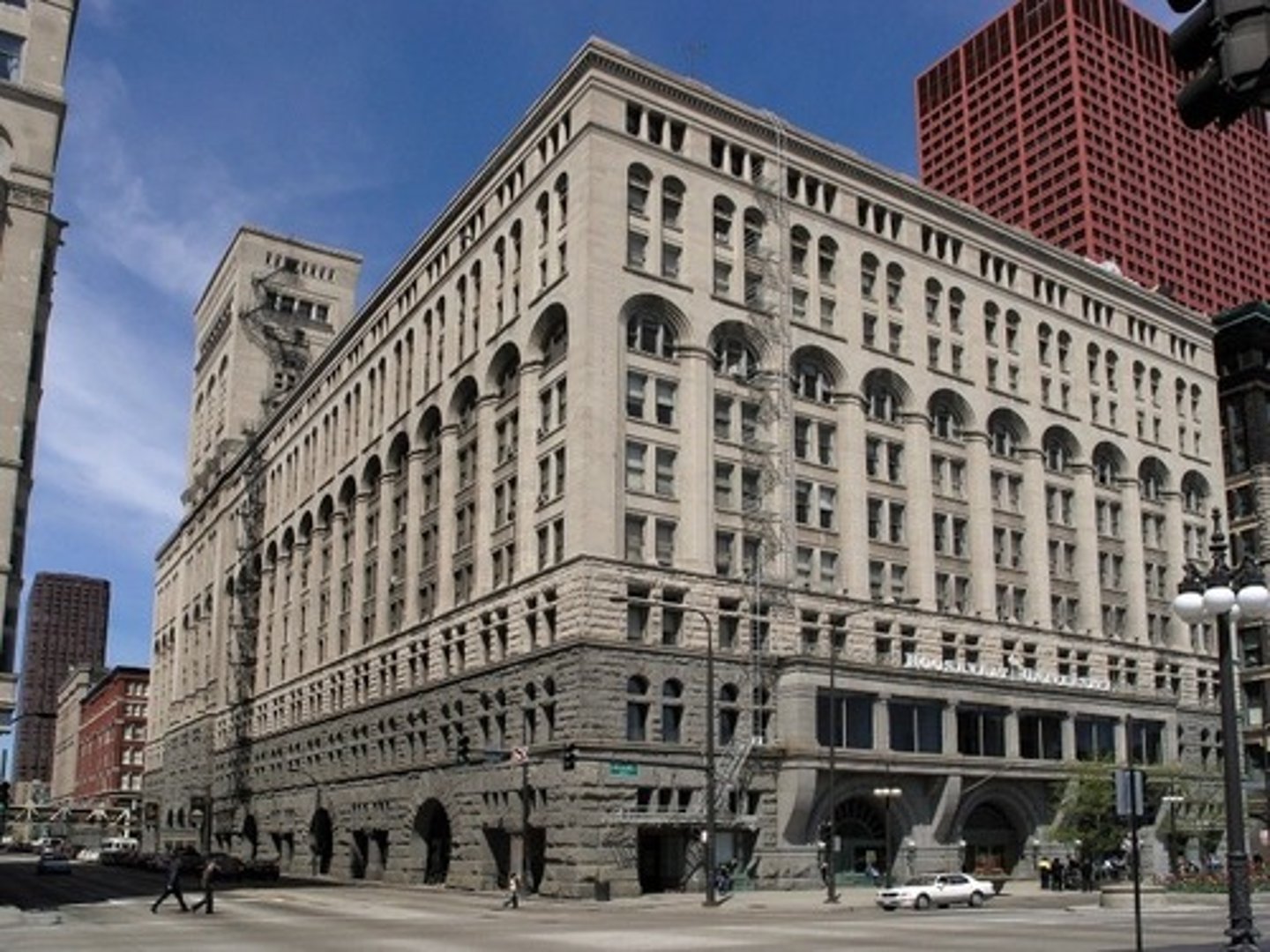
Who was Louis Sullivan?
Constructed the Chicago Opera House to celebrate and express verticality in high rises. The Chicago Opera House uses light curtain wall material and expresses 3 zones on facade
Image of the Chicago Opera House

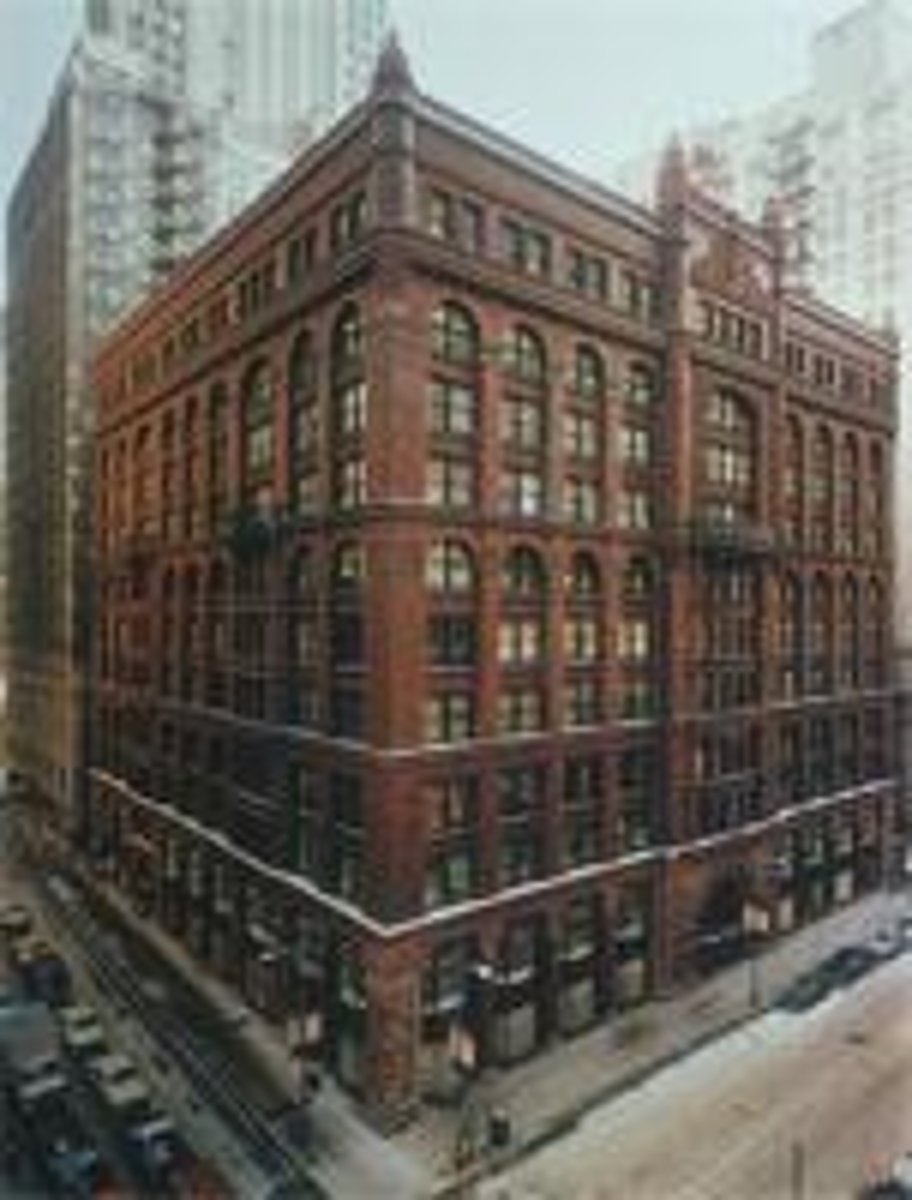
**Who were Burnham and Root?
Created the Rookery in Chicago
**Image of Rookery, Chicago
