Bones Test Study Guide
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Number of Bones in the Adult Body
206
5 Functions of the Skeletal System
Protect organs, supports body and gives shape, allows for movement of muscles, provides mineral storage, hematopoietic activity
Layers of the Bone (Outside to Inside)
Periosteum, compact bone, medullary canal, endosteum, yellow bone marrow
Minerals of the Bones
35% Organic material, 65% Inorganic material
Formation of the Bone
-The collagenous protein fibers secrete Osteoblasts
-Cartilage is deposited between the fibers
-8th week of embryonic development Ossification begins (hardening)
-Bones ossify from the Diaphysis towards the epiphyseal (center towards the ends)
-Bones increase in size by Osteoblast
-Dissolution of the bone from the medullary canal results from Osteoclasts (cells that secrete enzymes)
Bone Types
Long Bones, Flat Bones, Irregular Bones, and Short Bones
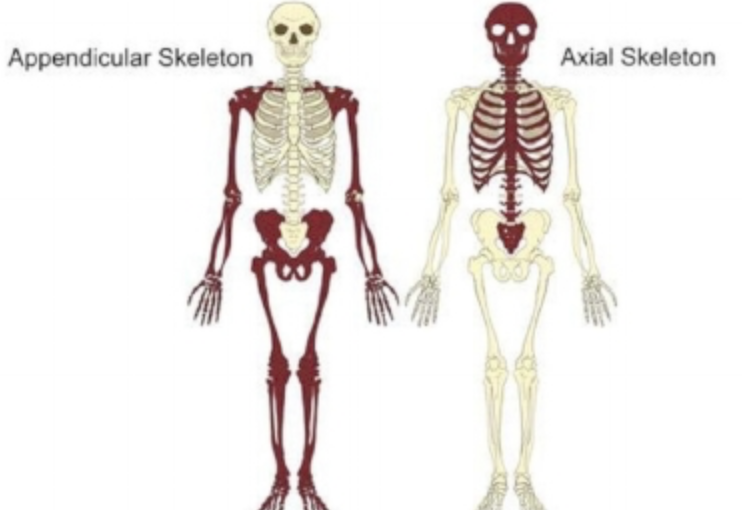
Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
Closed Fracture
Bone is broken but inside the skin
Open Compound Fracture
Bone is broken and outside of the skin
Transverse Fracture
Fracture that is horizontal on the bone
Oblique Fracture
Diagonal Fracture
Greenstick Fracture
Seen in children where one side is tact and other side is splintered. Femur can break with 1700 psi
Stages of Fracture Healing
Stage 1: Hematoma formation: A blood clot forms where the bone is broken due to torn blood vessels
Stage 2: Soft callus formation: Fibrocartilage and collagen form a soft callus
Stage 3: Hard callus formation: Osteoblasts deposit new bone tissue into the soft callus, transforming cartilage into bone
Stage 4: Remodeling: Excess material is removed and compact bone is produced.
Diarthroses
Moveable Joints
Amphiarthroses
Partially Moveable Joints
Synarthroses
Immovable Joints
Understand
Ball Socket Joints, Hinge Joints, Pivot Joints
Flexion
Bringing together 2 bones
Extension
Increasing the angle between two bones
Abduction
Away from the midline
Adduction
Towards the midline
Circumduction
Includes flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
Rotation
Moves around one axis
Pronation
Forearms turns the palms backwards/downwards
Supination
Palm is forward/upward
Diseases
Arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteosarcoma, rickets, osteomyelitis