DP-900 Reviewer
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Classifications of data
structured, semi-structured, unstructured
Structured data
adheres to a fixed schema; data has the same fields
tabular schema; consists of rows and columns, rows for each entity, columns for attributes
Semi-structured data
has some structure, but allows for some variation between entities
Common semi-structured data format
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)
Unstructured data
do not have a specific structure; documents, images, audio, video, binary, etc.
How are attributes represented in a JSON format?
name-value pairs
Give three common optimized file formats
Avro, ORC (Optimized Row-Columnar) format, Parquet
What data types are commonly stored as binary?
images, video, audio, application-specific documents, etc.
Describe Avro
row-based
each record contains a header that describes data structure in the record
header is stored as JSON
data stored as binary information
When should you use Avro format?
if you need to compress data and minimize storage and network bandwidth requirements
How are headers and data stored in an Avro record?
headers: JSON
data: binary
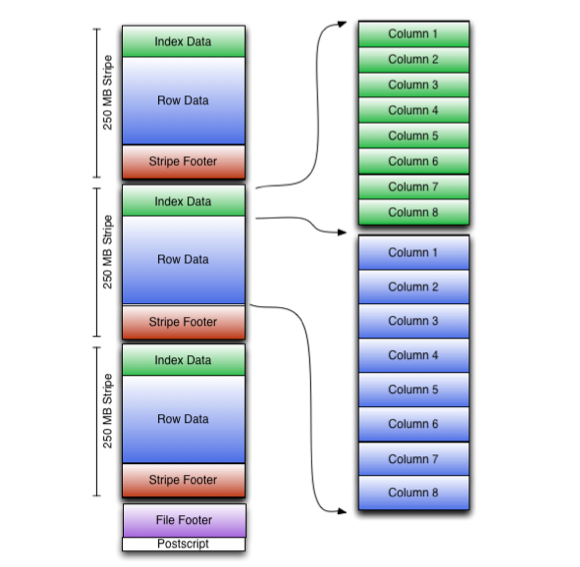
Describe ORC (what is ORC?)
optimized row-columnar format
organizes data into columns
contains stripes of data
Components of a stripe (ORC data)
data for a column or a set of columns
index into the rows
data for each row
footer that contains summary statistics (count, sum, max, min, etc.) for each column
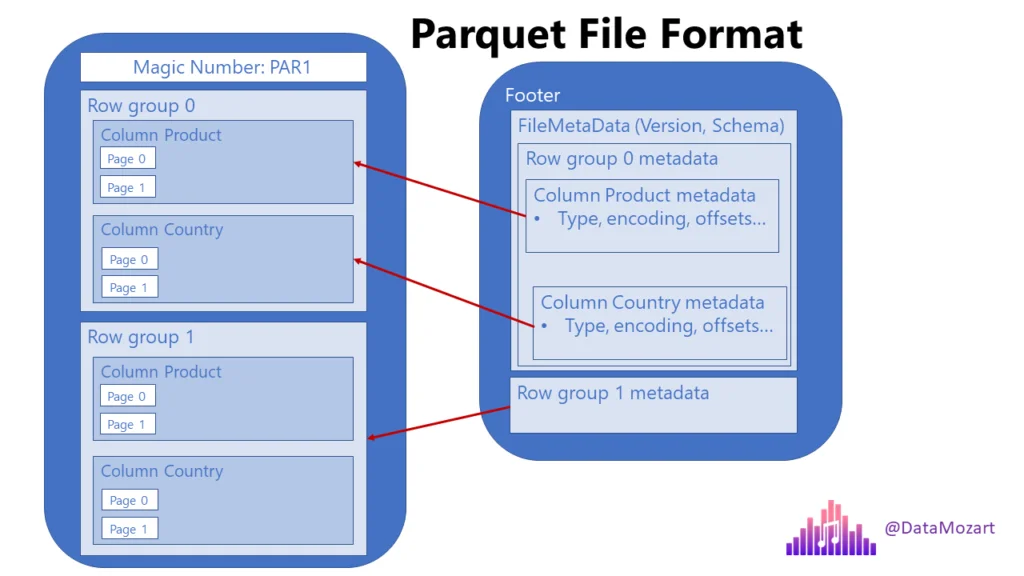
Describe Parquet
columnar
contains row groups for each column
each row group contains chunk/s of data
includes metadata for easy location of the correct chunk for a given set of rows and for easy retrieval of specific columns for the rows
When to use Parquet
if you need to store and process nested data types efficiently
Compare relational and non-relational databases
relational - for storing and querying structured data
non-relational - for data without a relational schema
Four common types of non-relational databases
key-value (any format; consists of a unique key and an associated value)
document (JSON)
column family (tabular data; columns are grouped logically into families)
graph (stores entities as nodes with links that define relationships between nodes)
What does OLTP stand for?
online transactional processing
What are CRUD operations? Why is it important for OLTP solutions?
create, delete, update, and delete
ensures data integrity for transactional data workloads
What do OLTP systems enforce to ensure data integrity? (hint: ACID)
atomicity - each transaction is a single unit that either succeeds or fails completely; cannot be both
consistency - transactions can only take the data in the database from one valid state or the other
isolation - concurrent transactions do not interfere with one another
durability - when a transaction has been committed, it will remain committed
line of business (LOB) applications
live applications that process business data
T/F: Analytical data processing typically uses read-write systems.
FALSE; read-only systems
Differentiate data warehouses, data lakes, and data lakehouses
data warehouses - store cleaned and processed data in a relational scheme optimized for read operations
data lakes - can store all types of raw data; storage for large amount of file-based data
data lakehouses - combines flexibility and scalability of a data lake with querying semantics of a data warehouse
What is an OLAP model?
online analytical processing - aggregated data storage optimized for analytical workloads
How and why is data aggregated in an OLAP model?
how: across dimensions at different levels
why: to enable drilling up/down data to view aggregations at multiple hierarchical levels
ex. finding total sales by region, city, or for an individual addresses
Three key job roles that deal with data and what they do
database administrators - manage databases, assigns permissions to users, administers backups and restores
data engineers - manage infrastructure, process data for integration across organizations (applies data cleaning routines, governance rules, and implements pipelines)
data analysts - explore and analyze data for decision-making
Services under Azure SQL
Azure SQL database - fully-managed PaaS database in Azure
Azure SQL managed instance - hosted SQL server instance with automated maintenance; more flexible than Azure SQL DB but with more administrative responsibility for the owner
Azure SQL VM - a VM that hosts a SQL server, allowing maximum configurability with full management responsibility
Azure Database for MySQL
open-source DBMS commonly used in Linux, Apache, MySQL, etc.
Azure DB for MariaDB
newer DBMS; optimized to improve performance and offers compatibility with Oracle
Azure DB for PostgreSQL
hybrid relational-object database; can store data in relational tables and in custom data types with non-relational properties
Azure CosmosDB
a global-scale non-relational (NoSQL) DB that supports multiple APIs
can store and manage JSON documents, key-value pairs, column-families, and graphs
Azure Storage
enables data storage in
blob containers - for binary files (BLOB - binary large object)
file shares - network file shares, typically in corporate networks
tables - key-value storage for quick read-write operations
Azure Data Factory
Azure service for defining and scheduling data pipelines for ETL solutions
enables integration of pipelines with other Azure services or other cloud data stores for data ingestion, processing, and storage
Microsoft Fabric
unified SaaS analytics platform that combines data ingestion pipelines, data warehouses, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and AI-powered insights through a single service centrally stored with Microsoft OneLake
Azure Databricks
Azure-integration version of Databricks, which combines Apache Spark with SQL database semantics
integrated management interface for large-scale data analytics
Azure Stream Analytics
real-time stream processing engine
captures data stream from an input, applies queries to extract and manipulate data, and stores results into an output for analysis or further processing
Azure Data Explorer
fully managed, standalone big data analytics platform for high-performance querying of log and telemetry data
Microsoft Purview
for enterprise-wide data governance and discoverability to ensure data integrity for analytical workloads
Why is it necessary to normalize data?
to avoid data duplication and enforce data integrity
Primary key
unique identifiers for each row in a database table
Foreign keys
link data in one table to data in another table
Differentiate primary key and unique key
primary key - uniquely identifies each record in a table and cannot store NULL values
unique key - prevents duplicate values in a column and can store NULL values
Composite key
key based on a unique combination of multiple columns
Transact-SQL
SQL version used by Microsoft SQL and Azure SQL services
pg-SQL
SQL version implemented in PostgreSQL
PL/SQL
SQL version used by Oracle (Procedural Language/SQL)
SQL statements are grouped into these logical groups:
Data Definition Language
Data Control Language
Data Manipulation Language
Enumerate the four commonly used DDL statements
Data Definition Language
CREATE
ALTER
DROP
RENAME
[DDL] CREATE
creates new objects in the database (table, view)
[DDL] ALTER
modifies structure of object (ex. to add a new column)
[DDL] DROP
removes object from db
[DDL] RENAME
renames existing object
T/F: DROP statement removes rows in the table permanently.
TRUE
What should you add in a CREATE statement when creating a mandatory column?
NOT NULL
Enumerate the three most common DCL statements. What are DCL statements for?
Data Control Language - to manage database access by specific users or groups
GRANT
DENY
REVOKE
[DCL] GRANT
grants permissions to perform specific actions
[DCL] DENY
denies permissions to perform specific actions
[DCL] REVOKE
revokes previously granted permission
Enumerate the four main DML statements. What are DML statements for?
Data Manipulation Language - manipulate rows in the table; retrieve, insert, modify, and delete rows
SELECT
INSERT
UPDATE
DELETE
T/F: The basic form of an INSERT statement can insert multiple rows simultaneously.
FALSE; one at a time
T/F: SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements are applied to every row in the table.
TRUE
Which SQL statement clause ensures that statements only apply to rows that meet specific criteria?
WHERE
How do you sort data retrieved by a query?
ORDER BY clause
How do you merge data from multiple tables?
JOIN clause; specify how rows in one table are connected with rows in the other
Can you assign aliases to tables?
YES, by using AS clause
ex.
SELECT o.OrderNo, o.OrderDate, c.Address, c.City
FROM Order AS o
JOIN Customer AS c
ON o.Customer = c.IDClauses in an INSERT statement
INTO - determines which table and columns the new entry will be stored
VALUES - values to be stored
ex.
INSERT INTO Product(ID, Name, Price)
VALUES (99, 'Drill', 4.99);What is a view?
virtual table that is outputted by the SELECT query
What is a stored procedure?
a set of statements that can be executed on command
What is an index?
makes querying more efficient by specifying a column from the table
How are indexes made?
a column from a table is specified, and the index creates a sorted copy of this data, with pointers to the corresponding rows in the table. when a query is run which has a WHERE clause, the DBMS uses the index to fetch the data more quickly
What is a possible downside of using indexes?
it may consume storage space which can slow down insert, delete, and update operations
SQL Server on Azure VMs is under which service type?
IaaS
Azure SQL Managed Instance
a PaaS option that provides abstraction of the hardware and OS for on-premises SQL Server instances
Differentiate Azure SQL DB and Managed Instance
DB
fully managed PaaS db service designed for the cloud
includes core database-level capabilities of on-prem SQL server
You can provision a single database in a dedicated, managed (logical) server; or you can use an elastic pool to share resources across multiple databases and take advantage of on-demand scalability.
ideal for new cloud solutions, or to migrate applications that have minimal instance-level dependencies.
Managed Instances
Each managed instance can support multiple databases. Additionally, instance pools can be used to share resources efficiently across smaller instances.
Use this option for most cloud migration scenarios, particularly when you need minimal changes to existing applications.
Azure SQL Edge
optimized for IoT scenarios; for workloads requiring time-series data streaming
Azure SQL Managed Instance supports which types of logins?
SQL Server DB engine logins
logins integrated with Microsoft Entra ID
Data Migration Assistant
analyzes your SQL server databases and reports any compatibility issues when migrating to different SQL offerings
Azure SQL Database is available as ____ and ____
single database
elastic pool
[Azure SQL DB] Single database vs elastic pool
single database
for quick setup of a single SQL server database
uses pre-allocated resources and charges are made per hour of use
also has a serverless configuration; server is provided by MS and is shared with other Azure subscribers
elastic pool
multiple databases share the same pool
you create the pool and only your databases can use the pool
for use cases when you have databases with varying resource requirements
Business benefits of Azure SQL database
automatic updates
scalable
high availability (99.995%)
advanced threat protection (vulnerability assessments, detection of suspicious activities, etc.)
conducts auditing (db activity, regulatory compliance, anomaly detection, etc.)
provides encryption for data at rest and in motion
MySQL
open-source DBMS
leading RDB for Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP (LAMP)
available in three editions: community (free), standard, and enterprise
MariaDB
supports temporal data; think version history for tables
PostgreSQL
hybrid relational-object DB
can store relational tables
can also store custom data types with non-relational properties
DBMS is extensible via code modules run by queries
also supports storage and manipulation of geometric data
uses pgSQL
Azure DB for MySQL is based on which MySQL edition?
community edition
T/F: All features of on-prem PostgreSQL databases are available in Azure DB for PostgreSQL.
FALSE; Azure DB for PostgreSQL does not support extensions and interacting directly with the OS
What is Azure Blob Storage used for? How is data stored in Azure Blob Storage?
massive amounts of unstructured data; data stored as blobs (binary large objects)
Three types of blobs supported by Azure Blob Storage
block blobs
page blobs
append blobs
Characteristics of block blobs
blobs are organized into blocks and these blocks are organized into a set
a block is the smallest amount of data that can be read/written as an individual unit
Characteristics of page blobs
a page blob is organized as a collection of fixed size 512-byte pages
optimized to support random read-write operations
can hold up to 8TB of data
used for implementing virtual disk storage for VMs
Characteristics of append blobs
block blobs optimized for append operations
can only add blocks to the end of an append blob
blocks can be 4MB in size and up to ~195 GB
T/F: It is possible to update or delete existing blocks in an append blob.
FALSE; not supported
Three Blob storage tiers
hot - used by default; for blobs that are accessed frequently
cool - has lower performance and storage charges than hot; for data accessed infrequently
archive - lowest storage cost with highest latency; for historical data that is needed but accessed rarely
T/F: You can migrate a blob from the hot to the cool tier but not vice versa.
FALSE; possible both ways
T/F: Blobs in the archive tier are stored online.
FALSE; offline state, that is why latency is high
What is rehydration in Azure Blob storage?
changing the tier from archive to hot/cool
How do you create an Azure Data Lake Store Gen2 files system?
enable the hierarchical namespace option of an Azure Storage Account
T/F: You can downgrade a storage account to disable hierarchical namespace support for blob storage.
FALSE; upgrade is one-way
What do you need to create an Azure File Storage?
Azure Storage Account
How much data can you store in Azure Files for a single storage account?
100TB of data
Two performance tiers of Azure File Storage
standard
premium