Hygiene principles LO1/2 (COPD and asthma)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
COPD
chronic bronchitis + emphysema are known as:
This is the 4th leading cause of death in the US.
Asthma
Intrinsic, extrinsic, ingenstion of drugs, excercise induce, and infectious. These are all types of:
COPD
The characteristics that are requires to be diagnosed with this are: presence of cough, sputum production, dyspnea, abnormal measurement of lung function, chronic airflow limitation, not fully reversible.
chronic bronchitis and emphysema
COPD encompasses 2 main diseases:
Chronic bronchitis
Excessive tracheobronchial mucus production and chronic cough with sputum for at least 3 months in 2 consecutive years.
Emphysema
Permanent enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles. Destruction of alveolar walls or septa without obvious fibrosis.
Smoking
This is the leading cause of COPD worldwide.
Occupational exposure, environmental pollutants, and absence or deficiency of alpha1-antitrypsin
Other than smoking, these are 3 other sources of risk for developing COPD.
Alpha1-antitrypsin
protease inhibitor made in the liver. Protects the body from attack by protease enzymes. Prevents attack of normal tissue by binding to protease enzymes.
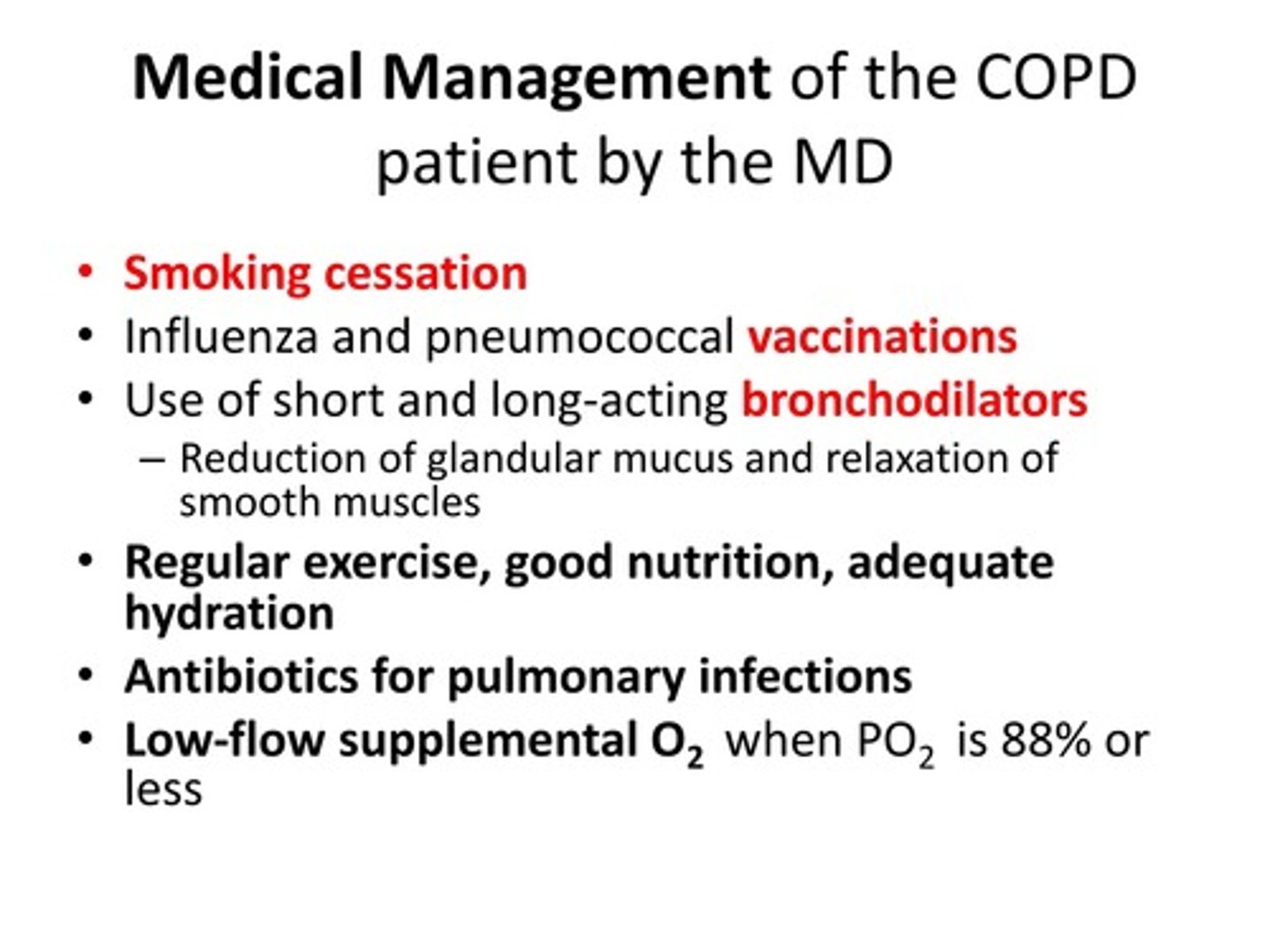
Semi supine or upright
For clients with COPD that are able to be seen (no respiratory infection present) they should be in what chair position?
Asthma
Chronic inflammatory respiratory disease resulting in recurrent episodes of dyspnea, coughing, wheezing. Bronchiolar lung tissue is particularly sensitive to a variety of stimuli: allergens, upper respiratory tract infection, exercise, cold air, chemicals, smoke, highly emotional states (anxiety, stress, and nervousness).
Extrinsic (allergic or atopic)
What type of asthma is this? 35% of all adult cases. Exaggerated inflammatory response to allergens. Usually seen in children and young adults. Bronchoconstriction occurs. Increased vascular permeability occurs. Increased bronchila hyperresponsiveness. Increased tissue edema occurs. Increased mucous secretion occurs. Fibrotic changes may occur in lunch tissue.
Intrinsic (idiosyncratic, nonallergic)
What type of asthma is this? 30% of asthma cases. Rare to have a family history, or allergy with a known case. Generally seen in middle-aged adults. Onset associated with: emotional stress, gastroesophageal acid reflux, and vagally mediated responses (related to the vagus nerve).
Ingestion of drugs
What type of asthma is this? ASA (10% of patients with asthma), nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, food substances (triggers): nuts, shellfish, strawberries, milk, tartrazine food dye yello no.5, metabisulfite preservatives of foods and drugs (LA containing epinephrine)-> may precipitate an asthma attack.
Exertion
What type of asthma is this? Inhalation of cold air-> mucosal and airway hyperactivity. More likely to affect children and young adults (greater degree of physical activity).
Infectious
What type of asthma is this? Inflammatory response to bronchial infection. Bronchial constriction. Increased airway resistance due to inflammatory response of the bronchi to infection. Caused by: virus, bacteria, dermatologic fungi, mycoplasma organisms. Treatment of the infection usually improves control of pulmonary constriction.