BIOL 300 Summer Class 2.5
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Why does alteration to chromosome number or structure affect phenotypes?
Changes in chromosome number or structure can affect many genes at once, causing major changes in traits.
What are the different centromere location types?
Centromeres can be in 4 places: metacentric (middle), submetacentric (off-center), acrocentric (near the end), telocentric (at the end).
What are the p arm and q arm of chromosomes?
The p arm is the short arm and the q arm is the long arm of a chromosome.
What are G bands and why are they useful?
G bands are dark/light patterns from staining that help tell chromosomes apart. They change during the cell cycle.
Deletions
Part of the chromosome is missing. This usually causes problems.
Duplications
Part of the chromosome is repeated. Can cause issues, especially if the duplicated part is large.
inversions
When a part of the chromosome is flipped. No material lost or added.
Simple Translocation
A piece of one chromosome attaches to a different one.
Reciprocal Translocations
Two chromosomes swap parts. If balanced (no material lost), effects might be small.
How do translocations relate to crossing over?
Both exchange DNA segments. However, translocations happen between nonhomologous chromosomes and shouldn’t happen
What mechanisms lead to deletions, duplications, etc.?
chromosome breaks, bad repair, or misaligned crossover.
What is the difference between terminal and interstitial deletions?
Terminal deletions are at the end. Interstitial deletions are in the middle.
How do duplications form and what mechanism is involved?
Duplications can happen if similar DNA parts (repeats) match up wrong during crossover.
non-allelic homologous recombination?
crossover happens at the wrong place (not alleles), often between repeats.
Are duplications more or less harmful than deletions?
Duplications are usually less harmful than deletions of the same size.
Gene Families?
A group of similar genes from duplication.
What does it mean for genes to be homologous?
Homologous genes come from a common ancestor.
Paralogs
Homologous genes in a species
What is the evolutionary significance of gene duplications?
Gene duplications let one gene stay the same and others evolve new jobs.
What is the globin family an example of?
Gene duplication and specialization.
How does duplication facilitate specialization?
Duplication lets some genes do new things while keeping the old job too.
Difference between pericentric and paracentric inversions?
Pericentric inversion includes the centromere. Paracentric doesn't.
inversion heterozygotes and their crossing over problems?
When one chromosome is normal and one has an inversion, it can mess up alignment during crossover.
What are acentric and dicentric chromosomes, and how are they produced?
Acentric = no centromere, dicentric = 2 centromeres. These can form during messed up crossover in inversions.
What does it mean that a translocation is balanced?
All the genetic material is still there, just moved around.
How does Down syndrome relate to translocations?
Parents with a balanced translocation can have kids with too much or too little chromosome 21 = Down syndrome.
Euploidy
Full sets of chromosomes (e.g., 2n, 3n, 4n).
Aneuploidy
Extra or missing chromosome in one set (e.g., trisomy = 3, monosomy = 1).
Why can aneuploidy have phenotypic consequences?
Problems caused by having too much or too little of some genes.
% of fertilized eggs have abnormal chromosomes?
5-10% of fertilized eggs have the wrong number of chromosomes.
% of spontaneous abortions are due to abnormal chromosome number?
About 50% of miscarriages are caused by chromosome number problems.
What is non-disjunction and how does it relate to trisomy?
Non-disjunction is when chromosomes don't separate properly during meiosis. It causes things like trisomy 21.
Do X chromosome variations have more or less effect than autosomal?
Extra or missing X chromosomes cause fewer problems than with autosomes because of X inactivation.
How can aneuploidy be caused during meiosis?
Non-disjunction in meiosis I or II can cause aneuploidy.
What is mitotic non-disjunction and what is mosaicism?
Mitotic non-disjunction causes mosaicism—some cells have different chromosome numbers.
Interspecific
Significant variation in chromosome #, ploidy, sex determination, etc.
Intraspecific
High similarity, except for sex chromosomes
Metacentric Chromosome
Centromere is positioned near middle
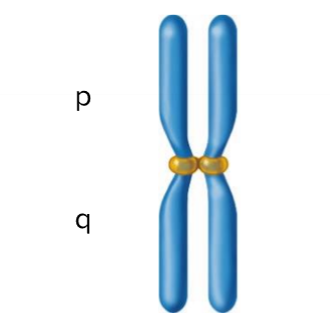
Submetacentric Chromosome
Centromere is positioned slightly off center
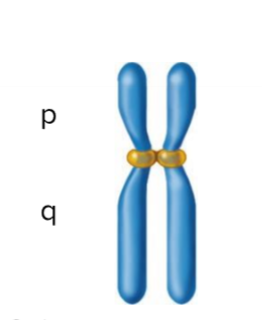
Acrocentric Chromosome
Centromere is slightly off center but not at the end
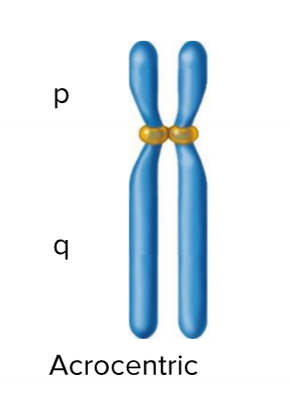
Telocentric Chromosome
Centromere positioned at one end
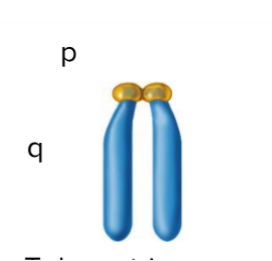
P arm
Short arm of chromosome
Q arm
Long arm of chromosome