geography globalisation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
how to measure globalisation
the KOF index measures:
economic globalisation: characterised as distance flow of goods, capital and services
social globalisation: expressed the spread of ideas, info, images and people
political globalisation: characterised by the diffusion of government policies
positives and negatives of globalisation: economically
adv:
there is a worlwide market for the companies and for the customer
creates a steady cash flow into the poorer and indebted countries
companies hiring foreign countries to work for them using telecommunications and online tools
dis:
immense pressure of countries keepign cost low or companies will moe
the home of agents of globalisation e.g. the MF and WOld bank are in wealthier nations
globalisation can lead to a labour drain since globalisation allows workers to move from one to another
example of TNC: Apple
headquaters: California, USA, European: Holly hill park, Ireland
manufacturing:
it uses a global supply chain, much of the hardware and R&D is done outside centres
assembly in India and Vietnam
other countries involved: Taiwan, Japan, South Korea
Sales / retail distribution:
Apple sells products worldwide, with most physical stores being in America and Europe, with none in South America or Africa
Apple: part 2
supply chain diversification: globalisation allows Apple to source components when needed e.g. more trade tensions during COVID, moving production beyond China
Positives for Apple: lower unit costs, greater recognition overtim, access to many suppliers when needed, keeping costs low
Negatives: risk of labour or safety scandals harming reputation, vulnerable for geopolitical tensions / tariffs
The Global Shift: def, pos neg
the movement of economic activity from HIC’s initially to NEE’s and more recently to LIC’s, especially in Asia and Latin America
pos: the improvement of infrastructure, tech
neg: Exploitation of workers, environmental degradation, overabundance on global markets
ways in which countries can group together:
trade - there are several trading blocks e.g. NAFTA
global governance - role in organising countries to combat environmental issues and poverty e.g. the UNDP and the UN
defence - there are defence groups topping wars e.g. NATO
social political and economic unions e.g. the UN
what is a trading bloc?
an arrangement from a group of nations to allow free trade between member countries but also to impose tariffs and charges on other countries that want to trade. Since WW2 there has been an increase in trading blocs, however not all of them have the same level of integration
the 4 types of trading blocs:
free trade areas - members abolish tariffs and quotas on trade but have restrictions on imports from non-member countries
customs union - a closer form of economic integration, having free trade between members, all members operate a common external tariff on imports from abroad
common market - free trade in goods, allows free movement of people and capital
economic union - the freedom of trade and people, also policies on agriculture industry and regional development
benefits and drawbacks: trade blocks
adv:
leads to increase trade creation, especially in smaller nations
increased specialisation, improving economies of scale
increasing competition, makign a greater choice for consumers as well as not allowing for market domination
dis:
increased import tariffs leading to trade diversion
increased interdependence on economic performance in other countries
increased influence of multinationals
loss in independence of trade
Trade blocs: Examples
ASEAN - a grouping of 10 states within South Asia, with the main aim to accelerate economic growth, cultural and social development, as well as regional peace and security
EU - political and economic union of 27 European countries, with its main aim in promoting peace around nations, especially after WW2. They als introduced the Eu currency to aid nations
Nafta - a 1994 treaty which created a free-trade agreement between the US, Canada and Mexico, however, was terminated in July 2020
international organisations:
the international monetary Fund: promotes international financial stability and monetary cooperation, also does international trade, promotes employent and reduces poverty
the world bank: a source of funding and knowledge to support governments of supporter member countries in their efforts to invest into facilities such as schools and health centres
drivers and consequences of international organisations
Drivers:
promote free trade and open markets: encouraging countries to reduce trade barriers, attracting foreign investment
facilitate global financial flows - providing loans and aid helping integrate developed economies into global systems
support infrastructure for global use
consequences:
created to manage economic integration: roles expended post ww2 due to liberalism
respond to global economic crises: the IMF steps in during financial struggles, showing how globalisation causes the want for international organisations
criticised for deepening inequalities
The IMF: def adv dis
provide short term loans to countries in financial instability, in return requiring governments to adopts structural adjustment programmes e.g. public spending
helps stable economies in crises and encouraged responsible fiscal policies and international cooperation
IMF loan conditions can be harsh, requiring large cuts to public services
The World Bank: def adv dis
offers long term loans and grants to support developing countries to support developing projects e.g. access to clean water and healthcare
the world bank has funded critical infastructure, supported education and health programmes and help lift millions out of poverty
they have been accues of funding large scale projects that displace communities or damage the environment
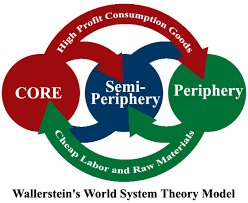
Immanuel Wallerstein - world system
looking at countries individually was to simplistic and suffers from developmentalism, with there being 3 tiers of countries:
the core: mostly HIC’s
the semi-periphery: countries where there are class struggles and social change
the periphery: LIC’s
How does the UN support globalisation?
creates financial cooperation
facilitating flow of ideas, people and goods
sets standards e..g WHO
how does the UN support development
sustainable development goals (17 goals)
UN development programme gives tech assistance
prevents conlfict so economies can grow
factors which effect Lic’s and HIC’s differently
money - more stable economies in more established markets (8 people own the same wealth as half the world)
people - HIC’s gain skilled migrants while LIC’s experience brain drain
IDEAS - Hic’s dominate the narrative and influence norms while LIC’s adopt external ideas, often disrupting conditions
unequal power relations
unequal flows of people, money, ideas and tech create unequal power relations between countries, which reinforces certain countries power
developed countries with lots of money and tech drive global systems to their advantage, as well a shave control over global economy and political events
Isreal - Hamas genocide
The Isreal – Gaza conflict presents the challenges of global governance is presented in how this war has been ever-lasting for roughly 100 years, with how multiple deals from within the country itself, as well as in other countries such as the USA’s one in a century, and even global unions trying to come to an agreement.
This helps create geological tensions between countries as these nations often involve boarders, especially in the Israel Gaza war
This international response shows the allience countries who support Gaza such as many lef,leaning countries and the countries supporting Isreal, with the right-leaning countries.
Case study - EU
made of 27 European counttries,working together to promote peace, stability, economic cooperation and shared values
each member state has a representation in the EU institution like the European parliament and European council and union
how to become a member:
stable democrati governance
functioning market
accepting EU laws and obligations, often using the euro
The Euro as a trading bloc
it is a single market, meaning free movement of goods, capital and people
it also has a customs union, with no tariffs between members and a common external tariff for non EU countries
eurozone: 20 out of the 27 use the Euro
trade agreementsL the eu negotiates trade deals on behalf of members
issues with the EU
some nations think the EU involves to much and intefere with national control
wealthy countries often contribute more than they recieve, while poorer nations heavily rely on EU funds
the freedom of movements can lead to immigration tension
an example of this being an issue is Brexit, as the Uk had enough of EU policies and payment and wanted to reduce immigraiton
TNC’s - origin nation and host nations:
TNC - companies that operate in more than one country e.g. Nike and Coca-Cola
origin nation - where a company originates from, often in HIC’s where decisions are made
Host nation - where goods are manufactured, often in LIC’s and lower-level workers
horizontal integration
vertical integration
vertical disintegration
horizontal integration - improving links with firms at the same stage of production, often occurs when a TNC acquires competitors in similar industries
vertical integration - an industry where one company either owns or control multiple stages of the production and distribution line
vertical disintegration - the process of a company breaking up its integrated production and distribution chain, outsource stages to different businesses.
distribution case study: Walmart - adv
R&D takes place in the origin nation of the USA, with production often being with the US as well, with many of it’s statistics centres being brought into the USA from other nations, such as the ai Israeli group, team8
positives of Walmart in the USA
socially - convenience for consumers, with over 4,000 stores in the USA, hosting over 2.2 million people in their workforce
economically - record profits have been reached, with it having a stake of 2% of the US GDP
environmentally opportunities of green energy plans and to be 0 emissions by 2040
distribution case study: Walmart - dis
socially - high wages in the USA compared to developing countries, higher working standards to be met, a need to become ethical and environmentally friendly under law
economically - much of the profit is put back into the USA, numerous jobs needed in construction and manufacturing
environmentally - invest into eco technology, has a responsibility to address cliimate change
uk food - illusion of choice
10 firms control 10% of food production and less than 10TNC’s control more than 50% of food on sale in UK supermarkets.
factor effecting food supply and how this is influenced by globalisation: climate, locaiton, population growth
climate - The UK climate is not meant for certain foods such as cocoa and bananas. this increases the need for trade during months when we cannot grow or for foods we cannot gain without them
location - a more centralised nation or land-locked can lead to increased trade, the growth in globalisation means that the concept of ‘far’ is irrelevant
population growth - more people means more products needed, with globalisaiton meaning global population is more often with immigration
factor effecting food supply and how this is influenced by globalisation: legislation, health
legislation - policies such as CAP introduced the EU incentivising the supply of products to be free, with mor international agreements being made, more countries use legislation for trade
health - many modern medicines have had recent consumer demand, with new discoveries meaning certain health products are needed more than ever, with globalisation meaning the abolishing of diseases such as polio and malaria from certain nations.
Case Study: the global trade in coffee
Coffee is getting more expensive annually, with rates rising drastically in recent years (2020 onwards)
One of the main reasons for coffee getting more expensive is the dramatic rise in global coffee bean prices. Arabica beans - commonly used in specialty coffee - have seen prices soar by over 80% in 2024, reaching $3.44 (£2.70) per pound
Another reason is the climate challenges withe the unpredictable weather in coffee-producing countroes. Brazil has suffered with extended droughts, while Vietnam faced crop damage due to erratic rainfall patterns
legalisation protecting coffee farmers:
farmer protection - the EUDR includes clauses requiring legislation for the hiring of farmers and giving human rights
CSDDD - requires companies to identify, prevent, and mitigate harmful human rights and environmental impacts
how the UN is organised
general assembly: - the main area of policymaking where all 193 member states vote
security council - maintaining internation peace and security with only 15 members elected every 2 years
economic and social council - specialised agencies on economic, social and environmental issues, with 54 members elected in
international court of justice - settkes legal disputes between states and provides advice
Secretariat - the secretary and the thousands of people who work at the base level of the organisation
Global commons - definition and examples
global commons- the parts of the planet that fall outside national jurisdictions to which all nations have access
the high sea and deep oceans
the atmosphere
the northern and southern polar regions - Antarctica
outer space
what is Antarctica like?
hasn’t rained in over 2 million years / makes it a desert
contains 70% of the earth’s rainwater
90% covered in an ice sheet which are fluid and travel
60 times bigger than the UK
threat to Antarctica: fishing and netting - tourism and mineral exploitation
fishing and netting - Overfishing removes vital animals in a small food chain and despite regulations, there are still reports fo illegal and unregulated fishing e.g. on Krill
tourism and mineral exploitation - over 74,000 tourists a year, elading to wildlife risk and risk of oil spills as well as trampling moss beds and soils, with mineral exploitaiton, up to 200 billion barrels of oil are in Antarctica that could be extracted through mining.