Bony Thorax
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What are axillary ribs?
The lateral portion of the ribs that curve around the side of the chest under the armpit (axilla)
If a patient has right anterior rib pain, which position is used?
Left anterior oblique (LAO) — it places the right anterior ribs away from the IR
If a patient has left anterior rib pain, which position is used?
Right anterior oblique (RAO) — it places the left anterior ribs away from the IR
Why are anterior rib obliques done with the side of interest away from the IR?
To project the axillary portion of the ribs away from the spine for better visualization
What projection would you use if a patient has right posterior rib pain?
AP projection — position the patient in a right posterior oblique (RPO) to place the right posterior ribs closest to the IR
What projection would you use if a patient has left posterior rib pain?
AP projection — position the patient in a left posterior oblique (LPO) to place the left posterior ribs closest to the IR
Why are posterior rib obliques done with the side of interest closest to the IR?
To project the axillary portion of the ribs away from the spine, reduced magnification, and better visualization.
What breathing instruction is used for imaging ribs above the diaphragm?
Take a deep breath and hold it (inspiration)
Why is inspiration used for ribs above the diaphragm?
It moves the diaphragm down and expands the lungs, allowing better visualization of upper ribs
What breathing instruction is used for imaging ribs below the diaphragm?
Exhale and hold it (expiration)
Why is expiration used for ribs below the diaphragm?
It moves the diaphragm upward, reducing lung overlap and improving visualization of lower ribs
Where do you center for all SC joint projections?
Level of T2-T3, at or just below the jugular notch
How are all SC joint projections performed?
PA projection
Are SC joints typically imaged unilateral or bilateral?
Bilateral, unless a specific side is requested
What are the two methods used to perform oblique SC joint projections?
Body rotation method, CR angulation method
How is the body positioned for the SC joint body rotation method?
Patient is rotated 10-15° toward the affected side
How is the CR angled for the SC joint CR angulation method?
CR is angled 15° toward the MSP to project the side of interest away from the IR
For the body rotation method, how do you position for right SC joint pain?
RAO (rotate right side toward IR)
For the CR angulation method, how do you position for right SC joint pain?
Keep patient straight; angle CR 15° left to right to project the right joint away from the spine
How is the body positioned for the SC joint body rotation method?
Patient is rotated 10-15° toward the affected side
For the body rotation method, how do you position for right SC joint pain?
RAO (rotate right side toward IR)
Where does the CR enter for a PA, RAO SC Joint projection?
Perpendicular to the affected SC joint, which is closer to the IR
What body position is used for the PA Oblique sternum projection?
15-20° RAO (right anterior oblique)
Why is the RAO position used for sternum imaging instead of LAO?
RAO projects the sternum over the heart shadow for better contrast
How does the patient's body habitus affect RAO positioning for the sternum?
Thin patients require more rotation (closer to 20°), larger patients need less (closer to 15°)
What breathing instruction is used for the PA Oblique sternum projection?
Shallow breathing (breathing technique); expiration is acceptable if patient can't cooperate
What SID is used for the lateral sternum projection and why?
72" SID to reduce magnification caused by increased OID
How should the patient position their arms for a lateral sternum projection?
Roll shoulders back and lock hands behind the back to move arms out of the way
What SID is used for all bony thorax projections except the lateral sternum?
40 inches
Which of the following form the bony thorax?
Sternum, 12 pairs of ribs, and 12 thoracic vertebrae
How are the anterior ends of the ribs positioned compared to the posterior ends?
3 to 5 inches lower
What part of the rib is indicated in the photo?
Head
3 multiple choice options
Which projection and body position is essential for demonstrating the sternum?
PA oblique, RAO
How much should the body be rotated for a PA oblique projection of the sternum?
15 to 20 degrees
Where is the IR centered for a PA oblique sternum?
Level of T7 (midsternum), which is also the level of the inferior angle of the scapula
Which breathing techniques can be used for an oblique sternum projection?
Expiration or slow, shallow breathing
How should the patient's hands be positioned for an upright lateral sternum?
Locked behind the back
What is unique about floating ribs?
They do not possess costocartilage
What is the name of the part indicated as v
Manubrium
3 multiple choice options
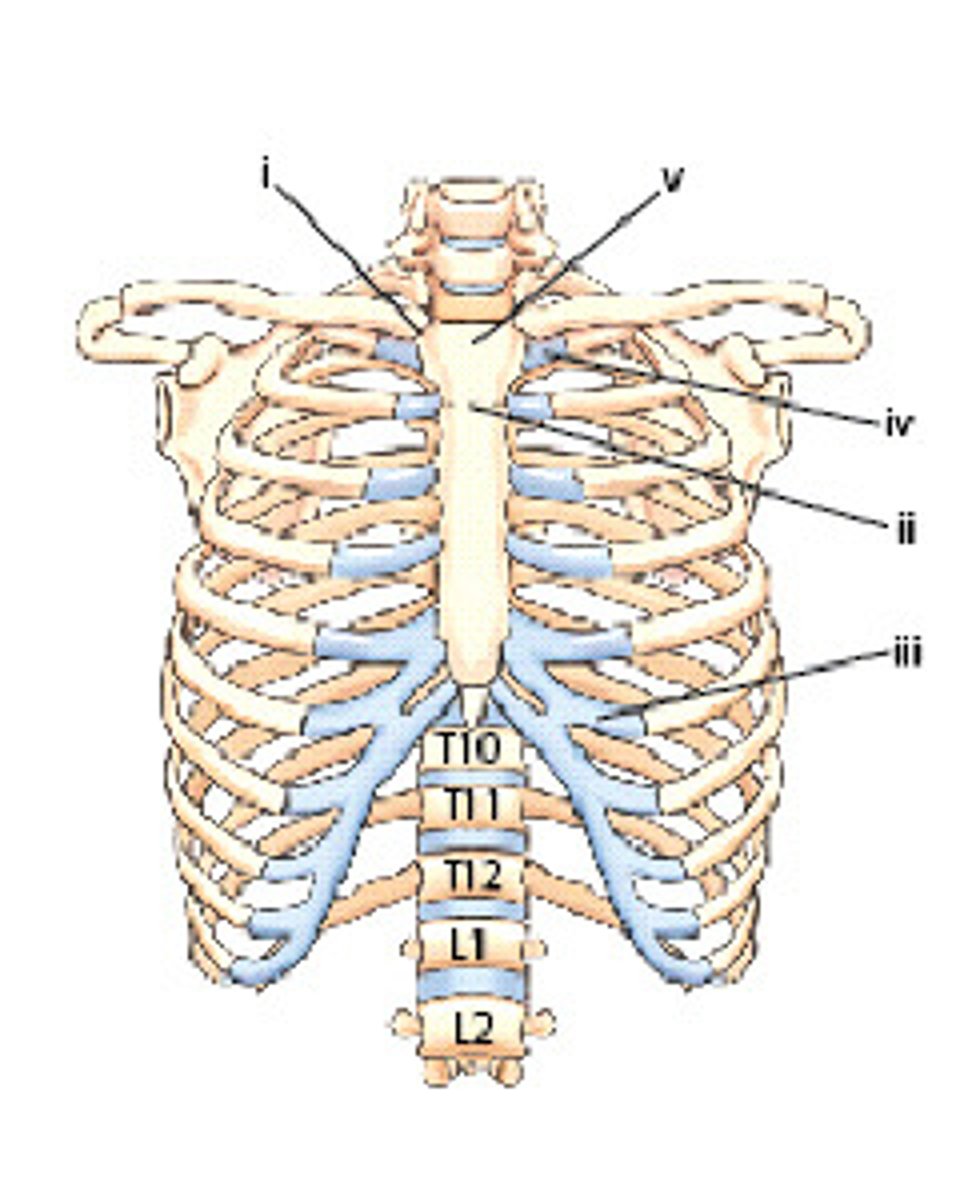
List the three parts of the sternum
Manubrium, body, xiphoid process
What is the most distal aspect of the sternum
Xiphoid process
What is the name of the palpable junction between the upper and midportion of the sternum?
Sternal angle (angle of Louis)
Which aspect of the sternum possesses the jugular notch
Manubrium
What distinguishes a true rib from a false rib
A true rib has its own direct attachment to the sternum via costocartilage
Which part of the sternum do the second ribs articulate?
Sternal Angle
What structures are found in the costal groove of each rib?
An artery, vein, and nerve
What type of joint movement is the sternoclavicular joint?
Plane (gliding) joint, diarthrodial
What type of joint movement is the costovertebral joint?
Plane (gliding) joint, diarthrodial
What type of joint movement is the first sternocostal joint?
Synarthrodial (immovable) joint
What type of joint movement is the eighth interchondral joint?
Plane (gliding) joint
What type of joint movement is the third costochondral union?
Synarthrodial (immovable) joint
Breathing instruction for study of ribs above the diaphragm
Suspended inspiration
kVp range for study of ribs above the diaphragm
Medium, 70-85
General body position for study of ribs above the diaphragm
Erect if patient is able
What is the range of body rotation for an RAO projection of the sternum?
15 to 20 degrees
Three pathological conditions that could result from a rib injury and may require that a PA and lateral chest projection be included in the rib routine.
Pneumothorax, hemothorax, pulmonary contusion
In a PA oblique sternum projection, does an asthenic patient require a little more or a little less obliquity than a hypersthenic patient?
A little more obliquity (closer to 20 degrees)
Nuclear medicine bone scans are not normally performed for which of the following conditions of the bony thorax? possible fractures, osteoporosis, history of multiple myeloma, osteomyelitis
multiple myeloma
Pathology of the sternum is most commonly caused by?
Blunt trauma
The most common cause of osteomyelitis is?
Bacterial Infection
What other position can be used for the sternum if the patient cannot assume the recumbent RAO position?
LPO
Which radiographic sign can be evaluated to determine whether rotation is present on a PA projection of the SC joints?
The SC joints are an equal distance from the midline of the spine
How much rotation of the thorax is required for the anterior oblique projection of the SC joints?
10 to 15 degrees toward the affected side
Where is the central ray centered for an AP bilateral projection of the posterior ribs below the diaphragm?
Centered midway between the xiphoid process and the lower rib margin (approximately at the level of L2-L3)
What range of kVp should be used for imaging ribs below the diaphragm?
75 to 85 kVp
Which projection and patient position would best demonstrate the right axillary ribs?
AP oblique with patient in RPO position
True/False: AEC is used for RAO sternum projection if the center chamber is used
False
Which ribs are classified as true ribs?
Pairs 1 through 7
Which ribs are classified as false ribs?
Pairs 8 through 10
Which ribs are classified as floating ribs?
Pairs 11 and 12
What is the space between ribs called?
Intercostal space
What is a key patient preparation for bony thorax imaging of females?
No bra (to avoid artifacts)
How are ambulatory patients generally positioned for bony thorax imaging?
Upright
What SID is used for a PA oblique projection of the sternum?
40 inches
What SID is used for a lateral projection of the sternum?
72 inches
When SID is not specified for sternum projections, what is the book's recommendation?
Use 40 inches
What are the essential projections for the sternum?
PA oblique (RAO) and lateral
What is the patient position for a PA oblique projection of the sternum?
15-20 degree RAO
Where does the CR enter for a PA oblique sternum?
On the elevated side, 1 inch lateral to the midsagittal plane at the level of T7
What is the collimated field size for a lateral sternum?
10 x 12 inches
Where is the IR centered for a PA projection of the SC joints?
To the spinous process of T3
What is the goal when positioning ribs in a projection?
To project the spine free of superimposition (away from the ribs of interest)
If the injury is right anterior rib pain, what oblique do you perform?
LAO
If the injury is right posterior rib pain, what projection and oblique do you perform?
AP with RPO
Why is an AP lower ribs projection used?
It places the ribs closer to the IR for more detail
What is the typical kVp for chest and ribs imaging?
Chest: 110 kVp; Ribs: 65 kVp
Why is the PA ribs projection typically done upright?
To allow the diaphragm to descend to its lowest position and to demonstrate air-fluid levels (when patient condition permits)
How is film orientation for rib imaging determined?
Based solely on body habitus
What is the breathing technique for PA ribs?
Full inspiration
What is the breathing instruction for AP projection of upper ribs?
Suspend at full inspiration
What is the breathing instruction for AP projection of lower ribs?
Suspend at full expiration
AP oblique ribs are used to evaluate which type of rib pain?
Posterior rib pain
In AP oblique ribs, which side is closer to the IR?
Affected side is closer to the IR
PA oblique ribs are used to evaluate which type of rib pain?
Anterior rib pain
Where should the lower edge of the IR be placed for PA oblique lower ribs?
At the level of the iliac crests