Honors biology unit 2 - biochemistry
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
acid
pH less than 7, releases H+ ions in water
amine
—NH2, hydrophilic, weak base
amine examples
caffeine, amino acids, nicotine
amino acid
an organic molecule that serves as the fundamental building block(AKA monomer) of proteins, contains an amine group and a carboxyl group
base
pH greater than 7, releases OH ions in water.
buffer
a solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added, maintaining a stable environment for biochemical reactions and processes like those in cells.
carbohydrate
Elements include C,H,O Monomer is a monosaccharide.
carbohydrate functions
main energy source, cellular recognition (stick out of the cell membrane like flags.
carbohydrate examples
glucose, sugar, chitin, cellulose, and glycogen
carboxyl
—COOH, hydrophilic, acidic
carboxyl examples
amino and fatty acids
covalent bond
a strong chemical bond formed when two atoms share electrons to achieve a stable, complete outer electron shell.
dehydration synthesis
the process of two smaller molecules joining together to form a larger molecule by removing a water molecule as a byproduct.
disaccharide
a type of carbohydrate made up of two monosaccharide (simple sugars).
fatty acid
type of lipid, a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) at one end, saturated and unsaturated.
functional group
group of atoms that have specific chemical properties. They are free to participate in chemical reactions.
glycerol
a three-carbon alcohol that serves as the structural backbone of triglycerides and phospholipids, crucial components of fats and cellular membranes
hydrogen bond
a specific type of electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom (like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and another nearby electronegative atom with an unshared electron pair
hydrolysis
a fundamental chemical reaction where a larger molecule is broken down into smaller parts by the addition of a water molecule
hydronium
H3O+, is a water molecule (H₂O) that has accepted an extra proton (H⁺) from an acid, making it a positively charged ion, determines a solution's pH level
hydroxide
OH-,a negatively charged ion formed from a water molecule
inorganic
molecules do not contain carbon, nonliving material.
inorganic examples
oxygen, gas, metals, minerals, water.
ionic bond
the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, formed by the transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another.
lipid
elements include C, H, O, and sometimes P. has two monomers; fatty acids and glycerol. Nonpolar.
saturated fats
carbon chain surrounded by the max number of hydrogen because all carbons are bonded with single bonds. bad for you. solid at room temperature.
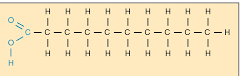
examples of saturated fats
chocolate, butter, cream, meat products, and cheese.
unsaturated fats
less than max number of hydrogen, liquid at room temperature, good for you, double bond causing a bend in the chain
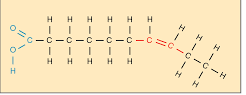
examples of unsaturated fats
avocado, fish, olive oil, peanuts
macromolecule
very large molecules made up of monomers bonded together, contain carbon.
methyl
—CH3, hydrophobic, nonpolar
methyl examples
hydrocarbons, when added to DNA it can control gene expression.
mixture
combination of two or more substances where each component retains its own chemical identity and properties, and they can be separated by physical means without undergoing a chemical reaction
monomer
individual/single subunits.
monosaccharide
the simplest form of sugar, serving as a fundamental building block for all carbohydrates
nonpolar
has no charge, insoluble in water
functions of lipids
stores high amount of metabolic energy, major component of cell membranes, waterproofing on plant leaves and fruit.
nucleic acids
elements include C,H,O,N,P, monomer is a nucleotide. DNA is a double helix and RNA is single stranded
Nucleotide
consists of a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and sugar (deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA
functions of nucleic acids
DNA stores info inside the nucleus and RNA transmits info outside of the nucleus.
examples of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA, steroids, and cholesterol
organic
molecules do have carbon, living organisms.
examples of organic material
wood, grass, petroleum, and ethanol
pH
scale of 0-14 measuring acidity
phosphate
PO4²-,hydrophilic, acidic
examples of phosphate
DNA/RNA, genetic material, energy(ATP)
polar
slightly charged, soluble in water
polymer
repeating units of many identical or nearly identical monomers covalently bonded to one another
polysachharide
3 or more monosaccharides bonded together, starch is an example
protein
elements include C,H,O,N, and sometimes S. Monomers are amino acids.
Primary protein structure
amino acid sequence
secondary protein structure
alpha helix or beta pleated sheet (basic folding pattern)
teritriary protein structure
3d shape (globuar)
quaternary protein structure
relationship among multiple polypeptides
glucose
immediate source of energy for cellualar respirartion, monosaccharide
functions of proteins
control the speed of reactions, used to send signals to cells, transport substances in and out of cells,
examples of proteins
enzymes, egg whites, ferritin, insulin, hemoglobin, antibodies, hair, collagen, muscles.
solute
the minor component in a solution, dissolved
solution
a liquid mixture in which the minor component (the solute) is uniformly distributed within the major component (the solvent).
solvent
the major component in a solution, dissolves other substances