Lab: Microscope and Cells
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Compound Light Microscope
Has two magnifying lenses: ocular and objective, uses light for viewing, most commonly used
Proper way to hold microscope
One hand on under base, one hand holding the arm, carry microscope close to your body
On/Off switch
Near light source
Magnification
Multiply Ocular and Objectives
Ocular Lens
Stays the same; 10x
Objective Lens
Changes magnification; 4x, 10x, 40x
Major Parts of the Cell
Cell membrane, Nucleus, and Cytoplasm
Cell Membrane
Boundary of the cell; transports particles in and out of cell
Nucleus
In the middle of the cell, control center, houses DNA
Cytoplasm
Space between DNA & membrane; holds organelles (where chemical reactions occur) & inclusions (stored material for cell)
Cell Cycle
Interphase (G1, S, G2), Mitosis, Cytokinesis
G1
Cell growth (2x) and metabolis
S
synthesis; replication of DNA
G2
additional growth, replication of all other internal components
G1 and G2 Checkpoints
Body stops cell cycle to examine cell and check for any mistakes
DNA Replication
Chromosome replicated, two chromatids bond and are held by centromere
Blastula
Ball of cells after fertilization
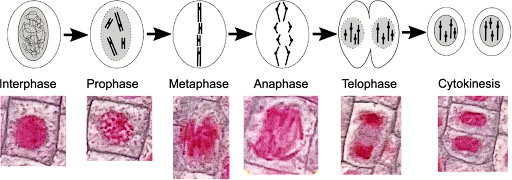
Prophase
Chromatin becomes visible, nuclear membrane disappears, spindle fibers form
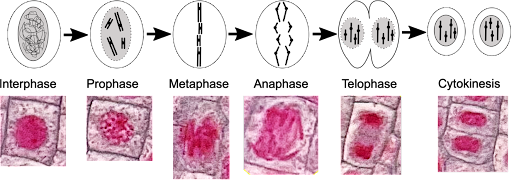
Metaphase
Centrioles at poles, chromosomes lined up in the middle, spindle fibers attach to chromosome at centromere
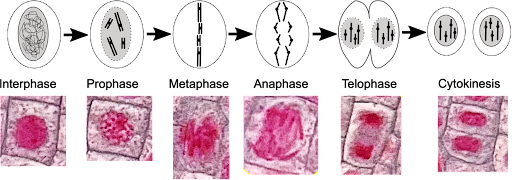
Anaphase
Centromeres divide, chromosomes separate
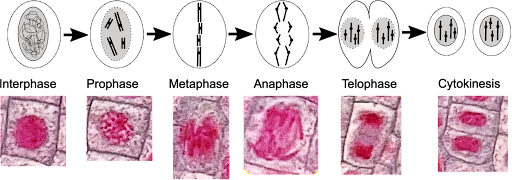
Telophase
Nucleus reforms, spindle fibers disappear, cytokinesis begins
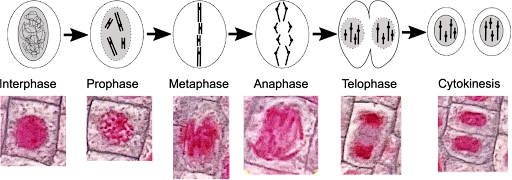
Cytokinesis
Produces two identical daughter cells
Mitosis
Two daughter cells, Identical to original cell, Growth and repair