BSAN 310 Programming
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Key Words
Predefined words used to write program in high level language. Each key word has specific meaning (e.g. import, if, for)
Operators
Perform operations on data. Ex: Math operators to perform arithmetic.
Syntax
Set of rules to be followed when writing program.
Statement
Individual instruction used in high-level language.
Variable
Name that represents a value stored in the computer memory. Used to access and manipulate data stored in memory. A variable references the value it represents.
Assignment statement
Used to create a variable make it reference data. General format is variable = expression. Ex: age = 29.
Condition
The if statement, Python syntax: if condition then result.
The if-else statement
Dual alternative decision structure: two possible paths of execution. One is taken if the condition is true, the other if false.
If-elif-else statement
Simpler to write, can include many. If condition, statements, elif, else.
The While Loop: Condition-Controlled
While: While condition is true, do something.
The While Loop Parts
Two Parts:
Conditions tested for true or false value
Statements repeated as long as condition is true
While Loop Format
General Format:
While condition:
statements
In flow chart, line goes back to previous part
The For Loop: A count-Controlled Loop
Iterates a specific number of times. Designed to work with sequence of data items. Iterates once for each item in the sequence.
For Loop Format
for variable in [val1, val2, etc]:
statements
Target Variable
The variable which is the target of the assignment at the beginning of each iteration
Funtion
Group of statements within a program that perform as specific task. Usually one task of a large program.
Can be executed in order to perform overall program task. Known as divide and conquer approach.
Function definition
Specifies what function does
def function_name():
statement
statement
Function header
First line of function. Includes keyword def and function name, followed by parentheses and colon.
Block
Set of statements that belong together as a group. Ex: the statements included in a function
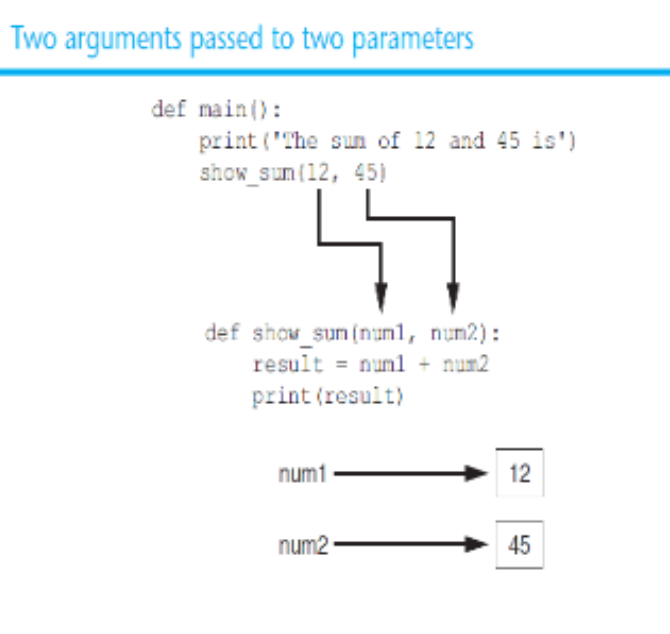
Argument
Piece of data that is sent into a function. Function can use argument in calculations. When calling the function, the argument is placed in parentheses following the function name.
Lists
An object that contains multiple data items. Anything with brackets.
Element
An item in a list
Format of List
list = [item1, item2, etc.]
Print function
Can be used to display an entire list
Tuple
An immutable sequence. Once it is created it cannot be changed.
Tuple Format
tuple_name = (item1, item2)
Tuples support operations as lists
Subscript indexing for retrieving elements
Methods such as index
Built in functions such as len, min, max
Slicing expressions
The in, +, and * operators
Dictionary
Object that stores a collection of data. Each element consists of a key and a value. To retrieve a specific value, use the key associated with it
Key and value
Often referred to as mapping of key to value. Key must be an immutable object
Dictionary Format
dictionary =
{key1:val1, key2:val2}
Set
Object that stores a collection of data in same way as mathematical set
Set Requirements
All items must be unique. Set is unordered. Elements can be of different data types. For empty set, call set().