Micro-economics Mid-term 2 (Mr. Monsky)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
1. Economists normally assume that the goal of a firm is to earn
(i) profits as large as possible, even if it means reducing output.
(ii) profits as large as possible, even if it means incurring a higher total cost.
(iii) revenues as large as possible, even if it reduces profits.
a. (i) and (ii) are true.
b. (i), (ii), and (iii) are true.
c. (i) and (iii) are true.
d. (ii) and (iii) are true.
a. (i) and (ii) are true.
Which of the following expressions is correct?
a. economic profit = total revenue - implicit costs
b. accounting profit = total revenue - explicit costs
c. economic profit = total revenue - explicit costs
d. Both a and b are correct.
b. accounting profit = total revenue - explicit costs
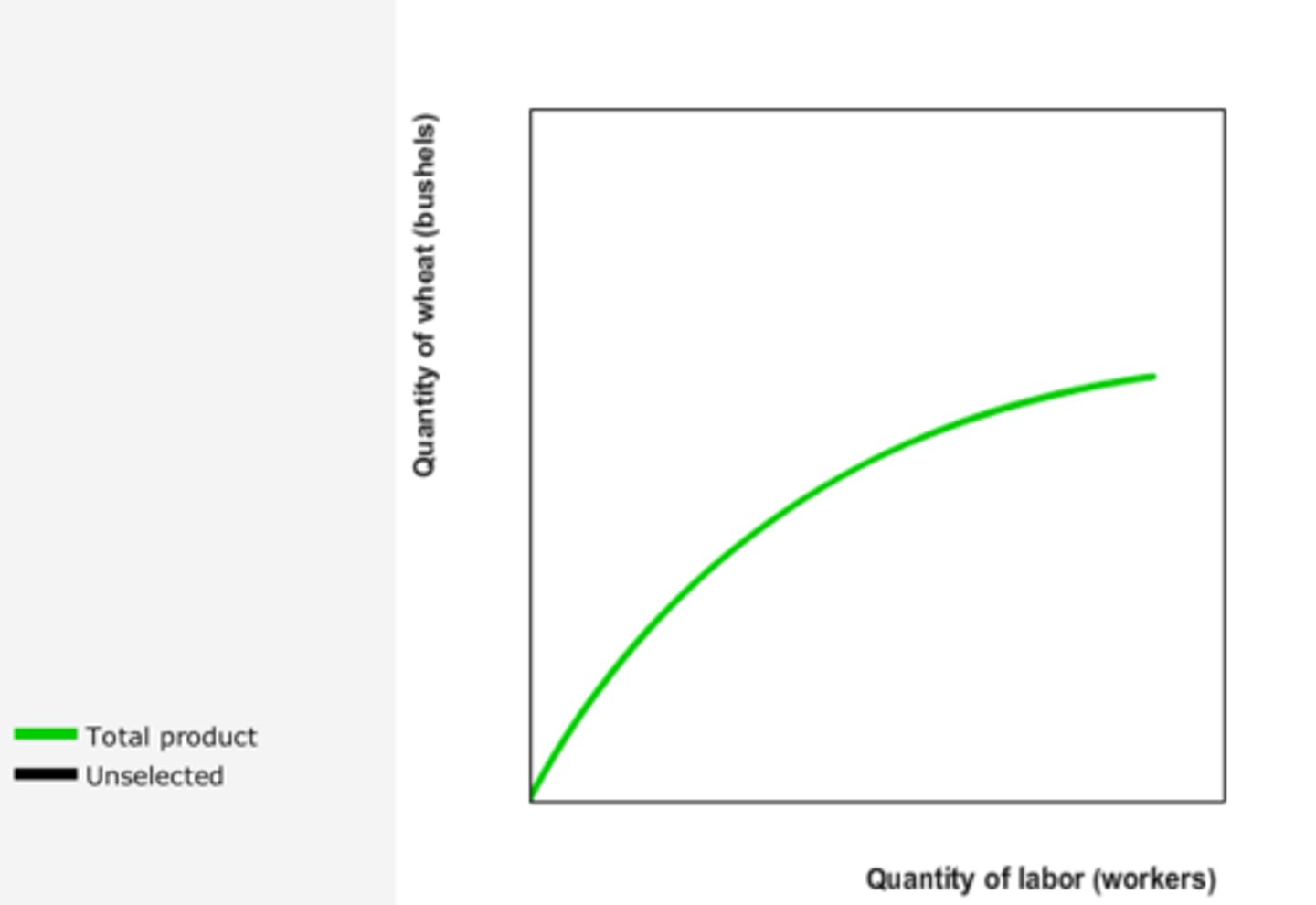
____ 3. Refer to Figure 13-2. The graph illustrates a typical
a. marginal product of labor curve.
b. production function.
c. total-cost curve.
d. production possibilities frontier.
a. marginal product of labor curve.
b. production function.

Refer to Figure 13-2. As the number of workers increases,
a. marginal product increases but at a decreasing rate.
b. marginal product increases at an increasing rate.
c. total output decreases.
d. total output increases but at a decreasing rate.
d. total output increases but at a decreasing rate.
Suppose a certain firm is able to produce 165 units of output per day when 15 workers are hired. The firm is able to produce 176 units of output per day when 16 workers are hired (holding other inputs fixed). Then the marginal product of the 16th worker is
a. 16 units of output.
b. 10 units of output.
c. 11 units of output.
d. 176 units of output.
c. 11 units of output.
In the short run, a firm incurs fixed costs
a. only if it incurs variable costs.
b. only if it produces no output.
c. only if it produces a positive quantity of output.
d. whether it produces output or not.
d. whether it produces output or not.
Which of the following costs of publishing a book is a fixed cost?
a. the costs of paper and binding
b. shipping and postage expenses
c. author royalties of 5% per book
d. composition, typesetting, and jacket design for the book
d. composition, typesetting, and jacket design for the book
If a firm produces nothing, which of the following costs will be zero?
a. opportunity cost
b. variable cost
c. fixed cost
d. total cost
b. variable cost
In the short run, a firm that produces and sells computers can adjust
a. the size of its factories.
b. where to produce along its long-run average-total-cost curve.
c. how many workers to hire.
d. All of the above are correct.
c. how many workers to hire.
Refer to Figure 13-9. The firm experiences economies of scale at which output levels?
a. output levels greater than N
b. output levels between M and N
c. output levels less than M
d. All of the above are correct as long as the firm is operating in the long run.
c. output levels less than M
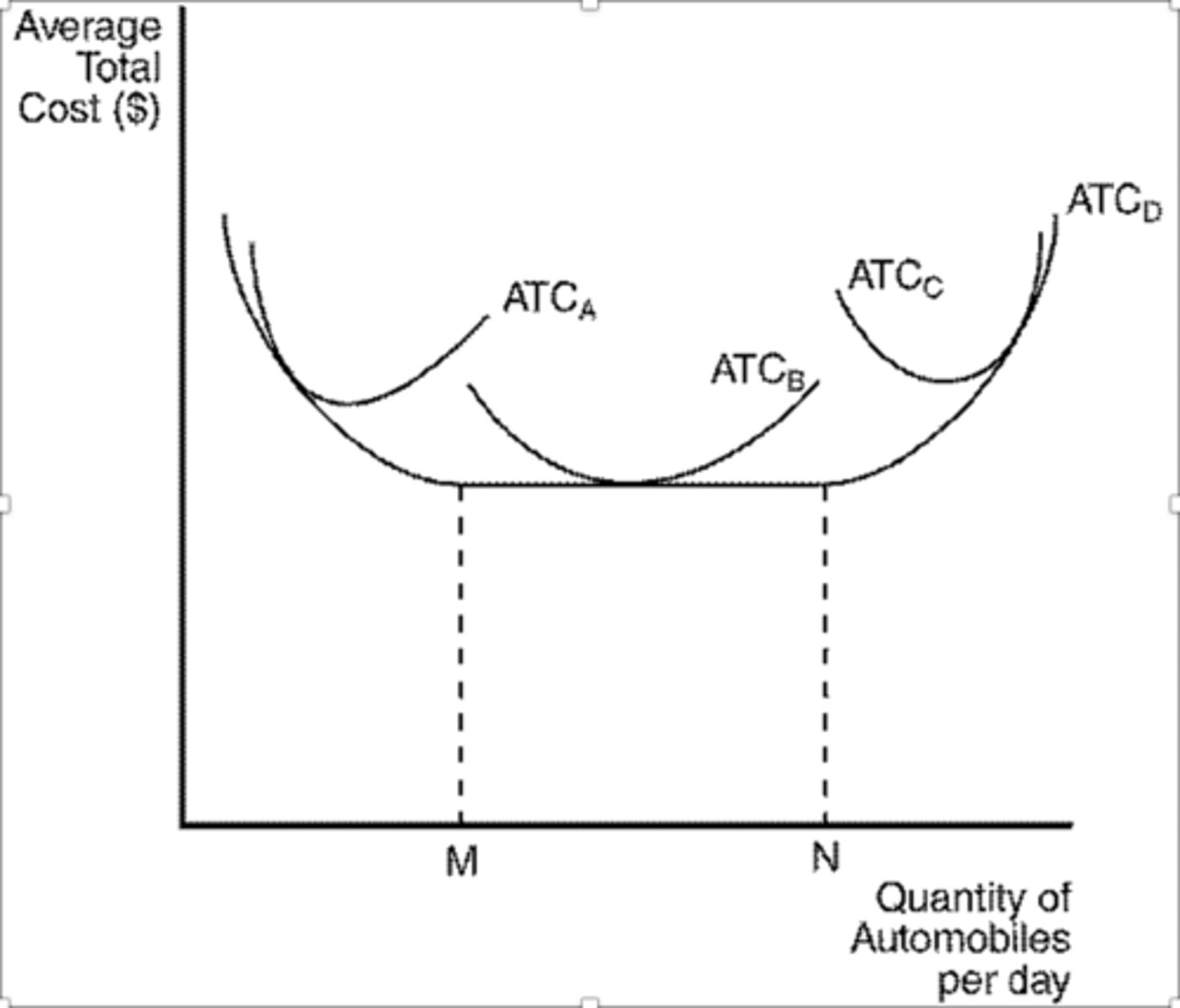
This firm experiences diseconomies of scale at what output levels?
a. output levels less than M
b. output levels greater than N
c. output levels between M and N
d. All of the above are correct as long as the firm is operating in the long run.
b. output levels greater than N
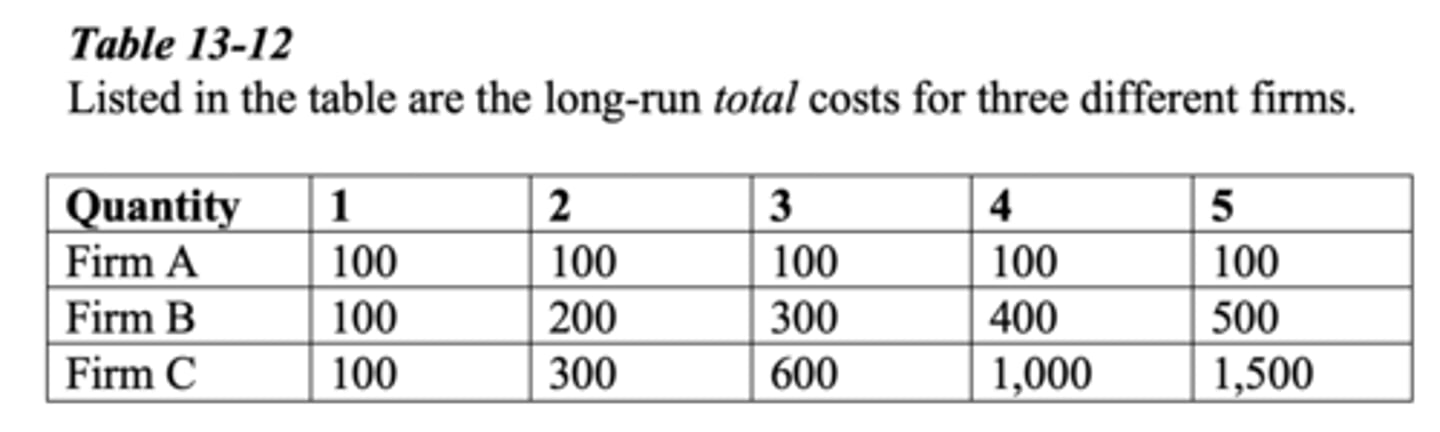
Which firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale?
a. Firm A and Firm B only
b. Firm A only
c. Firm C only
d. Firm B only
c. Firm C only
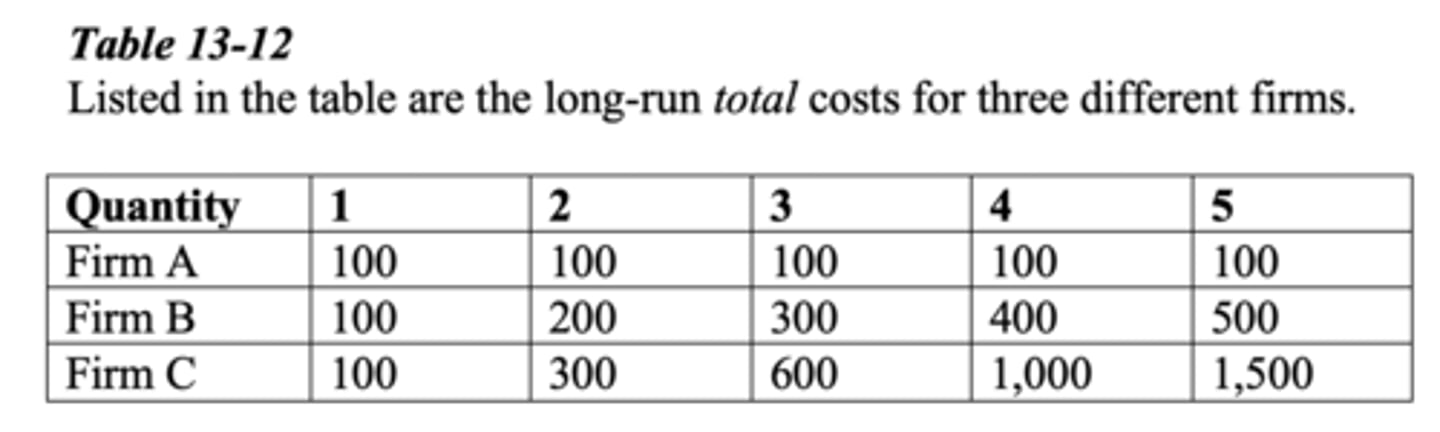
Which firm is experiencing constant returns to scale?
a. Firm A and Firm B only
b. Firm A only
c. Firm C only
d. Firm B only
d. Firm B only
When consumers face rising gasoline prices, they typically?
a. reduce their quantity demanded more in the long run than in the short run.
b. increase their quantity demanded in the short run but reduce their quantity demanded in the long run.
c. reduce their quantity demanded more in the short run than in the long run.
d. do not reduce their quantity demanded in the short run or the long run.
a. reduce their quantity demanded more in the long run than in the short run.
For a good that is a luxury, demand
a. cannot be represented by a demand curve in the usual way.
b. tends to be elastic.
c. has unit elasticity.
d. tends to be inelastic.
b. tends to be elastic.