Nursery Production Exam II
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
What are the shrinks and swells in nurseries?
Swell: February to May aka Spring increase
Swell: September to November aka Fall increase
Shrink: May/June to August aka Summer decrease
Shrink: November to February aka Winter decrease

Laborers needed for a __ nursery:
propagation
irrigation
fertilization
weed control
chemical and mechanical growth modification
pest scouting
pesticide application
labeling
inventory
order collection
shipping
Wholesale

Laborers needed for __ nurseries:
branch manager if there are multiple locations
selling
answering consumer questions
designing displays
irrigation
fertilization
weed control
chemical and mechanical
pest scouting
pesticide application
labeling
inventory
Retail

Laborers needed for __ nurseries:
irrigation
fertilization
weed control
chemical and mechanical growth modification
pest scouting
pesticide application
inventory
order collection
shipping
Re-wholesale

Laborers needed for __ nurseries:
propagation
irrigation
fertilization
weed control
chemical and mechanical growth modifications
pest scouting
pesticide application
labeling
inventory
boxing / shipping
Mail or Online Order
Main differences between H-2A and H-2B workers?
H-2A are temporary or seasonal AGRICULTURAL workers
H-2B are temporary NON-AGRICULTURAL workers
What must employers be required to do in order to hire H-2A workers?
Provide housing and transportation for workers. And prove there are no American workers who can fill the jobs or it won’t hurt the current American workers who are employed.
Name 3 key parts for time management for managers or supervisors.
Set responsibilities and expectations:
identify what you want/need to accomplish, make major tasks and time commitments to accomplish these goals
Set personal goals as a manager and employee:
analyze how you are spending your time and improve it
make goals for yourself and your employees
Identify proper time use:
develop a schedule which better allows you to focus your daily efforts on accomplishing your goals
How do you avoid co-worker conflicts?
Confront the trouble-makers quickly, ask questions to identify what is going wrong, avoid placing them together in future projects, and if needed consider mediation.
How does nursery layout affect the labor efficiency?
Decrease the amount of time workers are walking, make sure movement is efficient, and make sure unprofitable tasks are limited.
What are some steps to organization?
Plan tomorrow, today (make notes and group similar tasks together
prioritize daily tasks
take the time you need to do good work
10-minute rule, do something unpleasant for ten minutes a day
evaluate your time
limit distractions, say no and get off the phone
What role does training play in labor efficiency?
By training your employees they will prevent conflicts, increase efficiency because they will not need help, and help keep them safe.
Employees and managers should be trained.
__ - compensates employees a set amount for each unit of work completed
Advantages, it provides motivation for employees and can be cost effective for employers
Disadvantages, could lead to a decrease in quality and payroll will be difficult to calculate
Piecework Pay System
__ - the replacement of human power with mechanical power
Mechanization
__ - the replacement of both human power and human judgment by machines and computers
Automation
What are some incentives? (financial and non-financial)
Financial can be bonuses but will be effective short-term.
Non-financial is simple thanks, providing lunch, give time off, acknowledge employee in front of other workers, and give plants/merch to interested employees.
__ - heavily dependent on business type
Income taxes
__ - a social security and Medicare tax for the self-employed, must pay if net earnings from self-employment is over $400
Self-employment tax
__ - keep on record for 4-5 years, social security and Medicare, w-2 forms, W-4 forms (federal income tax withholding), and federal and state unemployment tax
Employment tax
__ - must be completed by Jan 31 by the employer, and a copy must be sent to the social security administration
Form W-2
__ - business tax, paid by corporations/LLC’s/Partnerships
Franchise tax, it is not paid by sole proprietorships or unique partnership situations
__ - agricultural appraisal is important, local taxing jurisdictions set these, land classified as agricultural land will lower this
Property tax

__ - only paid by retail nurseries, this must apply if:
sell or lease tangible personal property in Texas
sell taxable services in Texas
Retail sales tax
__ - form must be filled out for each employee within 3 days of hire, requires an approved form of ID or documentation, not turned into any governmental branch; employer must keep it on file for 3 years or for 1 year after termination
Employee Eligibility Verification (Form I-9)
When are employers required to declare all newly and re-hired employees?
Within 20 days of hiring
Employers can choose to offer health insurance, small businesses (2-50) employees are not required to give health insurance unless they work more than 30 hours
Less than 50 employees
Employers must offer health insurance, or they run the risk of paying a penalty, 50 employees includes “part-time equivalents”
Greater 50 employees
__ - covers most small businesses and some large businesses, they are not covered if you are a family member of the business operator / self employed / covered by some other legislation
They are a gauntlet of safety and health requirements, many nurseries will submit to voluntary inspections
Occupational Safety & Health Act (OSHA)

__ - provides worker protection standards, deals heavily with pesticide application and safety.
Environmental Protection Agency
__ requires each entity to register for the stated purpose of maintaining the immunity and protection of plants from diseases and insect pests
regulate traffic, growing, shipping, selling and leasing of nursery products
providing the inspection and control of florist items
regulating city, private, or public parks or shade, tree, shrubbery, and ornamentals along city streets or property or on city residences
Texas Department of Agriculture (TDA)


A nursery dealer or nursery agent must register with the department under this section before offering for sale or lease or otherwise distributing a nursery product.
Nursery Dealers and Agents must apply for __ registration and renew that registration annually!!
TDA
If they are not in compliance, they will have to pay fees.

__ - a person who grows more than 50% of the nursery products or florist items that the person either sells or leases, regardless of the variety sold, leased, or grown
Nursery grower
__ - person who buys and sells or leases or offers for sale or lease a nursery product and who has facilities that maintain or preserve the nursery product and prevent that product from becoming dry, infested, or diseased
Nursery dealer
__ - a person who sells or leases, offers for sale or lease, or takes mail orders for the sale or lease of a nursery product and:
is entirely under the control of a nursery grower or nursery dealer with whom the nursery product offered for sale or lease originates
operates on a cooperative basis for handling a nursery product with a nursery grower or nursery dealer.
Nursery agent
To ensure U.S. import regulations provide adequate protection against the risk posed by plants for planting, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) established a new regulated category called _____ which allows APHIS to more fully protect U.S. agriculture from foreign pests while minimizing adverse economic and trade impacts
Not Authorized Pending Pest Risk Analysis - NAPPRA
What are the two main product types sold by nurseries?
Plant material
propagative materials
Hard goods
anything not a plant
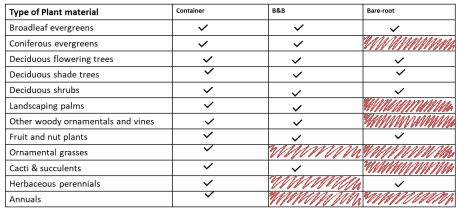
__ are typically asexual from cuttings, some tissue culture in large production system
They’re sold in: Liners (2-4” pots) • 1 gallon • 3 gallon • 7 gallon • 15 gallon • B&B – less frequently than broadleaf evergreen trees • Rarely sold as bareroot plants
Broadleaf evergreen shrubs
One example is Holly
__ - seedling propagation common; some species by cuttings, some tissue culture for certain cultivars
Sold as: Liners (2-4” pots) • 1 gallon (this size often skipped for higher value crops) • 3 gallon • 7 gallon • 15 gallon • 25-30 gallon • 45 gallon • 100 gallon • B&B – common in most parts of the country (not the southwest) • Sold as bareroot liners and seedlings
Broadleaf evergreen trees
One example if Magnolia
__ - from cuttings for “rootable” species, seedlings, and some grafting in select species
Sold as: Liners (2-4” pots) • 1 gallon (this size often skipped for higher value crops) • 3 gallon • 7 gallon • 15 gallon • 25-30 gallon • 45 gallon • 100 gallon • B&B – common in most parts of the country (not the southwest) • Sold bareroot as seedlings
Coniferous evergreen trees and shrubs
__ - seedling propagation common; cuttings also common, grafting for certain species (e.g. Pink Dogwood), some tissue culture for certain cultivars
Deciduous flowering trees

__ - seedling propagation common; cuttings also common for some species (especially in less mature plants)
Deciduous shade trees
__- cutting propagation most common; perhaps some seedlings (species dependent); grafting/budding in roses
Sold as: Liners (2-4” pots) • 1 gallon • 3 gallon • 7 gallon • 15 gallon • B&B – rare • Sold as bareroot liners and mature plants (e.g. hybrid tea roses
Deciduous shrubs
__ - seedling propagation common; if available, offshoots (pups) are preferred for some species because they are much quicker
Landscaping Palms

__ - seedling propagation common; cuttings most common method
Usually sold between the times of growing trees, among the quickest nursery crop.
Vines
__ - most fruit/nut trees are grafted/budded; seedlings are used as rootstocks; cuttings of select species are utilized
Grafted / budded Pecans are ready to be sold bareroot in 2-3 years, will not reliably fruit for another 3-5 years
Fruit and Nut Trees and Plants
__ - seedling propagation most common; nurseries will often grow from “plugs”; division is also a common method
Sold as: Plugs (70-140 count propagation flats) /Liners (2-4” pots) • 1 gallon (this size often skipped for higher value crops) • 3 gallon • 7 gallon
Ornamental grasses
__ - seedling propagation and division are both common methods of propagation
Sold as: Pups • 4-6” pots • 1 gallon • 3 gallon • 7 gallon • 15 gallon • Bareroot plants (online especially)
Cacti and succulents
__ - most of these crops propagated by cuttings; new plugs may be propagated by seedlings for some species
Herbaceous perennials
__ - Seed propagation
Very fast growing which makes them quick money crops
Annuals
advantages of __:
Don’t need as much maintenance as plants
Therefore your profit margins are more clear-cut
disadvantages of __:
Can require a lot of space
Often require specialized equipment for loading and/or delivery
Hard goods

Why should you stay away from dyed mulches?
these dyed mulches are made from woefully under-composted wood OR... Recycled wood that might contain CCA (chromated copper arsenate)

__ - is a seedling produced in a small volume of medium contained in a small cell, of which between 220 up to 800 plants are contained on a single sheet of polystyrene, Styrofoam, or other suitable material.
Plug
__ - plants produced from layering
Layers
__ - plant structure used for regenerating plants through adventitious root formation
Cutting
__ - ANY plant structure used for regenerating plants
Propagule
Pros:
Certainty of heritability
Products are genetically identical (can also be a con)
Cons
Labor intensive
More difficult to produce in mass quantities
Products are genetically identical (can also be a pro)
Asexual propagation
Pros:
Less expensive
Easier to produce large quantities
Genetic diversity (can also be a con)
Cons:
Genetic diversity (can also be a pro)
Uncertainty of heritability
Can be difficult to obtain proper seed
Sexual propagation
__ in Intermittent Mist
Low technology; widely available; inexpensive
Discarded material from pruning/shaping may be used; stock plant maintenance may be required
Species vary in ease of rooting
Species vary in growth resumption after rooting
Equipment required
Structure (greenhouse, shade house, ground beds)
Mist system and controller
Controlled (?) environment; bottom heat (?)
Clean substrate
Growth regulators (auxin analogs; k-IBA, NAA)
Cutting propagation
__ needs:
Advantageous for difficult to root species
Takes advantage of principle of juvenility
Types: simple layering, compound layering, air layering, stool bed (mound), tip layering, runners
Some species morphologically adapted to natural layering
Equipment required
Stock plant maintenance beds
Harvesting equipment
Layering
__ :
Important in difficult to root species
Results in compound genetic system
Rootstock can confer disease/insect resistance, salt or cold tolerance
Rootstock may cause plant to flower early, flower heavier, and be dwarf
Equipment required for grafting
Skilled grafters
Grafting tools/equipment varies
Reliable source of clonal or seedling rootstocks of known origin
Grafting and budding
__ also known as micropropagation, in vitro propagation:
High technology; equipment-, skill-intensive
Adaptable to many species
Economically-feasible in limited range of species
Suited to the creation and maintenance of virus-free plants
Rates of multiplication from limited explant material in short period of time possible; rapid release of new clones
__ requirements
Highly-trained lab manager
Highly-trained personnel in transferring stage
Precise environmentally- controlled facility
CLEAN facilities; limited traffic flow
Laminar flow hoods (HEPA); autoclaves
Precise environmental control in acclimation phase in the greenhouse
Tissue culture
What are some unintended consequences of tissue culture?
Chimeral reversion, somaclonal variation, tissue cultured liners need special handling

__ used for some woody ornamentals and many herbaceous annuals
__ need to be nearly true-to-type to be useful
Seedlings need to be uniform in growth rate and habit
Provenance from which seeds are collected is important
Dormancy requirements (if any) must be manageable
Must be disease free
Seed propagation
What are the functions of a substrate?
Reservoir for plant nutrients, water, good aeration, provide anchorage and support

Why should you use a soilless substrate instead of soil?
Crops are more profitable in soilless substrate
Superior physical and chemical characteristics
Low initial infestation of pathogens
Ease of disinfestation
Practical
Weight of soilless v. soil
Environmental
Harvesting native soils can be harmful

__ - (dry mass per unit volume (moist)) – low _ substrates are lighter, high _ substrates are heavier
bulk density
__ - a method of quantifying substrate texture
particle size distribution
__ - total volume of pore space in a substrate can be divided into air filled porosity and water-holding capacity
total porosity
__ - “air space” or Macropores – typically between 10-30% in substrates
Must be >20% in rooting substrates •
Can be a bit lower for bedding plants in shallow containers •
Can be as low as 10% in deep containers for trees (slowgrowing) •
AFP is directly correlated with Oxygen Diffusion Rate which allows roots to grow……….stagnant water cannot supply enough oxygen to produce a healthy plant
Air Filled Porosity (AFP)
__ - “water-holding capacity” – maximum volume of water a substrate can retain following irrigation and drainage due to gravity
Container capacity
__ - all containers maintain a PWT at the bottom of the container after drainage (this PWT is larger in fine-textured substrates)
perched water table
__ - the ease with which a fluid can move through pore spaces or fractures. Depends on both the substrate and the fluid
Hydraulic conductivity
__ - the ease with which a fluid can move through pore spaces or fractures BUT just measured on dry substrates. Gives indication of hydrophobic or hydrophilic tendencies
Unsaturated hydraulic conductivity
Why is the C:N ratio so important?

__ - A measure of the capacity of the fixed negative electrical charges in substrate to hold cations
__ = milliequivalents per 100g of dry substrate; 6 – 15 meq/100g is desirable
Cation exchange capacity (CEC)
Which substrates have a high CEC?
clay, peat moss, coir, vermiculite, compost
Which substrates have a low CEC?
sand, perlite, rockwool, polystyrene, peanut hull, and rice hulls
__ - measurement of the amount of Hydrogen ions that are present in a substrate, has significant effects on almost every aspect of plant growth
pH

__ - the ability of a substrate to transmit an electrical current, measure of the amount of salts in soil/substrate
Electrical conductivity (EC)
__ - some substrates contain nutrients before any are added
Nutrient content
__ - surface charge properties significantly effect chemical reactions in the rhizosphere
charge characteristics
name the 3 non-minerals which are obtained from the atmosphere:
Carbon (C): carbon dioxide
Hydrogen (H): water
Oxygen (O): water and dioxide
Name the primary and secondary macro nutrients:
PRIMARY: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K)
SECONDARY: Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulfur (S)
Name the 8 micronutrients
Boron (B), Chlorine (Cl), Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Molybdenum (Mb), Zinc (Zn), Nickel (Ni)
Available to plants in 2 forms:
Ammonium Nitrogen (NH4 +)
Adsorbed by soil particles doesn’t leach
Broken down into the nitrate form
Ammonium based fertilizers have an acidifying effect
Nitrate Nitrogen (NO3 - )
Not adsorbed by soil particles and leaches readily
Nitrate based fertilizers are basic
Aids in Amino Acid formation, essential for cell division (growth), directly involved in photosynthesis
Nitrogen
Available to plants in forms: HPO4 2- , H2PO4 -
Virtually immobile in soil
Plays a vital role in energy storage (ADP to ATP)
Important for seed production and maintenance
Aids in root development, flower initiation and fruit development
Phosphorus
Available in the form of K+
Unlike N and P, it doesn’t form any vital organic compounds in plants
Vital due to its activity as an enzyme activator (promotion of metabolism)
Controls the stomata of the leaf (water regulation)
Promotes the translocation of photosynthates for plant growth or storage
Potassium
What is the pH range for soilless media versus soil media?
Soilless - 5.5-6.5
Soil - 6.2 - 6.8
__ - A measure of water’s capacity to neutralize acids
Generally, acids are utilized to decrease the pH of irrigation water and substrates
Citric Acid
Nitric Acid
Phosphoric Acid
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric is the most commonly used due to the combination of safety and price considerations
Alkalinity
Whats the ideal pH range or irrigation versus substrate water?
Irrigation - 5.2 to 6.8
Substrate - 5.4 to 6.3
What are two generalizations of fertilizers and their applications?
Granular and water-soluble

__ - inorganic fertilizers that have been modified (typically by a coating) to release nutrients over a specific period of time
Controlled released fertilizer

__ - can be synthetic or organic and are released based on microbe activity
Slow released fertilizer
What do you use to raise pH?
lime and basic fertilizer
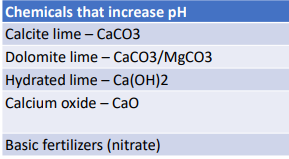
What do you use to lower pH?
Sulfur containing compounds and acidic fertilizer
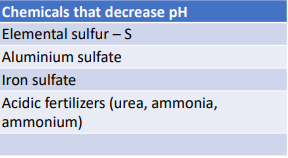
Whats the acceptable EC range for soilless substrates?
0.5 to 1.5 dS/m
__ substrates that contain high contents of soluble salts
Saline substrates
__ - saline soils that are made so predominately by the presence of sodium
sodic substrates
How do you monitor EC / pH?
Extraction Methods
Pour-through test
Saturated media extract test
1:2 dilution test
Suction lysimeter (SL)
Remote sensors
Probes that are designed/calibrated for soilless substrates
Define and know how to calculate for the Rule of 75.
It converts ppm to ounces/100 gallons
(desired ppm/75) = ounces of nutrients
